Novel Flexible Triboelectric Nanogenerator based on Metallized Porous PDMS and Parylene C
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of Flexible TENG
2.3. Characterization of Flexible TENG
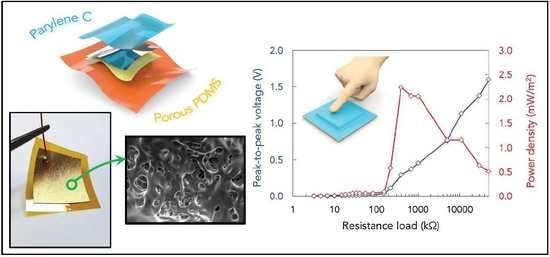
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, H.; Song, Y.; Guo, H.; Miao, L.; Chen, X.; Su, Z.; Zhang, H. Hybrid porous micro structured finger skin inspired self-powered electronic skin system for pressure sensing and sliding detection. Nano Energy 2018, 51, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, G.-J.N.; Rastak, R.; Molina-Lopez, F.; Chung, J.W.; Niu, S.; Feig, V.R.; Lopez, J.; et al. Skin electronics from scalable fabrication of an intrinsically stretchable transistor array. Nature 2018, 555, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chortos, A.; Liu, J.; Bao, Z. Pursuing prosthetic electronic skin. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Chen, H.; Wang, F.; Pu, Y.; Gao, C.; Li, S. Mini Review on Flexible and Wearable Electronics for Monitoring Human Health Information. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Li, X.; Hu, H.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Z.; Lin, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, Z.; Huang, B.; Gong, H.; et al. Monitoring of the central blood pressure waveform via a conformal ultrasonic device. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Emaminejad, S.; Nyein, H.Y.Y.; Challa, S.; Chen, K.; Peck, A.; Fahad, H.M.; Ota, H.; Shiraki, H.; Kiriya, D.; et al. Fully integrated wearable sensor arrays for multiplexed in situ perspiration analysis. Nature 2016, 529, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, M.; Fortunato, G.; Radacsi, N. Wearable flexible sweat sensors for healthcare monitoring: A review. J. R. Soc. Interface 2019, 16, 20190217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, B.C.-K.; Chortos, A.; Berndt, A.; Nguyen, A.K.; Tom, A.; McGuire, A.; Lin, Z.C.; Tien, K.; Bae, W.-G.; Wang, H.; et al. A skin-inspired organic digital mechanoreceptor. Science 2015, 350, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, K.-I.; Li, K.; Chung, H.U.; Xu, S.; Jung, H.N.; Yang, Y.; Kwak, J.W.; Jung, H.H.; Song, J.; Yang, C.; et al. Self-assembled three dimensional network designs for soft electronics. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, J.; Lee, Y.; Yoon, J.; Lee, B.; Oh, E.; Chung, S.; Lee, T.; Cho, K.-J.; Kim, J.; Hong, Y. Electronic skins for soft, compact, reversible assembly of wirelessly activated fully soft robots. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, Y.-C.; Deng, J.; Liu, R.; Hsiao, Y.-C.; Zhang, S.L.; Peng, W.; Wu, H.-M.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.L. Actively Perceiving and Responsive Soft Robots Enabled by Self-Powered, Highly Extensible, and Highly Sensitive Triboelectric Proximity- and Pressure-Sensing Skins. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1801114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, H.; Jeong, J.; Kwak, P.; Kwon, M.; Lee, J. Robotic Flexible Electronics with Self-Bendable Films. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Heo, S.W.; Lee, W.; Inoue, D.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, K.; Jinno, H.; Hashizume, D.; Sekino, M.; Yokota, T.; et al. Self-powered ultra-flexible electronics via nano-grating-patterned organic photovoltaics. Nature 2018, 561, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zou, H.; Liu, R.; Tao, C.; Fan, X.; Wang, Z.L. Micro-cable structured textile for simultaneously harvesting solar and mechanical energy. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Lee, H.E.; Choi, H.; Kim, Y.; We, J.H.; Shin, J.S.; Lee, K.J.; Cho, B.J. High-Performance Flexible Thermoelectric Power Generator Using Laser Multiscanning Lift-Off Process. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 10851–10857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Núñez, C.; Manjakkal, L.; Dahiya, R. Energy autonomous electronic skin. Npj Flex. Electron. 2019, 3, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagdeviren, C.; Yang, B.D.; Su, Y.; Tran, P.L.; Joe, P.; Anderson, E.; Xia, J.; Doraiswamy, V.; Dehdashti, B.; Feng, X.; et al. Conformal piezoelectric energy harvesting and storage from motions of the heart, lung, and diaphragm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1927–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Reuveny, A.; Reeder, J.; Lee, S.; Jin, H.; Liu, Q.; Yokota, T.; Sekitani, T.; Isoyama, T.; Abe, Y.; et al. A transparent bending-insensitive pressure sensor. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.-Z.; Qiu, K.; Meng, F.; Park, S.H.; McAlpine, M.C. 3D Printed Stretchable Tactile Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Huang, N.; Xu, F.; Tong, J.; Chen, Z.; Gui, X.; Fu, Y.; Lao, C. 3D Printing Technologies for Flexible Tactile Sensors toward Wearable Electronics and Electronic Skin. Polymers 2018, 10, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Hou, C.; Lin, J.; Li, Y.; Shi, Q.; Chen, T.; Sun, L.; Lee, C. A non-resonant rotational electromagnetic energy harvester for low-frequency and irregular human motion. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 203901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Li, P.; Yang, Y. On the design of an electromagnetic aeroelastic energy harvester from nonlinear flutter. Meccanica 2018, 53, 2807–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardini, E.; Serpelloni, M. Nonlinear electromagnetic generators with polymeric materials for power harvesting from vibrations. Procedia Eng. 2010, 5, 1168–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-A.; Chiu, C.-Y.; Pham, H.-T. Electromagnetic energy harvesting from vibrations induced by Kármán vortex street. Mechatronics 2012, 22, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaydin, H.D.; Elvin, N.; Andreopoulos, Y. Energy Harvesting from Highly Unsteady Fluid Flows using Piezoelectric Materials. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2010, 21, 1263–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagdeviren, C.; Joe, P.; Tuzman, O.L.; Park, K.-I.; Lee, K.J.; Shi, Y.; Huang, Y.; Rogers, J.A. Recent progress in flexible and stretchable piezoelectric devices for mechanical energy harvesting, sensing and actuation. Extreme Mech. Lett. 2016, 9, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hobeck, J.; Inman, D. Artificial piezoelectric grass for energy harvesting from turbulence-induced vibration. Smart Mater. Struct. 2012, 21, 105024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, K.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, B. Scavenging energy from human walking through a shoe-mounted piezoelectric harvester. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 143902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.-K.; Ho, J.-H.; Chai, A.-B. Performance of a piezoelectric energy harvester in actual rain. Energy 2017, 124, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrini, F.; Gkoumas, K. Piezoelectric energy harvesting from vortex shedding and galloping induced vibrations inside HVAC ducts. Energy Build. 2018, 158, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.; Kim, S.-W. Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Blue Energy Harvesting. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 6429–6432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, A.Y.; Lee, C.J.; Park, J.; Kim, D.; Kim, Y.T. Corrugated Textile based Triboelectric Generator for Wearable Energy Harvesting. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, T.-C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.-J.; Lin Wang, Z. Triboelectric nanogenerator built inside shoe insole for harvesting walking energy. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Kong, D.S.; Choi, M.; Kim, H.B.; Lee, J.-H.; Murillo, G.; Lee, M.; Kim, S.S.; Jung, J.H. Floating buoy-based triboelectric nanogenerator for an effective vibrational energy harvesting from irregular and random water waves in wild sea. Nano Energy 2018, 45, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, X.; Sun, J.; Du, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, J.; Hu, W.; Wang, Z.L. Ultrastretchable, transparent triboelectric nanogenerator as electronic skin for biomechanical energy harvesting and tactile sensing. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, F.-R.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Lin Wang, Z. Flexible triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lin, L.; Chen, J.; Niu, S.; Zi, Y. Triboelectric Nanogenerators; Green Energy and Technology; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-40038-9. [Google Scholar]
