Water Bacterial and Fungal Community Compositions Associated with Urban Lakes, Xi’an, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site Description
2.2. Sampling Process
2.3. Water Physicochemical Analysis
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Determination
2.5. Determination of Water Microbial Community Functional Diversity
2.6. Water Microbial Community DNA Extraction
2.7. Determination of the Water Bacterial and Fungal Community Compositions
2.8. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Number
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Water Quality Parameters
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Images
3.3. Functional Diversity of Water Bacterial Communities
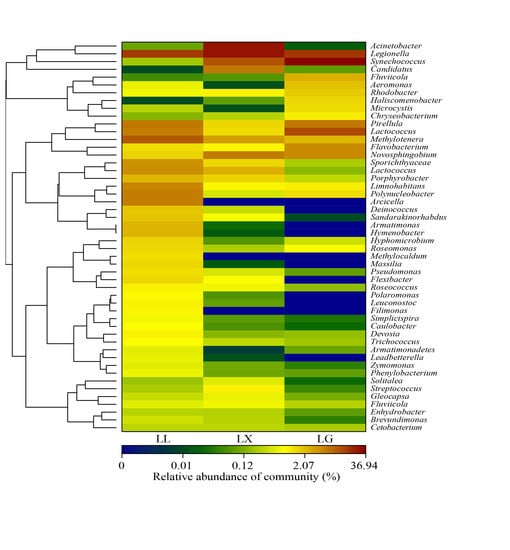
3.4. Water Bacterial and Fungal Community Compositions
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, R.; Meng, X.; Xu, J.; Qadeer, A.; Liu, M. Modeling and evaluating spatial variation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban lake surface sediments in Shanghai. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Fu, D.; Wang, Y.; Singh, R.P. Detailed sponge city planning based on hierarchical fuzzy decision-making: A case study on Yangchen Lake. Water 2017, 9, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henny, C.; Meutiab, A.A. Urban lakes in megacity Jakarta: Risk and management plan for future sustainability. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2014, 20, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Cheng, F.; Shen, Z. WetSpass-based study of the effects of urbanization on the water balance components at regional and quadrat scales in Beijing, China. Water 2018, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.C. Potential urban runoff impacts and contaminant distributions in shoreline and reservoir environments of Lake Havasu, southwestern United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Li, S.; Su, J.; Nie, S.; Gibson, V.; Li, H.; Zhu, Y. Does urbanization shape bacterial community composition in urban park soils? A case study in 16 representative Chinese cities based on the pyrosequencing method. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 87, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckert, E.M.; Cesare, A.D.; Kettner, M.T.; Arias-Andres, M.; Fontaneto, D.; Grossart, H.P.; Corno, G. Microplastics increase impact of treated wastewater on freshwater microbial community. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, T.; Chen, S.; Guo, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, T. Spatial pattern of bacterial community functional diversity in a drinking water reservoir, Shaanxi Province, Northwest China. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 7, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Huang, T.; Zhang, H. Effects of seasonal thermal stratification on the functional diversity and composition of the microbial community in a drinking water reservoir. Water 2015, 7, 5525–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibekwe, A.M.; Ma, J.; Murinda, S.E. Bacterial community composition and structure in an Urban River impacted by different pollutant sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; Huang, T.; Ma, W.; Xu, J.; Sun, X. Vertical distribution of bacterial community diversity and water quality during the reservoir thermal stratification. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 6933–6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, T.; Chen, S.; Guo, L.; Liu, T.; Yang, X. Microbial community functional diversity and enzymatic activity in the sediments of drinking water reservoirs, Northwest China. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 52, 1608–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Armisen, T.; İnceoğlu, Ö.; Ouattara, N.K.; Anzil, A.; Verbanck, M.A.; Brion, N.; Servais, P. Seasonal variations and resilience of bacterial communities in a sewage polluted urban river. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, D.; Zhao, G.