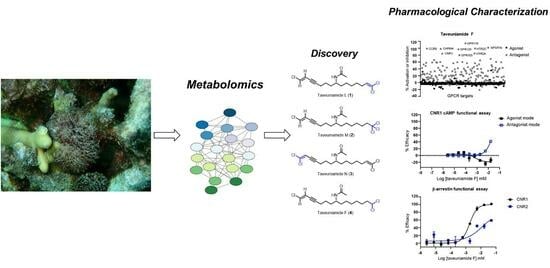
Chlorinated Enyne Fatty Acid Amides from a Marine Cyanobacterium: Discovery of Taveuniamides L-M and Pharmacological Characterization of Taveuniamide F as a GPCR Antagonist with CNR1 Selectivity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Isolation
2.2. Structure Elucidation
2.3. Biological Characterization
2.3.1. Cannabinoid CNR1 Receptor Binding
2.3.2. CNR1 Functional Response Induced by Taveunimide F (4) through G-Protein-Dependent Pathway
2.3.3. GPCR Target Selectivity Profiling and CNR1 Functional Selectivity Assessment
2.4. Assessment of Taveuniamide F (4) Cytotoxicity in HEK293 Cells
2.5. Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamic Simulations of Taveuniamide F (4) into CNR1
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedure
3.2. Biological Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Determination of the Absolute Configuration of Taveuniamide F (4)
3.5. Cannabinoid CNR1 Receptor Binding Assay
3.6. cAMP Hunter™ eXpress CNR1 (CB1) CHO-K1 GPCR Assay
3.7. PathHunter β-Arrestin GPCR Profiling
3.8. MTT Cell Viability Assay
3.9. Molecular Modeling and Simulations
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farrell, E.K.; Merkler, D.J. Biosynthesis, degradation and pharmacological importance of the fatty acid amides. Drug Discov. Today 2008, 13, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mock, E.D.; Gagestein, B.; van der Stelt, M. Anandamide and other N-acylethanolamines: A class of signaling lipids with therapeutic opportunities. Prog. Lipid Res. 2023, 89, 101194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greger, H. Alkamides: A critical reconsideration of a multifunctional class of unsaturated fatty acid amides. Phytochem. Rev. 2016, 15, 729–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demay, J.; Bernard, C.; Reinhardt, A.; Marie, B. Natural Products from Cyanobacteria: Focus on Beneficial Activities. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Matthews, J.H.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Pitiamides A and B, Multifunctional Fatty Acid Amides from Marine Cyanobacteria. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunnery, J.K.; Engene, N.; Byrum, T.; Cao, Z.; Jabba, S.V.; Pereira, A.R.; Matainaho, T.; Murray, T.F.; Gerwick, W.H. Biosynthetically intriguing chlorinated lipophilic metabolites from geographically distant tropical marine cyanobacteria. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 4198–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malloy, K.L.; Suyama, T.L.; Engene, N.; Debonsi, H.; Cao, Z.; Matainaho, T.; Spadafora, C.; Murray, T.F.; Gerwick, W.H. Credneramides A and B: Neuromodulatory phenethylamine and isopentylamine derivatives of a vinyl chloride-containing fatty acid from cf. Trichodesmium sp. nov. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, N.A.; Leão, T.; Rankin, M.R.; McCullough, T.M.; Qu, P.; Korobeynikov, A.; Smith, J.L.; Gerwick, L.; Gerwick, W.H. Ketoreductase Domain Dysfunction Expands Chemodiversity: Malyngamide Biosynthesis in the Cyanobacterium Okeania hirsuta. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 3385–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, J.I.; Vansach, T.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Sakamoto, B.; Pörzgen, P.; Horgen, F.D. Halogenated fatty acid amides and cyclic depsipeptides from an eastern Caribbean collection of the cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1573–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.J.; Marquez, B.L.; Nogle, L.M.; McPhail, K.; Goeger, D.E.; Roberts, M.A.; Gerwick, W.H. Structure and biosynthesis of the jamaicamides, new mixed polyketide-peptide neurotoxins from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. Chem. Biol. 2004, 11, 817–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.A.V.; Petitbois, J.G.; Vairappan, C.S.; Umezawa, T.; Matsuda, F.; Okino, T. Columbamides D and E: Chlorinated Fatty Acid Amides from the Marine Cyanobacterium Moorea bouillonii Collected in Malaysia. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 4231–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; McPhail, K.L.; Ligresti, A.; Di Marzo, V.; Gerwick, W.H. Semiplenamides A-G, fatty acid amides from a Papua New Guinea collection of the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya semiplena. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1364–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petitbois, J.G.; Casalme, L.O.; Lopez, J.A.V.; Alarif, W.M.; Abdel-Lateff, A.; Al-Lihaibi, S.S.; Yoshimura, E.; Nogata, Y.; Umezawa, T.; Matsuda, F.; et al. Serinolamides and Lyngbyabellins from an Okeania sp. Cyanobacterium Collected from the Red Sea. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2708–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mevers, E.; Byrum, T.; Gerwick, W.H. Parguerene and precarriebowmide, two classes of lipopeptides from the marine cyanobacterium Moorea producens. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1810–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, T.R.; Singh, I.P.; Gerwick, W.H. Taveuniamides: New chlorinated toxins from a mixed assemblage of marine cyanobacteria. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 7025–7033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, M.A.; Pannell, L.K.; Erickson, K.L. Polychlorinated acetamides from the cyanobacterium Microcoleus lyngbyaceus. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretsch, E.; Bühlmann, P.; Badertscher, M. Structure Determination of Organic Compound: Tables of Spectral Data; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.B. Organic Structural Spectroscopy; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Schedler, D.J.; Li, J.; Ganem, B. Reduction of Secondary Carboxamides to Imines. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 4115–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, A.; Ono, H.; Mikata, Y. Characteristic conformation of Mosher’s amide elucidated using the cambridge structural database. Molecules 2015, 20, 12880–12900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Immadi, S.S.; Wu, Z.; Kendall, D.A. Translational potential of allosteric modulators targeting the cannabinoid CB. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, L.M.; Abood, M.E. CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Signaling and Biased Signaling. Molecules 2021, 26, 5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Iyer, M.R.; Godlewski, G.; Jourdan, T.; Liu, J.; Coffey, N.J.; Zawatsky, C.N.; Puhl, H.L.; Wess, J.; Meister, J.; et al. Functional Selectivity of a Biased Cannabinoid-1 Receptor Antagonist. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groer, C.E.; Tidgewell, K.; Moyer, R.A.; Harding, W.W.; Rothman, R.B.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Bohn, L.M. An opioid agonist that does not induce mu-opioid receptor—Arrestin interactions or receptor internalization. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsing, D.E.; Anastasio, N.C.; Miszkiel, J.M.; Gilbertson, S.R.; Allen, J.A.; Cunningham, K.A. Biophysical validation of serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptor interaction. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.J. Novel cannabinoid receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 152, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira de Souza, C.; Sun, X.; Oh, D. Metabolic Functions of G Protein-Coupled Receptors and β-Arrestin-Mediated Signaling Pathways in the Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 715877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Mahri, S.; Malik, S.S.; Al Ibrahim, M.; Haji, E.; Dairi, G.; Mohammad, S. Free Fatty Acid Receptors (FFARs) in Adipose: Physiological Role and Therapeutic Outlook. Cells 2022, 11, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordqvist, A.; Kristensson, L.; Johansson, K.E.; Isaksson da Silva, K.; Fex, T.; Tyrchan, C.; Svensson Henriksson, A.; Nilsson, K. New Hits as Antagonists of GPR103 Identified by HTS. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prévost, G.; Picot, M.; Le Solliec, M.A.; Arabo, A.; Berrahmoune, H.; El Mehdi, M.; Cherifi, S.; Benani, A.; Nédélec, E.; Gobet, F.; et al. The neuropeptide 26RFa in the human gut and pancreas: Potential involvement in glucose homeostasis. Endocr. Connect. 2019, 8, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Library of Medicine. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/387129 (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Tapmeier, T.T.; Rahmioglu, N.; Lin, J.; De Leo, B.; Obendorf, M.; Raveendran, M.; Fischer, O.M.; Bafligil, C.; Guo, M.; Harris, R.A.; et al. Neuropeptide S receptor 1 is a nonhormonal treatment target in endometriosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabd6469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanamiya, R.; Takei, J.; Asano, T.; Tanaka, T.; Sano, M.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Hosono, H.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of Anti-Human CC Chemokine Receptor 9 Monoclonal Antibodies for Flow Cytometry. Monoclon. Antib. Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2021, 40, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, A.C.; Kobilka, B.K.; Gautam, D.; Sexton, P.M.; Christopoulos, A.; Wess, J. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors: Novel opportunities for drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.H.; Sim-Selley, L.J.; Selley, D.E. Cannabinoid CB1 receptor-interacting proteins: Novel targets for central nervous system drug discovery? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueras-Ortiz, C.; Yudowski, G.A. The Multiple Waves of Cannabinoid 1 Receptor Signaling. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Awadhi, F.H.; Gao, B.; Rezaei, M.A.; Kwan, J.C.; Li, C.; Ye, T.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Discovery, Synthesis, Pharmacological Profiling, and Biological Characterization of Brintonamides A-E, Novel Dual Protease and GPCR Modulators from a Marine Cyanobacterium. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 6364–6378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Z.; Yin, J.; Chapman, K.; Grzemska, M.; Clark, L.; Wang, J.; Rosenbaum, D.M. High-resolution crystal structure of the human CB1 cannabinoid receptor. Nature 2016, 540, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halgren, T.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Friesner, R.A.; Beard, H.S.; Frye, L.L.; Pollard, W.T.; Banks, J.L. Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 2. Enrichment factors in database screening. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, W.; Day, T.; Jacobson, M.P.; Friesner, R.A.; Farid, R. Novel procedure for modeling ligand/receptor induced fit effects. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 534–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger LLC. Schrödinger Release 2023-2; Schrödinger LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]






| C/H No. | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | COSY | HMBC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 128.8, CH | 6.43, d (13.6) | 2 | |
| 2 | 114.0, CH | 5.90, dt (13.6, 2.3) | 1, 5 | |
| 3 | 92.7, C | |||
| 4 | 76.1, C | |||
| 5 | 19.1, CH2 | 2.32, td (7.6, 2.3) | 1, 2, 6 | 1, 3, 4, 6, 7 |
| 6 | 24.8, CH2 | 1.55 | 5, 7a | 7, 8 |
| 7 | 34.4, CH2 | a: 1.41 b: 1.61 | 8, 7b, 6 8, 7a | 5, 8, 9 5, 8, 9 |
