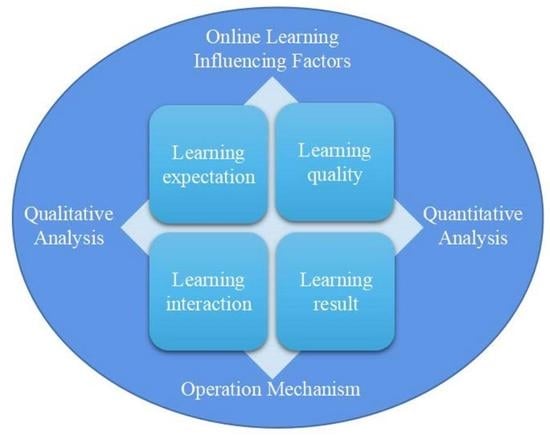
Study on the Influencing Factors of Online Learning and Its Operation Mechanism among Chinese College Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic—An Empirical Analysis Based on a Mixed Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- What are the factors that influence college students’ online learning?
- What is the relationship between these influencing factors?
2. Qualitative Research Design and the Theoretical Model
2.1. Grounded Theory and Interview
2.2. Coding Analysis
2.3. The Construction of a Theoretical Model and the Test of Saturation
2.3.1. The Construction of the Theoretical Model
2.3.2. The Testing of Theory Saturation
3. Quantitative Research Design and Data Analysis
3.1. Research Hypotheses
3.2. Questionnaire Design and Data Collection
3.2.1. Questionnaire Design
3.2.2. Data Collection
3.3. Data Analysis and Results
3.3.1. Reliability and Validity
3.3.2. Model Fitting and Hypothesis Testing
4. Discussion
4.1. The Mediating Role of LQ
4.2. The Mediating Role of LI
4.3. Chain Mediating Role of LQ and LI
5. Implications for Practice
6. Research Contribution and Limitation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Education: From Disruption to Recovery. Available online: http//en.unesco.org/covid19/educationreponse (accessed on 21 February 2021).
- Cranfield, D.J.; Tick, A.; Venter, I.M.; Blignaut, R.J.; Renaud, K. Higher Education Students’ Perceptions of Online Learning during COVID-19—A Comparative Study. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salto, D. COVID-19 and higher education in Latin America: Challenges and possibilities in the transition to online education. eLearn 2020, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andi, C.; Yusriadi, Y.; Asma, G. Transformation of the Education Sector during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Indonesia. Educ. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 8561759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. The New Normal—What Needs to Be Different than before? Available online: https://en.unesco.org/futuresofeducation/debates/the-new-normal (accessed on 27 August 2021).
- Hiltz, S.R. The “virtual classroom”: Using computer-mediated communication for university teaching. J. Commmun. 1986, 36, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Thurman, A. How Many Ways Can We Define Online Learning? A Systematic Literature Review of Definitions of Online Learning (1988–2018). Am. J. Distance Educ. 2019, 33, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, X.F. Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Online Learning and the Influence Mechanism of Junior High School Students’ Online Learning during COVID-19 Pandemic—From the Perspective of Techenology Acceptance Model; Central China Normal University: Wuhan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, Y.J.; Li, X.; Jiang, X. Analysis of Factors that Influence Behavioral Intention to Use Online Learning and Enlightenment in the Post COVID-19 Education. China Educ. Technol. 2021, 6, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Alismaiel, O.A.; Cifuentes-Faura, J.; Al-Rahmi, W.M. Online Learning, Mobile Learning, and Social Media Technologies: An Empirical Study on Constructivism Theory during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boca, G.D. Factors Influencing Students’ Behavior and Attitude towards Online Education during COVID-19. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agormedah, E.K.; Henaku, E.A.; Ayite, D.M.; Ansah, E.A. Online Learning in Higher Education during COVID-19 Pandemic: A case of Ghana. J. Educ. Technol. Online Learn. 2020, 5, 2256–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, M.; Hussain, G.; Shahid, M.; Riaz, A.; Muavia, M.; Fahed, Y.S.; Azam, F.; Abdullah, M.T. Medical Students’ Online Learning Perceptions, Online Learning Readiness, and Learning Outcomes during COVID-19: The Moderating Role of Teacher’s Readiness to Teach Online. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 9, 3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Ma, L. Students’ online interaction, self-regulation, and learning engagement in higher education: The importance of social presence to online learning. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 815220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Roy, D.; Sinha, K.; Parveen, C.; Sharma, G.; Joshi, G. Impact of COVID-19 and lockdown on mental health of children and adolescents: A narrative review with recommendations. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 293, 113429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, W.Y.; Lu, X.; Xu, W.W.; Gao, Z. How Online Learning Resources Affect Academic Emotions and Learning Outcomes—A Meta-Analysis Based on the Control-Value Theory. Mod. Dist. Educ. Res. 2021, 5, 82–93+102. [Google Scholar]
