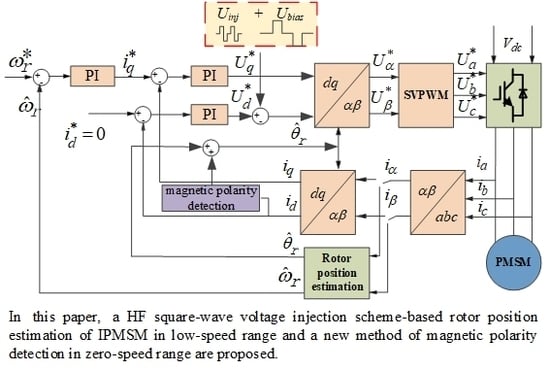
High Frequency Square-Wave Voltage Injection Scheme-Based Position Sensorless Control of IPMSM in the Low- and Zero- Speed Range
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Analysis of Rotor Position Estimation Strategy Based on Conventional Square-Wave Voltage Injection
2.1. Mathematical Model of IPMSM
2.2. Signal-Process Method in the Estimated Rotor Reference Frame
2.3. Voltage Vector Injection Scheme
3. Analysis of Rotor Position Estimation Strategy Based on Improved Square-Wave Voltage Injection
3.1. Improved Signal-Process Method in the Estimated Rotor Reference Frame
3.2. Improved Voltage Vector Injection Scheme
3.3. Determining the Direction of Magnetic Polarity
4. Simulation and Experimental Results
4.1. Simulationl Results
4.2. Experimental Platform
4.3. Initial Rotor Position Estimation
4.4. Estimation of Rotor Position at Low Speed
4.4.1. Comparison of Rotor Position Estimation Before and After Improvement
4.4.2. Rotor Position Observation Experiment Under Forward and Reverse
4.5. Judging Compensation of Magnetic Polarity Direction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Onambele, C.; Elsied, M.; Mpanda Mabwe, A.; El Hajjaji, A. Multi-Phase Modular Drive System: A Case Study in Electrical Aircraft Applications. Energies 2018, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Guo, Q.; Li, L. System Efficiency Improvement for Electric Vehicles Adopting a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Direct Drive System. Energies 2017, 10, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hua, W.; Zhou, K.L. Investigation of a Co-Axial Dual-Mechanical Ports Flux-Switching Permanent Magnet Machine for Hybrid Electric Vehicles. Energies 2015, 8, 14361–14379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, K.; Chen, K. An Improved Position-Sensorless Control Method at Low Speed for PMSM Based on High-Frequency Signal Injection into a Rotating Reference Frame. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 86510–86521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hou, B.; Mei, Y. Deadbeat Predictive Current Control of Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motors with Stator Current and Disturbance Observer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 3818–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Sul, S. Sensorless Control Method for PMSM Based on Frequency-Adaptive Disturbance Observer. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2014, 2, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, G.; Xu, D.; Zhao, N. ADALINE-Network-Based PLL for Position Sensorless Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 1450–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.Q.; Yang, S. Rotor Position Sensorless Control of Wound-Field Flux-Switching Machine Based on High Frequency Square-Wave Voltage Injection. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 48776–48784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Q.; Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Gerada, C. Enhanced Self-Sensing Capability of Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machines: A Novel Saliency Modulation Rotor End Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 3548–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yang, L.; Yuan, B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, G.; Xu, D. Pseudo-Random High-Frequency Square-Wave Voltage Injection Based Sensorless Control of IPMSM Drives for Audible Noise Reduction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7423–7433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yang, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, X.; Xu, D. Comparative Investigation of Pseudorandom High-Frequency Signal Injection Schemes for Sensorless IPMSM Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 2123–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xiao, D.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Xu, D. Low-Frequency Pulse Voltage Injection Scheme-Based Sensorless Control of IPMSM Drives for Audible Noise Reduction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 8415–8426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almarhoon, A.H.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Xu, P. Improved Rotor Position Estimation Accuracy by Rotating Carrier Signal Injection Utilizing Zero-Sequence Carrier Voltage for Dual Three-Phase PMSM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 4454–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seilmeier, M.; Piepenbreier, B. Sensorless Control of PMSM for the Whole Speed Range Using Two-Degree-of-Freedom Current Control and HF Test Current Injection for Low-Speed Range. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 4394–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, G.; Yuan, B.; Liu, R.; Xu, D. Active Disturbance Rejection Control Strategy for Signal Injection-Based Sensorless IPMSM Drives. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2018, 4, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Tang, Q.; Shen, A.; Zhang, Q. PMSM Sensorless Control by Injecting HF Pulsating Carrier Signal into Estimated Fixed-Frequency Rotating Reference Frame. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 2294–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Sul, S.; Morimoto, S.; Ide, K. High-Bandwidth Sensorless Algorithm for AC Machines Based on Square-Wave-Type Voltage Injection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, R.; Xu, D.; Blaabjerg, F.; Lu, K.; Wang, G.; Zhang, G. Square-Wave Voltage Injection Algorithm for PMSM Position Sensorless Control with High Robustness to Voltage Errors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 5425–5437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Ha, J.; Sul, S. PWM Switching Frequency Signal Injection Sensorless Method in IPMSM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2012, 48, 1576–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.; Kim, S. Simple sensorless algorithm for interior permanent magnet synchronous motors based on high-frequency voltage injection method. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2014, 8, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Götting, G.; Dietrich, S.; Hahn, I. Self-Sensing Control of Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machines with Multiple Saliencies Using Pulse-Voltage-Injection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 3480–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, L. Eddy Current Effects on Rotor Position Estimation and Magnetic Pole Identification of PMSM at Zero and Low Speeds. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2008, 23, 2565–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Ni, R.; Chen, W.; Blaabjerg, F.; Xu, D. High-Frequency Voltage-Injection Methods and Observer Design for Initial Position Detection of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 7971–7979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Lu, K.; Dwivedi, S.K.; Rosholm, J.R.; Blaabjerg, F. Minimum-Voltage Vector Injection Method for Sensorless Control of PMSM for Low-Speed Operations. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, B.; Li, S.; Feng, Y. Initial Rotor Position Detection of Surface Mounted Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. Proc. CSEE 2011, 31, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Yan-Jun, Y.U.; Gao, H.W.; Chai, F.; Cheng, S.K. Rotor magnetic polarity detection method for PMSM. Elect. Mach. Control. 2011, 15, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, Y.S.; Lorenz, R.D.; Jahns, T.M.; Sul, S.K. Initial rotor position estimation of an interior permanent-magnet synchronous machine using carrier-frequency injection methods. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2005, 41, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raute, R.; Caruana, C.; Staines, C.S.; Cilia, J.; Sumner, M.; Asher, G. Operation of a sensorless PMSM drive without additional test signal injection. In Proceedings of the 2008 4th IET Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives, York, UK, 2–4 April 2008; pp. 616–620. [Google Scholar]
























| Literature | Remove LPF | Remove BPF/HPF | Reduce Audible Noise | Nonlinearity of the Inverter | Magnetic Polarity Judgment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref. [4] | × | √ | × | × | × |
| Ref. [8] | √ | × | × | × | √ |
| Ref. [10] | × | × | √ | × | × |
| Ref. [11] | × | × | √ | × | × |
| Ref. [12] | √ | √ | √ | × | × |
| Ref. [13] | √ | × | × | × | √ |
| Ref. [15] | √ | √ | × | × | × |
| Ref. [16] | × | √ | × | × | √ |
| Ref. [18] | √ | √ | × | √ | × |
| Ref. [23] | √ | √ | × | × | √ |
| Ref. [24] | √ | √ | × | √ | × |
| This paper | √ | √ | × | √ | √ |
| Parameter | Quantity | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pole pairs | 2 | poles |
| Resistance | 1.6 | [Ω] |
| d-axis inductance | 15 | [mH] |
| q-axis inductance | 18.8 | [mH] |
| Rated speed | 3000 | [rpm] |
| Rated power | 400 | [W] |
| Rated voltage | 220 | [V] |
| Rated current | 2.28 | [A] |
| Rated torque | 1.27 | [N·m] |
| PWM switching frequency | 10 | [kHz] |
| Injection voltage magnitude | 70 | [V] |
| Injection Method | 30° | 60° | 120° | 150° | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (s) | error (°) | Time (s) | error (°) | Time (s) | error (°) | Time (s) | error (°) | |
| Conventional method | 0.018 | ±3.3 + 6.2 | 0.02 | ±3.4 + 6.4 | 0.016 | ±3.2 + 5.9 | 0.012 | ±3.6 + 6.2 |
| Improved method | 0.022 | ±3.4 + 3.2 | 0.032 | ±3.2 + 2.4 | 0.023 | ±2.9 + 1.9 | 0.017 | ±3.6 + 2.2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Yang, K. High Frequency Square-Wave Voltage Injection Scheme-Based Position Sensorless Control of IPMSM in the Low- and Zero- Speed Range. Energies 2019, 12, 4776. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12244776
Wang S, Zhao J, Yang K. High Frequency Square-Wave Voltage Injection Scheme-Based Position Sensorless Control of IPMSM in the Low- and Zero- Speed Range. Energies. 2019; 12(24):4776. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12244776
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shuang, Jianfei Zhao, and Kang Yang. 2019. "High Frequency Square-Wave Voltage Injection Scheme-Based Position Sensorless Control of IPMSM in the Low- and Zero- Speed Range" Energies 12, no. 24: 4776. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12244776
APA StyleWang, S., Zhao, J., & Yang, K. (2019). High Frequency Square-Wave Voltage Injection Scheme-Based Position Sensorless Control of IPMSM in the Low- and Zero- Speed Range. Energies, 12(24), 4776. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12244776