Verification of the Addiction Severity Index Japanese Version (ASI-J) as a Treatment-Customization, Prediction, and Comparison Tool for Alcohol-Dependent Individuals
Abstract
:Objective:
Methods:
Results:
Conclusions:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Independence of Each ASI Area: Usefulness in Measuring Multidimensional Problems
3.2. Prediction of Prognoses
3.2.1. Association between CSs and attitudes toward treatment in alcohol-dependent individuals
3.2.2. Comparison of CSs between abstinent and relapsed alcohol-dependent individuals
3.3. Comparison between Substance Abuse Groups
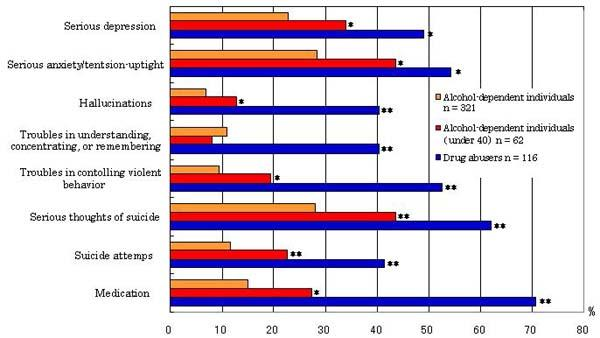
3.3.1. Comparison between alcohol-dependent individuals and drug abusers with individual ASI-J items
3.3.2. Comparison between alcohol-dependent individuals and drug abusers in CS and SR
3.3.3. Comparison of CS in Japanese alcohol-dependent individuals with CS in alcohol-dependent individuals in other countries
3.4. Internal Consistency and Concurrent Validity
4. Discussion
4.1. Usefulness of the ASI-J in Customized Treatment
4.2. Usefulness of ASI-J as a Prediction Tool
4.3. Usefulness of the ASI-J as a Comparison Tool
4.3.1. Features of alcohol-dependent individuals: comparison with drug abusers
4.3.2. Comparison of CSs of alcohol-dependent individuals among studies
4.4. Limitations and Further Study
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Hendriks, VM; Kaplan, CD; van Limbeek, J; Geerlings, P. The Addiction Severity Index: reliability and validity in a Dutch addict population. J. Subst. Abuse Treat 1989, 6, 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Shirakura, K. Introduction: Substance-Related Disorders. In Encyclopedia of Clinical Psychiatry [Rinsho Seishin Igaku Koza]; Volume 8, Matsushita, M, Asai, M, Sato, M, Suwaki, H, Eds.; Nakayamashoten: Tokyo, Japan, 1999; pp. 100–107. [Google Scholar]
- McLellan, AT; Cacciola, JS; Alterman, AI; Rikoon, SH; Carise, D. The Addiction Severity Index at 25: origins, contributions and transitions. Am. J. Addict 2006, 15, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- McLellan, AT; Luborsky, L; Woody, GE; O’Brien, CP. An improved diagnostic evaluation instrument for substance abuse patients: The Addiction Severity Index. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis 1980, 168, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- McLellan, AT; Kushner, H; Metzger, D; Peters, R; Smith, I; Grissom, G; Pettinati, H; Argeriou, M. The fifth edition of the addiction severity index. J. Subst. Abuse Treat 1992, 9, 199–213. [Google Scholar]
- Daeppen, JB; Burnand, B; Schnyder, C; Bonjour, M; Pécoud, A; Yersin, B. Validation of the Addiction Severity Index in French-speaking alcoholic patients. J. Stud. Alcohol 1996, 57, 585–590. [Google Scholar]
- Dejong, CA; Willems, JC; Schippers, GM; Hendriks, VM. The Addiction Severity Index: reliability and validity in a Datch alcoholic population. Int. J. Addict 1995, 30, 605–616. [Google Scholar]
- McLellan, AT; Luborsky, L; Cacciola, J; Griffith, J; Evans, F; Barr, HL; O’Brien, CP. New data from the Addiction Severity Index: reliability and validity in three centers. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis 1985, 173, 412–423. [Google Scholar]
