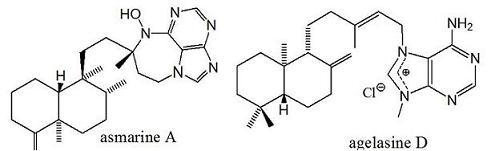
Terpenyl-Purines from the Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Alkylpurine Structures
3. Sources of Agelasines, Asmarines and Related Compounds
4. Biological Activity of Marine Terpenyl-Purine Alkaloids
4.1. Antifouling activity
4.2. Antituberculosis activity
4.3. Antimicrobial activity
4.4. Antiprotozoal activity
4.5. Cytotoxic activity
4.6. Inhibitory effect on the enzymatic reaction of Na+, K+-ATPase
5. Summary
Acknowledgments
References
- Newman, J; Cragg, G. Natural products in medicinal chemistry. Bioorg Med Chem 2009, 17, 2120. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M-Y; Xiao, O; Pan, JY; Wu, J. Natural products from semi-mangrove flora: Source, chemistry and bioactivities. Nat Prod Rep 2009, 26, 281–298. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, DJ; Cragg, GM; Kingston, DGI. Natural products as pharmaceuticals and sources for lead structures. In The Practice of Medicinal Chemistry, 3rd ed; Wermuth, CG, Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2003; pp. 159–186. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, DJ; Cragg, GM. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod 2007, 70, 461–477. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, DJ; Cragg, GM; Snader, KM. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the period 1981–2002. J. Nat. Prod 2003, 66, 1022–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan, A. The impact of natural products upon modern drug discovery. Curr Opin Chem Biol 2008, 12, 306–317. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, DJ. Natural products as leads to potential drugs: An old process or the new hope for drug discovery. J Med Chem 2008, 51, 2589–2599. [Google Scholar]
- Galm, U; Shen, B. Natural products drug discovery: The times have never been better. Chem Biol 2007, 14, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Paterson, I; Anderson, EA. The renaissance of natural products as drug candidates. Science 2005, 310, 451–453. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, AL. Natural products as a screening resource. Curr Opin Chem Biol 2007, 11, 480–484. [Google Scholar]
- Rishton, GM. Natural products as a robust source of new drugs and drug leads: Past successes and present day issues. Am J Cardiol 2008, 101(Suppl), 43D–49D. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, KS. New aspects of natural products in drug discovery. Trends Microbiol 2007, 15, 279–289. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, AL. Natural product in drug discovery. Drug Discov Today 2008, 13, 894–901. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, MS. Natural product to drug: Natural products derived compounds in clinical trials. Nat Prod Rep 2008, 25, 475–516. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, MS. Natural products to drugs: Natural products derived compounds in clinical trials. Nat Prod Rep 2005, 22, 162–195. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, RM; Danishefsky, SJ. Small molecule natural products in the discovery of therapeutic agents: The synthesis connection. J Org Chem 2006, 71, 8329–8351. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, JT. Naturally diverse: Highlights in versatile synthetic methods enabling target and diversity oriented synthesis. Nat Prod Rep 2009, 26, 11–26. [Google Scholar]
