A Review of Processes for Removing Antibiotics from Breeding Wastewater
Abstract
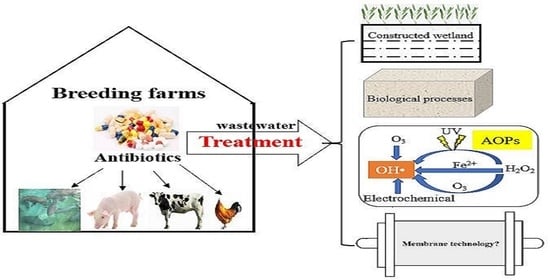
:1. Introduction
2. Treatment Technologies
2.1. Constructed Wetlands
2.2. Biological Treatment
2.2.1. The BAF System
2.2.2. The AD Process
2.2.3. The SBR Process
2.2.4. The MBR Process
2.3. Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs)
2.3.1. Electrochemical Oxidation
2.3.2. Ozonation Process
2.3.3. Fenton Process
2.3.4. The UV/H2O2 Method
2.4. Membrane Technology
2.5. Other Processes
3. Concluding Remarks and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mo, W.Y.; Chen, Z.; Leung, H.M.; Leung, A.O.W. Application of veterinary antibiotics in China’s aquaculture industry and their potential human health risks. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 8978–8989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muaz, K.; Riaz, M.; Akhtar, S.; Park, S.; Ismail, A. Antibiotic residues in chicken meat: Global prevalence, threats, and decontamination strategies: A review. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danner, M.-C.; Robertson, A.; Behrends, V.; Reiss, J. Antibiotic pollution in surface fresh waters: Occurrence and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-Q.; Ying, G.-G.; Pan, C.-G.; Liu, Y.-S.; Zhao, J.-L. Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: Source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6772–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marcantonio, C.; Chiavola, A.; Dossi, S.; Cecchini, G.; Leoni, S.; Frugis, A.; Spizzirri, M.; Boni, M.R. Occurrence, seasonal variations and removal of organic micropollutants in 76 wastewater treatment plants. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 141, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chu, L.; Wojnárovits, L.; Takács, E. Occurrence and fate of antibiotics, antibiotic resistant genes (ARGs) and antibiotic resistant bacteria (ARB) in municipal wastewater treatment plant: An overview. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cytryn, E. The soil resistome: The anthropogenic, the native, and the unknown. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 63, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruden, A.; Arabi, M.; Storteboom, H. Correlation between upstream human activities and riverine antibiotic resistance genes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11541–11549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, A.A.; Adekunle, C.F.; Thor, A.S. Residual antibiotics, antibiotic resistant superbugs and antibiotic resistance genes in surface water catchments: Public health impact. Phys. Chem. Earth 2018, 105, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.C.; Hu, Y.Y.; Cheng, J.H.; Chen, Y.C. Research progress on distribution, migration, transformation of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in aquatic environment. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 1195–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, R.; Pardeep, K.; Prinja, S.; Meena, R.; Varun, A. The World Health Report 2007: A Safer Future: Global Public Health Security in the 21st Century; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Vymazal, J. Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment. Ecol. Eng. 2005, 25, 475–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Hu, Z.; Liang, S.; Fan, J.; Liu, H. A review on the sustainability of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: Design and operation. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.-J.; Kim, L.-H.; Zoh, K.-D. Removal characteristics and mechanism of antibiotics using constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 91, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, C.; Li, K.; Su, J.; Zhu, G.; Liu, L. Performance of vertical up-flow constructed wetlands on swine wastewater containing tetracyclines and tet genes. Water Res. 2015, 70, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, C.; Zheng, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, G. Elimination of veterinary antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes from swine wastewater in the vertical flow constructed wetlands. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zheng, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Fan, H.; Zhang, T. Performance and bacterial community dynamics of vertical flow constructed wetlands during the treatment of antibiotics-enriched swine wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 316, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boto, M.; Almeida, C.M.R.; Mucha, A.P. Potential of constructed wetlands for removal of antibiotics from saline aquaculture effluents. Water 2016, 8, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y. Current research in treatment processes for antibiotics removal from livestock wastewater. Water Purif. Technol. 2018, 37, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, Q.; Hu, L.; Chen, H.; Chang, Z.; Zou, H. Removal of nutrients and veterinary antibiotics from swine wastewater by a constructed macrophyte floating bed system. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 2657–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yi, N.-K.; Xiong, Y.-J.; Huang, X.-F. Effect of constructed wetland configuration on the removal of nitrogen pollutants and antibiotics in aquaculture wastewater. Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 3430–3437. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, J.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, L.; Liu, C. Removal and response of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes during advanced treatment of livestock wastewater by aquatic plant filter bed. Acta Sci. Circum. 2015, 35, 2464–2470. [Google Scholar]
- Hijosa-Valsero, M.; Fink, G.; Schlüsener, M.P.; Sidrach-Cardona, R.; Martín-Villacorta, J.; Ternes, T.; Bécares, E. Removal of antibiotics from urban wastewater by constructed wetland optimization. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerakoon, G.M.P.R.; Jinadasa, K.B.S.N.; Herath, G.B.B.; Mowjood, M.I.M.; Van Bruggen, J.J.A. Impact of the hydraulic loading rate on pollutants removal in tropical horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 61, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijosa-Valsero, M.; Sidrach-Cardona, R.; Martín-Villacorta, J.; Bécares, E. Optimization of performance assessment and design characteristics in constructed wetlands for the removal of organic matter. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, T.; Sun, G. A review on nitrogen and organics removal mechanisms in subsurface flow constructed wetlands: Dependency on environmental parameters, operating conditions and supporting media. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 112, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forni, C.; Cascone, A.; Cozzolino, S.; Migliore, L. Drugs uptake and degradation by aquatic plants as a bioremediation technique. Minerva Biotechnol. 2001, 13, 151–152. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Gao, Y.; Luo, J.; Yan, S.H.; Rengel, Z.; Zhang, Z.H. Interaction of veterinary antibiotic tetracyclines and copper on their fates in water and water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes). J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 280, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meers, E.; Rousseau, D.P.L.; Blomme, N.; Lesage, E.; Du Laing, G.; Tack, F.M.G.; Verloo, M.G. Tertiary treatment of the liquid fraction of pig manure with phragmites australis. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2005, 160, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Huang, X. Removal of antibiotics in waste and wastewater treatment facilities of animal breeding industry: A review. Environ. Chem. 2017, 36, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, G.; Lu, L.; Liu, J. Typical pollutants removal efficiency from aquaculture wastewater by using constructed wetlands. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 10, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Lian, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, X.; Yan, B. Advances in treating antibiotics in water by constructed wetland. Wetl. Sci. 2016, 10, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.-B.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Lu, X.; Tang, W.-Y.; Yan, S.-H.; Luo, J.; Liu, L.-Z.; Fan, R.-Q. Advances in phytoremediation of antibiotics in breeding wastewater. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 33, 224–232. [Google Scholar]
