Effect of Ishige okamurae Extract on Osteoclastogenesis In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
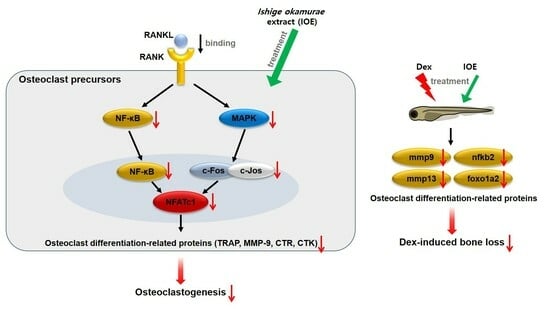
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of IOE on TRAP Activity in RANKL-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Cells
2.2. Effect of IOE on the Expression of Osteoclast Differentiation-Related Factors in RANKL-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Cells
2.3. Effect of IOE on the Expression of Osteoclast-Related Transcriptional Factors in RANKL-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Cells
2.4. Effect of IOE on ERK, JNK, and NF-κB Phosphorylation in RANKL-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Cells
2.5. Effect of IOE on Bone Mineralization in Dexamethasone-Induced Osteoporosis in Zebrafish Larvae
2.6. Analysis of DPHC and IPA in IOE
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Extraction of I. okamurae
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. MTT Assay
4.4. TRAP Staining
4.5. Western Blotting Analysis
4.6. Immunofluorescence (IF) Staining
4.7. Maintenance of Zebrafish and Survival Rate Measurement
4.8. Calcein Staining
4.9. Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
4.10. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meguid, E.A.; Ke, Y.; Ji, J.; El-Hashash, A.H.K. Stem cells applications in bone and tooth repair and regeneration: New insight, tools, and hops. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 1825–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, N. Bone cell communication factors provide a new therapeutic strategy for osteoporosis. Chonnam Med. J. 2020, 56, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, E.Y.; Yeom, M.; Jung, H.S.; Sohn, Y. Water extract of Cnidii Rhizoma suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenisis in RAW 264.7 cell by inhibiting NFATc1/c-Fos signaling and prevents ovariectomized bone loss in SD-rat. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsimbri, P. The biology of normal bone remodeling. Eur. J. Cancer Care 2017, 26, e12740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phetfong, J.; Sanvoranart, T.; Nartprayut, K.; Nimsanor, N.; Seenprachawong, K.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Supokawej, A. Osteoporosis: The current status of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2016, 21, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Zhu, W.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, S.; Liu, T.; Li, S.; Peng, D. Glycyrrhizic acid suppresses osteoclast differentiation and postmenopausal osteoporosis by modulating the NF-κB, ERK, and JNK signaling pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 895, 172550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chin, J.F.; Qu, X.; Bi, H.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhai, Z.; Qin, A.; Zhang, B.; Dai, M. The beneficial effect of praeruptorin C on osteoporotic bone in ovariectomized mice via suppression of osteoclast formation and bone resorption. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokegahara, N.; Kim, H.; Choi, Y. RANKL biology. Bone 2022, 159, 116353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, E.Y.; Lee, B.; Lee, S.Y.; Jun, J.Y.; Kim, M.B.; Sohn, Y.; Jung, H.S. Chaenomelis fructus inhibits osteoclast differentiation by suppressing NFATc1 expression and prevents ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Chen, F.; Liu, T.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Jiang, L.; Wang, X.; Sheng, J. Ellagic acid blocks RANKL-RANK interaction and suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting RANK signaling pathways. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 331, 109235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, S.; Shen, Y.; Liu, T.; Liu, T.; Liu, B.; Wan, L.; Li, S.; et al. Proanthocyanidins inhibits osteoclast formation and function by inhibiting the NF-κB and JNK signaling pathways during osteoporosis treatment. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 509, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thu, H.E.; Hussain, Z.; Mohamed, I.N.; Shuid, A.N. Eurycoma longifolia, a promising suppressor of RANKL-induced differentiation and activation of osteoclasts: An in vitro mechanistic evaluation. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2019, 10, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dömötör, Z.R.; Vörhendi, N.; Hanák, L.; Hegyi, P.; Kiss, S.; Csiki, E.; Szakó, L.; Párniczky, A.; Erőss, B. Oral treatment with bisphosphonates of osteoporosis does not increase the risk of severe gastrointestinal side effects: A metal-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 573976. [Google Scholar]
