Quantification of Xylanolytic and Cellulolytic Activities of Fungal Strains Isolated from Palmaria palmata to Enhance R-Phycoerythrin Extraction of Palmaria palmata: From Seaweed to Seaweed
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
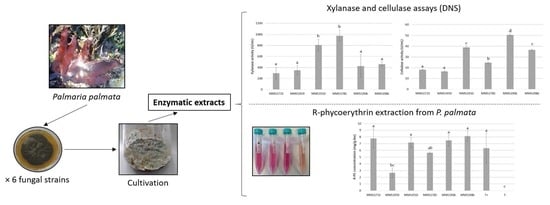
2.1. Quantifications of Xylanase and Cellulase Activities
2.2. Reducing Sugars, R-PE and Total Proteins Amounts from P. palmata Lysates
3. Discussion
3.1. Aspergillus, Penicillium and Cladosporium Marine Fungal Genera as Promising Xylanase and Cellulase Producers
3.2. Xylanolytic and Cellulolytic Profiles of Fungal Strains Related to Their Macroalgal Degradation Abilities and R-PE Recovery
3.3. Biotechnological Potential of Fungal Enzymatic Extracts
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Fungal Strains Isolation
4.2. Fungal Strain Identification
4.3. Strain Cultivation and Preparation of Conidia Suspension
4.4. Enzyme Production
4.5. Protein Quantification
4.6. Enzymatic Assays
4.7. R-PE Extraction from P. palmata
4.8. Dosage of R-PE, Proteins and Reducing Sugars
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mabeau, S.; Fleurence, J. Seaweed in food products: Biochemical and nutritional aspects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1993, 4, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Lee, W.; Jeon, Y.-J. Nutrients and bioactive potentials of edible green and red seaweed in Korea. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 21, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, D.; Melo, T.; Rey, F.; Meneses, J.; Monteiro, F.L.; Helguero, L.A.; Abreu, M.H.; Lillebø, A.I.; Calado, R.; Domingues, M.R. Valuing bioactive lipids from green, red and brown macroalgae from aquaculture, to foster functionality and biotechnological applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioanou, E.; Roussis, V. Natural products from seaweeds. In Plant-Derived Natural Products; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 47, pp. 51–81. [Google Scholar]
- Patwary, Z.P.; Paul, N.A.; Nishitsuji, K.; Campbell, A.H.; Shoguchi, E.; Zhao, M.; Cummins, S.F. Application of omics research in seaweeds with a focus on red seaweeds. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2021, 20, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.R.K.; Gupta, V.; Jha, B. Developments in biotechnology of red algae. In Red Algae in the Genomic Age; Seckbach, J., Chapman, D.J., Eds.; Cellular Origin, Life in Extreme Habitats and Astrobiology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 13, pp. 307–341. ISBN 978-90-481-3794-7. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul Malik, S.A.; Bedoux, G.; Garcia Maldonado, J.Q.; Freile-Pelegrín, Y.; Robledo, D.; Bourgougnon, N. Defence on surface: Macroalgae and their surface-associated microbiome. In Advances in Botanical Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 95, pp. 327–368. ISBN 978-0-08-102710-3. [Google Scholar]
- Rico, M.; González, A.G.; Santana-Casiano, M.; González-Dávila, M.; Pérez-Almeida, N.; de Tangil, M.S. Production of primary and secondary metabolites using algae. In Prospects and Challenges in Algal Biotechnology; Tripathi, B.N., Kumar, D., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 311–326. ISBN 978-981-10-1949-4. [Google Scholar]
- Rosales-Mendoza, S.; García-Silva, I.; González-Ortega, O.; Sandoval-Vargas, J.M.; Malla, A.; Vimolmangkang, S. The potential of algal biotechnology to produce antiviral compounds and biopharmaceuticals. Molecules 2020, 25, 4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhlal, R.; Riadi, H.; Bourgougnon, N. Antibacterial activity of the extracts of Rhodophyceae from the Atlantic and the Mediterranean coasts of Morocco. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2013, 2, 2431–2439. [Google Scholar]
- Hardouin, K.; Bedoux, G.; Burlot, A.-S.; Nyvall-Collén, P.; Bourgougnon, N. Enzymatic recovery of metabolites from seaweeds. In Advances in Botanical Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 71, pp. 279–320. ISBN 978-0-12-408062-1. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, A.; Kamthania, M.C.; Kumar, A. Bioactive compounds and properties of seaweeds—A review. OALib 2014, 1, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, N.C.; Catarino, M.D.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cardoso, S.M. Brown macroalgae as valuable food ingredients. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleurence, J. Seaweed proteins: Biochemical, nutritional aspects and potential uses. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1999, 10, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galland-Irmouli, A.-V.; Fleurence, J.; Lamghari, R.; Luçon, M.; Rouxel, C.; Barbaroux, O.; Bronowicki, J.-P.; Villaume, C.; Guéant, J.-L. Nutritional value of proteins from edible seaweed Palmaria palmata (Dulse). J. Nutr. Biochem. 1999, 10, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leandro, A.; Pereira, L.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Diverse applications of marine macroalgae. Mar. Drugs 2019, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lourenço-Lopes, C.; Fraga-Corral, M.; Jimenez-Lopez, C.; Pereira, A.G.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Carpena, M.; Prieto, M.A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Metabolites from macroalgae and its applications in the cosmetic industry: A circular economy approach. Resources 2020, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumay, J.; Morançais, M.; Munier, M.; Le Guillard, C.; Fleurence, J. Phycoerythrins. In Advances in Botanical Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 71, pp. 321–343. ISBN 978-0-12-408062-1. [Google Scholar]
