Novel Thermal Desalination Brine Reject-Sewage Effluent Salinity Gradient for Power Generation and Dilution of Brine Reject
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
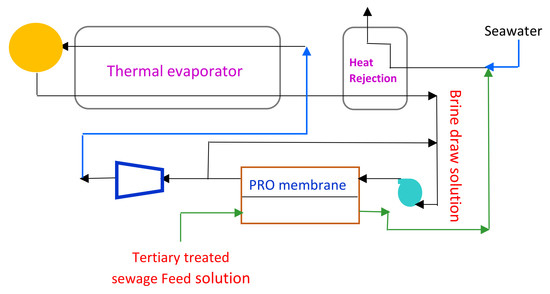
2.1. MSF-PRO Hybrid System
2.2. PRO Membranes
2.3. Mathematical Model
3. Results
3.1. Model Validation
3.2. PRO Water Flux and Power Density
3.3. Specific Power Consumption
3.4. Environmental Benefits of Brine Reject-TSE Salinity Gradient
- To reduce the impact of the MSF desalination plant that is associated with brine reject discharge to seawater as it will be the DS of the PRO process.
- To reduce the environmental impact of TSE discharge to seawater or send to evaporation ponds that would cause health problems.
- To convert wastewater streams into a renewable energy source when coupled together in the PRO process.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altaee, A.; Cippolina, A. Modelling and optimization of modular system for power generation from a salinity gradient. Renew. Energy 2019, 141, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaee, A.; Millar, G.; Zaragoza, G. Integration and Optimization of Pressure Retarded Osmosis with Reverse Osmosis for Power Generation and High Efficiency Desalination. Energy 2016, 103, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thorsen, T.; Holt, T. The potential for power production from salinity gradients by pressure retarded osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 335, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaee, A.; Palenzuela, P.; Zaragoza, G.; AlAnezi, A.A. Single and Dual Stage Closed-Loop Pressure Retarded Osmosis for Power Generation: Feasibility and Performance. Appl. Energy 2017, 191, 328–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, E. A general, resistance-In-Series, salt-and water flux models for forward osmosis and pressure-Retarded osmosis for energy generation. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 460, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Yasukawa, M.; Goda, S.; Sakurai, H.; Shibuya, M.; Takahashi, T.; Kishimoto, M.; Higa, M.; Matsuyama, H. Experimental and simulation studies of two types of 5-Inch scale hollow fiber membrane modules for pressure-Retarded osmosis. Desalination 2018, 447, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaee, A.; Zhou, J.; Alanezi, A.A.; Zaragoza, G. Pressure retarded osmosis process for power generation: Feasibility, energy balance and controlling parameters. Appl. Energy 2017, 206, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeb, S.; Van Hessen, F.; Shahaf, D. Production of energy from concentrated brines by pressure-Retarded osmosis: II. Experimental results and projected energy costs. J. Membr. Sci. 1976, 1, 249–269. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Wang, Y.; Sharif, A.; Shaheed, M.H. Thermodynamic analysis of a stand-Alone reverse osmosis desalination system powered by pressure retarded osmosis. Desalination 2014, 352, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plata, S.L.; Childress, A.E. Limiting power density in pressure-retarded osmosis: Observation and implications. Desalination 2019, 467, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Alanezi, A.A.; Zhou, J.; Altaee, A.; Shaheed, M.H. Optimization of module pressure retarded osmosis membrane for maximum energy extraction. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Li, J.; Tang, Q.; Hu, Y. Investigation of the reduced specific energy consumption of the RO-PRO hybrid system based on temperature-enhanced pressure retarded osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 581, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, J.; Arias, M.E.; Zhang, Q. A techno-Economic process model for pressure retarded osmosis based energy recovery in desalination plants. Desalination 2020, 476, 114218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.I.; Kim, J.; Hong, S. Changing membrane orientation in pressure retarded osmosis for sustainable power generation with low fouling. Desalination 2016, 389, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabita, M.S.; Hawarib, A.H.; Ammarb, M.H.; Zaidic, S.; Zaragozad, G.; Altaee, A. Evaluation of Forward Osmosis as a Pretreatment Process for Multi Stage Flash Seawater Desalination. Desalination 2019, 461, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, H.T.; Nissen, S.S.; Muff, J.; Søgaard, E.G. Pressure retarded osmosis from hypersaline solutions: Investigating commercial FO membranes at high pressures. Desalination 2017, 420, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandin, G.; Vervoort, H.; Le-Clech, P.; Verliefde, A.R.D. Fouling and cleaning of high permeability forward osmosis membranes. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 9, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, N.N.; Arena, J.T.; McCutcheon, J.R. Proper accounting of mass transfer resistances in forward osmosis: Improving the accuracy of model predictions of structural parameter. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 492, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cath, T.Y.; Elimelech, M.; McCutcheon, J.R.; McGinnis, R.L.; Achilli, A.; Anastasio, D.; Brady, A.R.; Childress, A.E.; Farr, I.V.; Hancock, N.T.; et al. Standard Methodology for Evaluating Membrane Performance in Osmotically Driven Membrane Processes. Desalination 2013, 312, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghaffari, A.; Ahmad Rahbar-Kelishami, R. MD simulation and evaluation of the self-Diffusion coefficients in aqueous NaCl solutions at different temperatures and concentrations. J. Mol. Liq. 2013, 187, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, J.; Zhu, C.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Z. Chemical cleaning protocols for thin film composite (TFC) polyamide forward osmosis membranes used for municipal wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 475, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaee, A.; Ismail, A.F.; Sharif, A.; Zaragoza, G. Dual stage PRO process: Impact of the membrane materials of the process performance. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 6172–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilli, A.; Cath, T.Y.; Childress, A.E. Power generation with pressure retarded osmosis: An experimental and theoretical investigation. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 343, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, A.; Haralambous, K.J.; Loizidou, M. Desalination brine disposal methods and treatment technologies-A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Zubari, W.K. Towards the establishment of a total water cycle management and re-Use program in the GCC countries. Desalination 1998, 120, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Membrane Type | Aw (L/m2h·bar) | B (L/m2h) | S (µ) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Porifera Thin Film Composit | 2.1 | 1.2 | 344 | [17] |
| Oasys This Film Composit | 3.92 | 1.34 | 375 | [18,19] |
| Hydration Technology Innovation Cellulose triacetate | 0.627 | 0.733 | 663 | [17] |
| Fluid Technolgy Solutions Thin Film Composit | 1.25 | 0.19 | 471 | [16] |
| PDS (bar) | PFS (bar) | QDS (L/h) | QFS (L/h) | ΔP (bar) | Jw-e (L/m2h) | Jw-t (L/m2h) | %Agreement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 2.8 | 720 | 480 | 2.2 | 6.2 | 6.46 | 96.0% |
| 11.5 | 2.9 | 8.6 | 5.5 | 5.3 | 96.4% | ||
| 14.7 | 3 | 11.7 | 5.10 | 4.95 | 97.1% | ||
| 17.5 | 3.4 | 14.1 | 4.75 | 4.58 | 96.4% | ||
| 24 | 3.8 | 20.2 | 3.80 | 3.67 | 96.6% |
| Energy kW/m3 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Process Description | Brine Reject-Wastewater | Net Energy Output |
| Pretreatment | 0.05 | |
| Pumping from source | 0.03 | |
| Pumping in module | 0.05 | |
| Loss in PX | 0.017 | |
| Total energy input | 0.147 | |
| Energy output: | ||
| Oasys-TFC | 0.194 | 0.047 |
| Porifera-TFC | 0.183 | 0.036 |
| FTS-TFC | 0.173 | 0.026 |
| HTI-CTA | 0.133 | - |
| Maximum specific power | 0.47 | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Altaee, A.; AlZainati, N. Novel Thermal Desalination Brine Reject-Sewage Effluent Salinity Gradient for Power Generation and Dilution of Brine Reject. Energies 2020, 13, 1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071756
Altaee A, AlZainati N. Novel Thermal Desalination Brine Reject-Sewage Effluent Salinity Gradient for Power Generation and Dilution of Brine Reject. Energies. 2020; 13(7):1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071756
Chicago/Turabian StyleAltaee, Ali, and Nahawand AlZainati. 2020. "Novel Thermal Desalination Brine Reject-Sewage Effluent Salinity Gradient for Power Generation and Dilution of Brine Reject" Energies 13, no. 7: 1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071756
APA StyleAltaee, A., & AlZainati, N. (2020). Novel Thermal Desalination Brine Reject-Sewage Effluent Salinity Gradient for Power Generation and Dilution of Brine Reject. Energies, 13(7), 1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071756