- Imam, B.; Aziz, K.; Khan, M.; Zubair, T.; Iqbal, A. Role of bisphosphonate in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis prevent future fractures: A literature review. Cureus 2019, 11, e5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennell, K.A.; Drake, M.T. Adverse effects of bisphosphonates: Implications for osteoporosis management. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2009, 84, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkordy, A.A.; Haj-Ahmad, R.R.; Awaad, A.S.; Zaki, R.M. An overview on natural product drug formulations from conventional medicines to nanomedicines: Past, present and future. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 102459. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, K.S. New aspects of natural products in drug discovery. Trends Microbiol. 2007, 15, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.W.; Son, M.; Choi, J.; Oh, S.; Jeon, Y.J.; Byun, K.; Ryu, B. Effect of isophloroglucin A, a component of Ishige okamurae, on glucose homeostasis in the pancreas and muscle of high fat diet-red mice. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiuru, P.; D’Auria, M.V.; Muller, C.D.; Tammela, P.; Vuorela, H.; Yli-Kauhaluoma, J. Exploring marine resources for bioactive compounds. Planta Medica 2014, 80, 1234–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, K.H.N.; Tang, H.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Jeon, Y.J.; Ryu, B. Ishige okamurae extract and its constituent ishophloroglucin A attenuated in vitro and in vivo high glucose-induced angiogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5542. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Oh, J.Y.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Jeon, Y.J.; Ryu, B. Anti-inflammatory and anti-melanogenesis activities of sulfated polysaccharides isolated from Hizikia fusiforme: Short communication. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 142, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, J.Y.; Jung, M.J.; Jeong, I.M.; Yamazaki, K.; Kawai, Y.; Kim, B.M. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of sulfated polysaccharides from marine algae against dental plaque bacteria. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Lee, W.W.; Kim, J.I.; Jeon, Y.J. Exploiting biological activities of brown seaweed Ishige okamurae Yendo for potential industrial applications: A review. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 3109–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Boo, G.H.; Riosmena-Rodriguez, R.; Boo, S.M. Classification of the genus Ishige (Ishigeales, Pyaeophyceae) in the north pacific ocean with recognition of Ishige foliacea based on plastid rbcl and mitochondrial cox3 gene sequences(1). J. Phycol. 2009, 45, 906–913. [Google Scholar]
- Min, K.H.; Kim, H.J.; Jeon, Y.J.; Han, J.S. Ishige okamurae ameliorates hyperglycemia and insulin resistance in C57BL/KsJ-db/db-mice. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 93, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, O.Y.; Lee, S.H. Ishige okamurae attenuates neuroinflammation and cognitive deficits in mice intracerebroventricularly injected with LPS via regulating TLR-4/MyD88-dependent pathways. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.J.; Yoon, K.D.; Kim, C.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, C.G.; Kim, J. Inhibitory activity on HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and integrase of a carmalol derivative from a brown Alga, Ishige okamurae. Phytother. Res. 2006, 20, 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.K.; Ren, R.; Hashimoto, T.; Kanazawa, K. Fucoxanthin induces apoptosis in osteoclast-like cells differentiated from RAW 264.7 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 6090–6095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahim, A.H.; Setiawan, B.; Dewi, F.R.P.; Noor, Z. Regulation by phloroglucinol of Nrf2/Maf-mediated expression of antioxidant enzymes and inhibition of osteoclastogenesis via the RANKL/RANK signaling pathway: In silico study. Acta Inform. Med. 2015, 23, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ihn, H.J.; Kim, J.A.; Cho, H.S.; Shin, H.I.; Kim, G.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Jeon, Y.J.; Park, E.K. Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol from Ishige okamurae suppresses osteoclast differentiation by downregulating the NF-κB signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2635. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ryu, B.; Jiang, Y.; Kim, H.S.; Hyun, J.M.; Lim, S.B.; Li, Y.; Jeon, Y.J. Ishophloroglucin A, a novel phlorotannin for standardizing the anti-α-glucosidase activity of Ishige okamurae. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Kim, H.S.; Jung, H.Y.; Park, J.I.; Jang, Y.J.; Ahn, J.; Kim, K.N. Effect of Ishophloroglucin A isolated from Ishige okamurae on in vitro osteoclastogenesis and osteoblastogenesis. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Dutta, M.K.; Jennane, R.; Lespessailles, E. Classification of the trabecular bone structure of osteoporotic patients using machine vision. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 91, 148–158. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Lee, Y.; Lee, J.; Oh, S.; Choi, J.W.; Kim, S.W.; Hwang, K.C.; Lim, S. Isoliquiritigenin derivatives inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by regulating p38 and NF-κB activation in RAW 264.7 cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orecchini, E.; Mondanelli, G.; Orabona, C.; Volpi, C.; Adorisio, S.; Calvitti, M.; Thuy, T.T.; Delfino, D.V.; Belladonna, M.L. Artocarpus tonkinensis extrct inhibits LPS-triggered inflammation markers and suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW 264.7. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 593829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, K.; Itoh, J.; Kawazoe, Y.; Miyazaki, S.; Doi, K.; Kubo, T.; Akagawa, Y.; Shiba, T. Polyphosphate-mediated inhibition of Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase and suppression of bone resorption of osteoclasts. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, I.S.; Kim, C. Taurine chloramine inhibits osteoclastic differentiation and osteoclast marker expression in RAW 264.7 cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 155, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, N.K.; Lee, S.Y. Current understanding of RANKL signaling in osteoclast differentiation and maturation. Mol. Cells 2017, 40, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Lu, L.; Hu, R.; Shetti, D.; Wei, K. Piceatannol attenuates RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption by suppressing MAPK, NF-κB and AKT signaling pathways and promotes caspase-3-mediated apoptosis of mature osteoclasts. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 190360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Seo, I.; Choi, M.H.; Jeon, D. Roles of mitogen-activated protein kinases in osteoclast biology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3004. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tankak, S.; Nakamura, K.; Takahasi, N.; Su, T. Role of RANKL in physiological and pathological bone resorption and therapeutics targeting the RANKL-RANK signaling system. Immunol. Rev. 2005, 208, 30–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, Y.; Deng, L.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.P. TRAP family member-associated NF-κB activator (TANK) indued by RANKL negatively regulates osteoclast survival and function. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.L.; Huang, L.Y.; Cheng, Y.T.; Li, F.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, C.; Shi, Q.H.; Guan, Z.Z.; Liao, J.; Hong, W. Zoledronic acid inhibits osteoclast differentiation and function through the regulation of NF-κB and JNK signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 44, 582–592. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, H.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Noh, E.M.; Kim, J.M.; You, Y.O.; Lee, G.; Koo, J.H.; Lim, H.; Ko, S.; Kim, J.S.; et al. Aqueous extract of Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat. inhibit RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation by suppressing the c-fos/NFATc1 pathway. Arch. Oral Biol. 2021, 122, 105029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, N. Regulation of NFATc1 in osteoclast differentiation. J. Bone Metab. 2014, 21, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, W.F.; Huang, T.L.; Liu, Y.W. (+)-Vitisin A inhibits osteoclast differentiation by preventing TRAF6 ubiquitination and TRAF6-TAK1 formation to suppress NFATc1 activation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.; Ryu, G.H.; Moon, J.H.; Lee, H.I.; Jung, H.S.; Sohn, Y. Gentianae macrophyllae Radix water extract inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and osteoclast specific genes. Korean J. Acupunct. 