Saringosterol from Sargassum fusiforme Modulates Cholesterol Metabolism and Alleviates Atherosclerosis in ApoE-Deficient Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Saringosterol Treatment Reduces Atherosclerotic Plaques in ApoE−/− Mice
2.2. Saringosterol Administration Improves Lipid Profiles in ApoE−/− Mice
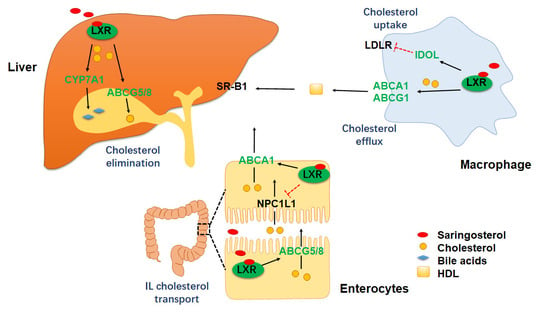
2.3. Saringosterol Treatment Modulates Cholesterol Metabolism in Macrophagess
2.4. Saringosterol Treatment Affects Cholesterol Metabolism in Liver and Intestine
2.5. Saringosterol Treatment Does Not Worsen Hepatic Steatosis in ApoE−/− Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice and Treatments
4.2. Determination of Serum and Liver Metabolic Parameters
4.3. Aortic Lesion Assessment
4.4. En Face Lesion Analysis
4.5. Immunofluorescence Analysis
4.6. Harvest Mouse Peritoneal Macrophages of ApoE−/− Mice
4.7. Cell Culture and Foam Cell Formation
4.8. Analysis of mRNA Expression
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Libby, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Hansson, G.K. Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis. Nature 2011, 473, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusis, A.J. Atherosclerosis. Nature 2000, 407, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jiang, J.; Chen, W.; Li, W.; Chen, Z. Vascular Macrophages in Atherosclerosis. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 4354786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehmann, J.M.; Kliewer, S.A.; Moore, L.B.; Smith-Oliver, T.A.; Oliver, B.B.; Su, J.-L.; Sundseth, S.S.; Winegar, D.A.; Blanchard, D.E.; Spencer, T.A.; et al. Activation of the Nuclear Receptor LXR by Oxysterols Defines a New Hormone Response Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 3137–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willy, P.J.; Umesono, K.; Ong, E.S.; Evans, R.; A Heyman, R.; Mangelsdorf, D. LXR, a nuclear receptor that defines a distinct retinoid response pathway. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Millatt, L.J.; Bocher, V.; Fruchart, J.C.; Staels, B. Liver X receptors and the control of cholesterol homeostasis: Potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of atherosclerosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2002, 1631, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcicka, G.; Jamroz-Wisniewska, A.; Horoszewicz, K.; Beltowski, J. Liver X receptors (LXRs). Part I: Structure, function, regulation of activity, and role in lipid metabolism. Postepy. Hig. Med. Dosw. 2007, 61, 736–759. [Google Scholar]
- Hozoji-Inada, M.; Munehira, Y.; Nagao, K.; Kioka, N.; Ueda, K. Liver X receptor beta (LXRbeta) interacts directly with ATP-binding cassette A1 (ABCA1) to promote high density lipoprotein formation during acute cholesterol accumulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 20117–20124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tangirala, R.K.; Bischoff, E.D.; Joseph, S.; Wagner, B.L.; Walczak, R.; Laffitte, B.A.; Daige, C.L.; Thomas, D.; Heyman, R.A.; Mangelsdorf, D.; et al. Identification of macrophage liver X receptors as inhibitors of atherosclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11896–11901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zelcer, N.; Hong, C.; Boyadjian, R.; Tontonoz, P. LXR Regulates Cholesterol Uptake Through Idol-Dependent Ubiquitination of the LDL Receptor. Science 2009, 325, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peet, D.J.; Turley, S.D.; Ma, W.; Janowski, B.A.; Lobaccaro, J.M.; Hammer, R.E.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Cholesterol and bile acid metabolism are impaired in mice lacking the nuclear oxysterol receptor LXR alpha. Cell 1998, 93, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Hammer, R.E.; Li-Hawkins, J.; von Bergmann, K.; Lutjohann, D.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Disruption of Abcg5 and Abcg8 in mice reveals their crucial role in biliary cholesterol secretion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16237–16242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Repa, J.J.; Berge, K.E.; Pomajzl, C.; Richardson, J.A.; Hobbs, H.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Regulation of ATP-binding cassette sterol transporters ABCG5 and ABCG8 by the liver X receptors alpha and beta. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 18793–18800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Gupta, S.; Xu, F.; Liverman, A.D.B.; Moschetta, A.; Mangelsdorf, D.; Repa, J.; Hobbs, H.H.; Cohen, J.C. Expression of ABCG5 and ABCG8 Is Required for Regulation of Biliary Cholesterol Secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 8742–8747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joseph, S.; McKilligin, E.; Pei, L.; Watson, M.A.; Collins, A.R.; Laffitte, B.A.; Chen, M.; Noh, G.; Goodman, J.; Hagger, G.N.; et al. Synthetic LXR ligand inhibits the development of atherosclerosis in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7604–7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calkin, A.; Tontonoz, P. Liver X Receptor Signaling Pathways and Atherosclerosis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 1513–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Tontonoz, P. Liver X receptors at the intersection of lipid metabolism and atherogenesis. Atherosclerosis 2015, 242, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schultz, J.R.; Tu, H.; Luk, A.; Repa, J.; Medina, J.C.; Li, L.; Schwendner, S.; Wang, S.; Thoolen, M.; Mangelsdorf, D.; et al. Role of LXRs in control of lipogenesis. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 2831–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Russo-Savage, L.; Schulman, I.G. Liver X receptors and liver physiology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis. Dis. 2021, 1867, 166121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, E.G.; Peterson, L.B.; Adams, A.D.; Lam, M.H.; Burton, C.A.; Chin, J.; Guo, Q.; Huang, S.; Latham, M.; Lopez, J.C.; et al. Different roles of liver X receptor alpha and beta in lipid metabolism: Effects of an alpha-selective and a dual agonist in mice deficient in each subtype. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 71, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Heinrich, M.; Myers, S.; Dworjanyn, S.A. Towards a better understanding of medicinal uses of the brown seaweed Srgassum in Traditional Chinese Medicine: A phytochemical and pharmacological review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 142, 591–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachter, G.A.; Franzblau, S.G.; Montenegro, G.; Hoffmann, J.J.; Maiese, W.M.; Timmermann, B.N. Inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis growth by saringosterol from Lessonia nigrescens. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1463–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.-G.; Zhou, M.; Jin, Q.-H.; Liu, B.-Y.; Guan, L.-P. Antidepressant-like effects of saringosterol, a sterol from Sargassum fusiforme by performing in vivo behavioral tests. Med. Chem. Res. 2017, 26, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Lee, J.; Cho, Y.-R.; Hong, S.S.; Ahn, E.-K. Anti-Obesity Activity of Saringosterol Isolated fromSargassum muticum(Yendo) Fensholt Extract in 3T3-L1 Cells. Phytother. Res. 2017, 31, 1694–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, N.; Schepers, M.; Zhan, N.; Leijten, F.; Voortman, G.; Tiane, A.; Rombaut, B.; Poisquet, J.; Sande, N.V.; Kerksiek, A.; et al. 24(S)-Saringosterol Prevents Cognitive Decline in a Mouse Model for Alzheimer’s Disease. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Fu, Z.; Ye, C.; Zhang, R.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Ying, H.; Liu, H. 24(S)-Saringosterol from edible marine seaweed Sargassum fusiforme is a novel selective LXRbeta agonist. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 6130–6137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, C.; Tontonoz, P. Liver X receptors in lipid metabolism: Opportunities for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulman, I.G. Liver X receptors link lipid metabolism and inflammation. FEBS Lett. 2017, 591, 2978–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, Y. Liver X Receptors as potential therapeutic targets in atherosclerosis. Clin. Investig. Med. 2009, 32, E383–E394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kratzer, A.; Buchebner, M.; Pfeifer, T.; Becker, T.M.; Uray, G.; Miyazaki, M.; Miyazaki-Anzai, S.; Ebner, B.; Chandak, P.G.; Kadam, R.S.; et al. Synthetic LXR agonist attenuates plaque formation in apoE-/- mice without inducing liver steatosis and hypertriglyceridemia. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nomura, S.; Endo-Umeda, K.; Makishima, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Ishikawa, M. Development of Tetrachlorophthalimides as Liver X Receptor beta (LXRbeta)-Selective Agonists. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 2347–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, T.; Okuda, A.; Watanabe, Y.; Miura, T.; Ozawa, H.; Tosaka, A.; Yamazaki, K.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kurobuchi, S.; Koura, M.; et al. Design and discovery of 2-oxochromene derivatives as liver X receptor β-selective agonists. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 1274–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangirala, R.K.; Rubin, E.M.; Palinski, W. Quantitation of atherosclerosis in murine models: Correlation between lesions in the aortic origin and in the entire aorta, and differences in the extent of lesions between sexes in LDL receptor-deficient and apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. J. Lipid Res. 1995, 36, 2320–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Y.; Niu, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhao, S.; Sun, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Ying, H.; Liu, H. Saringosterol from Sargassum fusiforme Modulates Cholesterol Metabolism and Alleviates Atherosclerosis in ApoE-Deficient Mice. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19090485
Yan Y, Niu Z, Wang B, Zhao S, Sun C, Wu Y, Li Y, Ying H, Liu H. Saringosterol from Sargassum fusiforme Modulates Cholesterol Metabolism and Alleviates Atherosclerosis in ApoE-Deficient Mice. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(9):485. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19090485
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Ying, Zhoumin Niu, Boyang Wang, Shangge Zhao, Chao Sun, Yuting Wu, Yuying Li, Hao Ying, and Hongbing Liu. 2021. "Saringosterol from Sargassum fusiforme Modulates Cholesterol Metabolism and Alleviates Atherosclerosis in ApoE-Deficient Mice" Marine Drugs 19, no. 9: 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19090485
APA StyleYan, Y., Niu, Z., Wang, B., Zhao, S., Sun, C., Wu, Y., Li, Y., Ying, H., & Liu, H. (2021). Saringosterol from Sargassum fusiforme Modulates Cholesterol Metabolism and Alleviates Atherosclerosis in ApoE-Deficient Mice. Marine Drugs, 19(9), 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19090485