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, Q.; Fang, Z.; Huang, L.; Ji, F. Microbial community structures and functions of wastewater treatment systems in plateau and cold regions. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 249, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida-Dalmet, S.; Sikaroodi, M.; Gillevet, P.M.; Litchfield, C.D.; Baxter, B.K. Temporal study of the microbial diversity of the North Arm of Great Salt Lake, Utah, U.S. Microorganisms 2015, 3, 310–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, J.M.; Baker, K.D.; Zamor, R.M.; Nikolai, S.; Elshahed, M.S.; Youssef, N.H. Spatiotemporal analysis of microbial community dynamics during seasonal stratification events in a freshwater lake (Grand Lake, OK, USA). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosińska, J.; Kozak, A.; Dondajewska, R.; Gołdyn, R. Cyanobacteria blooms before and during the restoration process of a shallow urban lake. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 198, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, P.; Huang, T.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; Shang, P.; Feng, J.; Jia, J. Water quality and diversity of denitrifier community structure of typical scenic water bodies in Xi’an. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 5174–5183. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, A.; Chang, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Q. Variations in the runoff-sediment relationship of the Weihe River basin based on the copula function. Water 2016, 8, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, T.; Chen, S.; Yang, X.; Lv, K.; Raju, S. Abundance and diversity of bacteria in oxygen minimum drinking water reservoir sediments studied by quantitative PCR and pyrosequencing. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 69, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, P.; Zhang, H.; Huang, T.; Chen, S.; Shang, P.; Feng, J.; Jia, J. Denitrification characteristics and community structure of aerobic denitrifiers of lake and reservoir sediments. Environ. Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Shi, H.; Pan, X.; Liu, F.; Cui, Y.; Xie, H. Integrating ecological restoration of agricultural non-point source pollution in Poyang Lake basin in China. Water 2017, 9, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ramírez, A.I.; Ramírez-Granillo, A.; Medina-Canales, M.G.; Rodríguez-Tovar, A.V.; Martínez-Rivera, M.A. Analysis and description of the stages of Aspergillus fumigatus biofilm formation using scanning electron microscopy. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M.; et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, J.; Singh, K.; Fern, A.; Kirton, E.S.; He, S.M.; Woyke, T.; Lee, J.; Chen, F.; Dang, J.L.; Tringe, S.G. Primer and platform effects on 16S rRNA tag sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degnan, P.H.; Ochman, H. Illumina-based analysis of microbial community diversity. ISME J. 2012, 6, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelfattah, A.; Wisniewski, M.; Droby, S.; Schena, L. Spatial and compositional variation in the fungal communities of organic and conventionally grown apple fruit at the consumer point-of-purchase. Hortic. Res. 2016, 3, 16047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Tao, P.; Tan, J.; Mu, H.; Peng, L.; Yang, D.; Tong, S.; Chen, L. Identification of bacterial community composition in freshwater aquaculture system farming of Litopenaeus vannamei reveals distinct temperature-driven patterns. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 13663–13680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kozak, A.; Gołdyn, R.; Dondajewska, R.; Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Holona, T. Changes in phytoplankton and water quality during sustainable restoration of an urban Lake used for recreation and water supply. Water 2017, 9, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Cai, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y. Water quality assessment based on the water quality index method in Lake Poyang: The largest freshwater lake in China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, B.; Laws, E.A. Nutrients and phytoplankton in a shallow, hypereutrophic urban lake: Prospects for restoration. Water 2017, 9, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Shen, Y. Development of the microbial communities in Lake Donghu in relation to water quality. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 127, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon-Bradley, N.; Li, N.; Williams, H.N. Bacterial community structure in freshwater springs infested with the invasive plant species Hydrilla verticillata. Hydrobiologia 2015, 742, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saarenheimo, J.; Aalto, S.L.; Rissanen, A.J.; Tiirola, M. Microbial community response on wastewater discharge in Boreal Lake sediments. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Jimenez, K.; Wurzbacher, C.; Bourne, E.C.; Chiuchiolo, A.; Priscu, J.C.; Grossart, H.P. Early diverging lineages within Cryptomycota and Chytridiomycota dominate the fungal communities in ice-covered lakes of the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, T.; Chen, S. Ignored sediment fungal populations in water supply reservoirs are revealed by quantitative PCR and 454 Pyrosequencing. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Gao, G.; Bartlam, M.G.; Wang, Y. Distribution and diversity of fungi in freshwater sediments on a river catchment scale. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.G.; Weldon, C.; Conradie, W.; Preez, L.H.D. Relationship among size, development, and Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis infection in African tadpoles. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2007, 74, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.S.; Kim, M.; Lee, C.; Yu, Z.T.; Lee, J. The microbiota of recreational freshwaters and the implications for environmental and public health. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittorf, L.; Bonilla-Rosso, G.; Jones, C.M.; Bäckman, O.; Hulth, S.; Hallin, S. Habitat partitioning of marine benthic denitrifier communities in response to oxygen availability. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2016, 8, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mieczan, T.; Adamczuk, M.; Tarkowska-Kukuryk, M.; Nawrot, D. Effect of water chemistry on zooplanktonic and microbial communities across freshwater ecotones in different macrophyte-dominated shallow lakes. Limnology 2016, 75, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luby, S.P.; Halder, A.K.; Huda, T.M.; Unicomb, L.; Islam, M.S.; Arnold, B.F.; Johnston, R.B. Microbiological contamination of drinking water associated with subsequent child diarrhea. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M. Microbial Inhabitants of Humans Their Ecology and Role in Health and Disease; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- João, P.; Cabral, S. Water microbiology. Bacterial pathogens and water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 3657–3703. [Google Scholar]
- Bandh, S.A.; Kamili, A.N.; Ganai, B.A.; Lone, B.A. Opportunistic fungi in lake water and fungal infections in associated human population in Dal Lake, Kashmir. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 93, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietryczuk, A.; Cudowski, A.; Hauschild, T. Effect of trophic status in lakes on fungal species diversity and abundance. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 109, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Urban Lakes | Latitude | Longitude | Surface Area (m2) | Built Year | Functions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LX | 34°15′33″ | 108°58′39″ | 100,000 | 1965 | Recreation |
| LG | 34°16′42″ | 108°57′69″ | 20,000 | 1927 | Recreation |
| LL | 34°16′30″ | 108°55′59″ | 380,000 | 1916 | Recreation |
