Effects of Co-Processing Sewage Sludge in the Cement Kiln on PAHs, Heavy Metals Emissions and the Surrounding Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. A Brief Introduction to the Cement Production Line
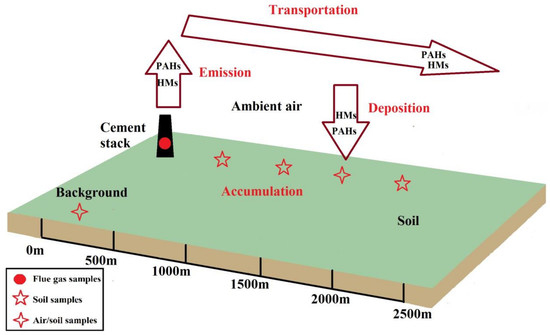
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Analytical Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Co-Processing Sewage Sludge on Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Heavy Metals Emissions
3.1.1. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Emissions
3.1.2. Heavy Metals Emissions
3.2. Effects of Co-Processing Sewage Sludge on Ambient Air
3.2.1. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons Concentrations in Ambient Air
3.2.2. Heavy Metals Concentrations in Ambient Air
3.3. Effects of Co-Processing Sewage Sludge on Soil Environment
3.3.1. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Concentrations in Soil
3.3.2. Heavy Metals Concentrations in Soil
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, Q.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wang, F.; Chi, Y.; Yan, J. Formation of PAHs during the pyrolysis of dry sewage sludge. Fuel 2014, 130, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.-P.; Li, L.-Y.; Morishita, K.; Xiao, X.-B.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Wei, X.-Y.; Takarada, T. Nitrogen transformations during fast pyrolysis of sewage sludge. Fuel 2013, 104, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovira, J.; Mari, M.; Nadal, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. Use of sewage sludge as secondary fuel in a cement plant: Human health risks. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasta, P.; Boran, J.; Bebar, L.; Stehlik, P.; Oral, J. Thermal processing of sewage sludge. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2006, 26, 1420–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, J.A.; Rey, L.; Egea, S.; Rey, M.D. Pollutant formation and emissions from cement kiln stack using a solid recovered fuel from municipal solid waste. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5878–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karstensen, K.H. Formation, release and control of dioxins in cement kilns. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 543–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuhmacher, M.; Nadal, M.; Domingo, J.L. Environmental monitoring of pcdd/fs and metals in the vicinity of a cement plant after using sewage sludge as a secondary fuel. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 1502–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, P.; Tang, Z.-J.; Huang, J.-H.; Cen, C.-P.; Tang, Z.-X.; Chen, X.-B. Using sewage sludge as a denitration agent and secondary fuel in a cement plant: A case study. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 137, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovira, J.; Mari, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Nadal, M.; Domingo, J.L. Monitoring environmental pollutants in the vicinity of a cement plant: A temporal study. Arch. Environ. Con. Tox. 2011, 60, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovira, J.; Mari, M.; Nadal, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. Levels of metals and pcdd/fs in the vicinity of a cement plant: Assessment of human health risks. J. Environ. Sci. Health. Tox. Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2011, 46, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conesa, J.A.; Ortuno, N.; Abad, E.; Rivera-Austrui, J. Emissions of pcdd/fs, pbdd/fs, dioxin like-pcbs and pahs from a cement plant using a long-term monitoring system. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conesa, J.A.; Galvez, A.; Mateos, F.; Martin-Gullon, I.; Font, R. Organic and inorganic pollutants from cement kiln stack feeding alternative fuels. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, F.; Liang, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xiong, Y. Utilization of solar energy in sewage sludge composting: Fertilizer effect and application. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2014–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, D.; Zhu, T.; Liu, R.; Lv, Q.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F. Effects of co-processing sewage sludge in cement kiln on nox, nh3 and pahs emissions. Chemosphere 2016, 159, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L.; Garreta, J. Pollutants emitted by a cement plant: Health risks for the population living in the neighborhood. Environ. Res. 2004, 95, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosca, S.; Torelli, G.N.; Tramontana, G.; Guerriero, E.; Rotatori, M.; Bianchini, M. Concentration of organic micropollutants in the atmosphere of trieste, italy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2012, 19, 1927–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldantoni, D.; De Nicola, F.; Alfani, A. Air biomonitoring of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons near a cement plant. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2014, 5, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprung, S.; Rechenberg, W.; Bachmann, G. Environmental compatibility of cement. Zement-Kalk-Gips Studies Environ. Sci. 1994, 60, 369–386. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, L. Problems about utilizing waste materials in cement: Plant-foreign research and rule of law. Cement 2002, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Galvez, A.; Conesa, J.A.; Martin-Gullon, I.; Font, R. Interaction between pollutants produced in sewage sludge combustion and cement raw material. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau-Guigon, E.; Alliot, F.; Gaspéri, J.; Blanchard, M.; Teil, M.-J.; Mandin, C.; Chevreuil, M. Seasonal fate and gas/particle partitioning of semi-volatile organic compounds in indoor and outdoor air. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 147, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Cement Raw Materials (mg/kg) | Coal (mg/kg) | Sewage Sludge (mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nap | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.46 |
| AcPy | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.05 |
| Acp | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.06 |
| Flu | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.20 |
| PA | 0.43 | 1.09 | 2.04 |
| Ant | 0.21 | 0.34 | 1.50 |
| FL | 0.34 | 0.55 | 1.13 |
| Pyr | 0.33 | 0.53 | 0.91 |
| BaA | 0.24 | 0.49 | 0.89 |
| CHR | 0.10 | 0.41 | 0.59 |
| BbF | 0.34 | 0.52 | 1.39 |
| BkF | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.83 |
| BaP | 0.12 | 0.21 | 0.43 |
| IND | 0.02 | 0.03 | 1.90 |
| DBA | 0.64 | 1.11 | 2.12 |
| BghiP | 0.54 | 1.16 | 4.91 |
| As | 8.4 | 7.0 | 24.8 |
| Co | 0.2 | 0.7 | 1.6 |
| Cr | 12.5 | 27.3 | 178.2 |
| Cu | 217 | 262.1 | 318.1 |
| Mn | 474.2 | 632.1 | 828.9 |
| Ni | 14.1 | 19.3 | 35.8 |
| Sb | 1.0 | 2.7 | 4.2 |
| Sn | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.5 |
| V | 45.2 | 30.4 | 21.3 |
| Zn | 46.8 | 83.2 | 172.3 |
| Pb | 9.3 | 16.5 | 83.4 |
| Cd | 1.2 | 2.4 | 13.4 |
| Sewage Sludge 0 t/d | Sewage Sludge 100 t/d | Increment, % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nap | 9.721 | 13.683 | 40.8 |
| AcPy | 1.120 | 1.503 | 34.1 |
| Acp | 0.486 | 0.762 | 56.9 |
| Flu | 0.168 | 0.441 | 162.5 |
| PA | 3.271 | 5.433 | 66.1 |
| Ant | 0.200 | 0.472 | 136.5 |
| LMW | 14.818 | 22.294 | 49.1 |
| FL | 0.096 | 0.312 | 225.4 |
| Pyr | 0.149 | 0.186 | 24.3 |
| BaA | 0.105 | 0.281 | 168.8 |
| CHR | 0.101 | 0.228 | 126.5 |
| MMW | 0.450 | 1.006 | 123.4 |
| BbF | 0.042 | 0.151 | 260.3 |
| BkF | 0.013 | 0.063 | 395.1 |
| BaP | 0.037 | 0.119 | 220.7 |
| IND | 0.045 | 0.066 | 49.0 |
| DBA | 0.027 | 0.124 | 369.7 |
