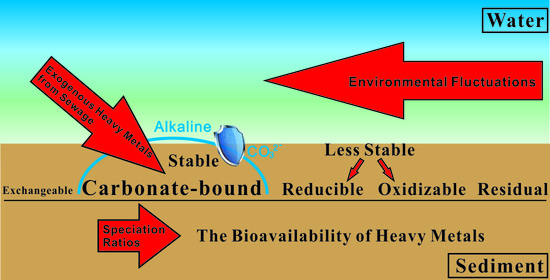
The Variation of Heavy Metals Bioavailability in Sediments of Liujiang River Basin, SW China Associated to Their Speciations and Environmental Fluctuations, a Field Study in Typical Karstic River
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Description of the Study Area and Field Sampling
2.2. Sample Preparation and Analysis
2.3. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Properties in Sediments and Their Overlying Water
3.2. The Concentration and Their Speciations of Heavy Metals in Sediments
3.3. The Bioavailability of Heavy Metals in Sediments
3.4. The Impacts of Heavy Metals Speciation on Their Bioavailability
3.5. The Impacts of Environmental Variations on the Bioavailability of Heavy Metals
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gashi, F.; Frančišković-Bilinski, S.; Bilinski, H.; Kika, L. Assessment of the effects of urban and industrial development on water and sediment quality of the Drenica River in Kosovo. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chao, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, A.; Cao, H. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, D.; Usero, J.; Morillo, J. Assessment of heavy metals bioavailability and toxicity toward Vibrio fischeri in sediment of the Huelva estuary. Chemosphere 2016, 153, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, L.-Z.; Shi, W.-L.; Meng, X.-Z. Comprehensive risk assessment of heavy metals in lake sediment from public parks in Shanghai. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 102, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zhao, C.; Luo, Y.; Liu, C.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, D.; An, S.; Zhu, H. Heavy metals in surface sediments of the Jialu River, China: Their relations to environmental factors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 270, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Hao, Y.; He, X.; Luo, S. The human Impacts level and migration of heavy metals in original inshore sediments of Dongying, China. J. Coast. Conserv. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Xu, N.; Liu, B.; Zhou, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Dai, B.; Xiong, W. Metal concentrations and risk assessment in water, sediment and economic fish species with various habitat preferences and trophic guilds from Lake Caizi, Southeast China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 157, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.L.; Ning, Z.P.; Xiao, Q.X.; Huang, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.Z.; Xiao, T.F.; Zhao, Y.L.; Shi-Liang, W.U. Spatial distribution, sources and bioavailability of heavy metals in the surface sediments of longjiang river, southern china. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 748–757. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, X.; Song, J.; Yuan, H.; Duan, L.; Li, X.; Li, N.; Liang, X.; Qu, B. Speciation of heavy metals in different grain sizes of Jiaozhou Bay sediments: Bioavailability, ecological risk assessment and source analysis on a centennial timescale. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 143, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, T.T. Use of partial dissolution techniques in geochemical exploration. J. Geochem. Explor. 1984, 20, 101–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaray, S.K.; Nayak, B.B.; Lin, S.; Bhatta, D. Geochemical speciation and risk assessment of heavy metals in the river estuarine sediments—A case study: Mahanadi basin, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Zuo, H.; Tian, M.; Zhang, L.; Meng, J.; Zhou, X.; Min, N.; Chang, X.; Liu, Y. Assessment of heavy metals contamination in sediments from three adjacent regions of the Yellow River using metal chemical fractions and multivariate analysis techniques. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, R.A. BCR®-701: A review of 10-years of sequential extraction analyses. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 680, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particular trace elements. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hass, A.; Fine, P. Sequential selective extraction procedures for the study of heavy metals in soils, sediments, and waste materials—A critical review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 40, 365–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shan, B.; Tang, W.; Dong, L.; Zhang, W.; Pei, Y. Heavy metal concentrations and speciation in riverine sediments and the risks posed in three urban belts in the Haihe Basin. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 139, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Guo, J.; Zhang, W.; Yu, K. Distribution, speciation, environmental risk, and source identification of heavy metals in surface sediments from the karst aquatic environment of the Lijiang River, Southwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 9122–9133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Peng, P.; Liu, C.; Song, J. Heavy metal contaminations and chemical speciation of farmland soils in an e-waste recycling town in South China. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2012, 21, 1742–1748. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Long, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Ye, X.; Chang, W.; Zeng, H. Effect of metal oxide nanoparticles on the chemical speciation of heavy metals and micronutrient bioavailability in paddy soil. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munir, M.A.M.; Liu, G.; Yousaf, B.; Mian, M.M.; Ali, M.U.; Ahmed, R.; Cheema, A.I.; Naushad, E. Contrasting effects of biochar and hydrothermally treated coal gangue on teachability, inviolability, speculation and accumulation of heavy metals by appeased in copper mine tailings. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.C.; Wong, M.H. Effects of bacteria on metal bioavailability, speciation, and mobility in different metal mine soils: A column study. J. Soils Sediments 2010, 10, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-F.; Ju, Y.-R.; Chen, C.-W.; Dong, C.-D. Changes in the total content and speciation patterns of metals in the dredged sediments after ocean dumping: Taiwan continental slope. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2019, 181, 104893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Ramteke, D.; Gadi, S.D.; Bardhan, P. Linkage between speciation of Cd in mangrove sediment and its bioaccumulation in total soft tissue of oyster from the west coast of India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 106, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Guo, H. Hot topics and trends in the study of high arsenic groundwater. Adv. Earth Sci. 2013, 28, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Amor, K.; Galer, S.J.G.; Thompson, G.; Porcelli, D. Using stable isotope fractionation factors to identify Cr(VI) reduction pathways: Metal-mineral-microbe interactions. Water Res. 2018, 151, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsenovich, Y.P.; Carvajal, D.A.; Wellman, D.M.; Lagos, L.E. Enhanced U(VI) release from autunite mineral by aerobic Arthrobacter sp. in the presence of aqueous bicarbonate. Chem. Geol. 2012, 308–309, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yan, J. Effects of land use on hydrochemistry and contamination of karst groundwater from nandong underground River system, China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 210, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D. Modern karstology and global changes study. Earthence Front. 1997, 4, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Wu, L.; Xin, C.; Yu, S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J. Impact of anthropogenic sulfate deposition via precipitation on carbonate weathering in a typical industrial city in a karst basin of southwest China: A case study in Liuzhou. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 110, 104417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yuan, D.; Tong, L.; Azim, M.; Yang, H.; Huang, F. An overview of karst ecosystem in Southwest China: Current state and future management. J. Resour. Ecol. 2015, 6, 247–256. [Google Scholar]
- Arain, M.B.; Kazi, T.G.; Jamali, M.K.; Jalbani, N.; Afridi, H.I.; Baig, J.A. Speciation of heavy metals in sediment by conventional, ultrasound and microwave assisted single extraction methods: A comparison with modified sequential extraction procedure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dundar, M.S.; Altundag, H.; Eyupoglu, V.; Keskin, C.S.; Tutunoglu, C. Sequential extraction speciation of heavy metals in sediments based on grain size. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2013, 22, 3184–3191. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.A.; Shi, Y.U.; Fu-Zhen, M.O.; Shi-Yi, H.E.; Ju-Fang, L.U.; Yuan, Y.Q. Hydrochemical characteristics and influencing factors in different geological background: A case study in darongjiang and lingqu basin, Guangxi, China. Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 123. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Miao, X.; Hao, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zou, S.; Zhou, C. Health risk assessment of metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, Cr, Cd, As, Hg, Se) in angling fish with different lengths collected from Liuzhou, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miao, X.; Hao, Y.; Liu, H.; Xie, Z.; Miao, D.; He, X. Effects of heavy metals speciations in sediments on their bioaccumulation in wild fish in rivers in Liuzhou—A typical karst catchment in southwest China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 214, 112099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Hao, Y.; Tang, X.; Xie, Z.; Liu, L.; Luo, S.; Huang, Q.; Zou, S.; Zhang, C.; Li, J. Analysis and health risk assessment of toxic and essential elements of the wild fish caught by anglers in Liuzhou as a large industrial city of China. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, J.; Yu, S. Heavy metal pollution of the drinking water sources in the liujiang river basin, and related health risk assessments. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, X.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zou, S.; Ye, S.; Xie, Z. Spatial distribution of heavy metals and their potential sources in the soil of Yellow River Delta: A traditional oil field in China. Environ. Geochem. health 2020, 42, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahuquillo, A.; Rigol, A.; Rauret, G. Overview of the use of leaching/extraction tests for risk assessment of trace metals in contaminated soils and sediments. Trends Anal. Chem. 2003, 22, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, X.; Jiang, R.; Chen, X. Hydrochemical characteristics and analysis of water-rock interaction in karst watershed—An example of Houzhai River watershed. Earth Environ. 2018, 46, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, P.M.; Allard, P.J.; Vigers, G.A. Development of sediment quality values for hong kong special administrative region: A possible model for other jurisdictions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1999, 38, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.L.; MacDonald, D.D.; Keenleyside, K.A.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Field, L.J. A preliminary evaluation of sediment quality assessment values for freshwater ecosystems. J. Great Lakes Res. 1996, 22, 624–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CNEMC. The Background Values of Soil Elements in China, 1st ed.; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Chen, J.; Sun, X.; Hu, Z.; Fan, D. Accumulation and transformation of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Yangtze River estuary to the East China Sea shelf. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Hu, S.; Deng, K.; Huang, D.; Cao, L. Chemical forms of Hg, Pb, Cd, Cu and Zn in Beijing urban soil and its environmental effects. Urban Geol. 2015, 10, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Yan, W.; Huang, X.; Shi, P. Distributional characteristics of heavy metal and its available phases in sediments from Zhujiang river mouth. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2003, 22, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Gamboa-Herrera, J.A.; Ríos-Reyes, C.A.; Vargas-Fiallo, L.Y. Mercury speciation in mine tailings amended with biochar: Effects on mercury bioavailability, methylation potential and mobility. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 143959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-S.; Kim, S.-H.; Chon, C.-M.; Kwon, S.; Kim, J.G.; Choi, H.W.; Ahn, J.S. Effect of FeS on mercury behavior in mercury-contaminated stream sediment: A case study of Pohang Gumu Creek in South Korea. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, K.; Li, Y. Enhancement of arsenic adsorption during mineral transformation from siderite to goethite: Mechanism and application. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, W.; Guo, H.; Jiaxing, S.; Shuai, L.; Susu, D.; Weiguo, H.; Jie, M.; Hailiang, D. Stimulation of Fe(II) oxidation, biogenic lepidocrocite formation, and arsenic immobilization by pseudogulbenkiania sp. strain 2002. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6449–6458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.P.; Gao, J.F.; Shi, G.Y. The contents and mineral and chemical compositions of suspended particulate materials in the Yangtze River, and their geological and environmental implications. Acta Geol. Sin. 2013, 87, 634–660. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G. Occurrence of anammox on suspended sediment (SPS) in oxic river water: Effect of the SPS particle size. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; He, J.; Lv, C.; Fan, Q. Species and distribution of heavy metals in different size fractions of sediments from the baotou section of the Yellow River. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2011, 29, 776–782. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Y.; Kong, X.; Li, C. Distribution, sources, and toxicity assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface soils of a heavy industrial city, Liuzhou, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, X.; Miao, D.; Hao, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zou, S. Potential health risks associated to heavy metal contamination of soils in the Yellow River Delta, China. J. Coast. Conserv. 