Enhanced Acetogenesis of Waste Activated Sludge by Conditioning with Processed Organic Wastes in Co-Fermentation: Kinetics, Performance and Microbial Response
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fermentation Setup
2.3. DNA Extraction and Illumina MiSeq Sequencing
2.4. Analytical Methods and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Compositions of Raw and Pretreated PWs
3.2. Effect of Different Feedstock on VFAs Production and Composition
3.3. Time-Course Profiles of Soluble Organics in Different Fermenters
3.4. Key Functional Microbiome Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Assessment of PWs Composition
4.2. Comprehensive Process Assessment Over Hydrolysis and Acidification Steps
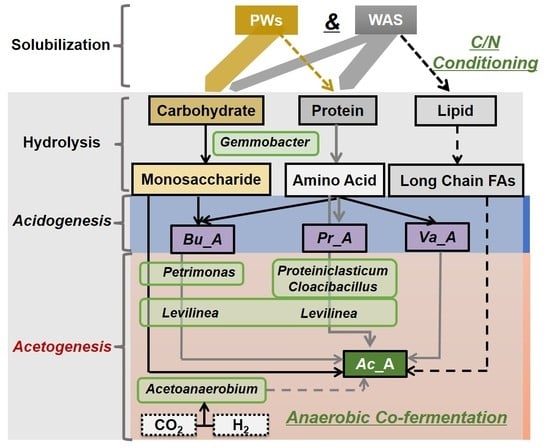
4.3. Potential Interrelation Between Process Performance and Key Microflora
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, G.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H. Current state of sludge production, management, treatment and disposal in China. Water Res. 2015, 78, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burniol-Figols, A.; Varrone, C.; Le, S.B.; Daugaard, A.E.; Skiadas, I.V.; Gavala, H.N. Combined polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) and 1, 3-propanediol production from crude glycerol: Selective conversion of volatile fatty acids into PHA by mixed microbial consortia. Water Res. 2018, 136, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Luan, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, A.; Yue, X. Hydrogen recovery from waste activated sludge: Role of free nitrous acid in a prefermentation-microbial electrolysis cells system. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3870–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, J.; Chen, M. Waste activated sludge fermentation liquid as carbon source for biological treatment of sulfide and nitrate in microaerobic conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu-Agyeman, I.; Plaza, E.; Cetecioglu, Z. Production of volatile fatty acids through co-digestion of sewage sludge and external organic waste: Effect of substrate proportions and long-term operation. Waste Manag. 2020, 112, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Tao, Z. Enhanced volatile fatty acids production from waste activated sludge anaerobic fermentation by adding tofu residue. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 274, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rughoonundun, H.; Holtzapple, M.T. Converting wastewater sludge and lime-treated sugarcane bagasse to mixed carboxylic acids—A potential pathway to ethanol biofuel production. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 105, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panjicko, M.; Zupancic, G.D.; Fanedl, L.; Logar, R.M.; Tisma, M.; Zelic, B. Biogas production from brewery spent grain as a mono-substrate in a two-stage process composed of solid-state anaerobic digestion and granular biomass reactors. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 166, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poerschmann, J.; Weiner, B.; Wedwitschka, H.; Baskyr, I.; Koehler, R.; Kopinke, F.D. Characterization of biocoals and dissolved organic matter phases obtained upon hydrothermal carbonization of brewer’s spent grain. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 164, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Feng, L.; Zhang, R.; He, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, C.; Liu, G. Anaerobic digestion performance of vinegar residue in continuously stirred tank reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 186, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J. Research development on the utilization of mash cake from soy sauce production. China Brew. 2007, 167, 5–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.-X.; Yu, J.-P. Advances in preservation and application of vinasse. J. Mt. Agric. Biol. 2016, 35, 66–71. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, X.; Xiao, X.; Ma, X.; Zhang, R.; He, Y.; Liu, G. Biochemical methane potential (BMP) of vinegar residue and the influence of feed to inoculum ratios on biogas production. Bioresources 2013, 8, 2487–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhu, Y.; Song, A.; Wang, L.; Shen, C.; Gui, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, J. Efficient short-chain fatty acids recovery from anaerobic fermentation of wine vinasse and waste activated sludge and the underlying mechanisms. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 145, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zhou, A.; Wen, K.