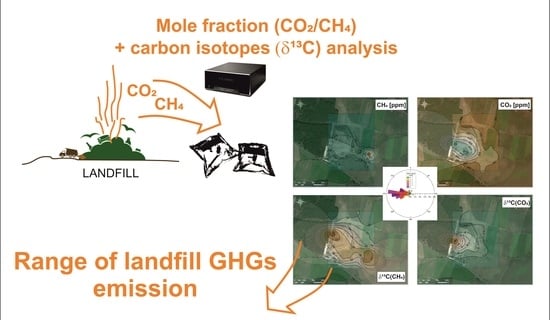
Assessment of GHG Interactions in the Vicinity of the Municipal Waste Landfill Site—Case Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Sampling Methodology
2.3. CO2 and CH4 Mole Fraction and Carbon Isotope Analysis
2.4. Meteorological Data
2.5. Data Analysis
- δmix—background C isotope mixing ratio;
- δsrc—mean source C isotope mixing ratio;
- Cmix—background atmospheric C concentration;
- Catm—C concentrations of the mean source.
3. Results
3.1. Weather Conditions
3.2. Mole Fraction and Stable Carbon Isotopic Composition of CH4 in the Vicinity of the Municipal Waste Landfill
3.3. Mole Fraction and Stable Carbon Isotopic Composition of CO2 in the Vicinity of the Municipal Waste Landfill
4. Discussion
4.1. General Divagation about GHGs on Investigated Landfill
4.2. CH4 Balance in the Vicinity of Municipal Waste Landfill
4.3. CO2 Balance in the Vicinity of Municipal Waste Landfill
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friedlingstein, P.; O’Sullivan, M.; Jones, M.W.; Andrew, R.M.; Hauck, J.; Olsen, A.; Peters, G.P.; Peters, W.; Pongratz, J.; Sitch, S.; et al. Global Carbon Budget 2020. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 3269–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.R.; Desai, M.A.; Rogers, J.V.; Houghton, R.A. Joint CO2 and CH4 accountability for global warming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2865–E2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saunois, M.; Stavert, A.R.; Poulter, B.; Bousquet, P.; Canadell, J.G.; Jackson, R.B.; Raymond, P.A.; Dlugokencky, E.J.; Houweling, S.; Patra, P.K.; et al. The Global Methane Budget 2000–2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 1561–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehme, K.-M.; Orupõld, K.; Kuusemets, V.; Tamm, O.; Jani, Y.; Tamm, T.; Kriipsalu, M. Field Study on the Efficiency of a Methane Degradation Layer Composed of Fine Fraction Soil from Landfill Mining. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speight, J. Natural Gas; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780128095706. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Y. Comparison study of landfill gas emissions from subtropical landfill with various phases: A case study in Wuhan, China. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2015, 65, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, T.; Dunbar, J. Guidance for evaluating landfill gas emissions from closed or abandoned facilities. In EPA Report; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- de Medeiros Engelmann, P.; dos Santos, V.H.J.M.; Barbieri, C.B.; Augustin, A.H.; Ketzer, J.M.M.; Rodrigues, L.F. Environmental monitoring of a landfill area through the application of carbon stable isotopes, chemical parameters and multivariate analysis. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldsen, P.; Barlaz, M.A.; Rooker, A.P.; Baun, A.; Ledin, A.; Christensen, T.H. Present and Long-Term Composition of MSW Landfill Leachate: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 32, 297–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białowiec, A. Some Aspects of Environmental Impact of Waste Dumps. In Contemporary Problems of Management and Environmental Protection; University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn: Olsztyn, Poland, 2011; ISBN 978-83-929462-7-4. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, D.M.J.; Gupta, R.; Sharma, K. Microbiological Degradation of Municipal Solid Waste in Landfills for LFG Generation. In National Conference on Synergetic Trends in engineering and Technology (STET-2014) International Journal of Engineering and Technical Research; ISSN 2321-0869. Special Issue; Available online: https://www.erpublication.org/published_paper/IJETR_APRIL_2014_STET_03.pdf (accessed on 2 November 2021).