- Langer, T; Laggner, C; Rollinger, JM; Stuppner, H. Pharmacophore-based screening for the successful identification of bio-active natural products. Chimia 2007, 61, 350–354. [Google Scholar]
- Gordaliza, M. Natural products as leads to anticancer drugs. Clin Transl Oncol 2007, 9, 767–776. [Google Scholar]
- Pla, D; Marchal, A; Olsen, CA; Albericio, F; Álvarez, M. Modular total synthesis of lamellarin D. J Org Chem 2005, 70, 8231–8234. [Google Scholar]
- Blunt, JW; Copp, BR; Hu, WP; Munro, MHG; Northcote, PT; Prinsep, MR. Marine natural products. Nat Prod Rep 2009, 26, 170–244. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, JC; Phillips, AJ. Marine natural products: Synthetic aspects. Nat Prod Rep 2009, 26, 245–265. [Google Scholar]
- Skropeta, D. Deep-sea natural products. Nat Prod Rep 2008, 25, 1131–1166. [Google Scholar]
- Haefner, B. Drugs from the deep: Marine natural products as drug candidates. Drug Discov Today 2003, 8, 536–544. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, AMS; Gustafson, KR. Marine pharmacology in 2005–2006: Antitumour and cytotoxic compounds. Eur J Cancer 2008, 44, 2357–2387. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, AMS; Rodríguez, AD; Berlinck, RGS; Hamann, MT. Marine pharmacology in 2005–6: Marine compounds with anthelmintic, antibacterial, anticoagulant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis, and antiviral activities; affecting the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Biochim Biophys–Gen 2009, 1790, 283–308. [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas, C; Francesch, A. Development of Yondelis® (trabectedin, ET-743). A semisynthetic process solves the supply problem. Nat Prod Rep 2009, 26, 322–333. [Google Scholar]
- Glaser, KB; Mayer, AMS. A renaissance in marine pharmacology: From preclinical curiosity to clinical reality. Biochem Pharmacol 2009, 78, 440–448. [Google Scholar]
- Molinski, TF; Dalisay, DS; Lievens, SL; Saludes, JP. Drug development from marine natural products. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2009, 8, 69–85. [Google Scholar]
- Bugni, TS; Richads, B; Bhoite, L; Cimbora, D; Harper, MK; Ireland, CM. Marine natural product libraries for high-throughput screening and rapid drug discovery. J Nat Prod 2008, 71, 1095–1598. [Google Scholar]
- Gordaliza, M; Miguel del Corral, JM; Mahiques, MM; San Feliciano, A; García-Grávalos, MD. Terpenequinone with antitumor activity. PCT Int Appl EP 0731078 A1 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Esteban, G; Rincón, R; Csákÿ, AG; Plumet, J. A convenient synthesis of the central core of helioporins, seco-pseudopterosins and pseudopterosins via BCA-annulation sequence. Nat Prod Comm 2008, 3, 495–504. [Google Scholar]
- Pla, D; Albericio, F; Alvarez, M. Recent advances in lamellarin alkaloids: Isolation, synthesis and activity. Anti-Cancer Agents Med Chem 2008, 8, 746–760. [Google Scholar]
- Vik, A; Hedner, E; Charnock, C; Tangen, LW; Samuelsen, O; Larsson, R; Bohlin, L; Gundersen, L-L. Antimicrobial and cytotoxic activity of agelasine and agelasimine analogs. Bioorg Med Chem 2007, 15, 4016–4037. [Google Scholar]
- Capon, RJ; Faulkner, DJ. Antimicrobial metabolites from a Pacific sponge. Agelas sp J Am Chem Soc 1984, 106, 1819–1822. [Google Scholar]
- Pappo, D; Shimony, S; Kashman, Y. Synthesis of 9-substituted tetrahydrodiazepinopurines: Studies toward the total synthesis of asmarines. J Org Chem 2005, 70, 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, K; Ishibashi, M; Shigemori, H; Sasaki, T; Kobayashi, J. Agelasine G, a new antileukemic alkaloid from the Okinawan marine sponge Agelas sp. Chem Pharm Bull 1992, 40, 766–767. [Google Scholar]