- Glaser, B.G.; Strauss, A.L.; Strutzel, E. The discovery of grounded theory; strategies for qualitative research. Nurs. Res. 1968, 17, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anne, S.T.; Zhang, Z.X. Management and Building Theory: The Strategies of Research on Chinese Native Management. Chongqing Daxue Xuebao 2011, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Charmaz, K. The power and potential of grounded theory. Med. Soc. Online 2012, 6, 2–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kurucay, M.; Inan, F.A. Examining the effects of learner-learner interactions on satisfaction and learning in an online undergraduate course. Comput. Educ. 2017, 115, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linstone, H.A.; Turoff, M. The Delphi Method: Techniques and Applications; Addison-Wesley Reading: Boston, MA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Pallant, J. SPSS Survival Manual; McGraw-Hill Education: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Xiang, P.; Jia, F.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z. An indicator system for evaluating operation and maintenance management of mega infrastructure projects in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, H.F. An index of factorial simplicity. Psychometrika 1974, 39, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E. Multivariate Data Analysis: A Global Perspective, 7th ed.; Pearson Education: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, B. Achieving horizontal integration of municipal e-government in China: Assessment of managerial mechanisms. Inf. Dev. 2013, 29, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.M.; Li, Y. A Policy Study on Students’ Learning Expectations Viewed from Respect: A Case of Shanghai. J. East China Norm. Univ. 2019, 5, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vroom, V.H. Work and Motivation, 1st ed.; Jossey-Bass: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, F.D. Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Q. 1989, 13, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y. School Readiness Approaches to Learning and Classroom Engagement: A Longitudinal Study. J. Shanghai Educ. Res. 2021, 9, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, B.J. A social cognitive view of self-regulated academic learning. J. Educ. Psychol. 1989, 81, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.G.; Qian, Z.; Jiang, L.D. Comparative Study on College Students’ Learning Expectation and Learning Habits Based on Theory of Zimmerman’s Self-regulated Learning. In Advances in Social Science, Education and Humanities Research, VOL.310, Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Culture, Education and Economic Development of Modern Society (ICCESE 2019), Moscow, Russia, 1–3 March 2019; Atlantis Press: Paris, France, 2019; pp. 1009–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, N.J.; Yin, F.; Wu, M.Z. A Research on the pelationshipe between students’ self -expected and teacher-encouraged mentalraits. Psychol. Sci. 1999, 3, 218–221+286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolman, E.C. Cognitive maps in rats and men. Psychol. Rev. 1948, 55, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuen, H.K.; Fox, R.; Sun, A.; Deng, L. Course management systems in higher education: Understanding student experiences. J. Edu. 2009, 6, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.J.; Bai, X.M.; Wu, W.C.; Luo, X.J. Research on the Structural Relationship of Influencing Factors of Online Learning Experience. Mod. Distance Educ. Res. 2019, 1, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T. Getting the mix right again: An updated and theoretical rationale for interaction. IRRODL 2003, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tennyson, R.D.; Volk, A. Learning theories and educational paradigms. In International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Huo, L.Y. The Main Factors Affecting Children’s Approaches to Learning: Research Progress and Implications. Comp. Educ. Rev. 2014, 5, 15–40. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z. On the Cognitive and Behavioral Choices of Current Graduate Students. Acad. Deg. Gr. Educ. 2002, Z2, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.W. An analysis of the development and stimulation of learning motivation. Educ. Voca. 2012, 271, 90–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J. The Research on the Learning Expectations and Learning Outcomes of College Students; Huazhong University of Science and Technology: Wuhan, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, S.X. Influence of learning expectations on assessment of teaching and its response. Educ. Rev. 2015, 1, 68–70. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.P.; Jin, X. Learning quality: The intrinsic need for college students to improve the quality of learning. Heilongjiang Educ. 2020, 10, 67–68. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.P.; Cao, Y.L. Classroom Interaction and Course Satisfaction in Synchronous Online Education—Taking the Ed. D in Graduate School of Education of Peking University for Example. Mod. Educ. Technol. 2020, 8, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y. Research on the Influencing Factors of Online Learners’ Continuous Learning Intention:Based on the ECM Perspective. J. Open Learn. 2021, 5, 9–16+26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q. Investigation Report on the Current Situation of Independent Learning of College Students in the Less Developed Western Region under the Internet Environment: Five Universities in Gansu Province as an Example. China Newsp. Ind. 2018, 6, 39–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.L. Research on Learning Experiences in Online Open Education Courses. Adl. Educ. 2021, 11, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Parra, B.J. Learning strategies and styles as a basis for building personal learning environments. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2016, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y. An Exploration of the Relationships between Interactive Forms of Online Course Teaching and Students’ Learning Engagement. J. East China Norm. Univ. 2021, 7, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Zhao, W.; Wang, P.J.; Wang, L.P. Realization of Individual Adaptive Online Learning Analysis Model Based Big Data. China Educ. Technol. 2015, 1, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.P. An Analysis of Online Learning Behaviors and Its Influencing Factors: A Case Study of Students’ Learning Process in Online Course “Open Education Learning Guide” in the Open University of China. Open Educ. Res. 2012, 4, 81–90+17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, J.C.; Caracelli, V.J.; Graham, W.F. Toward a conceptual framework for mixed-method evaluation designs. Educ. Eval. Policy Anal. 1989, 11, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clothey, R. Current trends in higher education: Expanding access in Asia Pacific through technology. J. Comp. Int. High. Educ. 2010, 2, 3–5. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/268289805 (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- Johnson, B.; Turner, L.A. Data collection strategies in mixed method research. In Handbook of Mixed Methods in Social and Behavioral Research; Tashakkori, A., Teddie, C., Eds.; Sage Publication: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2003; pp. 297–319. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, R.B.; Onwuegbuzie, A.J. Mixed Methods Research: A Research Paradigm Whose Time Has Come. Educ. Res. 2004, 33, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.-J.; Bonk, C.J. Cross-cultural Comparisons of Online Collaboration. J. Comput.-Mediat. Commun. 2002, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikaya, L.A.; Avanesian, G.; Dikiy, I.S.; Kirik, V.A.; Egorova, V.A. How Personality Traits Are Related to the Attitudes Toward Forced Remote Learning During COVID-19: Predictive Analysis Using Generalized Additive Modeling. Front. Educ. 2021, 6, 629213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoss, T.; Ancina, A.; Kaspar, K. Forced Remote Learning During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Germany: A Mixed-Methods Study on Students’ Positive and Negative Expectations. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 642616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Netto, C.; Wilkins, J.F.; Bröker, P.; Vargas, E.E.; Sealfon, C.; Puthipiroj, P.; Li, K.S.; Bowler, J.E.; Hinson, H.R.; et al. Insights Into Students’ Experiences and Perceptions of Remote Learning Methods: From the COVID-19 Pandemic to Best Practice for the Future. Front. Educ. 2021, 6, 647986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Core Category | Category | Concepts |
|---|---|---|
| Learning expectation (LE) | Self-expectation | Anticipation of your learning and results |
| Expectation of teacher | Anticipation of the teaching style, content, and evaluation of the lecturer | |
| The expectation of the environment | Anticipation of your physical environment, mobile devices, online learning platforms, and network quality | |
| Learning quality (LQ) | Learning tendency | Preferences for learning mood, method, content, approach, and environment |