- Naseri, A.; Marinho, G.S.; Holdt, S.L.; Bartela, J.M.; Jacobsen, C. Enzyme-assisted extraction and characterization of protein from red seaweed Palmaria palmata. Algal Res. 2020, 47, 101849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhang, J.; Liang, D. Structure and function of chromophores in R-phycoerythrin at 1.9 Å resolution. Proteins 1999, 34, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Oyanedel, J.; Contreras-Martel, C.; Bruna, C.; Bunster, M. Structural-functional analysis of the oligomeric protein R-phycoerythrin. Biol. Res. 2004, 37, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyabe, Y.; Furuta, T.; Takeda, T.; Kanno, G.; Shimizu, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Gai, Z.; Yasui, H.; Kishimura, H. Structural properties of phycoerythrin from dulse Palmaria palmata. J. Food Biochem. 2017, 41, e12301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, J.-F.; Wang, G.-C.; Tseng, C.-K. Method for large-scale isolation and purification of R-phycoerythrin from red alga Polysiphonia urceolata Grev. Protein Expr. Purif. 2006, 49, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleurence, J. R-phycoerythrin from red macroalgae: Strategies for extraction and potential application in biotechnology. Appl. Biotechnol. Food Sci. Policy 2003, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.-N.; Su, H.-N.; Yan, S.-G.; Shao, S.-M.; Xie, B.-B.; Chen, X.-L.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Zhou, B.-C.; Zhang, Y.-Z. Probing the pH sensitivity of R-phycoerythrin: Investigations of active conformational and functional variation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Bioenerg. 2009, 1787, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dumay, J.; Clément, N.; Morançais, M.; Fleurence, J. Optimization of hydrolysis conditions of Palmaria palmata to enhance R-phycoerythrin extraction. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 131, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharmoria, P.; Correia, S.F.H.; Martins, M.; Hernández-Rodríguez, M.A.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Ferreira, R.A.S.; Carlos, L.D.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Protein cohabitation: Improving the photochemical stability of R-phycoerythrin in the solid state. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 6249–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfriso, A.A.; Gallo, M.; Baldi, F. Phycoerythrin productivity and diversity from five red macroalgae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 2523–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekasova, O.D.; Ryvkina, N.G.; Chmutin, I.A.; Shtein-Margolina, V.A.; Kurganov, B.I. Electrical properties of R-phycoerythrin containing Ag0 nanoparticles in its channels. Inorg. Mater. 2017, 53, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, C.; Morançais, M.; Gaudin, P.; Fleurence, J. Effect of enzymatic digestion on thallus degradation and extraction of hydrosoluble compounds from Grateloupia turuturu. Bot. Mar. 2009, 52, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnedy, P.A.; FitzGerald, R.J. Extraction of protein from the macroalga Palmaria palmata. LWT 2013, 51, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, Y.; Fleurence, J. Simultaneous extraction of proteins and DNA by an enzymatic treatment of the cell wall of Palmaria palmata (Rhodophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 2008, 20, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Jónsdóttir, R.; Kristinsson, H.G.; Hreggvidsson, G.O.; Jónsson, J.Ó.; Thorkelsson, G.; Ólafsdóttir, G. Enzyme-enhanced extraction of antioxidant ingredients from red algae Palmaria palmata. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahaye, M.; Michel, C.; Barry, J.L. Chemical, physicochemical and in-vitro fermentation characteristics of dietary fibres from Palmaria palmata (L.) Kuntze. Food Chem. 1993, 47, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, K.C.; Wright, J.L.C.; Simpson, F.J. Review of chemical constituents of the red alga Palmaria palmata (dulse). Econ. Bot. 1980, 34, 27–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.P.T.; Morancais, M.; Fleurence, J.; Tran, T.N.L.; Dumay, J. Extracting and purifying pigment R-phycoerythrin from the red alga Mastocarpus stellatus. In Proceedings of the 2018 4th International Conference on Green Technology and Sustainable Development (GTSD), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 23–24 November 2018; pp. 573–577. [Google Scholar]