- Yosief, T; Rudi, A; Kashman, Y. Asmarines A-F, novel cytotoxic compounds from the marine sponge Raspailia species. J Nat Prod 2000, 63, 299–304. [Google Scholar]
- Gademann, K; Kobylinska, J. Antimalarial natural products of marine and freshwater origin. Chem Rec 2009, 9, 187–198. [Google Scholar]
- Vik, A; Proszenyak, A; Vermeersch, M; Cos, P; Maes, L; Gundersen, L-L. Screening of agelasine D and analogs for inhibitory activity against pathogenic protozoa; identification of hits for visceral leishmaniasis and chagas disease. Molecules 2009, 14, 279–288. [Google Scholar]
- Bakkestuen, AK; Gundersen, L-L; Petersen, D; Utenova, BT; Vik, A. Synthesis and antimycobacterial activity of agelasine E and analogs. Org Biomol Chem 2005, 3, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, M; Nakamura, H; Wu, H; Kobayashi, J; Ohizumi, Y. Mode of inhibition of brain sodium-potassium ATPase by agelasidines and agelasines from a sea sponge. Arch Biochem Biophys 1987, 259, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Sjogren, M; Dahlstrom, M; Hedner, E; Jonsson, PR; Vik, A; Gundersen, LL; Bohlin, L. Antifouling activity of the sponge metabolite agelasine D and synthesised analogs on Balanus improvisus. Biofouling 2008, 244, 251–258. [Google Scholar]
- Atta-ur-Rahman; Choudhary, MI. The Alkaloids; Brossi, A, Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; Volume 38, pp. 225–323. [Google Scholar]
- Aniszewski, T. Alkaloids. In Secrets of Life; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2007; pp. 237–286. [Google Scholar]
- Christophersen, C. Marine Alkaloids. In The Alkaloids: Chemistry and Pharmacology; Brossi, A, Ed.; Academic Press Inc: Orlando, FL, USA, 1985; Volume 24, pp. 25–111. [Google Scholar]
- Appenzeller, J; Mihci, G; Martin, M-T; Gallard, J-F; Menou, J-L; Boury-Esnault, N; Hooper, J; Petek, S; Chevalley, S; Valentin, A. Agelasines J, K, and L from the Solomon Islands marine sponge Agelas cf mauritiana. J Nat Prod 2008, 71, 1451–1454. [Google Scholar]
- Ohba, M; Kawase, N; Fujii, T. Total synthesis of (±)-agelasimine A, (±)-agelasimine B an (±)-purino-diterpene and the structure of diacetylagelasimin A. J Am Chem Soc 1996, 118, 8250–8257. [Google Scholar]
- Ohba, M; Iizuca, K; Ishibashi, H; Fujii, T. Synthesis and absolute configurations of marine sponge purines (+)-agelasimine A and (+)-agelasimine B. Tetrahedron 1997, 53, 16977–16986. [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros, MA; Lourenco, A; Tavares, MR; Curto, MJ; Marcelo, F; Savluchinske, S; Roseiro, JC. (−)-Agelasidine A from Agelas clathrodes. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci 2006, 61, 472–476. [Google Scholar]
- Yosief, T; Rudi, A; Stein, Z; Goldberg, I; Garcia Gravalos, MD; Schleyer, M; Kashman, Y. Asmarines A-C; three novel cytotoxic metabolites from the marine sponge Raspailia sp. Tetrahedron Lett 1998, 39, 3323–3326. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, J; Ishizuka, E; Nakao, Y; Yoshida, WY; Scheuer, PJ; Kelly-Borges, M. Isolation of 1-methylherbipoline salts of halisulfate-1 and of suvanine as serine protease inhibitors from a marine sponge Coscinoderma mathewsi. J Nat Prod 1998, 61, 248–250. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, SS; Whitehill, AB; Trapido-Rosenthal, HG; Ireland, CM. Isolation and characterization of 1,3-dimethylisoguanine from the Bermudian sponge Amphimedon viridis. J Nat Prod 1997, 60, 727–728. [Google Scholar]
