Psammaceratin A: A Cytotoxic Psammaplysin Dimer Featuring an Unprecedented (2Z,3Z)-2,3-Bis(aminomethylene)succinamide Backbone from the Red Sea Sponge Pseudoceratina arabica
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
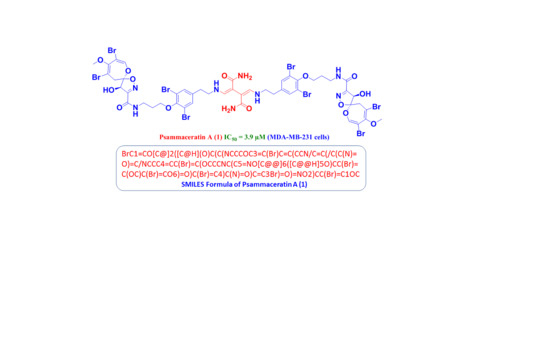
2.1. Structure of Psammaceratin A (1)
2.2. Structure of Psammaplysin A (2)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Biological Materials
3.3. Purification of 1 and 2
3.4. Spectral Data of the Compounds
3.5. Cytotoxicity of the Compounds
3.5.1. Preparation of Cell Lines and Cell Culture
3.5.2. Cytotoxicity and Antiproliferative Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, J.; Li, J.; Hamann, M.T. The marine bromotyrosine derivatives. In The Alkaloids: Chemistry and Biology; Knölker, H.J., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 82, pp. 59–262. [Google Scholar]
- Hamann, M.T.; Scheuer, P.J.; Kelly-Borges, M. Biogenetically diverse, bioactive constituents of a sponge, order Verongida: Bromotyramines and sesquiterpene-shikimate derived metabolites. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 6565–6569. [Google Scholar]
- Kornprobst, J.-M. Encyclopedia of Marine Natural Products; Wiley-Blackwell: Weinheim, Germany, 2010; Volume 2, Chapter 19; pp. 796–805. [Google Scholar]
- Roll, D.M.; Chang, C.W.J.; Scheuer, P.J.; Gray, G.A.; Shoolery, J.N.; Matsumoto, G.K.; Van Duyne, G.D.; Clardy, J. Structure of the psammaplysins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 2916–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copp, B.R.; Ireland, C.M.; Barrows, L.R. Psammaplysin C: A new cytotoxic dibromotyrosine-derived metabolite from the marine sponge Druinella (=Psammaplysilla) purpurea. J. Nat. Prod. 1992, 55, 822–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichiba, T.; Scheuer, P.J.; Kelly-Borges, M. Three bromotyrosine derivatives, one terminating in an unprecedented diketocyclopentenylidene enamine. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 4149–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Fu, X.; Schmitz, F.J.; Kelly-Borges, M. Psammaplysin F, a New bromotyrosine derivative from a sponge, Aplysinella sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 614–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Andrews, K.T.; Birrell, G.W.; Tran, T.L.; Camp, D.; Davis, R.A.; Quinn, R.J. Psammaplysin H, a new antimalarial bromotyrosine alkaloid from a marine sponge of the genus Pseudoceratina. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 846–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wright, A.D.; Schupp, P.J.; Schrör, J.-P.; Engemann, A.; Rohde, S.; Kelman, D.; Voogd, N.D.; Carroll, A.; Motti, C.A. Twilight zone sponges from Guam yield theonellin isocyanate and psammaplysins I and J. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudianta, I.W.; Skinner-Adams, T.; Andrews, K.T.; Davis, R.A.; Hadi, T.A.; Hayes, P.Y.; Garson, M.J. Psammaplysin derivatives from the Balinese marine sponge Aplysinella strongylata. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 2132–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Han, S.; Lee, H.S.; Kang, J.S.; Yun, J.; Sim, C.J.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, J.S. Cytotoxic psammaplysin analogues from a Suberea sp. marine sponge and the role of the spirooxepinisoxazoline in their activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1731–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Kato, H.; Hirota, H.; Fusetani, N. Ceratinamides A and B: New antifouling dibromotyrosine derivatives from the marine sponge Pseudoceratina purpurea. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 8181–8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.A. Cytotoxic psammaplysin analogues from the Verongid Red Sea sponge Aplysinella species. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Davis, R.A.; Buchanan, M.S.; Duffy, S.; Avery, V.M.; Camp, D.; Quinn, R.J. Antimalarial bromotyrosine derivatives from the Australian marine sponge Hyattella sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 985–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurimoto, S.I.; Ohno, T.; Hokari, R.; Ishiyama, A.; Iwatsuki, M.; Ōmura, S.; Kobayashi, J.; Kubota, T. Ceratinadins E and F, new bromotyrosine alkaloids from an Okinawan marine sponge Pseudoceratina sp. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiao, W.H.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.M.; Cui, J.; Gui, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.Y.; Liu, K.C.; Lin, H.W. Frondoplysins A and B, unprecedented terpene-alkaloid bioconjugates from Dysidea frondosa. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 6190–6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Badr, J.M.; Sulaiman, M.; Khedr, A.; El Sayed, K.A. Bioactive alkaloids from the Red Sea marine Verongid sponge Pseudoceratina arabica. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 7837–7841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, D.M.; Amirul, I.M.; Turnbull, L.; Davis, R.A.; Whitchurch, C.B.; McAlpine, S.R. Psammaplysin F: A unique inhibitor of bacterial chromosomal partitioning. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4862–4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaala, L.A.; Bamane, F.H.; Badr, J.M.; Youssef, D.T.A. Brominated arginine-derived alkaloids from the Red Sea sponge Suberea mollis. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Sulaiman, M.; Behery, F.A.; Foudah, A.I.; El Sayed, K.A. Subereamolline A as a potent breast cancer migration, invasion and proliferation inhibitor and bioactive dibrominated alkaloids from the Red Sea sponge Pseudoceratina arabica. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2509–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Shoer, M.I.; Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Badr, J.M.; Habib, A.M. Bioactive brominated metabolites from the Red Sea sponge Suberea mollis. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1464–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Badr, J.M.; Souliman, M.; Khedr, A. Bioactive secondary metabolites from a Red Sea marine Verongid sponge Suberea species. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1621–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mándi, A.; Mudianta, I.W.; Kurtán, T.; Garson, M.J. Absolute configuration and conformational study of psammaplysins A and B from the Balinese marine sponge Aplysinella strongylata. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2051–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, D.T.A.; Mooberry, S.L. Hurghadolide A and swinholide I, potent actin-microfilament disrupters from the Red Sea sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| No. | δC | δH | HMBC | NOESY |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1, 1′ | 146.8, CH | 7.13 (s) | C-2/2′, C-3/3′, C-6/6′ | H2-11/11′ |
| 2, 2′ | 104.4, qC | |||
| 3, 3′ | 149.9, qC | |||
| 4, 4′ | 104.6, qC | |||
| 5a,5a’ | 38.3, CH2 | 3.38 (d, 16.2) | C-3/3′, C-4/4′, C-6/6′, C-7/7′ | H-5b/5b′, H-7/7′ |
| 5b,5b’ | 3.05 (d, 16.2) | C-3/3′, C-4/4′, C-6/6′ | H-5a/5a′, H-7/7’ | |
| 6, 6′ | 120.9, qC | |||
| 7, 7′ | 80.5, CH | 4.98 (s) | C-6/6′, C-8/8′, C-9/9′ | H-5a/5a′, H-5b/5b′ |
| 8, 8′ | 158.8, qC | |||
| 9, 9′ | 160.7, qC | |||
| 10, 10′ | 38.1, CH2 | 3.60 (t, 6.5) | H2-11, H2-12 | |
| 11, 11′ | 30.6, CH2 | 2.12 (quin., 6.5) | H-5b/5b′, H2-9/9′, H2-10/10′, H2-12/12′ | |
| 12,12′ | 72.2, CH2 | 4.05 (t, 6.5) | H2-10/10′, H2-11/11′ | |
| 13, 13′ | 153.4, qC | |||
| 14, 14′ | 119.4, qC | |||
| 15, 15′ | 134.8, CH | 7.43 (s) | C-13/13′, C-14/14′, C-16/16′, C-18/18′, C-19/19′ | H2-19/19′ |
| 16, 16′ | 138.1, qC | |||
| 17, 17′ | 134.8, CH | 7.43 (s) | C-13/13′, C-14/14′, C-16/16′, C-18/18′, C-19/19′ | H2-19/19′ |
| 18, 18′ | 119.4, qC | |||
| 19, 19′ | 36.1, CH2 | 2.90 (t, 7.2) | C-15/15′, C-16/16′, C-17/17′, C-20/20′ | H2-20/20′ |
| 20, 20′ | 52.6, CH2 | 3.69 (t, 7.2) | C-16/16′, C-19/19′, C-21/21′ | H2-19/19′ |
| 21, 21′ | 157.1, CH | 7.54 (s) | C-20/20′, C-22/22′, C-23/23′ | |
| 22, 22’ | 119.2, qC | |||
| 23, 23′ | 171.1, qC | |||
| 24, 24′ | 59.4, CH3 | 3.64 (s) | C-3/3′ |
| Position | Psammaplysin A (2) * | Psammaceratin A (1) | Δδ (ppm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC * | δH * | δC | δH | ΔδH | ΔδC | |
| 19/19′ | 31.8 | 2.93 | 36.1 | 2.90 | −0.03 | +5.3 |
| 20/20′ | 40.0 | 3.18 | 52.6 | 3.69 | +0.51 | +12.6 |
| Compound | IC50 (μM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MDA-MB-231 | HeLa | HCT 116 | |
| 1 | 3.90 ± 0.20 | 8.50 ± 0.81 | 5.10 ± 0.41 |
| 2 | 5.25 ± 0.48 | 9.40 ± 0.89 | 3.10 ± 0.28 |
| 5-FU | 13.0 ± 0.30 | 12.3 ± 0.25 | 4.60 ± 0.23 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Youssef, D.T.A.; Asfour, H.Z.; Shaala, L.A. Psammaceratin A: A Cytotoxic Psammaplysin Dimer Featuring an Unprecedented (2Z,3Z)-2,3-Bis(aminomethylene)succinamide Backbone from the Red Sea Sponge Pseudoceratina arabica. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19080433
Youssef DTA, Asfour HZ, Shaala LA. Psammaceratin A: A Cytotoxic Psammaplysin Dimer Featuring an Unprecedented (2Z,3Z)-2,3-Bis(aminomethylene)succinamide Backbone from the Red Sea Sponge Pseudoceratina arabica. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(8):433. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19080433
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoussef, Diaa T. A., Hani Z. Asfour, and Lamiaa A. Shaala. 2021. "Psammaceratin A: A Cytotoxic Psammaplysin Dimer Featuring an Unprecedented (2Z,3Z)-2,3-Bis(aminomethylene)succinamide Backbone from the Red Sea Sponge Pseudoceratina arabica" Marine Drugs 19, no. 8: 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19080433
APA StyleYoussef, D. T. A., Asfour, H. Z., & Shaala, L. A. (2021). Psammaceratin A: A Cytotoxic Psammaplysin Dimer Featuring an Unprecedented (2Z,3Z)-2,3-Bis(aminomethylene)succinamide Backbone from the Red Sea Sponge Pseudoceratina arabica. Marine Drugs, 19(8), 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19080433