Pseurotin A Validation as a Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Recurrence-Suppressing Lead via PCSK9-LDLR Axis Modulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. CWR-R1ca Cells Demonstrated Significant PCSK9 Axis Dysregulation
2.2. PCSK9 Knockdown in CWR-R1ca Cells
2.3. PCSK9 Knockdown Did Not Notably Affect CWR-R1ca Cells’ Proliferation
2.4. PCSK9 Knockdown Suppressed the CWR-R1ca Cells’ Migration Activity
2.5. PS Suppressed CWR-R1ca Cells’ Clonogenicity
2.6. TMA Immunohistochemistry
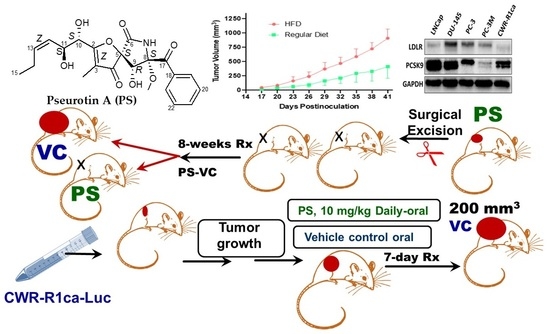
2.7. High Fat Diet-Induced CWR-R1ca CRPC Progression and Metastasis in a Nude Mouse Xenograft Model
2.8. Effect of HFD on the Total Serum Cholesterol and LDL-C Levels
2.9. Effect of HFD on Serum PCSK9 Levels
2.10. Effect of HFD on Serum PSA Levels
2.11. Effect of HFD on PCSK9 Expression Levels in Nude Mice CWR-R1ca-Luc Tumors
2.12. Pseurotin A Daily Oral 10 mg/kg Significantly Suppressed CWR-R1ca-Luc Tumor Locoregional and Distant Recurrences
2.13. Pseurotin A Reduced Nude Mice Serum Total Cholesterol and LDL-C Levels
2.14. Pseurotin A Reduced Nude Mice Serum PCSK9 Levels
2.15. Pseurotin A Reduced Nude Mice Serum PSA Levels
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals, Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
4.3. CWR-R1ca Cell Transfection
4.4. Luciferase-Labeled Cells Lentivirus Transduction
4.5. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.6. Cell Migration Wound Healing Scratch Assay
4.7. Colony Formation Assay
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Tissue Microarray Immunohistochemistry and Histochemical Score
4.10. In Vivo Studies
4.10.1. Animals
4.10.2. Diet Impact on CWR-R1ca-Luc Cells Tumor Progression and Metastasis
4.10.3. Recurrence Study
4.11. Serum Cholesterol Levels
4.12. Serum LDL-C Levels
4.13. Serum PCSK9 Levels
4.14. Serum Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Level
4.15. Statistical Analysis
4.16. Ethical Considerations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karantanos, T.; Corn, P.G.; Thompson, T.C. Prostate cancer progression after androgen deprivation therapy: Mechanisms of castrate resistance and novel therapeutic approaches. Oncogene 2013, 32, 5501–5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labrecque, M.P.; Coleman, I.M.; Brown, L.G.; True, L.D.; Kollath, L.; Lakely, B.; Nguyen, H.M.; Yang, Y.C.; da Costa, R.M.G.; Kaipainen, A.; et al. Molecular profiling stratifies diverse phenotypes of treatment-refractory metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4492–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bluemn, E.G.; Coleman, I.M.; Lucas, J.M.; Coleman, R.T.; Hernandez-Lopez, S.; Tharakan, R.; Bianchi-Frias, D.; Dumpit, R.F.; Kaipainen, A.; Corella, A.N.; et al. Androgen receptor pathway-independent prostate cancer is sustained through FGF signaling. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 474–489.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, C.; Yoshioka, M.; Boivin, A.; Gan, L.; Takase, Y.; Labrie, F.; St-Amand, J. Atlas of dihydrotestosterone actions on the transcriptome of prostate in vivo. Prostate 2009, 69, 293–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, R.B.; Mostaghel, E.A.; Vessella, R.; Hess, D.L.; Kalhorn, T.F.; Higano, C.S.; True, L.D.; Nelson, P.S. Maintenance of intratumoral androgens in metastatic prostate cancer: A mechanism for castration-resistant tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4447–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Locke, J.A.; Guns, E.S.; Lubik, A.A.; Adomat, H.H.; Hendy, S.C.; Wood, C.A.; Ettinger, S.L.; Gleave, M.E.; Nelson, C.C. Androgen levels increase by intratumoral de novo steroidogenesis during progression of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6407–6415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mostaghel, E.A.; Nelson, P.S. Intracrine androgen metabolism in prostate cancer progression: Mechanisms of castration resistance and therapeutic implications. Best Practice Res. Clin. Endocr. Metab. 2008, 22, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bryce, A.; Ryan, C.J. Development and clinical utility of abiraterone acetate as an androgen synthesis inhibitor. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 91, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.H.; Gulati, R.; Azad, A.; Nadal, R.; Twardowski, P.; Vaishampayan, U.N.; Agarwal, N.; Heath, E.I.; Pal, S.K.; Rehman, H.T.; et al. Activity of enzalutamide in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer is affected by prior treatment with abiraterone and/or docetaxel. Prost. Can. Prost. Dis. 2015, 18, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guerrero, J.; Alfaro, I.E.; Gómez, F.; Protter, A.A.; Bernales, S. Enzalutamide, an androgen receptor signaling inhibitor, induces tumor regression in a mouse model of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Prostate 2013, 73, 1291–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostaghel, E.A.; Marck, B.T.; Plymate, S.R.; Vessella, R.L.; Balk, S.; Matsumoto, A.M. Nelson PS, Montgomery RB. Resistance to CYP17A1 inhibition with abiraterone in castration-resistant prostate cancer: Induction of steroidogenesis and androgen receptor splice variants. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 5913–5925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikonen, E. Cellular cholesterol trafficking and compartmentalization. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, K. How cells handle cholesterol. Science 2000, 290, 1721–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Vizio, D.; Solomon, K.R.; Freeman, M.R. Cholesterol and cholesterol-rich membranes in prostate cancer: An update. Tumori 2008, 94, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.R.; Solomon, K.R. Cholesterol and prostate cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 91, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vance, J.E.; Vance, D. Biochemistry of Lipids, Lipoproteins and Membranes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. Receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science 1986, 232, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seidah, N.G.; Prat, A. The biology and therapeutic targeting of the proprotein convertases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahed, K.S.; Siddique, A.B.; Mohyeldin, M.M.; Qusa, M.H.; Goda, A.A.; Singh, S.S.; Ayoub, N.M.; King, J.A.; Jois, S.D.; El Sayed, K.A. Pseurotin A as a novel suppressor of hormone dependent breast cancer progression and recurrence by inhibiting PCSK9 secretion and interaction with LDL receptor. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 158, 104847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Essalmani, R.; Day, R.; Khatib, A.M.; Seidah, N.G.; Prat, A. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 deficiency reduces melanoma metastasis in liver. Neoplasia 2012, 12, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonaventura, A.; Grossi, F.; Montecucco, F. PCSK9 is a promising prognostic marker in patients with advanced NSCLC. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 491–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Bao, X.; Hu, M.; Chang, H.; Jiao, M.; Cheng, J.; Xie, L.; Huang, Q.; Li, F.; Li, C.Y. Inhibition of PCSK9 potentiates immune checkpoint therapy for cancer. Nature 2020, 588, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Li, S.; Fang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Song, D.; Zhang, S.; Cai, Y. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 promotes gastric cancer metastasis and suppresses apoptosis by facilitating MAPK signaling pathway through HSP70 up-regulation. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 609663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, S.; Reaven, E. Scavenger receptor class BI and selective cholesteryl ester uptake: Partners in the regulation of steroidogenesis. Mol. Cell. Endocr. 2002, 195, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krycer, J.R.; Kristiana, I.; Brown, A.J. Cholesterol homeostasis in two commonly used human prostate cancer cell-lines, LNCaP and PC-3. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leon, C.G.; Locke, J.A.; Adomat, H.H.; Etinger, S.L.; Twiddy, A.L.; Neumann, R.D.; Nelson, C.C.; Guns, E.S.; Wasan, K.M. Alterations in cholesterol regulation contribute to the production of intratumoral androgens during progression to castration-resistant prostate cancer in a mouse xenograft model. Prostate 2010, 70, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, Y.; Koike, H.; Nakano, T.; Nakajima, K.; Takahashi, S.; Suzuki, K. Remnant lipoproteins induced proliferation of human prostate cancer cell, PC-3 but not LNCaP, via low density lipoprotein receptor. Cancer Epidemiol. 2009, 33, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, S.; Luo, H.; Lu, Q.; Yu, S. PCSK9 promotes the progression and metastasis of colon cancer cells through regulation of EMT and PI3K/AKT signaling in tumor cells and phenotypic polarization of macrophages. J. Experim. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleem, S.; Qin, L.; Yi, W.; Lian, X.-Y.; Zhang, Z. Bioactive metabolites from the Mariana Trench sediment-derived fungus Penicillium sp. SY2107. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Liu, M.; Jenkins, I.D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Quinn, R.J.; Feng, Y. Genome-inspired chemical exploration of marine fungus Aspergillus fumigatus MF071. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, K.; Bi, H.; Chai, W.; Lian, X.Y.; Zhang, Z. Antiglioma pseurotin A from marine Bacillus sp. FS8D regulating tumour metabolic enzymes. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1353–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Wang, S.W.; Wang, G.J.; Pang, K.L.; Lee, C.Q.; Kuo, Y.H.; Cha, H.J.; Lin, R.K.; Lee, T.H. Angiogenesis inhibitors and anti-Inflammatory agents from Phoma sp. NTOU4195. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2983–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchoa, P.K.S.; Pimenta, A.T.A.; Braz-Filho, R.; de Oliveira, M.C.F.; Saraiva, N.N.; Rodrigues, B.S.F.; Pfenning, L.H.; Abreu, L.M.; Wilke, D.V.; Florêncio, K.G.D.; et al. New cytotoxic furan from the marine sediment-derived fungi Aspergillus niger. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 2599–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copmans, D.; Rateb, M.; Tabudravu, J.N.; Pérez-Bonilla, M.; Dirkx, N.; Vallorani, R.; Diaz, C.; del Palacio, J.P.; Smith, A.J.; Ebel, R.; et al. Zebrafish-based discovery of antiseizure compounds from the Red Sea: Pseurotin A2 and azaspirofuran A. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 1652–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelwahed, K.; Siddique, A.B.; Qusa, M.; King, J.A.; Souid, S.; Abd Elmageed, Z.; El Sayed, K.A. The PCSK9 axis-targeting pseurotin A as a novel prostate cancer recurrence suppressor lead. ACS Pharmacol. Translat. Sci. 2021, 4, 1771–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGehee, O.C.; Ebrahim, H.Y.; Rad, A.H.; Abdelwahed, K.S.; Mudhish, E.A.; King, J.A.; Helal, I.E.; Meyer, S.A.; El Sayed, K.A. Towards developing novel prostate cancer recurrence suppressors: Acute toxicity of pseurotin A, an orally active PCSK9 axis-targeting small-molecule in Swiss albino mice. Molecules 2023, 28, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinov, I.V.; Antony, L.; Dalrymple, S.L.; Becker, R.; Cheng, L.; Isaacs, J.T. PC3, but not DU145, human prostate cancer cells retain the coregulators required for tumor suppressor ability of androgen receptor. Prostate 2006, 66, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shourideh, M.; DePriest, A.; Mohler, J.L.; Wilson, E.M.; Koochekpour, S. Characterization of fibroblast-free CWR-R1ca castration-recurrent prostate cancer cell line. Prostate 2016, 76, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riss, T.L.; Moravec, R.A. Use of multiple assay endpoints to investigate the effects of incubation time, dose of toxin, and plating density in cell-based cytotoxicity assays. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2004, 2, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.J.; Fakurnejad, S.; Ma, Q.; Hashizume, R. Bioluminescence imaging of an immunocompetent animal model for glioblastoma. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 107, e53287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddique, A.B.; Kilgore, P.C.S.R.; Tajmim, A.; Singh, S.S.; Meyer, S.A.; Jois, S.D.; Cvek, U.; Trutsch, M.; El Sayed, K.A. (−)-Oleocanthal as a dual c-MET-COX2 inhibitor for the control of lung cancer. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, A.; Ebrahim, H.Y.; Tajmim, A.; King, J.; Abdelwahed, K.; Abd Elmageed, Z.Y.; El Sayed, K.A. Oleocanthal attenuates metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer progression and recurrence by targeting SMYD2. Cancers 2022, 14, 3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awasthi, S.; Gerke, T.; Park, J.Y.; Asamoah, F.A.; Williams, V.L.; Fink, A.K.; Balkrishnan, R.; Lee, D.I.; Malkowicz, S.B.; Lal, P.; et al. Optimizing time to treatment to achieve durable biochemical disease control after surgery in prostate cancer: A multi-institutional cohort study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 3, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelton, K.; Freeman, M.R.; Solomon, K.R. Cholesterol and prostate cancer. Current Opin. Pharmacol. 2012, 12, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamnagerwalla, J.; Howard, L.E.; Allott, E.H.; Vidal, A.C.; Moreira, D.M.; Castro-Santamaria, R.; Andriole, G.L.; Freeman, M.R.; Freedland, S.J. Serum cholesterol and risk of high-grade prostate cancer: Results from the REDUCE study. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2018, 21, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murtola, T.J.; Kasurinen, T.V.; Talala, K.; Taari, K.; Tammela, T.L.; Auvinen, A. Serum cholesterol and prostate cancer risk in the Finnish randomized study of screening for prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2019, 22, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopsack, K.H.; Gerke, T.A.; Andrén, O.; Andersson, S.O.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Mucci, L.A.; Rider, J.R. Cholesterol uptake and regulation in high-grade and lethal prostate cancer. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohler, J.L.; Gregory, C.W.; Ford, O.H.; Kim, D.; Weaver, C.M.; Petrusz, P.; Wilson, E.M.; French, F.S. The androgen axis in recurrent prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mostaghel, E.A.; Solomon, K.R.; Pelton, K.; Freeman, M.R.; Montgomery, R.B. Impact of circulating cholesterol levels on growth and intratumoral androgen concentration of prostate tumors. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, S.; Nara, T.; Sato, H.; Koizumi, A.; Huang, M.; Inoue, H.T. Research evidence on high-fat diet-induced prostate cancer development and progression. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paciullo, F.; Fallarino, F.; Bianconi, V.; Mannarino, M.R.; Sahebkar, A.; Pirro, M. PCSK9 at the crossroad of cholesterol metabolism and immune function during infections. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 2330–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, K.N.; Fisher, E.A.; Breslow, J.L. Overexpression of PCSK9 accelerates the degradation of the LDLR in a post-endoplasmic reticulum compartment. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2069–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pettersen, D.; Fjellström, O. Small molecule modulators of PCSK9–A literature and patent overview. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 1155–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Yarmolinsky, J.; Gill, D.; Bull, C.J.; Perks, C.M.; The PRACTICAL Consortium; Smith, G.D.; Gaunt, T.R.; Richardson, T.G. Genetically proxied PCSK9 inhibition provides indication of lower prostate cancer risk: A Mendelian randomization study. PLoS Med. 2023, 20, e1003988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athavale, D.; Chouhan, S.; Pandey, V.; Mayengbam, S.S.; Singh, S.; Bhat, M.K. Hepatocellular carcinoma-associated hypercholesterolemia: Involvement of proprotein-convertase-subtilisin-kexin type-9 (PCSK9). Cancer Metab. 2018, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obenauf, A.C.; Massagué, J. Surviving at a distance: Organ-specific metastasis. Trends Cancer 2015, 1, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, D.X.; Bos, P.D.; Massagué, J. Metastasis: From dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://imagej.net/ij/index.html (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Gaballah, M.S.A.; Ali, H.E.A.; Hassan, Z.A.; Mahgoub, S.; Ali, H.I.; Rhim, J.S.; Zerfaoui, M.; El Sayed, K.A.; Stephen, D.; Sylvester, P.W.; et al. Small extracellular vesicle-associated miR-6068 promotes aggressive phenotypes of prostate cancer through miR-6068/HIC2/SIRT1 axis. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2022, 12, 4015–4027. [Google Scholar]
- Abd Elmageed, Z.Y.; Moroz, K.; Srivastav, S.K.; Fang, Z.; Crawford, B.E.; Moparty, K.; Thomas, R.; Abdel-Mageed, A.B. High circulating estrogens and selective expression of ER-beta in prostate tumors of Americans: Implications for racial disparity of prostate cancer. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 2017–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]












Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelwahed, K.S.; Siddique, A.B.; Ebrahim, H.Y.; Qusa, M.H.; Mudhish, E.A.; Rad, A.H.; Zerfaoui, M.; Abd Elmageed, Z.Y.; El Sayed, K.A. Pseurotin A Validation as a Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Recurrence-Suppressing Lead via PCSK9-LDLR Axis Modulation. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21040215
Abdelwahed KS, Siddique AB, Ebrahim HY, Qusa MH, Mudhish EA, Rad AH, Zerfaoui M, Abd Elmageed ZY, El Sayed KA. Pseurotin A Validation as a Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Recurrence-Suppressing Lead via PCSK9-LDLR Axis Modulation. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(4):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21040215
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelwahed, Khaldoun S., Abu Bakar Siddique, Hassan Y. Ebrahim, Mohammed H. Qusa, Ethar A. Mudhish, Ashkan H. Rad, Mourad Zerfaoui, Zakaria Y. Abd Elmageed, and Khalid A. El Sayed. 2023. "Pseurotin A Validation as a Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Recurrence-Suppressing Lead via PCSK9-LDLR Axis Modulation" Marine Drugs 21, no. 4: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21040215
APA StyleAbdelwahed, K. S., Siddique, A. B., Ebrahim, H. Y., Qusa, M. H., Mudhish, E. A., Rad, A. H., Zerfaoui, M., Abd Elmageed, Z. Y., & El Sayed, K. A. (2023). Pseurotin A Validation as a Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Recurrence-Suppressing Lead via PCSK9-LDLR Axis Modulation. Marine Drugs, 21(4), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21040215