Characterization of Fast Pyrolysis Bio-Oil from Hardwood and Softwood Lignin
Abstract
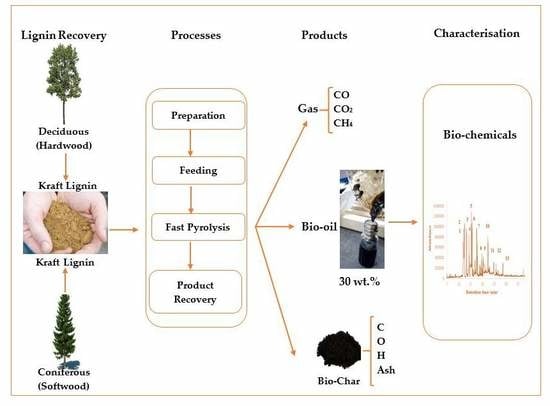
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Crude Bio-Oil Production
2.3. Characterisation of Bio-Oil
2.3.1. Fractionation of Bio-Oil
2.3.2. GCMS Analysis of Obtained Fractionations of Bio-Oil
2.3.3. Elemental Analysis (CHNO) and Heating Values
2.3.4. Water Content and pH
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Distribution of Product Yield
3.2. Properties of Bio-Oil
3.2.1. Elemental Analysis (CHSO) and Heating Values
3.2.2. Water Content and pH Values
3.3. GCMS Analysis of Sigma Kraft and Chouka Kraft Lignin Bio-Oil Fractions
3.3.1. Effect of Organic Solvents on the Extraction of Total Chemicals
3.3.2. GCMS Analysis of Sigma Kraft Lignin and Chouka Kraft Lignin Bio-Oil Fractions
GCMS Analysis of Sigma Kraft Lignin Bio-Oil Fractions
Sigma Kraft Lignin-Toluene Soluble
Sigma Kraft Lignin-Methanol (MeOH) Soluble
Sigma Kraft Lignin-Water Soluble
GCMS Analysis of Chouka Kraft Lignin Bio-Oil Fractions
Chouka Kraft Lignin-Toluene Soluble
Chouka Kraft Lignin-Methanol Soluble
Chouka Kraft Lignin-Water Soluble
3.4. Applications and Future Perspective for the Production of Fuels and Chemicals
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeong, Y.W.; Choi, S.K.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, S.J. Production of biocrude-oil from swine manure by fast pyrolysis and analysis of its characteristics. Renew. Energy 2015, 79, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Q.; Lei, H.; Wang, L.; Yadavalli, G.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Y. Biofuel production from catalytic microwave pyrolysis of Douglas fir pellets over ferrum-modified activated carbon catalyst. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2015, 112, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wei, L.; Crandall, Z.; Julson, J.; Gu, Z. Combining Mo-Cu/HZSM-5 with a two-stage catalytic pyrolysis system for pine sawdust thermal conversion. Fuel 2015, 150, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aboelazayem, O.; Gadalla, M.; Saha, B. Biodiesel production from waste cooking oil via supercritical methanol: Optimisation and reactor simulation. Renew. Energy 2018, 124, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzeh, Y.; Ashori, A.; Mirzaei, B.; Abdulkhani, A.; Molaei, M. Current and potential capabilities of biomass for green energy in Iran. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 4934–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, S.M.; Jae, J.; Park, Y.K. Overview of the recent advances in lignocellulose liquefaction for producing biofuels, bio-based materials and chemicals. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 279, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damartzis, T.; Zabaniotou, A. Thermochemical conversion of biomass to second generation biofuels through integrated process design-A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, R.E.H.; Mabee, W.; Saddler, J.N.; Taylor, M. An overview of second generation biofuel technologies. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1570–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suurs, R.A.A.; Hekkert, M.P. Competition between first and second generation technologies: Lessons from the formation of a biofuels innovation system in the Netherlands. Energy 2009, 34, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naik, S.N.; Goud, V.V.; Rout, P.K.; Dalai, A.K. Production of first and second generation biofuels: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 578–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaswad, A.; Dassisti, M.; Prescott, T.; Olabi, A.G. Technologies and developments of third generation biofuel production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 1446–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, W.H.; Hassim, M.H.; Ng, D.K.S. Review of evolution, technology and sustainability assessments of biofuel production. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 71, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Energy Agency. Deploying Renewables 2011: Best and Future Policy Practice; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gopu, C.; Gao, L.; Volpe, M.; Fiori, L.; Goldfarb, J.L. Valorizing municipal solid waste: Waste to energy and activated carbons for water treatment via pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 133, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Dong, J.I.; Jeon, J.K.; Park, Y.K.; Yoo, K.S.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, J.; Kim, S. Effects of the operating parameters on the production of bio-oil in the fast pyrolysis of Japanese larch. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 49, 3187–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgwater, A.V.; Peacocke, G.V.C. Fast pyrolysis processes for biomass. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2000, 4, 1–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Hassan, M.; Ocone, R.; Makkawi, Y. A CFD study of biomass pyrolysis in a downer reactor equipped with a novel gas-solid separator-II thermochemical performance and products. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 133, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.; Yin, L.; Wang, H.; He, P. Reprint of: Pyrolysis technologies for municipal solid waste: A review. Waste Manag. 2015, 37, 116–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echresh, Z.; Abdulkhani, A.; Saha, B. Analytical pyrolysis study of different lignin biomass. In Proceedings of the 27th European Biomass Conference and Exhibition Proceedings, Lisbon, Portugal, 26 May 2019; pp. 1241–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, A.A.; Vogel, F.; Lachance, R.P.; Fröling, M.; Antal, M.J.; Tester, J.W. Thermochemical biofuel production in hydrothermal media: A review of sub- and supercritical water technologies. Energy Environ. Sci. 2008, 1, 32–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libra, J.A.; Ro, K.S.; Kammann, C.; Funke, A.; Berge, N.D.; Neubauer, Y.; Titirici, M.M.; Fühner, C.; Bens, O.; Kern, J.; et al. Hydrothermal carbonization of biomass residuals: A comparative review of the chemistry, processes and applications of wet and dry pyrolysis. Biofuels 2011, 2, 89–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shirmohammadli, Y.; Moradpour, P.; Abdulkhani, A.; Efhamisisi, D.; Pizzi, A. Water resistance improvement by polyethyleneimine of tannin-furfuryl alcohol adhesives. Int. Wood Prod. J. 2019, 10, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.T.; Lee, M.K.; Chang, Y.M. Fast pyrolysis of rice straw, sugarcane bagasse and coconut shell in an induction-heating reactor. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2006, 76, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Kim, J.; Park, Y.H.; Park, Y.K. Pyrolysis kinetics and decomposition characteristics of pine trees. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 9797–9802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelaziz, O.Y.; Hulteberg, C.P. Physicochemical characterisation of technical lignins for their potential valorisation. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2017, 8, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdulkhani, A.; Karimi, A.; Mirshokraie, A.; Hamzeh, Y.; Marlin, N.; Mortha, G. Isolation and chemical structure characterization of enzymatic lignin from populus deltoides wood. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 118, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, S.; Abdulkhani, A.; Karimi, A.; Ghazali, A.H.B.; Ahmadun, F.R. The effect of combination enzymatic and advanced oxidation process treatments on the colour of pulp and paper mill effluent. Environ. Technol. 