- Scheurich, A; Müller, MJ; Wetzel, H; Anghelescu, I; Klawe, C; Ruppe, A; Lörch, B; Himmerich, H; Heidenreich, M; Schmid, G; Hautzinger, M; Szegedi, A. Reliability and validity of the German version of the European Addiction Severity Index (EuropASI). J. Stud. Alcohol 2000, 61, 916–919. [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä, K. Studies of the reliability and validity of the Addiction Severity Index. Addiction 2004, 99, 398–418. [Google Scholar]
- Zanis, DA; McLellan, AT; Cnaan, RA; Randall, M. Reliability and validity of the Addiction Severity Index with a homeless sample. J. Subst. Abuse Treat 1994, 11, 541–548. [Google Scholar]
- Senoo, E; Ogai, Y; Haraguchi, A; Kondo, A; Ishibashi, Y; Umeno, M; Kikumoto, H; Hori, T; Komiyama, T; Kato, R; Aso, K; Asukai, N; Wada, K; Saitoh, S; Ikeda, K. Reliability and validity of the Japanese version of the Addiction Severity Index (ASI-J). Nihon Arukoru Yakubutsu Igakkai Zasshi 2006, 41, 368–379. [Google Scholar]
- Argeriou, M; McCarty, D; Mulvey, K; Daley, M. Use of the Addiction Severity Index with homeless substance abusers. Subst. Abuse Treat 1994, 11, 359–365. [Google Scholar]
- Kosten, TR; Rounsaville, BJ; Kleber, HD. Concurrent validity of the Addiction Severity Index. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis 1983, 171, 606–610. [Google Scholar]
- Krenz, S; Dieckmann, S; Favrat, B; Spagnoli, J; Leutwyler, J; Schnyder, C; Daeppen, JB; Besson, J. French version of the Addiction Severity Index (5th edition): validity and reliability among Swiss opiate-dependent patients. French validation of the Addiction Severity Index. Eur. Addict. Res 2004, 10, 173–179. [Google Scholar]
- Hodgins, DC; El-Guebaly, N. More data on the Addiction Severity Index: reliability and validity with the mentally ill substance abuser. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis 1992, 180, 197–201. [Google Scholar]
- Cotton, NS. The familial incidence of alcoholism: a review. J. Stud. Alcohol 1979, 40, 89–116. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, S. Marital interaction and the transmission across generations in alcoholic families. Seishin Shinkeigaku Zasshi 1988, 90, 717–748. [Google Scholar]
- Iwakura, N; Sera, M; Yonezawa, H; Juukuroki, H; Shingai, N. A study on the relationship between alcoholics and alcohol-related problems of the parental generation. Jpn. J. Addict. Fam 2006, 23, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Rounsaville, BJ; Dolinsky, ZS; Babor, TF; Meyer, RE. Psychopathology as a predictor of treatment outcome in alcoholics. Arch. Gen. Psychiat 1987, 44, 505–513. [Google Scholar]
- Woody, GE; McLellan, AT; Luborsky, L; O’Brien, CP. Sociopathy and psychotherapy outcome. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1985, 42, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, T. Trends in therapy for alcoholism. Seishin Shinkeigaku Zasshi 2007, 109, 536–540. [Google Scholar]
- McGahan, LP; Griffith, AJ; McLellan, AT. Composite scores from the Addiction Severity Index: Manual and Computer Software; Veterans Administration Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Rikoon, SH; Cacciola, JS; Carise, D; Alterman, AI; McLellan, AT. Predicting DSM-IV dependence diagnoses from Addiction Severity Index composite scores. J. Subst. Abuse Treat 2006, 31, 17–24. [Google Scholar]




| Composite score | Mean ± SD | Employment | Alcohol use | Drug use | Legal | Family/Social | Psychiatric |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medical | 0.24 ± 0.30 | 0.13* | −0.19** | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| Employment | 0.54 ± 0.28 | −0.06 | 0.04 | 0.12* | 0.07 | −0.03 | |
| Alcohol use | 0.67 ± 0.28 | −0.01 | 0.02 | 0.16** | 0.11* | ||