- Charoensiddhi, S.; Conlon, M.A.; Franco, C.M.M.; Zhang, W. The development of seaweed-derived bioactive compounds for use as prebiotics and nutraceuticals using enzyme technologies. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 70, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.P.T.; Morançais, M.; Fleurence, J.; Pham, T.T.M.; Nguyen-Le, C.T.; Mai, T.P.C.; Tran, T.N.L.; Dumay, J. Optimisation of hydrolysis conditions for extraction of R-phycoerythrin from Gracilaria gracilis by enzyme polysaccharidase and response surface methodology. Int. Food Res. J. 2020, 27, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, R.; Raghavarao, K.S.M.S. Extraction of R-phycoerythrin from marine macro-algae, Gelidium pusillum, employing consortia of enzymes. Algal Res. 2018, 34, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzkar, N.; Sohail, M. An overview on marine cellulolytic enzymes and their potential applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 6873–6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kumar, B.; Agrawal, K.; Verma, P. Current perspective on production and applications of microbial cellulases: A review. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2021, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Anwar, Z.; Irshad, M.; Asad, M.J.; Ashfaq, H. Cellulase production from species of fungi and bacteria from agricultural wastes and its utilization in industry: A review. Adv. Enzym. Res. 2016, 4, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motta, F.L.; Andrade, C.C.P.; Santana, M.H.A. A review of xylanase production by the fermentation of xylan: Classification, characterization and applications. In Sustainable Degradation of Lignocellulosic Biomass—Techniques, Applications and Commercialization; Chandel, A., Ed.; InTech: Rang-Du-Fliers, France, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 251–275. ISBN 978-953-51-1119-1. [Google Scholar]
- Sampath-Wiley, P.; Neefus, C.D. An improved method for estimating R-phycoerythrin and R-phycocyanin contents from crude aqueous extracts of Porphyra (Bangiales, Rhodophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 2007, 19, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le Strat, Y.; Ruiz, N.; Fleurence, J.; Pouchus, Y.-F.; Déléris, P.; Dumay, J. Marine fungal abilities to enzymatically degrade algal polysaccharides, proteins and lipids: A review. J. Appl. Phycol. 2022, 34, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghukumar, S. Fungi: Characteristics and classification. In Fungi in Coastal and Oceanic Marine Ecosystems; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–15. ISBN 978-3-319-54303-1. [Google Scholar]
- Suryanarayanan, T.S. Fungal endosymbionts of seaweeds. In Biology of Marine Fungi; Raghukumar, C., Ed.; Progress in Molecular and Subcellular Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 53, pp. 53–69. ISBN 978-3-642-23341-8. [Google Scholar]
- Balabanova, L.; Slepchenko, L.; Son, O.; Tekutyeva, L. Biotechnology potential of marine fungi degrading plant and algae polymeric substrates. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marrion, O.; Schwertz, A.; Fleurence, J.; Guéant, J.L.; Villaume, C. Improvement of the digestibility of the proteins of the red alga Palmaria palmata by physical processes and fermentation. Nahrung 2003, 47, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, S.; Eshel, A. Determining phycoerythrin and phycocyanin concentrations in aqueous crude extracts of red algae. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1985, 36, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalla, S.M.M.; Ahmed, N.E.; Awad, H.M.; El Gamal, N.G.; El Shamy, A.R. Statistical optimization of xylanase production, using different agricultural wastes by Aspergillus oryzae MN894021, as a biological control of faba bean root diseases. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control. 2020, 30, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, F.A.; El Aty, A.A.A.; Wehaidy, H.R. Improved xylanase production by mixing low cost wastes and novel co-culture of three marine-derived fungi in solid state fermentation. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 336–349. [Google Scholar]
- Patyshakuliyeva, A.; Falkoski, D.L.; Wiebenga, A.; Timmermans, K.; de Vries, R.P. Macroalgae derived fungi have high abilities to degrade algal polymers. Microorganisms 2019, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raghukumar, C.; Muraleedharan, U.; Gaud, V.R.; Mishra, R. Xylanases of marine fungi of potential use for biobleaching of paper pulp. J. Ind. Microbiol. 2004, 31, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienert, R.; Baier, K.; Volkmer, R.; Lockau, W.; Heinemann, U. Crystal structure of NblA from Anabaena Sp. PCC 7120, a small protein playing a key role in phycobilisome degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 5216–5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomaa, M.; Hifney, A.F.; Fawzy, M.A.; Issa, A.A.; Abdel-Gawad, K.M. Biodegradation of Palisada perforata (Rhodophyceae) and Sargassum sp. (Phaeophyceae) biomass by crude enzyme preparations from algicolous fungi. J. Appl. Phycol. 2015, 27, 2395–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaeva, E.V.; Usov, A.I.; Sinitsyn, A.P.; Tambiev, A.H. Degradation of agarophytic red algal cell wall components by new crude enzyme preparations. J. Appl. Phycol. 