- Njoku, P.O.; Odiyo, J.O.; Durowoju, O.S.; Edokpayi, J.N. A Review of Landfill Gas Generation and Utilisation in Africa. Open Environ. Sci. 2018, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaverková, M.D. Landfill Impacts on the Environment—Review. Geosciences 2019, 9, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brennan, R.B.; Healy, M.G.; Morrison, L.; Hynes, S.; Norton, D.; Clifford, E. Management of landfill leachate: The legacy of European Union Directives. Waste Manag. 2016, 55, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozbay, G.; Jones, M.; Gadde, M.; Isah, S.; Attarwala, T. Design and Operation of Effective Landfills with Minimal Effects on the Environment and Human Health. J. Environ. Public Health 2021, 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toro, R.; Morales, L. Landfill fire and airborne aerosols in a large city: Lessons learned and future needs. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2018, 11, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.N.; Sultana, R.; Kota, S. Solid and Hazardous Waste Management; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; ISBN 9780128098769. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. International Best Practices Guide for Landfill Gas Energy Projects; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- Xu, L.; Lin, X.; Amen, J.; Welding, K.; McDermitt, D. Impact of changes in barometric pressure on landfill methane emission. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2014, 28, 679–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldsmith, C.D.; Chanton, J.; Abichou, T.; Swan, N.; Green, R.; Hater, G. Methane emissions from 20 landfills across the United States using vertical radial plume mapping. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2012, 62, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menoud, M.; van der Veen, C.; Necki, J.; Bartyzel, J.; Szénási, B.; Stanisavljević, M.; Pison, I.; Bousquet, P.; Röckmann, T. Methane (CH4) sources in Krakow, Poland: Insights from isotope analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 13167–13185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimnoch, M.; Necki, J.; Chmura, L.; Jasek, A.; Jelen, D.; Galkowski, M.; Kuc, T.; Gorczyca, Z.; Bartyzel, J.; Rozanski, K. Quantification of carbon dioxide and methane emissions in urban areas: Source apportionment based on atmospheric observations. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2019, 24, 1051–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, J.; Wen, X.; Sun, X. Mixing ratio and carbon isotopic composition investigation of atmospheric CO2 in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Górka, M.; Lewicka-Szczebak, D.; Fuß, R.; Jakubiak, M.; Jędrysek, M.O. Dynamics and origin of atmospheric CH4 in a Polish metropolitan area characterized by wetlands. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 45, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolper, D.A.; Martini, A.M.; Clog, M.; Douglas, P.M.; Shusta, S.S.; Valentine, D.L.; Sessions, A.L.; Eiler, J.M. Distinguishing and understanding thermogenic and biogenic sources of methane using multiply substituted isotopologues. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 161, 219–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Douglas, P.M.J.; Stolper, D.A.; Eiler, J.M.; Sessions, A.L.; Lawson, M.; Shuai, Y.; Bishop, A.; Podlaha, O.G.; Ferreira, A.A.; Santos Neto, E.V.; et al. Methane clumped isotopes: Progress and potential for a new isotopic tracer. Org. Geochem. 2017, 113, 262–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaefer, H.; Fletcher, S.E.M.; Veidt, C.; Lassey, K.R.; Brailsford, G.W.; Bromley, T.M.; Dlugokencky, E.J.; Michel, S.E.; Miller, J.B.; Levin, I.; et al. A 21st-century shift from fossil-fuel to biogenic methane emissions indicated by 13CH4. Science 2016, 352, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazzeri, G.; Lowry, D.; Fisher, R.E.; France, J.L.; Lanoisellé, M.; Kelly, B.F.J.; Necki, J.M.; Iverach, C.P.; Ginty, E.; Zimnoch, M.; et al. Carbon isotopic signature of coal-derived methane emissions to the atmosphere: From coalification to alteration. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 13669–13680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tait, D.R.; Maher, D.T.; Santos, I.R. Seasonal and Diurnal Dynamics of Atmospheric Radon, Carbon Dioxide, Methane, δ13C-CO2 and δ13C-CH4 in a Proposed Australian Coal Seam Gas Field. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, I.; Bergamaschi, P.; Dörr, H.; Trapp, D. Stable isotopic signature of methane from major sources in Germany. Chemosphere 1993, 26, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hare, V.J.; Loftus, E.; Jeffrey, A.; Ramsey, C.B. Atmospheric CO2 effect on stable carbon isotope composition of terrestrial fossil archives. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jasek, A.; Zimnoch, M.; Gorczyca, Z.; Smula, E.; Rozanski, K. Seasonal variability of soil CO2 flux and its carbon isotope composition in Krakow urban area, Southern Poland. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2014, 50, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graven, H.; Keeling, R.F.; Rogelj, J. Changes to Carbon Isotopes in Atmospheric CO2 Over the Industrial Era and Into the Future. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2020, 34, e2019GB006170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, J.C.; Frew, R.D.; Van Hale, R. Can stable isotopes be used to monitor landfill leachate impact on surface waters? J. Geochem. Explor. 2006, 88, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raco, B.; Dotsika, E.; Battaglini, R.; Bulleri, E.; Doveri, M.; Papakostantinou, K. A Quick and Reliable Method to Detect and Quantify Contamination from MSW Landfills: A Case Study. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, B.; Hrad, M.; Huber-Humer, M.; Watzinger, A.; Wyhlidal, S.; Reichenauer, T.G. Stable isotope signatures for characterising the biological stability of landfilled municipal solid waste. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widory, D.; Proust, E.; Bellenfant, G.; Bour, O. Assessing methane oxidation under landfill covers and its contribution to the above atmospheric CO2 levels: The added value of the isotope (δ13C and δ18O CO2; δ13C and δD CH4) approach. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamaschi, P.; Lubina, C.; Königstedt, R.; Fischer, H.; Veltkamp, A.C.; Zwaagstra, O. Stable isotopic signatures (•13C, gD) of methane from European landfill sites. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 8251–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shalan, A.; Lowry, D.; Fisher, R.E.; Nisbet, E.G.; Zazzeri, G.; Al-Sarawi, M.; France, J.L. Methane emissions in Kuwait: Plume identification, isotopic characterisation and inventory verification. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 268, 118763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkaloglu, S.; Lowry, D.; Fisher, R.; France, J.; Lanoiselle, M.; Fernandez, J. Characterization and Quantification of Methane Emissions from Waste in the UK. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2020, Online, 4–8 May 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghdam, E.F.; Fredenslund, A.M.; Chanton, J.; Kjeldsen, P.; Scheutz, C. Determination of gas recovery efficiency at two Danish landfills by performing downwind methane measurements and stable carbon isotopic analysis. Waste Manag. 2018, 73, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanci, R.; Panarello, H.O. Carbon stable isotopes as indicators of the origin and evolution of CO2 and CH4 in urban solid waste disposal sites and nearby areas. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiticar, M.J. Stable isotope geochemistry of coals, humic kerogens and related natural gases. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1996, 32, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiticar, M.; Faber, E.; Schoell, M. Biogenic methane formation in marine and freshwater environments: CO2 reduction vs. acetate fermentation—Isotope evidence. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1986, 50, 693–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassare, F.J.; Laughrey, C.D. Identifying the sources of stray methane by using geochemical and isotopic fingerprinting. Environ. Geosci. 1997, 4, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Tecle, D.; Lee, J.; Hasan, S. Quantitative analysis of physical and geotechnical factors affecting methane emission in municipal solid waste landfill. Environ. Geol. 2009, 56, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, T.; Feng, H.; Chen, S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Landfills: A Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haro, K.; Ouarma, I.; Nana, B.; Bere, A.; Tubreoumya, G.C.; Kam, S.Z.; Laville, P.; Loubet, B.; Koulidiati, J. Assessment of CH4 and CO2 surface emissions from Polesgo’s landfill (Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso) based on static chamber method. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2019, 10, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Valencia, R.; Magana-Rodriguez, F.; Martinez-Cruz, K.; Fochesatto, G.J.; Thalasso, F. Spatial and temporal distribution of methane emissions from a covered landfill equipped with a gas recollection system. Waste Manag. 2021, 121, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, S. Temporal and spatial variation of greenhouse gas emissions from a limited-controlled landfill site. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate-Data.org. Available online: https://en.climate-data.org/europe/poland/lower-silesian-voivodeship-456/ (accessed on 9 October 2021).
