Anti-Fine Dust Effect of Fucoidan Extracted from Ecklonia maxima Leaves in Macrophages via Inhibiting Inflammatory Signaling Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Proximate Chemical Composition of E. Maxima and its Polysaccharide Fractions
2.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectra and Molecular Weight Determination of the Isolated Fucoidan Fractions
2.3. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR) and Monosaccharide Composition of the Active Fraction
2.4. Fucoidan Extracted from E. Maxima Inhibited NO Production in PM-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Cells
2.5. EMLF7 Attenuated PGE2 and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Secretion in PM-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Cells
2.6. EMLF7 Reduced the Expression Levels of iNOS and COX-2 Proteins in PM-Stimulated Macrophage Cells
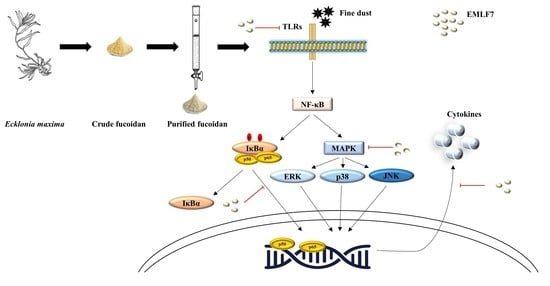
2.7. Inhibition of the NF-κB Phosphorylation and MAPK Signaling Pathways by EMLF7
2.8. Downregulation of the iNOS and COX-2 Gene Expressions, and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine mRNA Expression in PM-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Cells by EMLF7
2.9. Inhibition of PM-Stimulated Toll-Like Receptor (TLR)-2 and TLR-4 mRNA Expressions by the EMLF7 Treatment in RAW 264.7 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. CRM No. 28 Particulate Matter
4.3. Collection and Preparation of the Crude Polysaccharide Sample
4.4. Proximate Composition Analysis
4.5. Separation and Purification by Anion-Exchange Chromatography
4.6. FTIR Spectroscopy, NMR Analysis, and Monosaccharide Quantification, and Molecular Weight Determination of the Fucoidan Fractions
4.7. Cell Culture
4.8. Cell Viability and NO Production
4.9. Determination of PGE2 and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Production
4.10. Western Blot Analysis
4.11. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, T.; Hu, R.; Chen, Z.; Li, Q.; Huang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, L.-F. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5): The culprit for chronic lung diseases in China. Chronic Dis. Transl. Med. 2018, 4, 176–186. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, F.; Sancini, G.; Battaglia, C.; Tinaglia, V.; Mantecca, P.; Camatini, M.; Palestini, P. Milano Summer Particulate Matter (PM10) Triggers Lung Inflammation and Extra Pulmonary Adverse Events in Mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.O.; Thundiyil, J.G.; Stolbach, A. Clearing the Air: A Review of the Effects of Particulate Matter Air Pollution on Human Health. J. Med. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peden, D.; Reed, C.E. Environmental and occupational allergies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125 (Suppl. 2), S150–S160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarnieri, M.; Balmes, J.R. Outdoor air pollution and asthma. Lancet 2014, 383, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, K.H.I.N.M.; Kim, H.J.; Jang, J.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, H.J.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Jee, Y. Mojabanchromanol Isolated from Sargassum horneri Attenuates Particulate Matter Induced Inflammatory Responses via Suppressing TLR2/4/7-MAPK Signaling in MLE-12 Cells. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, H.G.; Je, J.-G.; Jee, Y.; Jeon, Y.-J. Sargassum horneri (Turner) inhibit urban particulate matter-induced inflammation in MH-S lung macrophages via blocking TLRs mediated NF-κB and MAPK activation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 249, 112363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.X.; Thiyagarasaiyar, K.; Tan, C.-Y.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Nadzir, M.S.M.; Wu, Y.-J.; Low, L.-E.; Atanasov, A.G.; Ming, L.C.; Liew, K.B.; et al. Algae-Derived Anti-Inflammatory Compounds against Particulate Matters-Induced Respiratory Diseases: A Systematic Review. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Lee, H.G.; Kim, H.-S.; Vaas, A.P.J.P.; De Silva, H.I.C.; Nanayakkara, C.M.; Abeytunga, D.T.U.; Lee, W.W.; Lee, D.-S.; et al. Characterization and cytoprotective properties of Sargassum natans fucoidan against urban aerosol-induced keratinocyte damage. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-J.; Yoon, K.-Y.; Lee, B.-Y. Low molecular weight fucoidan from the sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida suppresses inflammation by promoting the inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinases and oxidative stress in RAW264.7 cells. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 1628–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Weelden, G.; Bobiński, M.; Okła, K.; Van Weelden, W.J.; Romano, A.; Pijnenborg, J.M.A. Fucoidan Structure and Activity in Relation to Anti-Cancer Mechanisms. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xing, M.; Cao, Q.; Ji, A.; Liang, H.; Song, S. Biological Activities of Fucoidan and the Factors Mediating Its Therapeutic Effects: A Review of Recent Studies. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, C.; Chen, L.; Yang, L.; Ji, X. An insight into anti-inflammatory effects of natural polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, W.A.; Duffy, C.A.J. Chnoospora minima (Phaeophyta) in Port Underwood, Marlborough—A curious new algal record for New Zealand. N. Z. J. Bot. 1991, 29, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, F.; Wei, X.; Zhao, R. Fucoidan: Structure and Bioactivity. Molecules 2008, 13, 1671–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-B.; Hayashi, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Nakano, T.; Hayashi, T.J.C.; Bulletin, P. Novel antiviral fucoidan from sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida (Mekabu). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 1091–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce, N.M.A.; Pujol, C.A.; Damonte, E.B.; Flores, M.L.; Stortz, C.A. Fucoidans from the brown seaweed Adenocystis utricularis: Extraction methods, antiviral activity and structural studies. Carbohydr. Res. 2003, 338, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laihao, L.; Changhu, X.; Yong, X.; Zhaojie, L.; Xueyan, F. The effects of fucoidans from Laminaria japonica on AAPH mediated oxidation of human low-density lipoprotein. J. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2006, 25, 124–130. [Google Scholar]
- Chandía, N.P.; Matsuhiro, B. Characterization of a fucoidan from Lessonia vadosa (Phaeophyta) and its anticoagulant and elicitor properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 42, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.Y.; Han, M.H.; Park, C.; Jin, C.-Y.; Kim, G.-Y.; Choi, I.-W.; Kim, N.D.; Nam, T.-J.; Kwon, T.K.; Choi, Y.H. Anti-inflammatory effects of fucoidan through inhibition of NF-κB, MAPK and Akt activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV2 microglia cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1745–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, J.; Kim, T.S.; Kwon, H.J.; Lee, S.P.; Kang, M.H.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, M.N. Efficacy of Cistanche tubulosa and Laminaria japonica Extracts (MK-R7) Supplement in Preventing Patterned Hair Loss and Promoting Scalp Health. Clin. Nutr Res. 2015, 4, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phull, A.-R.; Majid, M.; Haq, I.-u.; Khan, M.R.; Kim, S.J. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of anti-arthritic, antioxidant efficacy of fucoidan from Undaria pinnatifida (Harvey) Suringar. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C. Extraction and characterization of fucoidan from six brown macroalgae. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2016, 24, 319–328. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.-H.; Choi, S.-H.; Park, S.-J.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, J.H.; Song, P.H.; Cho, C.-M.; Ku, S.-K.; Song, C.