Forced Convection in Porous Media Using Al2O3 and TiO2 Nanofluids in Differing Base Fluids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Measurement Error Analysis
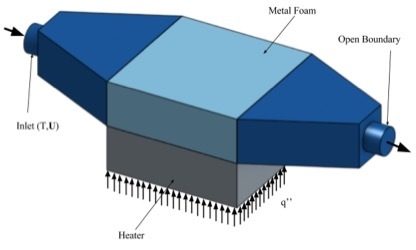
3. Finite Element Analysis
3.1. Governing Equations and Boundary Conditions
3.1.1. Mathematical Formulation
3.1.2. Darcy–Brinkman Model
3.2. Mesh Sensitivity Analysis
3.3. Convergence Criteria
4. Results
4.1. Experimental Measurements
4.1.1. Water Working Fluid
4.1.2. Nanofluid Working Fluid
4.2. Comparison of Heat Enhancement between TiO2/Water Nanofluid and Al2O3/Water Nanofluid via Numerical Simulations
4.3. Effectiveness of Base Fluid in Nanofluid
4.4. Importance of Nanofluid with Base Fluid
4.5. Friction Factor and Pumping Power
5. Discussion
- A numerical model was successfully adapted to recreate experimental conditions for Al2O3-water nanofluid at various operating conditions. The maximum difference found between the experimental and numerical results was found to be less than two degrees Celsius;
- When comparing ethylene glycol and water as heat transfer fluids operating within porous media, water was found to outperform the ethylene glycol by 10%;
- When comparing TiO2 and Al2O3 nanoparticles suspended at 5% vol in water it was found that, at both high and low heat flux ranges, the TiO2-water nanofluid had superior performance by around 1%;
- When all four combinations of nanofluids were compared it was found that the mixtures based on ethylene glycol outperformed those of water from the perspective of the Nusselt number. However, when pumping power was considered to be a key element, the highly viscous base fluid showed potential weakness.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Azmi, W.H.; Hamid, K.A.; Usri, N.A.; Mamat, R.; Sharma, K.V. Heat transfer augmentation of ethylene glycol: Water nanofluids and applications. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 75, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, P.K.; Mallik, A.K.; Ganguly, R.; Santra, A.K. Synthesis and characterization of TiO2-water nanofluids with different surfactants. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 75, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashirnezhad, K.; Bazri, S.; Safaei, M.R.; Goodarzi, M.; Dahari, M.; Mahian, O.; Dalkilica, A.S.; Wongwises, S. Viscosity of nanofluids: A review of recent experimental studies. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 73, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghir, M.Z.; Welsford, C.; Thanapathy, P.; Bayomy, A.M.; Delisle, C. Experimental measurements and numerical computation of nano heat transfer enhancement inside a porous material. ASME J. Therm. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2019, 12, 011003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayomy, A.; Saghir, M.Z. Thermal Performance of Finned Aluminum Heat Sink Filled with ERG Aluminum Foam: Experimental and Numerical Approach. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 4411–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhajaj, Z.; Bayomy, A.M.; Saghir, M.Z.; Rahman, M.M. Flow of Nanofluid and Hybrid Fluid in Porous Channels: Experimental and Numerical Approach. Int. J. Thermofluids 2020, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsford, C.; Delisle, C.; Plant, R.D.; Saghir, M.Z. Effects of Nanofluid Concentration and Channeling on the Thermal Effectiveness of Highly Porous Open-Cell Foam Metals: A Numerical and Experimental Study. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 140, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delisle, C.; Welsford, C.; Saghir, M.Z. Forced convection study with micro-porous channels and nanofluid: Experimental and numerical. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 140, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duangthongsuk, W.; Wongwises, S. Measurement of temperature dependent thermal conductivity and viscosity of TiO2-water nanofluids. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2009, 33, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastoriza-Gallego, M.J.; Lugo, L.; Legido, J.L.; Pineiro, M.M. Thermal conductivity and viscosity measurements of ethylene glycol based Al2O3 nanofluids. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussein, A.M.; Bakar, R.A.; Kadirgama, K.; Sharma, K.V. Experimental measurement of nanofluids thermal properties. Int. J. Automot. Mech. Eng. 2013, 7, 850–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usri, N.A.; Azmi, W.H.; Mamat, R.; Hamid, K.A.; Najafi, G. Thermal conductivity enhancement of Al2O3 nanofluid in ethylene glycol and water mixture. Energy Procedia 2015, 79, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khedkar, R.S.; Shrivastava, N.; Sonawane, S.S.; Wasewar, K.L. Experimental investigations and theoretical determination of thermal conductivity and viscosity of TiO2-ethylene glycol nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 73, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, Z.; Saidur, R.; Hepbasli, A.; Rahim, N.A. New thermophysical properties of water based TiO2 nanofluid- the hysteresis phenomenon revisited. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 58, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utomo, A.T.; Poth, H.; Robbins, P.T.; Pacek, A.W. Experimental and theoretical studies of thermal conductivity, viscosity and heat transfer coefficient of titania and alumina nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 7772–7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puliti, G.; Paolucci, S.; Sen, M. Nanofluids and their properties. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2011, 64, 030803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifpur, M.; Solomon, A.B.; Ottermann, T.L.; Meyer, J.P. Optimum concentration of nanofluids for heat transfer enhancement under cavity flow natural convection with TiO2-water. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 98, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamzamian, A.; Oskouie, S.N.; Doosthoseini, A.; Joneidi, A.; Pazouki, M. Experimental investigation of forced convective heat transfer coefficient in nanofluids of Al2O3/EG and CuO/EG in a double pipe and plate heat exchangers under Turbulent flow. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2011, 35, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Tavakoli, M.R.; Mirsoleimani, M.A.; Gholami, A.; Salimpour, M.R. Experimental and numerical investigation on forced convection heat transfer and pressure drop in helically coiled pipes using TiO2/water nanofluid. Int. J. Refrig. 2017, 74, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayhani, M.H.; Soltanzadeh, H.; Heyhat, M.M.; Nazari, M.; Kowsary, F. Experimental study of convective heat transfer and pressure drop of TiO2/water nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 39, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.D.; Liu, R.; Wang, J.; Du, M. The characteristics of convective heat transfer in microchannel heat sinks using Al2O3 and TiO2 nanofluids. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 76, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, D.P.; Vajjha, R.S.; Das, D.K.; Oliva, D. Application of aluminum oxide nanofluids in diesel electric generator as jacket water coolant. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2008, 28, 1774–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, V.; Kumar, D.S.; Thirumalini, S. Experimental investigation of heat transfer characteristics of automobile radiator using TiO2-nanofluid coolant. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 225, 12101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyghambarzadeh, S.M.; Hashemabadi, S.H.; Hoseini, S.M.; Jamnani, N.S. Experimental study of heat transfer enhancement using water/ethylene glycol based nanofluids as a new coolant for car radiators. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 38, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhya, D.; Reddy, M.C.S.; Rao, V.V. Improving the cooling performance of automobile radiator with ethylene glycol water based TiO2 nanofluids. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 78, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- COMSOL. COMSOL Software User Manual; COMSOL: Newton, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]










| Fluid | 3) | Pr (Prandtl Number) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 0.001002 | 998.2 | 4182 | 0.613 | 6.8358303 |
| Ethylene glycol | 0.0191 | 1127.966 | 2470.212 | 0.2463 | 191.56 |
| 0.5% Al2O3-0.995 Water | 0.001032 | 1011.209 | 4121.17 | 0.62232483 | 6.8342 |
| 0.5% TiO2-0.995 Water | 0.00144 | 1014 | 4111 | 0.775 | 7.64 |
| 0.5% TiO2-0.995 Ethylene glycol | 0.0185 | 1143.2012 | 2437.7416 | 0.255 | 176.8558 |
| 0.5% Al2O3-0.995 Ethylene glycol | 0.0209 | 1140.3262 | 2443.2952 | 0.26 | 196.4033 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saghir, M.Z.; Welsford, C. Forced Convection in Porous Media Using Al2O3 and TiO2 Nanofluids in Differing Base Fluids. Energies 2020, 13, 2665. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102665
Saghir MZ, Welsford C. Forced Convection in Porous Media Using Al2O3 and TiO2 Nanofluids in Differing Base Fluids. Energies. 2020; 13(10):2665. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102665
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaghir, M. Z., and C. Welsford. 2020. "Forced Convection in Porous Media Using Al2O3 and TiO2 Nanofluids in Differing Base Fluids" Energies 13, no. 10: 2665. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102665
APA StyleSaghir, M. Z., & Welsford, C. (2020). Forced Convection in Porous Media Using Al2O3 and TiO2 Nanofluids in Differing Base Fluids. Energies, 13(10), 2665. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102665