| Water Quality Parameters | LG | LL | LX | ANOVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 24.1 ± 1.2A | 25.3 ± 1.1A | 23.6 ± 1.4A | NS |
| pH | 9.6 ± 0.8A | 9.4 ± 0.9A | 8.3 ± 1.2A | NS |
| Dissolved oxygen (mg/L) | 10.2 ± 0.02A | 8.3 ± 0.01B | 9.1 ± 0.04AB | * |
| NO3−-N (mg/L) | 5.3 ± 0.4A | 5.1 ± 0.5A | 1.2 ± 0.07B | *** |
| NH4+-N (mg/L) | 2.8 ± 0.06A | 1.9 ± 0.04B | 1.5 ± 0.05B | * |
| Total nitrogen (mg/L) | 5.6 ± 0.03C | 12.1 ± 0.04A | 8.4 ± 0.04B | ** |
| Total phosphorus (mg/L) | 0.21 ± 0.01A | 0.08 ± 0.00B | 0.06 ± 0.01B | ** |
| CODMn (mg/L) | 21.6 ± 2.3B | 35.4 ± 2.9A | 28.8 ± 1.6AB | ** |
| Fe (mg/L) | 0.08 ± 0.01A | 0.07 ± 0.01B | 0.01 ± 0.00C | ** |
| Parameters | LG | LL | LX | ANOVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWCD590nm | 0.49 ± 0.03C | 0.90 ± 0.12A | 0.67 ± 0.06B | ** |
| Amino acids | 0.17 ± 0.01C | 0.74 ± 0.2A | 0.57 ± 0.07B | *** |
| Carboxylic acids | 0.30 ± 0.08B | 0.78 ± 0.2A | 0.44 ± 0.03B | *** |
| Carbohydrates | 0.83 ± 0.1B | 1.05 ± 0.2A | 0.85 ± 0.05B | ** |
| Amines | 0.55 ± 0.03B | 0.96 ± 0.1A | 0.68 ± 0.02B | ** |
| Phenolic compounds | 0.41 ± 0.1B | 0.67 ± 0.1A | 0.68 ± 0.1A | * |
| Polymers | 0.85 ± 0.1B | 1.26 ± 0.2A | 0.87 ± 0.1B | ** |
| Richness diversity (R) | 17 ± 1.20B | 23 ± 0.9A | 20 ± 2.3AB | * |
| Shannon’s diversity (H’) | 3.50 ± 0.6C | 5.4 ± 0.7A | 4.48 ± 0.9B | * |
| Urban Lakes | Microbe | Reads | 0.97 Level | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OTUs | ACE | Chao1 | Shannon Diversity (H’) | Simpson Diversity (D) | |||
| LG | Bacteria | 13,598 | 231 | 254 (243, 276) | 257 (242, 290) | 3.52 (3.49, 3.55) | 0.0766 (0.0742, 0.0790) |
| LL | 26,252 | 380 | 393 (386, 407) | 394 (385, 414) | 4.55 (4.54, 4.57) | 0.0198 (0.0194, 0.0202) | |
| LX | 22,892 | 283 | 302 (293, 321) | 305 (292, 335) | 3.48 (3.46, 3.51) | 0.0854 (0.0833, 0.0875) | |
| LG | Fungi | 24,523 | 102 | 105 (103, 112) | 103 (102, 108) | 2.34 (2.32, 2.36) | 0.1555 (0.1532, 0.1579) |
| LL | 19,742 | 83 | 105 (93, 132) | 98 (89, 126) | 0.89 (0.87, 0.91) | 0.6137 (0.6058, 0.6215) | |
| LX | 11,081 | 93 | 95 (93, 103) | 94 (93, 103) | 2.59 (2.56, 2.62) | 0.1662 (0.1611, 0.1712) | |
| Water Bacterial Species | LG | LL | LX | Potential Disease [42,43,44] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trichococcus sp. | 1 | 10 | 4 | Intestinal infection |
| Aeromonas sp. | 264 | 143 | 2 | Diarrhea |
| Brevundimonas sp. | 5 | 77 | 64 | Intracranial infection |
| Deinococcus sp. | 0 | 85 | 2 | Infections |
| Flavobacterium sp. | 597 | 338 | 207 | Bloodstream Infections |
| Kocuria sp. | 1 | 69 | 2 | Respiratory tract infection |
| Lactobacillus sp. | 0 | 66 | 2 | Diarrhea |
| Legionella sp. | 10 | 86 | 3 | Pulmonary infection |
| Pseudomonas sp. | 11 | 324 | 102 | Respiratory system infection |
| Streptococcus sp. | 0 | 32 | 12 | Respiratory system infection |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Z.; Feng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, K.; Jia, J. Water Bacterial and Fungal Community Compositions Associated with Urban Lakes, Xi’an, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15030469
Zhang H, Wang Y, Chen S, Zhao Z, Feng J, Zhang Z, Lu K, Jia J. Water Bacterial and Fungal Community Compositions Associated with Urban Lakes, Xi’an, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(3):469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15030469
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Haihan, Yue Wang, Shengnan Chen, Zhenfang Zhao, Ji Feng, Zhonghui Zhang, Kuanyu Lu, and Jingyu Jia. 2018. "Water Bacterial and Fungal Community Compositions Associated with Urban Lakes, Xi’an, China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 3: 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15030469
APA StyleZhang, H., Wang, Y., Chen, S., Zhao, Z., Feng, J., Zhang, Z., Lu, K., & Jia, J. (2018). Water Bacterial and Fungal Community Compositions Associated with Urban Lakes, Xi’an, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(3), 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15030469