2010, 118, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulkhani, A.; Amiri, E.; Sharifzadeh, A.; Hedjazi, S.; Alizadeh, P. Concurrent production of sodium lignosulfonate and ethanol from bagasse spent liquor. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Luo, Z.; Cen, K. Mechanism study of wood lignin pyrolysis by using TG–FTIR analysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2008, 82, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Hu, X.; Li, W.; Shi, Y. Preparation and characterization of bio-oil from biomass. In Progress in Biomass and Bioenergy Production; InTech Publisher: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 198–222. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Lyu, H.; Chen, K.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J. Selective extraction of bio-oil from hydrothermal liquefaction of salix psammophila by organic solvents with different polarities through multistep extraction separation. BioResources 2014, 9, 5219–5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- David, E.; Kopac, J. Pyrolysis of rapeseed oil cake in a fixed bed reactor to produce bio-oil. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 134, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czernik, S.; Bridgwater, A.V. Overview of applications of biomass fast pyrolysis oil. Energy Fuels 2004, 18, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Torre, M.J.; Moral, A.; Hernández, M.D.; Cabeza, E.; Tijero, A. Organosolv lignin for biofuel. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 45, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Ye, X.P.; Borole, A.P. Separation of chemical groups from bio-oil water-extract via sequential organic solvent extraction. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 123, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bridgwater, A.V. Principles and practice of biomass fast pyrolysis processes for liquids. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1999, 51, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.S.; Wu, Y.L.; Yang, M. De Fractionation of bio-oil produced from hydrothermal liquefaction of microalgae by liquid-liquid extraction. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 108, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmadi, M.; Kawamoto, H.; Saka, S. Characteristics of softwood and hardwood pyrolysis in an ampoule reactor. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 124, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkhani, A.; Mirshokraie, A.; Karimi, A.; Hamzeh, Y. Chemical structure characterization of lignin from populus deltoides. In Proceedings of the 16th International Symposium on Wood, Fiber and Pulping Chemistry (ISWFPC 2011), Tianjing, China, 8–10 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Yao, J.; Chen, G.; Ma, W.; Yan, B.; Qi, Y. Overview of upgrading of pyrolysis oil of biomass. Energy Proced. 2014, 61, 1306–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.S. Production, separation and applications of phenolic-rich bio-oil—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 178, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Li, W.Z.; Zhu, X.F. Overview of fuel properties of biomass fast pyrolysis oils. Energy Convers. Manag. 2009, 50, 1376–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample ID | Carbon% | Hydrogen% | Sulphur% | Oxygen% | HHV (MJ/kg) | LHV (MJ/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma Kraft Lignin | 68.50 | 6.63 | 1.96 | 22.91 | 29.97 | 28.56 |
| Chouka Kraft Lignin | 64.80 | 6.13 | 2.09 | 26.98 | 28.63 | 27.33 |
| Sample ID | Properties | |
|---|---|---|
| Water Content% | pH | |
| Sigma Kraft Lignin | 10.43 | 5.33 |
| Chouka Kraft Lignin | 12.00 | 4.57 |
| Peak No | Component | RT (min) | Chemical Family | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toluene Soluble 773 K | 1 | Phenol | 13.94 | Phenolics |
| 2 | Phenol, 2-methoxy | 14.44 | Phenolics | |
| 3 | Phenol, 3-methyl | 15.30 | Phenolics | |