-H. Promoting Wound Healing Using Low Molecular Weight Fucoidan in a Full-Thickness Dermal Excision Rat Model. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinsbroek, S.E.M.; Gordon, S. The role of macrophages in inflammatory bowel diseases. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2009, 11, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Flisyuk, E.V.; Shikov, A.N. Formulation, Optimization and In Vivo Evaluation of Fucoidan-Based Cream with Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Qi, X.; Liu, H.; Xue, K.; Xu, S.; Tian, Z. The anti-cancer effects of fucoidan: A review of both in vivo and in vitro investigations. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, C.L.; Robinson, T.B.; Lange, L.; Mead, A.J.P.O. Marine Biodiversity in South Africa: An Evaluation of Current States of Knowledge. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Border, A.; Goosen, N.; Thomsen, M. Environmental life cycle assessment of cascade valorisation strategies of South African macroalga Ecklonia maxima using green extraction technologies. Algal Res. 2021, 58, 102348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörschmann, P.; Bittkau, K.S.; Neupane, S.; Roider, J.; Alban, S.; Klettner, A. Effects of Fucoidans from Five Different Brown Algae on Oxidative Stress and VEGF Interference in Ocular Cells. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daub, C.D.; Mabate, B.; Malgas, S.; Pletschke, B.I. Fucoidan from Ecklonia maxima is a powerful inhibitor of the diabetes-related enzyme, α-glucosidase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Yang, H.-W.; Lee, H.-G.; Jeon, Y.-J. The Potential of Sulfated Polysaccharides Isolated from the Brown Seaweed Ecklonia maxima in Cosmetics: Antioxidant, Anti-melanogenesis, and Photoprotective Activities. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayawardena, T.U.; Fernando, I.P.S.; Lee, W.W.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Kim, H.-S.; Lee, D.-S.; Jeon, Y.-J. Isolation and purification of fucoidan fraction in Turbinaria ornata from the Maldives; Inflammation inhibitory potential under LPS stimulated conditions in in-vitro and in-vivo models. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Samarakoon, K.W.; Lee, W.W.; Kim, H.-S.; Kang, N.; Ranasinghe, P.; Lee, H.-S.; Jeon, Y.-J. A fucoidan fraction purified from Chnoospora minima; a potential inhibitor of LPS-induced inflammatory responses. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marais, M.-F.; Joseleau, J.-P. A fucoidan fraction from Ascophyllum nodosum. Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 336, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.J.; Wan Aida, W.M.; Maskat, M.Y.; Mamot, S.; Ropien, J.; Mazita Mohd, D. Isolation and antioxidant capacity of fucoidan from selected Malaysian seaweeds. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 42, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilan, M.I.; Grachev, A.A.; Ustuzhanina, N.E.; Shashkov, A.S.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. Structure of a fucoidan from the brown seaweed Fucus evanescens C.Ag. Carbohydr. Res. 2002, 337, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilan, M.I.; Grachev, A.A.; Ustuzhanina, N.E.; Shashkov, A.S.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. A highly regular fraction of a fucoidan from the brown seaweed Fucus distichus L. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synytsya, A.; Kim, W.-J.; Kim, S.-M.; Pohl, R.; Synytsya, A.; Kvasnička, F.; Čopíková, J.; Il Park, Y. Structure and antitumour activity of fucoidan isolated from sporophyll of Korean brown seaweed Undaria pinnatifida. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, S.; Vinosha, M.; Marudhupandi, T.; Rajasekar, P.; Prabhu, N.M. Isolation of fucoidan from Sargassum polycystum brown algae: Structural characterization, in vitro antioxidant and anticancer activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, A.; Ottani, A.; Sandrini, M. Dual acting anti-inflammatory drugs: A reappraisal. Pharmacol. Res. 2001, 44, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Xu, X.; Zheng, X.; Reponen, T.; Chen, A.; Huo, X. Heavy metals in PM2.5 and in blood, and children’s respiratory symptoms and asthma from an e-waste recycling area. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.H.; Hsu, S.-I.; Yan, B.; Moors, K.; Chillrud, S.N.; Ross, J.; Wang, S.; Perzanowski, M.S.; Kinney, P.L.; Whyatt, R.M.; et al. Childhood exposure to fine particulate matter and black carbon and the development of new wheeze between ages 5 and 7 in an urban prospective cohort. Environ. Int. 2012, 45, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikula, K.; Chaika, V.; Zakharenko, A.; Savelyeva, A.; Kirsanova, I.; Anisimova, A.; Golokhvast, K. Toxicity of Carbon, Silicon, and Metal-Based Nanoparticles to the Hemocytes of Three Marine Bivalves. Animals 2020, 10, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnani, N.D.; Muresan, X.M.; Belmonte, G.; Cervellati, F.; Sticozzi, C.; Pecorelli, A.; Miracco, C.; Marchini, T.; Evelson, P.; Valacchi, G. Skin damage mechanisms related to airborne particulate matter exposure. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 149, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Dias, M.K.H.M.; Madusanka, D.M.D.; Han, E.J.; Kim, M.J.; Heo, S.-J.; Lee, K.; Cheong, S.H.; Ahn, G. Low molecular weight fucoidan fraction ameliorates inflammation and deterioration of skin barrier in fine-dust stimulated keratinocytes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Kim, H.-S.; Lee, W.W.; Vaas, A.P.J.P.; De Silva, H.I.C.; Abayaweera, G.S.; Nanayakkara, C.M.; Abeytunga, D.T.U.; Lee, D.-S.; et al. Beijing urban particulate matter-induced injury and inflammation in human lung epithelial cells and the protective effects of fucosterol from Sargassum binderi (Sonder ex J. Agardh). Environ. Res. 2019, 172, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafini, M.; Peluso, I.; Raguzzini, A. Flavonoids as anti-inflammatory agents. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2010, 69, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grauffel, V.; Kloareg, B.; Mabeau, S.; Durand, P.; Jozefonvicz, J. New natural polysaccharides with potent antithrombic activity: Fucans from brown algae. Biomaterials 1989, 10, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Dias, M.K.H.M.; Madusanka, D.M.D.; Han, E.J.; Kim, M.J.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Lee, K.; Cheong, S.H.; Han, Y.S.; Park, S.R. Human Keratinocyte UVB-Protective Effects of a Low Molecular Weight Fucoidan from Sargassum horneri Purified by Step Gradient Ethanol Precipitation. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-X.; Wijesekara, I.; Li, Y.; Kim, S.-K. Phlorotannins as bioactive agents from brown algae. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 2219–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, T.; Lang, S.; Ulber, R.; Muffler, K. Novel procedures for the extraction of fucoidan from brown algae. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Fernando, I.P.S.; Kim, E.-A.; Ahn, G.; Jee, Y.; Jeon, Y.-J. Anti-inflammatory activity of a sulfated polysaccharide isolated from an enzymatic digest of brown seaweed Sargassum horneri in RAW 264.7 cells. nrp 2016, 11, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Samarakoon, K.W.; Lee, W.W.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, E.A.; Gunasekara, U.K.D.S.S.; Abeytunga, D.T.U.; Nanayakkara, C.; de Silva, E.D.; et al. FTIR characterization and antioxidant activity of water soluble crude polysaccharides of Sri Lankan marine algae. Algae 2017, 32, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Wang, S.-H.; Huang, C.-Y.; Dong, C.-D.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chang, C.-C.; Chang, J.-S. Effect of molecular mass and sulfate content of fucoidan from Sargassum siliquosum on antioxidant, anti-lipogenesis, and anti-inflammatory activity. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2021, 132, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncada, S.; Higgs, A. The L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 2002–2012. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, S.-J.; Yoon, W.-J.; Kim, K.-N.; Ahn, G.-N.; Kang, S.-M.; Kang, D.-H.; Affan, A.; Oh, C.; Jung, W.-K.; Jeon, Y.-J. Evaluation of anti-inflammatory effect of fucoxanthin isolated from brown algae in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 2045–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, C. Interleukin-6 and chronic inflammation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K. Role of ERK/MAPK signalling pathway in anti-inflammatory effects of Ecklonia cava in activated human mast cell line-1 cells. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2014, 7, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Shikov, A.N. Mechanisms of Bioactivities of Fucoidan from the Brown Seaweed Fucus vesiculosus L. of the Barents Sea. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asanka Sanjeewa, K.K.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, S.-Y.; Shanura Fernando, I.P.; Wang, L.; Abetunga, D.T.U.; Kim, W.-S.; Lee, D.-S.; Jeon, Y.-J. Fucoidan isolated from Padina commersonii inhibit LPS-induced inflammation in macrophages blocking TLR/NF-κB signal pathway. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 224, 115195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-G.; Je, J.-G.; Hwang, J.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Nagahawatta, D.P.; Lu, Y.A.; Kim, H.-S.; Kang, M.-C.; Lee, D.-S.; Jeon, Y.-J. Comparision of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of enzyme assisted hydrolysate from Ecklonia maxima blades and stipe. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2021, 24, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.S.; Yoon, Y.D.; Lee, K.H.; Park, S.-K.; Kim, H.M. Costunolide inhibits interleukin-1β expression by down-regulation of AP-1 and MAPK activity in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 313, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardena, T.U.; Kim, H.-S.; Asanka Sanjeewa, K.K.; Han, E.J.; Jee, Y.; Ahn, G.; Rho, J.-R.; Jeon, Y.-J. Loliolide, isolated from Sargassum horneri; abate LPS-induced inflammation via TLR mediated NF-κB, MAPK pathways in macrophages. Algal Res. 2021, 56, 102297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Verma, I.M. NF-κB regulation in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjeewa, K.A.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, S.-Y.; Ahn, G.; Kim, H.-J.; Fu, X.; Jee, Y.; Jeon, Y.-J. Ethanol extract separated from Sargassum horneri (Turner) abate LPS-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 22, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S. Toll-like Receptors and Innate Immunity. Adv. Immunol. 2001, 78, 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kaminska, B. MAPK signalling pathways as molecular targets for anti-inflammatory therapy—From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic benefits. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2005, 1754, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid, L.V.; Wang, C.-Y.; Guttridge, D.C.; Schottelius, A.J.G.; Baldwin, A.S.; Mayo, M.W. Akt Suppresses Apoptosis by Stimulating the Transactivation Potential of the RelA/p65 Subunit of NF-κB. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 1626–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardena, T.U.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Lee, H.-G.; Nagahawatta, D.P.; Yang, H.-W.; Kang, M.-C.; Jeon, Y.-J. Particulate Matter-Induced Inflammation/Oxidative Stress in Macrophages: Fucosterol from Padina boryana as a Potent Protector, Activated via NF-κB/MAPK Pathways and Nrf2/HO-1 Involvement. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahawatta, D.; Sanjeewa, K.A.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Kim, H.-S.; Yang, H.-W.; Jiang, Y.; Je, J.-G.; Lee, T.-K.; Jeon, Y.