- Tasdemir, D; Mangalindan, GC; Concepcion, GP; Harper, MK; Ireland, CM. 3,7-Dimethylguanine, a new purine from a Philippine sponge Zyzzya fuliginosa. Chem Pharm Bull 2001, 49, 1628–1630. [Google Scholar]
- Cafieri, F; Fattorusso, Er; Mangoni, A; Taglialetela-Scafati, O. 3,7-Dimethylisoguanine, two novel alkaloids from the marine sponge Agelas longissima. Tetrahedron Lett 1995, 36, 7893–7896. [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman, FA; Fuhrman, GF; Kim, YH; Pavelki, LA; Mosher, HS. Doridosine: A new hipotensive N-methylpurine riboside from the nudibranch Anisodoris nobilis. Science 1980, 207, 193–195. [Google Scholar]
- Cullen, E; Devlin, JP. Agelasine, a novel quaternary 9-methyladenine from the sponge Agelas dispar. Can J Chem 1975, 53, 1690–1691. [Google Scholar]
- Fathi-Afshar, R; Allen, TM. Biological active metabolites from Agelas mauritania. Can J Chem 1988, 66, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, H; Wu, H; Ohizumi, Y; Hirata, Y. Physiologically active marine natural products from Porifera. IV. Agelasine A, B, C and D, novel bicyclic diterpenoids with a 9-methyladeninium unit possessing inhibitory effects on sodium-potassium ATPase from the Okinawan sea sponge Agelas sp. Tetrahedron Lett 1984, 25, 2989–2989. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H; Nakamura, Hi; Kobayashi, J; Kobayashi, M; Ohizumi, Y; Hirata, Y. Physiologically active marine natural products from Porifera. XII. Structures of agelasines, diterpenes having a 9-methyladeninium chromophore isolated from the Okinawan marine sponge Agelas nakamurai Hoshino. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 1986, 59, 2495–2504. [Google Scholar]
- Fathi-Afshar, R; Allen, TM. Some pharmacological activities of novel adenine-related compounds isolated from a marine sponge Agelas mauritiana. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 1989, 67, 276–281. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H; Nakamura, H; Kobayashi, J; Ohizumi, Y. Agelasine E and F, novel monocyclic diterpenoids with a 9-methyladeninium unit possessing inhibitory effects on Na,K-ATPase isolated from the Okinawian sea sponge Agelas nakamurai Hoshino. Tetrahedron Lett 1984, 25, 3719–3722. [Google Scholar]
- Mangalindan, GC; Talaue, MT; Cruz, LJ; Franzblau, SG; Adams, LB; Richardson, AD; Ireland, CM; Concepcion, GP. Agelasine F from a Philippine Agelas sp. sponge exhibits in vitro antituberculosis activity. Planta Med 2000, 66, 364–365. [Google Scholar]
- Hattori, T; Adachi, K; Shizuri, Y. New agelasine compound from the marine sponge Agelas mauritiana as an antifouling substance against macroalgae. J Nat Prod 1997, 60, 411–413. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X; Schmitz, FJ; Tanner, RS; Kelly-Borges, M. Agelasines H and I, 9-methyladenine-containing diterpenoids from an Agelas sponge. J Nat Prod 1998, 61, 548–550. [Google Scholar]
- Iwagawa, T; Kaneko, M; Okamura, H; Nakatani, M; Van, S; Rob, WM. New alkaloids from Paua New Guinea sponge Agelas nakamurai. J Nat Prod 1998, 61, 1310–1312. [Google Scholar]
- Pina, IC; Crews, P; Tenney, K. A new agelasine derivative from the Caribbean sponge Agelas clathrodes. Abstracts of Papers, 232nd ACS National Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, September 10–14, 2006.