- OpenStreetMap. Available online: OpenStreetMap.org (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Information on Individual Types of Municipal Waste Collected from the Wroclaw Urban Area. Available online: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjXt-vzwpr0AhUEt4sKHdw9CDcQFnoECAkQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fbip.um.wroc.pl%2Fattachments%2Fdownload%2F57300&usg=AOvVaw3O4-ZvhtKb5GEwKlTRZ1yG (accessed on 2 November 2021).
- GIOŚ. Chief Inspectorate of Environmental Protection (GIOS, Poland). Inspection Report no. WIOŚ-Wroc 301/2018; GIOŚ: Wrocław, Poland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chybiński, S.; Gaworecka, M.; Olearnik, M.; Krzyśków, A. Analysis of the State of Municipal Precipitation Management in the Kobierzyce Commune; Gmina Kobierzyce: Wrocław, Poland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- NOAA. Carbon Cycle Gases Mace Head, County Galway, Ireland. Available online: https://gml.noaa.gov/dv/iadv/graph.php?code=MHD&program=ccgg&type=lg (accessed on 28 April 2021).
- Keeling, C.D. The concentration and isotopic abundances of atmospheric carbon dioxide in rural areas. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1958, 13, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pataki, D.E. Seasonal cycle of carbon dioxide and its isotopic composition in an urban atmosphere: Anthropogenic and biogenic effects. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezyk, Y.; Sówka, I.; Górka, M.; Blachowski, J. GIS-Based Approach to Spatio-Temporal Interpolation of Atmospheric CO2 Concentrations in Limited Monitoring Dataset. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, N. Assessment of Greenhouse Gas Emissions from the Municipal Waste Landfill in Rudna Wielka on the Basis of Concentrations and Carbon Isotopic Composition of Atmospheric CO2 and CH4. Master’s thesis, University of Wroclaw, Wroclaw, Poland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ezekwe, I.C.; Arokoyu, S.B. Landfill Emissions and their Urban Planning and Environmental Health Implications in Port Harcourt, South-South Nigeria. Desenvolv. E Meio Ambiente 2017, 42, 42–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- KOBiZE. Poland’s National Database on Greenhouse Gases and other Substances Emissions. Data on the Waste Management Plant. Installations and Sources, Emission Levels of Selected Substances for 2016–2020; IOŚ-PIB: Warsaw, Poland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bezyk, Y.; Sówka, I.; Górka, M. Assessment of urban CO2 budget: Anthropogenic and biogenic inputs. Urban Clim. 2021, 39, 100949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackley, K.C.; Liu, C.L.; Coleman, D.D. Environmental Isotope Characteristics of Landfill Leachates and Gases. Ground Water 1996, 34, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bréas, O.; Guillou, C.; Reniero, F.; Wada, E. The Global Methane Cycle: Isotopes and Mixing Ratios, Sources and Sinks. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2001, 37, 257–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, D.D.; Liu, C.L.; Hackley, K.C.; Pelphrey, S.R. Isotopic Identification of Landfill Methane. AAPG Div. Environ. Geosci. J. 1995, 2, 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, B.A.; Jahren, A.H. The effect of atmospheric CO2 concentration on carbon isotope fractionation in C3 land plants. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 96, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezyk, Y.; Dorodnikov, M.; Sówka, I. Effects of climate factors and vegetation on the CO2 fluxes and δ13C from re-established grassland. E3S Web Conf. 2017, 22, 00017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Werth, M.; Kuzyakov, Y. 13C fractionation at the root–microorganisms–soil interface: A review and outlook for partitioning studies. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1372–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Waste Component | Classification Codes for Waste in EU | Assumed (Mg·Year−1) | % Mass in Wet Basis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organic, biodegradable | 20 02 01 | 23,797.33 | 20.53 |
| Non-combustible mixed waste | 20 03 01, 20 03 07 | 85,701.55 | 73.95 |
| Minerals | 20 02 02; 20 02 03 | 1792.27 | 1.55 |
| Textile | 20 01 11 | 2.63 | 0.00 |
| Mixed construction and demolition debris | 17 01 07; 17 09 04 | 587.70 | 0.51 |
| Packaging fractions: | |||
| - glass | 15 01 07 | 3814.43 | 3.29 |
| - multilayer packages | 15 01 06 | 202.60 | 0.17 |
| * Total | 115,898.51 | 100 |
| No Sample | Wind Direction [◦] | Wind Velocity [m/s] | Temperature [°C] | RH [%] | Pressure [hPa] | CO2 [ppm] | 1/CO2 [ppm−1] | δ13C(CO2) [‰] | CH4 [ppm] | 1/CH4 [ppm−1] | δ13C(CH4) [‰] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 * | 249 | 1.6 | 18.6 | 52.8 | 1005.2 | 394.3 | 2.536 | −7.8 | 2.21 | 0.452 | −50.9 |
| 2 * | 253 | 3.8 | 18.3 | 55.1 | 1005.4 | 388.4 | 2.575 | −7.4 | 2.02 | 0.495 | −51.6 |
| 3 * | 264 | 3.3 | 17.9 | 55.4 | 1005.7 | 386.6 | 2.587 | −7.3 | 2.01 | 0.497 | −52.2 |
| 4 * | 220 | 0.0 | 20.2 | 54.2 | 1005.5 | 390.5 | 2.561 | −7.5 | 1.92 | 0.521 | −51.4 |
| 5 * | 272 | 3.7 | 17.5 | 51.3 | 1005.9 | 385.9 | 2.591 | −7.3 | 1.90 | 0.528 | −51.5 |
| 6 * | 270 | 5.5 | 18.1 | 53.6 | 1006.2 | 386.4 | 2.588 | −7.3 | 1.90 | 0.528 | −52.1 |
| 7 * | 283 | 5.2 | 17.7 | 53.1 | 1006.4 | 388.8 | 2.572 | −7.5 | 1.90 | 0.527 | −52.0 |