- Kizito, S.; Lv, T.; Wu, S.; Ajmal, Z.; Luo, H.; Dong, R. Treatment of anaerobic digested effluent in biochar-packed vertical flow constructed wetland columns: Role of media and tidal operation. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Lv, T.; He, K.; Wu, S.; Dong, X.; Dong, R. Removal of organic matter, nitrogen and faecal indicators from diluted anaerobically digested slurry using tidal flow constructed wetlands. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 5486–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.-H.; Lin, A.Y.-C.; Panchangam, S.C.; Hong, P.-K.A.; Yang, P.-Y.; Lin, C.-F. Biodegradation and bio-sorption of antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs using immobilized cell process. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Y.-S.; Zhang, J.-N.; Yang, Y.-Q.; Hu, L.-X.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Zhao, J.-L.; Chen, F.-R.; Ying, G.-G. Removal of antibiotics from piggery wastewater by biological aerated filter system: Treatment efficiency and biodegradation kinetics. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Feng, F.; Chai, Y.; Meng, X.; Sui, Q.; Chen, M.; Wei, Y.; Qi, K. Screening and quantitation of residual antibiotics in two different swine wastewater treatment systems during warm and cold seasons. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 1542–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, R.; Lei, Z. Removal of veterinary antibiotics from anaerobically digested swine wastewater using an intermittently aerated sequencing batch reactor. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 65, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Song, X.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Luo, W. Removal of antibiotics by sequencing-batch membrane bioreactor for swine wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.-L.; Liu, R.; Zheng, W.; Song, X.-Y.; Yu, W.-J.; Ye, Z.-X.; Chen, L.-J.; Zhang, Y.-M. Performance of an intermittent aeration membrane bioreactor for removal of veterinary antibiotics from piggery wastewater. Environ Sci. 2015, 36, 4148–4153. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, L. Characteristics and utilization of biologically aerated filter backwashed sludge. Desalination 2007, 208, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Espinosa, L.S. Tom A review of biological aerated filters (BAFs) for wastewater treatment. Environ. Eng. Sci. 1999, 16, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, G.-H.; Song, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Li, S.; Ye, Z. Biological treatment of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) red water by immobilized anaerobic–aerobic microbial filters. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindmark, J.; Thorin, E.; Bel Fdhila, R.; Dahlquist, E. Effects of mixing on the result of anaerobic digestion: Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 40, 1030–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.S.; Liu, Y.W.; Zhou, J.L.; Chang, S.W.; Nguyen, D.D.; Bui, X.T.; Zhang, X.B. Bioprocessing for elimination antibiotics and hormones from swine wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 1664–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mace, S.; Mata-Alvarez, J. Utilization of SBR technology for wastewater treatment:an overview. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 5539–5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Ding, D.; Feng, C.; Tong, S.; Suemura, T.; Zhang, F. Performance of sequencing batch biofilm reactors with different control systems in treating synthetic municipal wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 104, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Cicek, N. Treatment of swine wastewater by submerged membrane bioreactors with consideration of estrogenic activity removal. Desalination 2008, 231, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Liu, R.; Chen, L.; Kawagishi, T. Comparative experiment on treating digested piggery wastewater with a biofilm MBR and conventional MBR: Simultaneous removal of nitrogen and antibiotics. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2017, 11, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, B.; Sellamuthu, B.; Ouarda, Y.; Drogui, P.; Tyagi, R.D.; Buelna, G. Review on fate and mechanism of removal of pharmaceutical pollutants from wastewater using biological approach. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) from wastewater: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 620–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipma, J.; Osuna, B.; Collado, N.; Monclús, H.; Ferrero, G.; Comas, J.; Rodriguez-Roda, I. Comparison of removal of pharmaceuticals in MBR and activated sludge systems. Desalination 2010, 250, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, W.; Qiang, Z.; Yin, X.; Qu, J.; Pan, X. Adsorption behavior of sulfamethazine in an activated sludge process treating swine wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaze, W.; Kang, J.-W.; Chapin, D.H. The chemistry of water treatment processes involving ozone, hydrogen peroxide and ultraviolet radiation. Ozone-Sci. Eng. 1987, 9, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, W. Study on Removal of Antibiotics by Catalytic Ozonation from Factory Marine Aquaculture Wastewater. Master’s Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Miyata, M.; Ihara, I.; Yoshid, G.; Toyod, K.; Umetsu, K. Electrochemical oxidation of tetracycline antibiotics using a Ti/IrO2 anode for wastewater treatment of animal husbandry. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-G.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Li, X.-Q.; Zeng, W.-Y.; Diao, X.-W. Removal of antibiotics and hormones by electrolytic oxidation in livestock wasterwater. J. Southwest Univ. 2013, 35, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chu, D.; Gong, W.; Dongmei, Y.; Fu, F.; Gao, Y.; Wang, S. Treatment of piggery wastewater by ozone purification technology study on antibiotic residues. Heilongjiang Anim. Husb. Veter. Med. 2017, 7, 184–187. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Tian, W.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, J. Advanced oxidation of olaquindox and tetracydline antibiotics in biogas slurry by microwave-fenton. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 7, 164–168. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.J.; Lan, M.; Peng, X. Removal of antibiotics from swine wastewater by UV/H2O2 combined oxidation. Environ. Poll. Control. 2011, 33, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, Z.C.; Zhou, M.H.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Yin, X.Y.; Li, Y.W. Comprehensive treatment of marine aquaculture wastewater by a cost-effective flow-through electro-oxidation process. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasprzyk, B.; Maria, Z.; Nawrocki, J. Catalytic ozonation and methods of enhancing molecular ozone reactions in water treatment. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 46, 639–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, E.; Lee, C.-H.; Lee, K. Degradation of chlorotetracycline and bacterial disinfection in livestock wastewater by ozone-based advanced oxidation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2011, 17, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, O.; Contreras, D.; Mondaca, M.A.; Pérez-Moya, M.; Mansilla, H.D. Experimental design of fenton and photo-fenton reactions for the treatment of ampicillin solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Huang, J.; Wang, L.; Fan, Z. Property and application in wastewater treatment of fenton. Chem. Eng. 2001, 3, 24–25. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Du, Y.; Lei, L. Kinetics of p-chlorophenol wastewater treatment by UV/H2O2 oxidation. Environ. Sci. 2003, 5, 106–109. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yang, C. Advanced oxidation technology for water treatment. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2008, 26, 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, J. Removal of trace antibiotics from wastewater: A systematic study of nanofiltration combined with ozone-based advanced oxidation processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 240, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Kong, X.; Sun, H.; Li, C.; Liu, D. High removal efficiency of antibiotic resistance genes in swine wastewater via nanofiltration and reverse osmosis processes. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, W.; Qiang, Z.; Pan, X.; Chen, M. Removal of veterinary antibiotics from sequencing batch reactor (SBR) pretreated swine wastewater by fenton’s reagent. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4392–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, M.; Yang, L.; Chen, X.; Li, K.; Shen, G. The treatment of veterinary antibiotics in swine wastewater by biodegradation and fenton-like oxidation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 710, 136299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, X.