| BghiP | 0.041 | 0.157 | 260.3 |
| HMW | 0.204 | 0.680 | 234.2 |
| ∑PAHs | 15.472 | 23.981 | 53.7 |
| As | 9.361 | 12.538 | 34.0 |
| Co | 0.972 | 1.258 | 29.4 |
| Cr | 65.315 | 69.289 | 6.1 |
| Cu | 36.166 | 38.576 | 6.7 |
| Mn | 27.251 | 28.471 | 4.5 |
| Ni | 9.734 | 13.047 | 34.0 |
| Sb | 3.956 | 4.029 | 1.9 |
| Sn | 2.395 | 2.597 | 8.4 |
| V | 4.170 | 4.772 | 14.5 |
| Zn | 24.046 | 26.928 | 12.0 |
| NV-HMs | 183.366 | 201.505 | 9.9 |
| Pb | 52.048 | 112.927 | 117.0 |
| Cd | 0.572 | 2.064 | 260.9 |
| LV-HMs | 52.620 | 114.991 | 118.5 |
| ∑HMs | 235.986 | 316.496 | 34.1 |
| Sewage Sludge 0 t/d | Sewage Sludge 100 t/d | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Background | Downwind | Increment, % | Background | Downwind | Increment, % | |
| Nap | 1052.6 | 1231.5 | 17.0 | 1089.9 | 1312.5 | 20.4 |
| AcPy | 12.7 | 15.4 | 21.5 | 14.5 | 18.7 | 29.4 |
| Acp | 16.3 | 19.7 | 21.1 | 17.5 | 23.8 | 36.3 |
| Flu | 20.0 | 23.0 | 15.3 | 24.3 | 30.8 | 26.7 |
| PA | 21.0 | 28.3 | 34.9 | 26.9 | 37.5 | 39.1 |
| Ant | 6.6 | 9.1 | 37.6 | 10.1 | 16.0 | 58.8 |
| LMW | 1129.1 | 1327.1 | 17.5 | 1183.2 | 1439.4 | 21.7 |
| FL | 3.6 | 4.7 | 29.4 | 4.3 | 6.3 | 46.4 |
| Pyr | 5.5 | 6.3 | 14.7 | 5.5 | 7.8 | 40.5 |
| BaA | 7.0 | 10.3 | 47.1 | 7.4 | 12.1 | 62.7 |
| CHR | 2.6 | 4.3 | 67.2 | 2.8 | 5.0 | 81.8 |
| MMW | 18.7 | 25.7 | 36.9 | 20.0 | 31.1 | 55.7 |
| BbF | 0.8 | 1.3 | 52.0 | 0.7 | 1.7 | 128.5 |
| BkF | 1.3 | 1.8 | 39.4 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 49.1 |
| BaP | 1.2 | 1.9 | 60.3 | 1.4 | 2.7 | 91.1 |
| IND | 1.3 | 1.8 | 45.1 | 1.4 | 2.5 | 73.0 |
| DBA | 1.4 | 2.2 | 53.7 | 1.8 | 3.2 | 81.8 |
| BghiP | 2.0 | 3.2 | 57.9 | 2.6 | 5.1 | 100.6 |
| HMW | 8.1 | 12.3 | 51.9 | 9.5 | 17.5 | 85.2 |
| ∑PAHs | 1155.9 | 1365.0 | 18.1 | 1212.6 | 1488.0 | 22.7 |
| As | 9.8 | 11.7 | 19.6 | 11.2 | 13.6 | 21.1 |
| Co | 1.7 | 1.9 | 14.1 | 1.8 | 2.1 | 17.4 |
| Cr | 42.6 | 50.3 | 18.0 | 45.5 | 53.9 | 18.6 |
| Cu | 16.5 | 17.7 | 7.4 | 20.1 | 21.7 | 7.8 |
| Mn | 103.6 | 122.8 | 18.5 | 108.0 | 129.5 | 20.0 |
| Ni | 13.9 | 14.7 | 6.0 | 13.7 | 15.0 | 9.2 |
| Sb | 3.9 | 4.4 | 13.1 | 4.0 | 4.9 | 21.9 |
| Sn | 8.6 | 9.2 | 7.9 | 9.0 | 9.5 | 5.7 |
| V | 8.7 | 9.7 | 12.4 | 8.9 | 10.5 | 17.9 |
| Zn | 101.9 | 113.9 | 11.8 | 103.4 | 117.6 | 13.7 |
| NV-HMs | 311.0 | 356.4 | 14.6 | 325.6 | 378.2 | 16.1 |
| Pb | 32.9 | 45.3 | 37.6 | 39.5 | 61.2 | 55.0 |
| Cd | 0.7 | 1.0 | 41.7 | 0.9 | 1.8 | 92.8 |
| LV-HMs | 33.6 | 46.3 | 37.7 | 40.4 | 63.0 | 55.8 |
| ∑HMs | 344.6 | 402.6 | 16.8 | 366.0 | 441.1 | 20.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, D.; Zhu, T.; Liu, R.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Q. Effects of Co-Processing Sewage Sludge in the Cement Kiln on PAHs, Heavy Metals Emissions and the Surrounding Environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15040698
Lv D, Zhu T, Liu R, Li X, Zhao Y, Sun Y, Wang H, Zhang F, Zhao Q. Effects of Co-Processing Sewage Sludge in the Cement Kiln on PAHs, Heavy Metals Emissions and the Surrounding Environment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(4):698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15040698
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Dong, Tianle Zhu, Runwei Liu, Xinghua Li, Yuan Zhao, Ye Sun, Hongmei Wang, Fan Zhang, and Qinglin Zhao. 2018. "Effects of Co-Processing Sewage Sludge in the Cement Kiln on PAHs, Heavy Metals Emissions and the Surrounding Environment" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 4: 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15040698
APA StyleLv, D., Zhu, T., Liu, R., Li, X., Zhao, Y., Sun, Y., Wang, H., Zhang, F., & Zhao, Q. (2018). Effects of Co-Processing Sewage Sludge in the Cement Kiln on PAHs, Heavy Metals Emissions and the Surrounding Environment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(4), 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15040698