1999, 11, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, A.; Singh, N.K.; Kaushal, A.; Madamwar, D. Characterization of an intact phycoerythrin and its cleaved 14kDa functional subunit from marine cyanobacterium Phormidium sp. A27DM. Process. Biochem. 2011, 46, 1793–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zaky, A.A.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Jia, Y. Purification and characterization of a new xylanase with excellent stability from Aspergillus flavus and its application in hydrolyzing pretreated corncobs. Protein Expr. Purif. 2019, 154, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhu, K.M.; Beena, P.S.; Chandrasekaran, M. Extracellular β-glucosidase production by a marine Aspergillus sydowii BTMFS 55 under solid state fermentation using statistical experimental design. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2009, 14, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.M.; Lee, J.P.; Baek, S.C.; Kim, S.G.; Jo, Y.D.; Kim, J.; Kim, H. Characterization of two extracellular β-glucosidases produced from the cellulolytic fungus Aspergillus sp. YDJ216 and their potential applications for the hydrolysis of flavone glycosides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulyman, A.O.; Igunnu, A.; Malomo, S.O. Isolation, purification and characterization of cellulase produced by Aspergillus niger cultured on Arachis hypogaea shells. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, K.; Jensen, K.; Meyer, A.S.; Frisvad, J.C.; Lange, L. Fungal secretome profile categorization of CAZymes by function and family corresponds to fungal phylogeny and taxonomy: Example Aspergillus and Penicillium. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benoit, I.; Culleton, H.; Zhou, M.; DiFalco, M.; Aguilar-Osorio, G.; Battaglia, E.; Bouzid, O.; Brouwer, C.P.J.M.; El-Bushari, H.B.O.; Coutinho, P.M.; et al. Closely related fungi employ diverse enzymatic strategies to degrade plant biomass. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2015, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horta, M.A.C.; Filho, J.A.F.; Murad, N.F.; de Oliveira Santos, E.; dos Santos, C.A.; Mendes, J.S.; Brandão, M.M.; Azzoni, S.F.; de Souza, A.P. Network of proteins, enzymes and genes linked to biomass degradation shared by Trichoderma species. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tedersoo, L.; Naadel, T.; Bahram, M.; Pritsch, K.; Buegger, F.; Leal, M.; Kõljalg, U.; Põldmaa, K. Enzymatic activities and stable isotope patterns of ectomycorrhizal fungi in relation to phylogeny and exploration types in an afrotropical rain forest. New Phytol. 2012, 195, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wychen, S.; Laurens, L.M. Determination of Total Carbohydrates in Algal Biomass: Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP); No. NREL/TP-5100-60957; National Renewable Energy Lab (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2016. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beg, Q.K.; Kapoor, M.; Mahajan, L.; Hoondal, G.S. Microbial xylanases and their industrial applications: A review. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 56, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiatrault-Chastel, C.; Heiss-Blanquet, S.; Margeot, A.; Berrin, J.-G. From fungal secretomes to enzymes cocktails: The path forward to bioeconomy. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 52, 107833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Bajar, S.; Devi, A.; Pant, D. An overview on the recent developments in fungal cellulase production and their industrial applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 14, 100652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galland-Irmouli, A.V.; Pons, L.; Lucon, M.; Villaume, C.; Mrabet, N.T.; Guéant, J.L.; Fleurence, J. One-step purification of R-phycoerythrin from the red macroalga Palmaria palmata using preparative polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. B 2000, 739, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickerham, L.J. A critical evaluation of the nitrogen assimilation tests commonly used in the classification of yeasts. J. Bacteriol. 1946, 52, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Weng, H.; Zhu, D.; Yuan, M.; Guan, F.; Xi, Y. Production and characterization of cellulolytic enzymes from the thermoacidophilic fungal Aspergillus terreus M11 under solid-state cultivation of corn stover. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7623–7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Jasso, R.M.; Mussatto, S.I.; Sepúlveda, L.; Agrasar, A.T.; Pastrana, L.; Aguilar, C.N.; Teixeira, J.A. Fungal fucoidanase production by solid-state fermentation in a rotating drum bioreactor using algal biomass as substrate. Food Bioprod. Process. 2013, 91, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailey, M.J.; Biely, P.; Poutanen, K. Interlaboratory testing of methods for assay of xylanase activity. J. Biotechnol. 1992, 23, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassambara, A. Pipe-Friendly Framework for Basic Statistical Tests. Available online: https://rpkgs.datanovia.com/rstatix/ (accessed on 11 April 2022).