| Drug use | 0.01 ± 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.14* | 0.23** | |||
| Legal | 0.01 ± 0.04 | 0.02 | −0.07 | ||||
| Family/Social | 0.25 ± 0.22 | 0.32** | |||||
| Psychiatric | 0.15 ± 0.20 | ||||||
| Attitude toward treatment | Medical | Employment | Alcohol use | Drug use | Legal | Family/Social | Psychiatric |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lack of cooperation | 0.016 | 0.119* | −0.069 | 0.053 | 0.028 | 0.055 | 0.113* |
| Lack of leadership | −0.024 | 0.065 | −0.114 | 0.092 | 0.040 | 0.021 | 0.122* |
| Rule breaking | 0.020 | 0.114* | 0.018 | 0.122* | 0.110 | 0.159** | 0.127* |
| Relapse | 0.009 | −0.034 | 0.016 | 0.028 | −0.006 | 0.118 * | 0.021 |
| Substance abuse | 0.032 | 0.080 | 0.000 | 0.408 ** | −0.027 | 0.150* | 0.267 ** |
| Undesirable attitude total | 0.029 | 0.075 | −0.042 | 0.119 * | 0.043 | 0.125 * | 0.120 * |
| Characteristics | Alcohol-dependent individuals (n= 321) | Drug abusers (n= 116) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (% Males) | 100.0 | 70.0 | |
| Mean age (SD) (years) | 49.7 (11.0) | 32.9 (9.4) | <0.001 |
| Education | |||
| Mean education (SD) (years) | 11.8 (2.7) | 11.5 (2.2) | n.s. |
| % Junior high school graduate | 29.3 | 23.3 | n.s. |
| % Some high school | 10.9 | 25.0 | <0.001 |
| % High school graduate | 34.3 | 29.3 | n.s. |
| % Some college | 3.7 | 11.2 | 0.005 |
| % College graduate | 18.4 | 9.5 | 0.015 |
| % Unclear | 3.4 | 1.7 | n.s. |
| Employment (past 3 years) | |||
| % Full-time | 69.5 | 30.2 | <0.001 |
| % Part-time | 10.6 | 35.3 | <0.001 |
| % Retired | 6.9 | 0.0 | n.s. |
| % Unemployment | 10.9 | 25.0 | <0.001 |
| % Other | 2.1 | 9.5 | n.s. |
| % Public assistance recipient (past 30 days) | 8.4 | 21.6 | <0.001 |
| Marital status | |||
| % Married | 54.2 | 7.8 | <0.001 |
| % Never married | 21.2 | 67.2 | <0.001 |
| % | 24.6 | 23.3 | n.s. |
| Separated/Widowed/Divorced Cohabitant | |||
| % Family | 45.8 | 12.1 | <0.001 |
| % Spouse | 14.6 | 12.1 | n.s. |
| % Parents | 13.4 | 41.4 | <0.001 |
| % Alone | 21.8 | 16.4 | n.s. |
| % Other | 4.4 | 18.0 | n.s. |
| Years of current cohabitation | |||
| % Within 10 years | 41.1 | 80.2 | <0.001 |
| % 10–20 years | 26.5 | 15.5 | 0.010 |
| % 20 years+ | 32.4 | 1.7 | <0.001 |
| Abuse | |||
| % Emotional abuse | 22.2 | 28.3 | n.s. |
| % Physical abuse | 6.9 | 28.3 | <0.001 |
| % Sexual abuse | 0.0 | 4.4 | 0.001 |
| Voluntary abstinence | |||
| % Less than 1month | 47.7 | 19.8 | <0.001 |
| % 1–3 months | 27.1 | 20.7 | n.s. |
| % 3–6 months | 8.4 | 19.0 | 0.003 |
| % 6–12 months | 8.1 | 12.9 | n.s. |
| % 1–2 years | 5.0 | 13.8 | 0.003 |
| % 2–5 years | 2.5 | 12.1 | <0.001 |
| % 5 years+ | 1.2 | 1.7 | n.s. |
| Study country (n) | Alcohol-dependent individuals Haraguchi et al., Japan(n= 321) | Drug abusers Senoo et al., Japan(n= 111) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical | |||
| CS | 0.24 (0.30) | 0.09 (0.21) | <0.001 |
| SR | 2.41 (2.71) | 0.69 (1.72) | <0.001 |
| Days of medical problems | 6.67 (11.19) | 1.83 (5.87) | <0.001 |
| Employment | |||
| CS | 0.54 (0.28) | 0.70 (0.24) | <0.001 |
| SR | 3.00 (2.81) | 5.21 (2.86) | <0.001 |
| Days worked | 11.41 (13.01) | 6.77 (10.55) | 0.001 |
| Money earned (1000 yen) | 140.34 (204.95) | 79.85 (182.86) | 0.005 |
| Alcohol use | |||
| CS | 0.55 (0.22) | 0.11 (0.19) | <0.001 |
| SR | 6.20 (1.69) | 1.39 (2.25) | <0.001 |
| Days drinking | 18.19 (12.04) | 5.83 (10.03) | <0.001 |
| Days intoxicated | 13.58 (12.92) | 5.03 (9.43) | <0.001 |