- Henniker, J. Triboelectricity in Polymers. Nature 1962, 196, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Fan, X.; Zi, Y.; Jing, Q.; Guo, H.; Wen, Z.; Pradel, K.C.; Niu, S.; et al. Networks of Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Harvesting Water Wave Energy: A Potential Approach toward Blue Energy. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3324–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhang, L.M.; Chen, X.; Han, C.B.; Tang, W.; Zhang, C.; Xu, L.; Wang, Z.L. Structural Optimization of Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Water Wave Energy. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 12562–12572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariello, M.; Guido, F.; Mastronardi, V.M.; Todaro, M.T.; Desmaële, D.; De Vittorio, M. Nanogenerators for harvesting mechanical energy conveyed by liquids. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, Y.; Niu, S.; Wang, J.; Wen, Z.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Standards and figure-of-merits for quantifying the performance of triboelectric nanogenerators. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Zhou, Y.S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical Investigation and Structural Optimization of Single-Electrode Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3332–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.; Shin, D.-M.; Heon Jeon, S.; Young Kang, T.; Han, P.; Han Kim, G.; Kook Kim, H.; Kim, K.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Won Hong, S. Aerodynamic and aeroelastic flutters driven triboelectric nanogenerators for harvesting broadband airflow energy. Nano Energy 2017, 33, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, B.; Chen, J.; Jin, L.; Deng, W.; Tang, J.; Zhang, H.; Pan, H.; Zhu, M.; Yang, W.; et al. Lawn Structured Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Scavenging Sweeping Wind Energy on Rooftops. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1650–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; He, J.; Song, L.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, Z.; Wen, T.; Zhai, C.; Chen, Y.; Cho, J.; Chou, X.; et al. Flexible one-structure arched triboelectric nanogenerator based on common electrode for high efficiency energy harvesting and self-powered motion sensing. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 45022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Guo, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Xi, Y.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z. Eye motion triggered self-powered mechnosensational communication system using triboelectric nanogenerator. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.D.; Tang, W.; He, C.; Deng, C.R.; Yang, L.J.; Zhu, L.P.; Chen, J.; Shao, J.J.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.L. Water wave energy harvesting and self-powered liquid-surface fluctuation sensing based on bionic-jellyfish triboelectric nanogenerator. Mater. Today 2018, 21, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Z.; Han, C.B.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Robust Thin Films-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator Arrays for Harvesting Bidirectional Wind Energy. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1501799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.-H.; Cheng, G.; Li, X.; Yang, P.-K.; Wen, X.; Lin Wang, Z. A multi-layered interdigitative-electrodes-based triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting hydropower. Nano Energy 2015, 15, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, R.; Guo, J.; Yu, A.; Zhang, K.; Kou, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.-W.; Zhai, J. Remarkably enhanced triboelectric nanogenerator based on flexible and transparent monolayer titania nanocomposite. Nano Energy 2018, 50, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcot Narasimulu, A.; Zhao, P.; Soin, N.; Kovur, P.; Ding, P.; Chen, J.; Dong, S.; Chen, L.; Zhou, E.; Montemagno, C.; et al. Significant triboelectric enhancement using interfacial piezoelectric ZnO nanosheet layer. Nano Energy 2017, 40, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kil Yun, B.; Soo Kim, H.; Joon Ko, Y.; Murillo, G.; Hoon Jung, J. Interdigital electrode based triboelectric nanogenerator for effective energy harvesting from water. Nano Energy 2017, 36, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, A.N.; Ramuz, M.; Blayac, S. Increasing surface charge density by effective charge accumulation layer inclusion for high-performance triboelectric nanogenerators. MRS Commun. 2019, 9, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Yim, E.-C.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, S.-J.; Park, J.-Y.; Oh, I.