| 4 | Phenylmethyl alcohol | 16.33 | Phenolics | |
| 5 | 2-Methoxy-6-methylphenol | 17.36 | Phenolics | |
| 6 | Phenol, 4-ethyl-2-methoxy | 18.99 | Phenolics | |
| 7 | Phenol, 2,3,6-trimethyl | 19.55 | Phenolics | |
| 8 | Phenol, 2-methoxy-4-propyl | 21.69 | Phenolics | |
| 9 | 1,2-Benzenediol | 22.27 | Phenolics | |
| 10 | 1,2,4-Trimethoxybenzene | 24.63 | Aromatics | |
| 11 | Benzene methanol, 4-hydroxy | 26.02 | Aromatics | |
| 12 | Vanillyl methyl ketone | 27.75 | Aromatics | |
| 13 | Phenol, 4-(ethoxymethyl)-2-methoxy | 30.60 | Phenolics | |
| MeOH Soluble 773 K | 1 | Phenol | 13.97 | Phenolics |
| 2 | Phenol, 2-methoxy | 14.34 | Phenolics | |
| 3 | Fumaric acid, 2-ethylcyclohexyl isobutyl ester | 15.03 | Esters | |
| 4 | Phenol, 3-methyl | 16.32 | Phenolics | |
| 5 | 2-Methoxy-6-methylphenol | 17.23 | Phenolics | |
| 6 | Phenol, 2-ethyl | 18.72 | Phenolics | |
| 7 | 4-Ethyl guaiacol | 19.46 | Phenolics | |
| 8 | Phenol, 2-ethyl-5-methyl | 19.85 | Phenolics | |
| 9 | Phenol, 2-methoxy-4-propyl | 21.62 | Phenolics | |
| 10 | 1,2-Benzenediol | 22.25 | Phenolics | |
| 11 | Phenol, 2-methoxy-4-propenyl | 24.25 | Phenolics | |
| 12 | 3-Methoxy-4-hydroxy acetophenone | 26.67 | Aromatics | |
| 13 | Vanillyl methyl ketone | 27.68 | Aromatics | |
| 14 | Methyl-(2-hydoxy-3-ethoxy-benzyl)ether | 30.54 | Aromatics | |
| Water Soluble 773 K | 1 | Acetic acid | 2.36 | Acids |
| 2 | Propane, 1-(1-methylethoxy) | 4.14 | Ethers | |
| 3 | Phenol, 2-methoxy | 14.23 | Phenolics | |
| 4 | 2-Methoxy-6-methylphenol | 17.12 | Phenolics | |
| 5 | 1,2-Benzenediol | 22.27 | Phenolics | |
| 6 | 1,3-Benzenediol, 2-methyl- | 24.25 | Phenolics | |
| 7 | Acetoguaiacon | 26.68 | Aromatics | |
| 8 | 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl | 27.69 | Aromatics | |
| 9 | Phenol, 4-(ethoxymethyl)-2-methoxy | 30.59 | Phenolics |
| Peak No | Component | RT (min) | Chemical Family | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toluene Soluble 773 K | 1 | Formic acid phenyl ester | 14.07 | Aromatics |
| 2 | Benzenemethanol | 15.44 | Aromatics | |
| 3 | Phenol, 3-methyl | 16.47 | Phenolics | |
| 4 | 2-Methyl-4-nitro-5-pyrrolidin-1-yl-phenylamine | 18.79 | Aromatics | |
| 5 | Phenol, 2-ethyl-6-methyl | 20.97 | Phenolics | |
| Methanol Soluble 773 K | 1 | Phenol | 14.02 | Phenolics |
| 2 | Phenol, 3-methyl | 15.40 | Phenolics | |
| 3 | Phenol, 4-methyl | 16.42 | Phenolics | |
| 4 | Phenol, 2,3-dimethyl | 17.69 | Phenolics | |
| 5 | Phenol, 2,5-dimethyl | 18.73 | Phenolics | |
| Water Soluble 773 K | 1 | Phenol | 12.87 | Phenolics |
| 1 | Phenol, 2,6-dimethyl | 16.62 | Phenolics | |
| 2 | Phenol, 4-(2-methylpropyl) | 19.26 | Phenolics | |
| 3 | 1,2,3-Trimethoxybenzene | 20.34 | Phenolics | |
| 4 | 2,3,6-Trimethylphenol | 22.55 | Phenolics | |
| 5 | Phenol, 3,4-dimethoxy | 25.32 | Phenolics | |
| 6 | 1,2,4-Trimethoxybenzene | 27.30 | Phenolics | |
| 7 | Benzene, 1,2,3-trimethoxy-5-methyl | 29.15 | Phenolics | |
| 8 | 2,6-Dimethyl-4-nitrophenol | 33.38 | Phenolics | |
| 9 | Methyl 14-methylpentadecanoate | 12.87 | Esters |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Echresh Zadeh, Z.; Abdulkhani, A.; Saha, B. Characterization of Fast Pyrolysis Bio-Oil from Hardwood and Softwood Lignin. Energies 2020, 13, 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040887
Echresh Zadeh Z, Abdulkhani A, Saha B. Characterization of Fast Pyrolysis Bio-Oil from Hardwood and Softwood Lignin. Energies. 2020; 13(4):887. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040887
Chicago/Turabian StyleEchresh Zadeh, Zahra, Ali Abdulkhani, and Basudeb Saha. 2020. "Characterization of Fast Pyrolysis Bio-Oil from Hardwood and Softwood Lignin" Energies 13, no. 4: 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040887
APA StyleEchresh Zadeh, Z., Abdulkhani, A., & Saha, B. (2020). Characterization of Fast Pyrolysis Bio-Oil from Hardwood and Softwood Lignin. Energies, 13(4), 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040887