2020, 37, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.J.; Jia, Y.F.; Chen, N.; Bian, W.P.; Li, Q.K.; Ma, Y.B.; Chen, Y.L.; Pei, D.S. Zebrafish as a model system to study toxicology. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Veldman, M.B.; Lin, S. Zebrafish as a developmental model organism for pediatric research. Pediatr. Res. 2008, 64, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehrmann-Cartes, K.; Coronado, M.; Hernández, A.J.; Allende, M.L.; Feijoo, C.G. Anti-inflammatory effects of aloe vera on soy meal-induced intestinal inflammation in zebrafish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 95, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Le, H.D.; Kim, T.N.T.; The, H.P.; Nguyen, T.M.; Cornet, V.; Lambert, J.; Kestemont, P. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of the ethanol extract of Clerodendrum cyrtophyllum Turcz in copper sulfate-induced inflammation in zebrafish. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.M.; Su, W.C.; Li, C.; Shi, Y.; Chen, Q.X.; Zheng, J.; Tang, D.L.; Wang, Q. Anti-melanogenesis of novel kojic acid derivatives in B16F10 cells and zebrafish. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronchetti, S.; Ayroldi, E.; Ricci, E.; Gentili, M.; Migliorati, G.; Riccardi, C. A glance at the use of glucocorticoids in rare inflammatory and autoimmune diseases: Still an indispensable pharmacological tool? Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 613435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordag, N.; Klie, S.; Jürchott, K.; Vierheller, J.; Schiewe, H.; Albrecht, V.; Tonn, J.C.; Schwart, C.; Schichor, C.; Selbig, J. Glucocorticoid (dexamethasone)-induced metabolome changes in healthy males suggest prediction of response and side effect. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhong, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhang, J.; Cui, L. Tanshinol stimulates bone formation and attenuates dexamethasone-induced inhibition of osteogenesis in larvae zebrafish. J. Orthop. Transl. 2016, 4, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.Y.; Chen, J.F.; Zhong, Z.G.; Lv, X.H.; Yang, Y.J.; Zhang, J.J.; Cui, L. Salvianolic acid B stimulates osteogenesis in dexamethasone-treated zebrafish larvae. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 1370–1380. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.R.; Lai, Y.H.; Tsai, J.J.; Hsiao, C.D. Live fluorescent staining platform for drug-screening and mechanism-analysis in zebrafish for bone mineralization. Molecules 2017, 22, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Wang, L.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Kim, E.A.; Heo, S.J.; Fernando, I.P.S.; Lee, J.H.; Jeon, Y.J. High-performance centrifugal partition chromatography (HPCPC) for efficient isolation of diphlorethohydroxycarmalol (DPHC) and screening of its antioxidant activity in a zebrafish model. Process Biochem. 2020, 88, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| mmp9 | tcggcctaccaagcgactt | tcatgtgaatcaatgggcactc |
| mmp13 | agaccaggacacactcgcagag | tcgggccgcatctcttcact |
| nfkb2 | acaagacgcaaggagcccag | aactgtctcttgcacaaagggc |
| foxo1a2 | cgcatccccagcaacagcat | aatgtggacctcggctgcct |
| β-actin | ccatccttcttgggtatgga | acaggtccttacggatgtc |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, S.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Ahn, J.; Ryu, B.; Jea, J.-G.; Lee, K.; Kim, K.; Ahn, G.; Lee, W.; Choi, K.-M.; et al. Effect of Ishige okamurae Extract on Osteoclastogenesis In Vitro and In Vivo. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22030137
Cho S-H, Kim H-S, Ahn J, Ryu B, Jea J-G, Lee K, Kim K, Ahn G, Lee W, Choi K-M, et al. Effect of Ishige okamurae Extract on Osteoclastogenesis In Vitro and In Vivo. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(3):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22030137
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Su-Hyeon, Hyun-Soo Kim, Juhee Ahn, Bomi Ryu, Jun-Geon Jea, Kyubin Lee, Kyunghwan Kim, Ginnae Ahn, WonWoo Lee, Kyung-Min Choi, and et al. 2024. "Effect of Ishige okamurae Extract on Osteoclastogenesis In Vitro and In Vivo" Marine Drugs 22, no. 3: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22030137
APA StyleCho, S.-H., Kim, H.-S., Ahn, J., Ryu, B., Jea, J.-G., Lee, K., Kim, K., Ahn, G., Lee, W., Choi, K.-M., & Kim, K.-N. (2024). Effect of Ishige okamurae Extract on Osteoclastogenesis In Vitro and In Vivo. Marine Drugs, 22(3), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22030137