2019, 23, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, M.; Guo, L.; Wang, W.X. Size partitioning and mixing behavior of trace metals and dissolved organic matter in a South China estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 603–604, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.M.; Yao, L.A.; Ma, Q.L.; Zhou, G.J.; Wang, L.; Fang, Q.L.; Xu, Z.C. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of cadmium in water and sediment in Longjiang River, China: Implication on water quality management after pollution accident. Chemosphere 2017, 194, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| DO (mg/L) | EC (μs/cm) | pH | Eh (mV) | TDS (ppm) | Turbidity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overlying water chemistry | ||||||
| Min–Max | 6.22–8.43 | 141.5–252.2 | 6.79–8.48 | 94.89–161.1 | 71.1–127.2 | 8.13–28.1 |
| Mean | 7.2 | 168.1 | 7.81 | 114.03 | 84.9 | 13.61 |
| OM (%) | Mz (μm) | Sand (%) | Silt (%) | Clay (%) | ||
| Sediment properties | ||||||
| Min–Max | 0.37–1.37 | 10.24–27.63 | 0.05–7.24 | 62.74–79.84 | 15.74–27.63 | |
| Mean | 0.72 | 21.23 | 3.79 | 74.05 | 22.16 | |
| Location | Cd | Pb | Cr | Cu | Zn | As | Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/kg | |||||||
| BSG | 0.267 | 24 | 82.1 | 27.8 | 75.6 | 20.5 | 0.152 |
| Liujiang River Basin | 0.44–6.36 | 17.74–43.31 | 27.64–91 | 19.98–35.86 | 68.47–196.95 | 8.29–69.76 | 0.09–1.32 |
| 1.27 | 30.10 | 53.53 | 25.20 | 124.93 | 23.24 | 0.19 | |
| TEL | 0.6 a | 35 a | 42 a | 36 a | 123 a | 7.2 b | 0.17 a |
| PEL | 3.5 a | 91 a | 160 a | 197 a | 315 a | 42 b | 0.49 a |
| BCu | BPb | BZn | BCr | BCd | BAs | BHg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fr1 | 0.244 | 0.182 | 0.466 * | 0.309 | 0.696 ** | 0.424 * | 0.061 |
| Fr2 | 0.511 * | 0.887 ** | 0.970 ** | 0.538 ** | 0.998 ** | 0.793 ** | 0.295 |
| Fr3 | 0.720 ** | 0.970 ** | 0.958 ** | 0.732 ** | 0.982 ** | 0.947 ** | 0.202 |
| Fr4 | 0.599 ** | 0.882 ** | 0.817 ** | 0.455 * | 0.872 ** | 0.612 ** | 0.232 |
| Fr5 | 0.668 ** | 0.426 * | 0.681 ** | 0.069 | 0.369 | 0.842 ** | −0.125 |
| Total | 0.839 ** | 0.957 ** | 0.959 ** | 0.135 | 0.998 ** | 0.842 ** | −0.08 |
| Cr | Cu | Zn | Cd | Pb | As | Hg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F5 | |||||||
| F1 | 0.640 ** | 0.593 ** | 0.448 * | 0.201 | 0.234 | 0.163 | 0.781 ** |
| F2 | 0.361 | 0.185 | 0.672 ** | 0.372 | 0.225 | 0.622 ** | 0.063 |
| F3 | 0.366 | 0.647 ** | 0.606 ** | 0.383 | 0.467 * | 0.892 ** | 0.068 |
| F4 | 0.616 ** | 0.407 | 0.741 ** | 0.423 * | 0.623 ** | 0.905 ** | −0.032 |
| Do | Ec | pH | Eh | TDS | Turbidity | OM | Mz | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCu | 0.257 | 0.213 | 0.054 | 0.286 | 0.215 | −0.466 * | 0.768 ** | −0.559 ** |
| BPb | 0.366 | 0.318 | −0.021 | 0.602 ** | 0.317 | −0.631 ** | 0.255 | −0.244 |
| BZn | 0.286 | 0.3 | 0.063 | 0.511 * | 0.298 | −0.522 * | 0.175 | −0.274 |
| BCr | 0.291 | 0.325 | 0.089 | 0.053 | 0.324 | −0.306 | 0.455 * | −0.449 * |
| BCd | 0.114 | 0.737 ** | −0.500 * | 0.738 ** | 0.734 ** | −0.308 | 0.035 | −0.033 |
| BAs | 0.209 | −0.057 | 0.209 | 0.526 ** | −0.058 | −0.539 ** | −0.082 | 0.027 |
| BHg | 0.136 | 0.302 | −0.321 | 0.01 | 0.303 | −0.149 | 0.797 ** | −0.526 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, Y.; Miao, X.; Liu, H.; Miao, D. The Variation of Heavy Metals Bioavailability in Sediments of Liujiang River Basin, SW China Associated to Their Speciations and Environmental Fluctuations, a Field Study in Typical Karstic River. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18083986
Hao Y, Miao X, Liu H, Miao D. The Variation of Heavy Metals Bioavailability in Sediments of Liujiang River Basin, SW China Associated to Their Speciations and Environmental Fluctuations, a Field Study in Typical Karstic River. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(8):3986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18083986
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Yupei, Xiongyi Miao, Hongwei Liu, and Dan Miao. 2021. "The Variation of Heavy Metals Bioavailability in Sediments of Liujiang River Basin, SW China Associated to Their Speciations and Environmental Fluctuations, a Field Study in Typical Karstic River" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 8: 3986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18083986
APA StyleHao, Y., Miao, X., Liu, H., & Miao, D. (2021). The Variation of Heavy Metals Bioavailability in Sediments of Liujiang River Basin, SW China Associated to Their Speciations and Environmental Fluctuations, a Field Study in Typical Karstic River. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(8), 3986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18083986