| 8 | 48.7, CH | 3.93, dtd (12.7, 8.8, 4.5) | 7a, 7b, 9a, 9b, NH | 9, 10 |
| 9 | 35.3, CH2 | a: 1.33 b: 1.49 | 8, 9b 8, 9a | |
| 10 | 25.5, CH2 | 1.33 | ||
| 11 | 28.8, CH2 | 1.32 | ||
| 12 | 28.0, CH2 | 1.40 | 13 | 10 |
| 13 | 29.4, CH2 | 2.15, dt (7.3, 7.4) | 12, 14 | 12, 14, 15 |
| 14 | 129.8, CH | 5.83, t (7.3) | 13 | |
| 15 | 119.8, C | |||
| 16 | 169.5,C | |||
| 17 | 23.5, CH3 | 1.98, s | 16 | |
| NH | 5.07, d (9.3) | 8 |
| C/H No. | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | COSY | HMBC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 128.6, CH | 6.43, d (13.6) | 2, 5 | 2, 4 |
| 2 | 114.0, CH | 5.90, dt (13.6, 2.3) | 1, 5 | 1, 3 |
| 3 | 92.7, C | |||
| 4 | 76.2, C | |||
| 5 | 19.1, CH2 | 2.32, td (7.4, 2.0) | 1, 2, 6 | 1, 3, 4, 6, 7 |
| 6 | 24.8, CH2 | 1.55 | 5, 7a | 5, 7, 8 |
| 7 | 34.4, CH2 | a: 1.41 b: 1.61 | 8, 7b, 6 8, 7a | 5, 8, 9 5, 8, 9 |
| 8 | 48.7, CH | 3.94, dtd (12.7, 8.8, 4.5) | 7a, 7b, 9a, 9b, NH | 9, 10 |
| 9 | 35.3, CH2 | a: 1.34 b: 1.49 | 8, 9b 8, 9a | 8, 10, 11 |
| 10 | 25.5, CH2 | 1.34 | ||
| 11 | 28.9, CH2 | 1.33 | ||
| 12 | 28.4, CH2 | 1.38 | 13 | 11, 10 |
| 13 | 26.2, CH2 | 1.76, dtd (11, 7.8, 5.8) | 12, 14 | 12, 14, 15 |
| 14 | 55.0, CH2 | 2.66, m | 13 | 12, 13, 15 |
| 15 | 100.3, C | |||
| 16 | 169.6, C | |||
| 17 | 23.5, CH3 | 1.98, s | 16 | |
| NH | 5.08, d (9.3) | 8 | 8, 16 |
| C/H No. | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | COSY | HMBC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 130.1, C | |||
| 2 | 111.1, CH | 5.93, t (2.3) | 5 | |
| 3 | 98.8, C | |||
| 4 | 74.9, C | |||
| 5 | 19.6, CH2 | 2.40, td (6.8, 2.3) | 2, 6 | 1, 3, 4, 6, 7 |
| 6 | 24.8, CH2 | 1.59 | 5, 7a, 7b | |
| 7 | 34.4, CH2 | a: 1.44 b: 1.66 | 8, 7b, 6 8, 7a, 6 | |
| 8 | 48.8, CH | 3.94, ddq (13.3, 8.9, 4.9) | 7a, 7b, 9a, 9b, NH | |
| 9 | 35.3, CH2 | a: 1.34 b: 1.48 | 8, 9b 8, 9a | |
| 10 | 25.8, CH2 | 1.33 | ||
| 11 | 29.2, CH2 | 1.32 | ||
| 12 | 28.2, CH2 | 1.40 | 13 | 10, 11 |
| 13 | 29.6, CH2 | 2.15, q (7.3) | 12, 14 | 12, 14, 15 |
| 14 | 129.8, CH | 5.84, t (7.4) | 13 | |
| 15 | 119.5, C | |||
| 16 | 169.5, C | |||
| 17 | 23.7, CH3 | 1.98, s | 16 | |
| NH | 5.08, d (9.3) | 8 |
| GPCR Target | IC50 (µM) |
|---|---|
| CNR1 | 1.84 |
| CHRM4 | 1.92 |
| NPSR1b | 4.36 |
| GPR120 | 4.72 |
| HTR2A | 4.83 |
| CCR9 | 7.38 |
| GPR119 | 11.67 |
| GPR103 | 14.07 |
| HTR2C | >50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elsadek, L.A.; Ellis, E.K.; Seabra, G.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Chlorinated Enyne Fatty Acid Amides from a Marine Cyanobacterium: Discovery of Taveuniamides L-M and Pharmacological Characterization of Taveuniamide F as a GPCR Antagonist with CNR1 Selectivity. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22010028
Elsadek LA, Ellis EK, Seabra G, Paul VJ, Luesch H. Chlorinated Enyne Fatty Acid Amides from a Marine Cyanobacterium: Discovery of Taveuniamides L-M and Pharmacological Characterization of Taveuniamide F as a GPCR Antagonist with CNR1 Selectivity. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(1):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22010028
Chicago/Turabian StyleElsadek, Lobna A., Emma K. Ellis, Gustavo Seabra, Valerie J. Paul, and Hendrik Luesch. 2024. "Chlorinated Enyne Fatty Acid Amides from a Marine Cyanobacterium: Discovery of Taveuniamides L-M and Pharmacological Characterization of Taveuniamide F as a GPCR Antagonist with CNR1 Selectivity" Marine Drugs 22, no. 1: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22010028
APA StyleElsadek, L. A., Ellis, E. K., Seabra, G., Paul, V. J., & Luesch, H. (2024). Chlorinated Enyne Fatty Acid Amides from a Marine Cyanobacterium: Discovery of Taveuniamides L-M and Pharmacological Characterization of Taveuniamide F as a GPCR Antagonist with CNR1 Selectivity. Marine Drugs, 22(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22010028