| Fungal Isolate | Assignation | Molecular Marker | Isolation Culture Medium | Genbank Accession Numbers | BLASTn NCBI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identity (%) | Query Cover (%) | |||||
| MMS1733 | Aspergillus sp. | ITS | Palm | ON217540 | 100 | 100 |
| MMS1785 | Aspergillus sp. | ITS | Palm | ON217539 | 100 | 100 |
| MMS1906 | Penicillium sp. | ITS | Wick | ON331769 | 100 | 100 |
| MMS1910 | Penicillium brevicompactum | ITS/β-tubulin | Wick | ON217538/ON217535 | 100/100 | 100/100 |
| MMS1959 | Cladosporium ramotenellum | ITS/actin | Palm | ON217537/ON209120 | 100/100 | 100/100 |
| MMS1986 | Penicillium sp. | ITS | Palm | ON331783 | 100 | 100 |
| Fungal Isolate | Volume of Fungal Extract (mL) | Volume of Acetate Buffer (mL) | Cut P. palmata Thalli (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aspergillus sp. MMS1733 | 44.5 | 155.5 | 15 |
| Aspergillus sp. MMS1785 | 14 | 186 | 15 |
| Penicillium sp. MMS1906 | 32.3 | 167.7 | 15 |
| Penicillium brevicompactum MMS1910 | 16.6 | 183.4 | 15 |
| Cladosporium ramotenellum MMS1959 | 39.5 | 160.5 | 15 |
| Penicillium sp. MMS1986 | 29.6 | 170.4 | 15 |
| Positive control | 35.6 mg * | 200 | 15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le Strat, Y.; Mandin, M.; Ruiz, N.; Robiou du Pont, T.; Ragueneau, E.; Barnett, A.; Déléris, P.; Dumay, J. Quantification of Xylanolytic and Cellulolytic Activities of Fungal Strains Isolated from Palmaria palmata to Enhance R-Phycoerythrin Extraction of Palmaria palmata: From Seaweed to Seaweed. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21070393
Le Strat Y, Mandin M, Ruiz N, Robiou du Pont T, Ragueneau E, Barnett A, Déléris P, Dumay J. Quantification of Xylanolytic and Cellulolytic Activities of Fungal Strains Isolated from Palmaria palmata to Enhance R-Phycoerythrin Extraction of Palmaria palmata: From Seaweed to Seaweed. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(7):393. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21070393
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe Strat, Yoran, Margaux Mandin, Nicolas Ruiz, Thibaut Robiou du Pont, Emilie Ragueneau, Alexandre Barnett, Paul Déléris, and Justine Dumay. 2023. "Quantification of Xylanolytic and Cellulolytic Activities of Fungal Strains Isolated from Palmaria palmata to Enhance R-Phycoerythrin Extraction of Palmaria palmata: From Seaweed to Seaweed" Marine Drugs 21, no. 7: 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21070393
APA StyleLe Strat, Y., Mandin, M., Ruiz, N., Robiou du Pont, T., Ragueneau, E., Barnett, A., Déléris, P., & Dumay, J. (2023). Quantification of Xylanolytic and Cellulolytic Activities of Fungal Strains Isolated from Palmaria palmata to Enhance R-Phycoerythrin Extraction of Palmaria palmata: From Seaweed to Seaweed. Marine Drugs, 21(7), 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21070393