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qian, M.; Chen, X.; Zhao, H.; Sheng, M.; Cao, G.; et al. Removal of veterinary antibiotics from swine wastewater using anaerobic and aerobic biodegradation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, N.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, H. Simultaneous antibiotic degradation, nitrogen removal and power generation in a microalgae-bacteria powered biofuel cell designed for aquaculture wastewater treatment and energy recovery. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 10871–10881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Processes | Antibiotics | Plant | Fill Material | HRT (d) | HLR (cm/d) | Initial Concentration of Antibiotics (μg·L−1) | Removal Efficiency (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical flow constructed wetlands | SM2 | Hybrid pennisetum | Zeolite | 1.25 | 3 | 40 | 73 | [16] |
| Volcanic rocks | 68 | |||||||
| OTC | Zeolite | 95 | ||||||
| Volcanic rocks | 91 | |||||||
| CIP | Zeolite | 85 | ||||||
| Volcanic rocks | 82 | |||||||
| Artificial plant floating bed system | SD | Ryegrass | - | - | - | 100 | 99 | [20] |
| SMZ | 100 | 999–100 | ||||||
| SMX | 10 | 89–92 | ||||||
| Horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands | SMX | Phragmits communis | Gravel and zeolite | 1 | 25.2 | 0.0987 | 4 | [21] |
| 3 | 59 | |||||||
| Integrated vertical flow constructed wetlands | SMX | Phragmits communis | Gravel and zeolite | 1 | 8.4 | 0.0987 | 3 | [21] |
| 3 | 55 | |||||||
| Aquatic plant filter bed | TCs | Celery | - | 60 | 5 | 30 | 33 | [22] |
| Spinach | 72 | |||||||
| SMs | Celery | 20 | ||||||
| Spinach | 47 | |||||||
| QNs | Celery | 7 | ||||||
| Spinach | 22 |
| Processes | Biological Treatment | Antibiotics | Operation Conditions | Removal Efficiency (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aerobic methods | BAF | SMM, SCP, SMZ, TMP, NOR, OTX, LIN, LCM, OTC | HRT = 40–48 h, HLR = 2.8 cm/h | 89–91 (total antibiotics) | [37] |
| Anaerobic methods | AD | TCs | 1.38–2.16 kg COD/m3·d, 37 ± 1 °C, HRT = 16 d | 65 | [38] |
| QNs | 85 | ||||
| Aerobic–anaerobic combined methods | SBR | TC | HRT = 3–5 d | 88 | [39] |
| SMs | 96 | ||||
| MBR | SMs | HRT = 33–51 h | >90 | [40] | |
| TCs | >90 | ||||
| QNs | <70 | ||||
| IAMBR | TC, CTC, OTC, DC, SMX, SMZ, CIP, NOR, ENR, TYL, RTM | COD/TN = 2.1, HRT = 3 d | 4–53 (total antibiotics) | [41] | |
| COD/TN = 2.1, HRT = 5 d | 78–80 (total antibiotics) | [41] |
| Processes | Antibiotic | Operation Conditions | Initial Concentration of Antibiotics (mg/L) | Removal Efficiency (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical oxidation | TCs | Na2SO4 as electrolyte and Ti/IrO2 as anode, electrochemical treatment was carried out for 6 h | 100 | 99 | [58] |
| TC | Voltage = 5 V, pH = 9, aeration time = 3 h, electrolysis = 2 min | 2.5 | 98 | [59] | |
| OTC | 2.0 | 91 | |||
| CTC | 2.0 | 91 | |||
| OLA | 2.0 | 99 | |||
| Ozonation process | TCs | [O3]0 = 7.8 mg/L, t = 20 min | (5.846–8.444) × 10−3 | 96 | [60] |
| SMs | (1.395–3.341) × 10−3 | 98 | |||
| QNs | (3.709–4.915) × 10−3 | 97–98 | |||
| Fenton process | OTC | [H2O2]0 = 40 mg/L, [Fe2+]0 = 12 mg/L, pH0 = 4, microwave radiation time = 2 min, microwave radiation power = 445 W | 1.3 | 93 | [61] |
| TC | 1.3 | 91 | |||
| CTC | 1.8 | 88 | |||
| OLA | 2.8 | 67 | |||
| UV/H2O2 process | SMs | pH = 5.0, UV = 254 nm, [H2O2]0 = 7.0 mM | 2.0 | 95 | [62] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, A.; Yan, M.; Lin, J.; Xu, L.; Gong, H.; Gong, H. A Review of Processes for Removing Antibiotics from Breeding Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094909
Huang A, Yan M, Lin J, Xu L, Gong H, Gong H. A Review of Processes for Removing Antibiotics from Breeding Wastewater. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(9):4909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094909
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Airu, Muting Yan, Jingjun Lin, Lijie Xu, He Gong, and Han Gong. 2021. "A Review of Processes for Removing Antibiotics from Breeding Wastewater" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 9: 4909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094909
APA StyleHuang, A., Yan, M., Lin, J., Xu, L., Gong, H., & Gong, H. (2021). A Review of Processes for Removing Antibiotics from Breeding Wastewater. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(9), 4909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094909