- Kashman, Y; Rudi, A; Yosief, T; Gravalos, DG. Cytotoxic alkaloid derivatives including asmarine A and B isolated from a sponge. PCT Int Appl WO 9933832 A1 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rudi, A; Shalom, H; Schleyer, M; Benayahu, Y; Kashman, Y. Asmarines G and H and barekol, three new compounds from the marine sponge Raspailia sp. J Nat Prod 2004, 67, 106–109. [Google Scholar]
- Rudi, A; Aknin, M; Gaydou, E; Kashman, Y. Asmarines I, J, and K and nosyberkol: Four new compounds from the marine sponge Raspailia sp. J Nat Prod 2004, 67, 1932–1935. [Google Scholar]
- Roggen, H; Gundersen, L-L. Synthetic studies directed towards agelasine analogs-synthesis, tautomerism, and alkylation of 2-substituted N-methoxy-9-methyl-9H-purin-6-amines. Eur J Org Chem 2008, 30, 5099–5106. [Google Scholar]
- Piers, E; Breau, ML; Han, Y; Plourde, Guy, L; Yeh, W-L. Total synthesis of cis-clerodane diterpenoids: (−)-Agelasine A and (+)-(3R,4S,5R,8S,9R,10S)-3,4-epoxyclerod-13-en-15,16-olide. J Chem Soc, Perkin Trans 1: Org Bioorg Chem 1995, 8, 963–966. [Google Scholar]
- Piers, E; Roberge, JY. Total syntheses of the diterpenoids (−)-kolavenol and (−)-agelasine B. Tetrahedron Lett 1992, 33, 6923–6926. [Google Scholar]
- Iio, H; Asao, K; Tokoroyama, T. Syntheses of agelasin B and its analogs. J Chem Soc, Chem Com 1985, 774–775. [Google Scholar]
- Asao, K; Monden, M; Asada, To; Iio, H; Tokoroyama, T. Synthetic studies on clerodane diterpenoids. Asymmetric synthesis of (−)-kolavenic acid and synthesis of agelasins. Tennen Yuki Kagobutsu Toronkai Koen Yoshishu 1985, 27, 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Marcos, IS; Garcia, N; Sexmero, MJ; Basabe, P; Diez, D; Urones, JG. Synthesis of (+)-agelasine C. A structural revision. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 11672–11678. [Google Scholar]
- Utenova, BT; Gundersen, L-L. Synthesis of (+)-agelasine D from (+)-manool. Tetrahedron Lett 2004, 45, 4233–4235. [Google Scholar]
- Vik, A; Hedner, E; Colin, C; Samuelsen, O; Larsson, R; Gundersen, L-L; Bohlin, L. (+)-Agelasine D: Improved synthesis and evaluation of antibacterial and cytotoxic activities. J Nat Prod 2006, 69, 381–386. [Google Scholar]
- Bakkestuen, AK; Gundersen, LL. Synthesis of (+)-trixagol and its enantiomer, the terpenoid side chain of (−)-agelasine E. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Proszenyak, A; Braendvang, M; Charnock, C; Gundersen, L-L. The first synthesis of ent-agelasine F. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 194–199. [Google Scholar]
- Proszenyak, A; Charnock, C; Hedner, E; Larsson, R; Bohlin, L; Gundersen, L-L. Synthesis, antimicrobial and antineoplastic activities for agelasine and agelasimine analogs with a beta-cyclocitral derived substituent. Arch Pharm 2007, 340, 625–34. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, I; Defant, A; Guella, G. Recent synthesis of marine natural products with antibacterial activities. Anti-Infect Agents Med Chem 2007, 6, 17–48. [Google Scholar]
- Vik, A; Gundersen, LL. Synthetic studies directed towards asmarines; construction of the tetrahydrodiazepinopurine moiety by ring closing metathesis. Tetrahedron Lett 2007, 48, 1931–1934. [Google Scholar]
- Ohba, M; Tashiro, T. Preparatory study for the synthesis of the marine sponge alkaloids asmarines A-F: Synthesis of their heterocyclic portions. Heterocycles 2002, 57, 1235–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Pappo, D; Kashman, Y. Synthesis of 9-substituted tetrahydrodiazepinopurines-asmarine A analogues. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 6493–6501. [Google Scholar]
- Rodgen, SA; Schaus, SE. Efficient construction of the clerodane decalin core by an asymmetric Morita-Baylis-Hillman reaction/Lewis acid promoted annulation strategy. Ang Chem, Int Ed 2006, 45, 4929–4932. [Google Scholar]
- Rodgen, SA; Schaus, SE. Total synthesis of Asmarine B. Abstracts of Papers, 234th ACS National Meeting, Boston, MA, USA, August 19–23, 2007.