-K. Bacterial Nano-Cellulose Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2017, 33, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xia, L.; Dang, S.; Shi, L.; Cao, A.; Deng, Q.; Du, C. A flexible single-electrode-based triboelectric nanogenerator based on double-sided nanostructures. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 75221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, V.; Kelly, S.; Yang, R. Piezoelectric peptide-based nanogenerator enhanced by single-electrode triboelectric nanogenerator. APL Mater. 2017, 5, 74108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, N.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ning, C.; Tian, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Mao, Y.; Liang, E. Single-electrode triboelectric nanogenerators based on sponge-like porous PTFE thin films for mechanical energy harvesting and self-powered electronics. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 12252–12257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorham, W.F. A New, General Synthetic Method for the Preparation of Linear Poly-p-xylylenes. J. Polym. Sci. 1966, 4, 3027–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.; Tai, Y.-C. Parylene-based electret power generators. J. Micromechanics Microeng. 2008, 18, 104006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Genter, S.; Langhof, T.; Paul, O. Electret-based Out-Of-Plane Micro Energy Harvester with Parylene-C Serving as the Electret and Spring Material. Proc. Eng. 2015, 120, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, G.S.; Baek, D.-H.; Jung, H.C.; Song, J.H.; Moon, J.H.; Hong, S.W.; Kim, I.Y.; Lee, S.-H. Solderable and electroplatable flexible electronic circuit on a porous stretchable elastomer. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priya, S. Modeling of electric energy harvesting using piezoelectric windmill. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 184101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, P.; He, X.; Dai, G.; Zheng, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, A.; Xu, C.; et al. Quantifying the triboelectric series. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiong, J.; Cui, P.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Parida, K.; Lin, M.-F.; Lee, P.S. Skin-touch-actuated textile-based triboelectric nanogenerator with black phosphorus for durable biomechanical energy harvesting. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.-N.; Wuu, D.-S.; Wu, C.-C.; Chiang, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-P.; Horng, R.-H. Improvements of Permeation Barrier Coatings Using Encapsulated Parylene Interlayers for Flexible Electronic Applications. Plasma Process. Polym. 2007, 4, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Rodger, D.; Menon, P.; Tai, Y.C. Corrosion Behavior of Parylene-Metal-Parylene Thin Films in Saline. ECS Trans. 2008, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mariello, M.; Guido, F.; Mastronardi, V.M.; Giannuzzi, R.; Algieri, L.; Qualteri, A.; Maffezzoli, A.; De Vittorio, M. Reliability of Protective Coatings for Flexible Piezoelectric Transducers in Aqueous Environments. Micromachines 2019, 10, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mariello, M.; Guido, F.; Mastronardi, V.M.; De Donato, F.; Salbini, M.; Brunetti, V.; Qualtieri, A.; Rizzi, F.; De Vittorio, M. Captive-air-bubble aerophobicity measurements of antibiofouling coatings for underwater MEMS devices. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mariello, M.; Scarpa, E.; Algieri, L.; Guido, F.; Mastronardi, V.M.; Qualtieri, A.; De Vittorio, M. Novel Flexible Triboelectric Nanogenerator based on Metallized Porous PDMS and Parylene C. Energies 2020, 13, 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071625
Mariello M, Scarpa E, Algieri L, Guido F, Mastronardi VM, Qualtieri A, De Vittorio M. Novel Flexible Triboelectric Nanogenerator based on Metallized Porous PDMS and Parylene C. Energies. 2020; 13(7):1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071625
Chicago/Turabian StyleMariello, Massimo, Elisa Scarpa, Luciana Algieri, Francesco Guido, Vincenzo Mariano Mastronardi, Antonio Qualtieri, and Massimo De Vittorio. 2020. "Novel Flexible Triboelectric Nanogenerator based on Metallized Porous PDMS and Parylene C" Energies 13, no. 7: 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071625
APA StyleMariello, M., Scarpa, E., Algieri, L., Guido, F., Mastronardi, V. M., Qualtieri, A., & De Vittorio, M. (2020). Novel Flexible Triboelectric Nanogenerator based on Metallized Porous PDMS and Parylene C. Energies, 13(7), 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071625