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W.; Wang, A.; Yue, X. Upgrading VFAs bioproduction from waste activated sludge via co-fermentation with soy sauce residue. Front. Env. Sci. Eng. 2018, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Liu, Z.; Varrone, C.; Luan, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, A.; Yue, X. Efficient biorefinery of waste activated sludge and vinegar residue into volatile fatty acids: Effect of feedstock conditioning on performance and microbiology. Environ. Sci. Wat. Res. 2018, 4, 1819–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carranzo, I.V. APHA: Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington DC, USA; America Water Works Association: Denver, CO, USA; Water Environment Federation: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Goel, R.; Mino, T.; Satoh, H.; Matsuo, T. Enzyme activiries under anaerobic and aerobic conditions in activated sludge sequencing batch reactor. Water Res. 1998, 32, 2081–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, K.; Helmreich, B.; Drewes, J.E. Co-digestion of food waste in municipal wastewater treatment plants: Effect of different mixtures on methane yield and hydrolysis rate constant. Appl. Energy 2015, 137, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.L.; O’Connor, R.T. Relation of certain infrared bands to cellulose crystallinity and crystal latticed type. Part I. Spectra of lattice types I, II, III and of amorphous cellulose. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1964, 8, 1311–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemdar, A.; Sain, M. Biocomposites from wheat straw nanofibers: Morphology, thermal and mechanical properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.K.; Pitman, A.J. FTIR studies of the changes in wood chemistry following decay by brown-rot and white-rot fungi. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2003, 52, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Zhang, J.; Wen, K.; Liu, Z.; Wang, G.; Liu, W.; Wang, A.; Yue, X. What could the entire cornstover contribute to the enhancement of waste activated sludge acidification? Performance assessment and microbial community analysis. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.X.; Li, W.L.; Lee, J.; Loh, K.C.; Dai, Y.J.; Tong, Y.W. Enhancement of biogas production in anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and waste activated sludge by biological co-pretreatment. Energy 2017, 137, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitamo, T.; Treu, L.; Boldrin, A.; Sartori, C.; Angelidaki, I.; Scheutz, C. Microbial population dynamics in urban organic waste anaerobic co-digestion with mixed sludge during a change in feedstock composition and different hydraulic retention times. Water Res. 2017, 118, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kato, S.; Haruta, S.; Cui, Z.J.; Ishii, M.; Yokota, A.; Igarashi, Y. Clostridium straminisolvens sp. nov., a moderately thermophilic, aerotolerant and cellulolytic bacterium isolated from a cellulose-degrading bacterial community. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micr. 2004, 54, 2043–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lenin Babu, M.; Venkata Subhash, G.; Sarma, P.N.; Venkata Mohan, S. Bio-electrolytic conversion of acidogenic effluents to biohydrogen: An integration strategy for higher substrate conversion and product recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 133, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleat, R.; Mah, R.A.; Robinson, R. Acetoanaerobium noterae gen. nov., sp. nov.: An anaerobic bacterium that forms acetate from H2 and CO2. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micr. 1985, 35, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Song, L.; Dong, X. Proteiniclasticum ruminis gen. nov., sp. nov., a strictly anaerobic proteolytic bacterium isolated from yak rumen. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micr. 2010, 60, 2221–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Hanada, S.; Imachi, H.; Ohashi, A.; Harada, H.; Kamagata, Y. Anaerolinea thermolimosa sp. nov., Levilinea saccharolytica gen. nov., sp. nov. and Leptolinea tardivitalis gen. nov., sp. nov., novel filamentous anaerobes, and description of the new classes Anaerolineae classis nov. and Caldilineae classis nov. in the bacterial phylum Chloroflexi. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micr. 2006, 56, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar]