- Pappo, D; Rudi, A; Kashman, Y. A synthetic approach towards the synthesis of asmarine analogues. Tetrahedron Lett 2001, 42, 5941–5943. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F-L; Vasella, A. Synthesis of spiropyrimidodiazepines and spirodiazepinopurines by tandem nitroso-ene/Diels-Alder reactions. Helv ChimActa 2007, 90, 2315–2329. [Google Scholar]
- Clare, AS. Towards non-toxic antifouling. J Mar Biotechnol 1998, 6, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nikomenko, BV; Protopopova, M; Samala, R; Einck, I; Nacy, CA. Drug therapy of experimental tuberculosis (tb): Improved outcome by combining SQ109, a new diamine antibiotic, with existing TB drugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2007, 51, 1563–1565. [Google Scholar]
- Copp, BR; Pearce, AN. Natural product growth inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nat Prod Rep 2007, 24, 278–297. [Google Scholar]
- Kishore, N; Mishra, BB; Tripathi, V; Tiwari, VK. Alkaloids as potential antitubercular agents. Fitoterapia 2009, 80, 149–163. [Google Scholar]
- Palomino, JC; Ramos, DF; da Silva, PA. New anti-tuberculosis drugs: Strategies, sources and new molecules. Curr Med Chem 2009, 16, 1898–1904. [Google Scholar]
- Alksnis, E; Korneeva, D; Lukevics, E. Adenine and uracil derivatives with antitubercular activity. Chem Het Com 2001, 37, 743–746. [Google Scholar]
- Cos, P; Vlietinck, AJ; Berghe, DV; Maes, L. Anti-infective potential of natural products: How to develop a stronger in vitro ‘proof-of-concept’. J Ethnopharmacol 2006, 106, 290–302. [Google Scholar]
- Gademann, K; Kobylinska, J. Antimalarial natural products of marine and freshwater origin. Chem Rec 2009, 9, 187–198. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, H; Kobayashi, J; Wu, H; Deng, S; Kobayashi, M; Nakamura, Y; Ohizumi, Y; Hirata, Y. Enzyme inhibitors isolated from Okinawan marine sponges. Tennen Yuki Kagobutsu Toronkai Koen Yoshishu 1985, 27, 608–615. [Google Scholar]
- Lio, H; Asao, K; Tokoroyama, T. Syntheses of agelasin B and its analogues. J Chem Soc, Chem Commun 1985, 774–775. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, P-L; Yen, M-H; Shyu, W-S; Chern, J-W. Doridosine derivatives: Binding at adenosine receptors and in vivo effect. Eur J Pharmacol 1993, 243, 135–139. [Google Scholar]
- Fossa, P; Mosti, L; Bondavalli, F; Schenone, S; Ranise, A; Casolino, C; Forina, M. Affinity prediction on A1 adenosine receptor agonists: The chemometric approach. Bioorg Med Chem 2006, 14, 1348–1363. [Google Scholar]










© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Gordaliza, M. Terpenyl-Purines from the Sea. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 833-849. https://doi.org/10.3390/md7040833
Gordaliza M. Terpenyl-Purines from the Sea. Marine Drugs. 2009; 7(4):833-849. https://doi.org/10.3390/md7040833
Chicago/Turabian StyleGordaliza, Marina. 2009. "Terpenyl-Purines from the Sea" Marine Drugs 7, no. 4: 833-849. https://doi.org/10.3390/md7040833
APA StyleGordaliza, M. (2009). Terpenyl-Purines from the Sea. Marine Drugs, 7(4), 833-849. https://doi.org/10.3390/md7040833