-J. Drying seaweeds using hybrid hot water Goodle dryer (HHGD): Comparison with freeze-dryer in chemical composition and antioxidant activity. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2021, 24, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodgson, K.; Price, R.J. A note on the determination of the ester sulphate content of sulphated polysaccharides. Biochem. J. 1962, 84, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, V.T.; Dai Hung, N.; Se-Kwon, K. Pharmaceutical properties of marine polyphenols: An overview. ACTA Pharm. Sci. 2019, 57, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.-C.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, E.-A.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Yu, S.-K.; Chae, J.B.; Choe, I.-H.; Cho, J.H.; Jeon, Y.-J. Antioxidant activity of polysaccharide purified from Acanthopanax koreanum Nakai stems in vitro and in vivo zebrafish model. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 127, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornsson, S. Size-Dependent Separation of Proteoglycans by Electrophoresis in Gels of Pure Agarose. Anal. Biochem. 1993, 210, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, G.-S.; Lee, D.-S.; Li, B.; Byun, E.; Kwon, D.-Y.; Park, H.; Kim, Y.-C. Protective effect of sauchinone by upregulating heme oxygenase-1 via the P38 MAPK and Nrf2/ARE pathways in HepG2 cells. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Polysaccharide Content % | Sulfate Content % | Protein Content % | Polyphenol Content % | Sulfated Polysaccharide Content % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude fucoidan | 60.54 | 23.63 | 2.82 | 2.01 | 84.17 |
| EMLF1 | 76.53 | 11.98 | 1.41 | 1.08 | 88.51 |
| EMLF2 | 72.38 | 18.69 | 0.86 | 1.07 | 91.07 |
| EMLF3 | 69.55 | 22.64 | 0.86 | 0.95 | 92.19 |
| EMLF4 | 65.49 | 25.16 | 0.61 | 0.74 | 90.65 |
| EMLF5 | 60.14 | 32.67 | 0.55 | 0.64 | 92.81 |
| EMLF6 | 56.89 | 35.11 | 0.53 | 0.47 | 92 |
| EMLF7 | 51.44 | 39.76 | 0.48 | 0.32 | 91.2 |
| EMLF1 | EMLF2 | EMLF3 | EMLF4 | EMLF5 | EMLF6 | EMLF7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fucose | 0.73 | 16.46 | 28.82 | 33.01 | 36.83 | 56.68 | 81.83 |
| Rhamnose | ND | 1.34 | 0.96 | 0.86 | 1.86 | 1.08 | 0.33 |
| Arabinose | ND | 0.66 | 4.1 | 0.14 | 0.23 | 0.12 | 0.04 |
| Galactose | ND | 11.51 | 20.42 | 18.7 | 34.17 | 25.01 | 14.67 |
| Glucose | 99.27 | 46.27 | 4.31 | 5.76 | ND | ND | ND |
| Mannose | ND | 23.76 | 41.38 | 41.5 | 26.91 | 17.11 | 3.13 |
| Yield % | 9.55 ± 0.56 | 9.04 ± 0.22 | 10.74 ±0.42 | 11.32 ± 0.26 | 9.51 ± 0.62 | 9.36 ± 0.49 | 9.11 ± 0.68 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagahawatta, D.P.; Liyanage, N.M.; Jayawardhana, H.H.A.C.K.; Lee, H.-G.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Jeon, Y.-J. Anti-Fine Dust Effect of Fucoidan Extracted from Ecklonia maxima Leaves in Macrophages via Inhibiting Inflammatory Signaling Pathways. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20070413
Nagahawatta DP, Liyanage NM, Jayawardhana HHACK, Lee H-G, Jayawardena TU, Jeon Y-J. Anti-Fine Dust Effect of Fucoidan Extracted from Ecklonia maxima Leaves in Macrophages via Inhibiting Inflammatory Signaling Pathways. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(7):413. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20070413
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagahawatta, D.P., N.M. Liyanage, H.H.A.C.K. Jayawardhana, Hyo-Geun Lee, Thilina U. Jayawardena, and You-Jin Jeon. 2022. "Anti-Fine Dust Effect of Fucoidan Extracted from Ecklonia maxima Leaves in Macrophages via Inhibiting Inflammatory Signaling Pathways" Marine Drugs 20, no. 7: 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20070413
APA StyleNagahawatta, D. P., Liyanage, N. M., Jayawardhana, H. H. A. C. K., Lee, H. -G., Jayawardena, T. U., & Jeon, Y. -J. (2022). Anti-Fine Dust Effect of Fucoidan Extracted from Ecklonia maxima Leaves in Macrophages via Inhibiting Inflammatory Signaling Pathways. Marine Drugs, 20(7), 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20070413