- Looft, T.; Levine, U.Y.; Stanton, T.B. Cloacibacillus porcorum sp. nov., a mucin-degrading bacterium from the swine intestinal tract and emended description of the genus Cloacibacillus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micr. 2013, 63, 1960–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Luo, Y.; Qi, B.; Wan, Y. Simultaneous extraction of oil and soy isoflavones from soy sauce residue using ultrasonic-assisted two-phase solvent extraction technology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 128, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awual, M.R. Solid phase sensitive palladium(II) ions detection and recovery using ligand based efficient conjugate nanomaterials. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awual, M.R.; Hasan, M.M. Fine-tuning mesoporous adsorbent for simultaneous ultra-trace palladium(II) detection, separation and recovery. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awual, M.R.; Hasan, M.M.; Znad, H. Organic–inorganic based nano-conjugate adsorbent for selective palladium(II) detection, separation and recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouskova, A.; Dohanyos, M.; Schmidt, J.E.; Angelidaki, I. Strategies for changing temperature from mesophilic to thermophilic conditions in anaerobic CSTR reactors treating sewage sludge. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahreini, G.; Nazari, L.; Ho, D.; Flannery, C.C.; Elbeshbishy, E.; Santoro, D.; Nakhla, G. Enzymatic pre-treatment for enhancement of primary sludge fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 305, 123071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Ros, C.; Conca, V.; Eusebi, A.L.; Frison, N.; Fatone, F. Pilot-scale municipal wastewater micro-sieving and volatile fatty acids recovery. Water Res. 2020, 174, 115633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rughoonundun, H.; Mohee, R.; Holtzapple, M.T. Influence of carbon-to-nitrogen ratio on the mixed-acid fermentation of wastewater sludge and pretreated bagasse. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 112, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Dai, X.; Zhang, D.; Dai, L.; Wang, R.; Zhao, J. Improved bioproduction of short-chain fatty acids from waste activated sludge by perennial ryegrass addition. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4576–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhou, A.; Yang, C.; Liang, B.; Sangeetha, T.; He, Z.; Wang, L.; Cai, W.; Wang, A.; Liu, W. Enhanced short chain fatty acids production from waste activated sludge conditioning with typical agricultural residues: Carbon source composition regulates community functions. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2015, 8, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Randall, A.A.; McCue, T. The efficiency of enhanced biological phosphorus removal from real wastewater affected by different ratios of acetic to propionic acid. Water Res. 2004, 38, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Parameter | Concentrated WAS a,b | |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.95 ± 0.03 | |
| TSS | 18.07 ± 1.20 | |
| VSS | 12.7 ± 0.60 | |
| VFAs (as COD) | 165 ± 10 | |
| COD | SCOD | 448 ± 6 |
| TCOD | 17.82 ± 1.54 | |
| Proteins | Soluble proteins (as COD) | 132 ± 31 |
| Total proteins (as COD) | 10.79 ± 0.29 | |
| Carbohydrates | Soluble carbohydrates (as COD) | 47 ± 1 |
| Total carbohydrates (as COD) | 1429 ± 72 | |
| Lipid and oil | 165 ± 17 | |
| Parameter | Raw/ Pretreated PWs a,c | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VR | SR | SSR | ||
| VSS b | 93.1 ± 2.7 81.3 ± 0.3 | 87.2 ± 1.9 75.9 ± 1.1 | 76.8 ± 0.8 60.4 ± 1.4 | |
| Total proteins (as COD) | 11.2 ± 0.2 | 15.5 ± 0.5 | 22.6 ± 1.2 | |
| Carbohydrates | Cellulose | 24.9 ± 0.1 20.2 ± 0.2 | 17.8 ± 0.3 24.7 ± 0.1 | 13.8 ± 0.2 19.4 ± 0.3 |
| Hemicellulose | 36.6 ± 0.2 11.2 ± 0.2 | 13.3 ± 0.2 5.9 ± 0.4 | 15.2 ± 0.1 10.8 ± 0.5 | |
| Lignin | 18.8 ± 0.7 9.0 ± 0.3 | 19.5 ± 0.2 11.8 ± 0.1 | 5.7 ± 0.0 4.1 ± 0.2 | |
| Lipid and oil | 2.4 ± 0.3 | 7.0 ± 0.1 | 8.4 ± 0.0 | |
| Ash | 6.9 ± 0.2 18.7 ± 0.6 | 12.8 ± 0.6 24.1 ± 0.3 | 23.2 ± 0.5 39.6 ± 0.8 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Sun, R.; Varrone, C.; Wei, Y.; Shyryn, A.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, J. Enhanced Acetogenesis of Waste Activated Sludge by Conditioning with Processed Organic Wastes in Co-Fermentation: Kinetics, Performance and Microbial Response. Energies 2020, 13, 3630. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13143630
Zhang Y, Sun R, Varrone C, Wei Y, Shyryn A, Zhou A, Zhang J. Enhanced Acetogenesis of Waste Activated Sludge by Conditioning with Processed Organic Wastes in Co-Fermentation: Kinetics, Performance and Microbial Response. Energies. 2020; 13(14):3630. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13143630
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yu, Rui Sun, Cristiano Varrone, Yaoli Wei, Alimzhanova Shyryn, Aijuan Zhou, and Jie Zhang. 2020. "Enhanced Acetogenesis of Waste Activated Sludge by Conditioning with Processed Organic Wastes in Co-Fermentation: Kinetics, Performance and Microbial Response" Energies 13, no. 14: 3630. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13143630
APA StyleZhang, Y., Sun, R., Varrone, C., Wei, Y., Shyryn, A., Zhou, A., & Zhang, J. (2020). Enhanced Acetogenesis of Waste Activated Sludge by Conditioning with Processed Organic Wastes in Co-Fermentation: Kinetics, Performance and Microbial Response. Energies, 13(14), 3630. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13143630