| Learning attitude | A state in which behavioral dispositions and psychological responses to learning can be maintained in a more sustained and stable manner | |
| Learning habit | Automated personal learning behaviors formed and developed through repeated practice | |
| Learning style | Learning style that is preferred or unique and personal | |
| Learning interaction (LI) | Teacher–student interaction | Interaction and communication between teachers and students for the purpose of promoting student development |
| Student–student interaction | Exchange and communication between students to work together on a task or have an intellectual discussion | |
| Media interaction | Interaction of students with the system of knowledge, courses, and resources | |
| Learning result (LR) | Knowledge | Mental progress through continuous learning and experience |
| Skill | Improvement in operational skills acquired through continuous learning and experience | |
| Thinking ability | Progress in the ability to identify, integrate, understand and apply through continuous learning and experience |
| Name | Option | Frequency | Percentage (%) | Accumulative Perception (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geographical area | City | 114 | 33.14 | 33.14 |
| Country | 60 | 17.44 | 50.58 | |
| Township | 63 | 18.31 | 68.90 | |
| Rural | 107 | 31.10 | 100.00 | |
| Grade | Freshmen | 38 | 11.05 | 11.05 |
| Sophomore | 32 | 9.30 | 20.35 | |
| Junior | 65 | 18.90 | 39.24 | |
| Senior | 177 | 51.45 | 90.70 | |
| Master’s student | 31 | 9.01 | 99.71 | |
| PhD student | 1 | 0.29 | 100.00 | |
| Nationality | Han | 208 | 60.47 | 60.47 |
| Uighur | 68 | 19.77 | 80.23 | |
| Kazakh | 24 | 6.98 | 87.21 | |
| Mongolian | 7 | 2.03 | 89.24 | |
| Others | 37 | 10.76 | 100.00 | |
| Total | 344 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Construct (No. of Items) | Cronbach’s Alpha | Loadings | CR | AVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LE(6) | 0.923 | 0.668, 0.789, 0.822, 0.799, 0.821, 0.817 | 0.924 | 0.671 |
| LQ(5) | 0.921 | 0.782, 0.703, 0.800, 0.814, 0.746 | 0.922 | 0.702 |
| LI(4) | 0.844 | 0.693, 0.713, 0.593, 0.649 | 0.863 | 0.558 |
| LR(6) | 0.925 | 0.647, 0.646, 0.764, 0.703, 0.630, 0.624 | 0.926 | 0.678 |
| LQ | LE | LR | LI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LQ | 0.838 | |||
| LE | 0.508 | 0.819 | ||
| LR | 0.788 | 0.579 | 0.823 | |
| LI | 0.661 | 0.657 | 0.742 | 0.760 |
| Common Indicators | χ² | df | p | CMIN/DF | GFI | RMSEA | RMR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Judgment criteria | - | - | >0.05 | <3 | >0.9 | <0.10 | <0.05 |
| Value | 515.246 | 183 | 0.000 | 2.816 | 0.871 | 0.073 | 0.040 |
| Other indicators | CFI | NFI | NNFI | TLI | IFI | SRMR | RMSEA 90% CI |
| Judgment criteria | >0.9 | >0.9 | >0.9 | >0.9 | >0.9 | <0.1 | - |
| Value | 0.943 | 0.915 | 0.935 | 0.935 | 0.943 | 0.048 | 0.065~0.080 |
| Hypothesses | Path Coefficients | Finding |
|---|---|---|
| H1: LE⇒LQ | 0.508 *** | Supported |
| H2: LE⇒LI | 0.433 *** | Supported |
| H3: LE⇒LR | 0.093 * | Supported |
| H4: LQ⇒LI | 0.441 *** | Supported |
| H5: LQ⇒LR | 0.515 *** | Supported |
| H6: LI⇒LR | 0.340 *** | Supported |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Duan, B.; Wang, Y.; Di, H.; Ge, H. Study on the Influencing Factors of Online Learning and Its Operation Mechanism among Chinese College Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic—An Empirical Analysis Based on a Mixed Method. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15161. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215161
Li H, Duan B, Wang Y, Di H, Ge H. Study on the Influencing Factors of Online Learning and Its Operation Mechanism among Chinese College Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic—An Empirical Analysis Based on a Mixed Method. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(22):15161. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215161
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Huanhuan, Bingyu Duan, Yifang Wang, Huijuan Di, and Hongxuan Ge. 2022. "Study on the Influencing Factors of Online Learning and Its Operation Mechanism among Chinese College Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic—An Empirical Analysis Based on a Mixed Method" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 22: 15161. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215161
APA StyleLi, H., Duan, B., Wang, Y., Di, H., & Ge, H. (2022). Study on the Influencing Factors of Online Learning and Its Operation Mechanism among Chinese College Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic—An Empirical Analysis Based on a Mixed Method. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(22), 15161. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215161