| Frequency of alcohol delerium tremens (lifetime) | 1.30 (3.22) | 0.39 (1.73) | 0.005 |
| Drug use | |||
| CS | 0.01 (0.04) | 0.10 (0.10) | <0.001 |
| SR | 0.24 (1.19) | 5.11 (2.94) | <0.001 |
| Frequency of drug overdose (lifetime) | 0.23 (3.00) | 1.16 (2.44) | 0.004 |
| Legal | |||
| CS | 0.01 (0.04) | 0.03 (0.10) | <0.001 |
| SR | 0.10 (0.66) | 0.54 (1.54) | <0.001 |
| Charges resulting in convictions (lifetime) | 0.14 (0.74) | 1.00 (1.57) | 0.044 |
| Family & Social | |||
| CS | 0.23 (0.21) | 0.24 (0.23) | n.s. |
| SR | 2.77 (2.87) | 3.66 (2.63) | 0.003 |
| Days of conflicts w/family | 5.57 (10.24) | 2.53 (6.91) | 0.004 |
| Days of conflicts w/others | 2.72 (7.96) | 2.20 (5.97) | n.s. |
| Psychiatric | |||
| CS | 0.15 (0.20) | 0.31 (0.27) | <0.001 |
| SR | 1.84 (2.39) | 3.85 (3.33) | <0.001 |
| Days of psychological Problems | 5.68 (10.58) | 10.10 (13.00) | <0.001 |
| ASI-J area | Cronbach’s α (Number of CS items [SD]) | Correlation between CS and SR |
|---|---|---|
| Medical | 0.794 (3) | 0.688 ** |
| Employment | 0.667 (4) | 0.290 ** |
| Alcohol use | 0.671 (6) | 0.217 ** |
| Drug use | 0.700 (17) | 0.623 ** |
| Legal | 0.712 (5) | 0.520 ** |
| Family/Social | 0.534 (5) | 0.584 ** |
| Psychiatric | 0.836 (11) | 0.664 ** |
| GOT (at hospitalization) | GPT (at hospitalization) | γ-GTP (at hospitalization) | GPT (at hospital discharge) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alcohol use CS | 0.233 ** | 0.169 ** | 0.245 ** | 0.066 |
| Alcohol use SR | 0.129 * | 0.061 | 0.007 | 0.168 ** |
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Haraguchi, A.; Ogai, Y.; Senoo, E.; Saito, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Yoshino, A.; Ino, A.; Yanbe, K.; Hasegawa, M.; Murakami, M.; et al. Verification of the Addiction Severity Index Japanese Version (ASI-J) as a Treatment-Customization, Prediction, and Comparison Tool for Alcohol-Dependent Individuals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2009, 6, 2205-2225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph6082205
Haraguchi A, Ogai Y, Senoo E, Saito S, Suzuki Y, Yoshino A, Ino A, Yanbe K, Hasegawa M, Murakami M, et al. Verification of the Addiction Severity Index Japanese Version (ASI-J) as a Treatment-Customization, Prediction, and Comparison Tool for Alcohol-Dependent Individuals. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2009; 6(8):2205-2225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph6082205
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaraguchi, Ayako, Yasukazu Ogai, Eiichi Senoo, Satoru Saito, Yoshihiro Suzuki, Aihide Yoshino, Aro Ino, Kenji Yanbe, Mitsuru Hasegawa, Masaru Murakami, and et al. 2009. "Verification of the Addiction Severity Index Japanese Version (ASI-J) as a Treatment-Customization, Prediction, and Comparison Tool for Alcohol-Dependent Individuals" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 6, no. 8: 2205-2225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph6082205
APA StyleHaraguchi, A., Ogai, Y., Senoo, E., Saito, S., Suzuki, Y., Yoshino, A., Ino, A., Yanbe, K., Hasegawa, M., Murakami, M., Murayama, M., Ishikawa, T., Higuchi, S., & Ikeda, K. (2009). Verification of the Addiction Severity Index Japanese Version (ASI-J) as a Treatment-Customization, Prediction, and Comparison Tool for Alcohol-Dependent Individuals. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 6(8), 2205-2225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph6082205