| 8 * | 330 | 3.0 | 17.7 | 55.6 | 1006.2 | 385.1 | 2.596 | −7.2 | 1.90 | 0.525 | −51.8 |
| 9 * | 255 | 3.2 | 18.8 | 54.5 | 1006.4 | 385.5 | 2.594 | −7.4 | 2.16 | 0.463 | −53.0 |
| 10 * | 252 | 3.9 | 18.2 | 54.6 | 1006.5 | 387.2 | 2.583 | −7.3 | 2.07 | 0.484 | −52.9 |
| 11 * | 345 | 4.4 | 18.4 | 54.0 | 1006.2 | 386.7 | 2.586 | −7.4 | 1.92 | 0.520 | −53.1 |
| 12 * | 297 | 0.8 | 19.5 | 49.6 | 1006.2 | 385.9 | 2.591 | −7.3 | 2.43 | 0.411 | −54.1 |
| 13 * | 300 | 6.9 | 17.1 | 50.5 | 1006.5 | 390.8 | 2.559 | −7.4 | 2.12 | 0.471 | −53.2 |
| 14 * | 267 | 5.1 | 17.6 | 53.5 | 1006.5 | 386.2 | 2.590 | −7.2 | 2.17 | 0.461 | −53.8 |
| 15 * | 248 | 9 | 18.2 | 52.8 | 1006.2 | 393.6 | 2.540 | −7.3 | 129.48 | 0.008 | −57.9 |
| 16 * | 264 | 2.4 | 19.6 | 54.1 | 1006.2 | 392.4 | 2.548 | −7.5 | 18.85 | 0.053 | −56.9 |
| 17 * | 285 | 3.7 | 20.2 | 52.6 | 1006.0 | 390.1 | 2.564 | −7.6 | 4.49 | 0.223 | −56.3 |
| 18 * | 305 | 2.2 | 19.1 | 52.8 | 1006.0 | 391.0 | 2.558 | −7.4 | 4.71 | 0.212 | −57.7 |
| 19 * | 240 | 6.9 | 18.9 | 48.8 | 1006.2 | 386.7 | 2.586 | −7.1 | 2.37 | 0.421 | −53.8 |
| 20 * | 274 | 4.1 | 19.3 | 49.6 | 1005.9 | 392.8 | 2.546 | −7.5 | 1.92 | 0.522 | −52.2 |
| 21 * | 276 | 1.7 | 19.2 | 49.2 | 1005.9 | 390.8 | 2.559 | −7.4 | 2.41 | 0.415 | −54.4 |
| 22 * | 286 | 2.6 | 19.8 | 50.3 | 1005.5 | 390.5 | 2.561 | −7.3 | 3.03 | 0.331 | −55.9 |
| 23 * | 273 | 3.3 | 18.9 | 50.6 | 1005.5 | 384.9 | 2.598 | −7.4 | 1.89 | 0.528 | −52.1 |
| 24 * | 273 | 4.0 | 18.5 | 47.9 | 1005.0 | 384.9 | 2.598 | −7.2 | 2.01 | 0.499 | −52.5 |
| 25 * | 300 | 3.3 | 19.9 | 48.8 | 1005.2 | 389.9 | 2.565 | −7.4 | 3.04 | 0.329 | −55.7 |
| 26 * | 259 | 5.0 | 18.4 | 47.4 | 1005.5 | 388.2 | 2.576 | −7.3 | 1.90 | 0.525 | −51.6 |
| 27 * | 203 | 0.5 | 18.4 | 55.6 | 1005.2 | 396.4 | 2.523 | −7.6 | 2.50 | 0.400 | −54.0 |
| 28 * | 248 | 3.5 | 18.7 | 56.2 | 1005.4 | 406.4 | 2.461 | −8.4 | 11.48 | 0.087 | −56.2 |
| 29 * | 27 | 0.6 | 19.3 | 56.5 | 1005.0 | 417.1 | 2.398 | −12.4 | 23.72 | 0.042 | −56.2 |
| 30 * | 111 | 1.9 | 17.8 | 52.2 | 1004.7 | 395.7 | 2.527 | −7.5 | 5.63 | 0.178 | −59.1 |
| 31 * | 261 | 4.6 | 18.9 | 55.9 | 1005.0 | 419.0 | 2.387 | −7.8 | 21.12 | 0.047 | −57.0 |
| 32 * | 277 | 4.7 | 17.7 | 53.7 | 1006.5 | 385.0 | 2.598 | −7.1 | 2.17 | 0.462 | −52.9 |
| Min. | 27 | 0.0 | 17.1 | 47.4 | 1004.7 | 384.9 | 2.387 | −12.4 | 1.89 | 0.008 | −59.1 |
| Max. | 345 | 6.9 | 20.2 | 56.5 | 1006.5 | 419.0 | 2.598 | −7.1 | 129.48 | 0.528 | −50.9 |
| AVG | 258 | 3.4 | 18.6 | 52.6 | 1005.8 | 391.4 | 2.556 | −7.6 | 8.48 | 0.380 | −53.9 |
| Median | 269 | 3.4 | 18.6 | 53.0 | 1005.9 | 389.3 | 2.569 | −7.4 | 2.17 | 0.461 | −53.2 |
| SD | 57 | 1.7 | 0.8 | 2.6 | 0.5 | 8.2 | 0.051 | 0.9 | 22.46 | 0.171 | 2.2 |
| Wind Direction [°] | Wind Velocity [m/s] | Temperature [°C] | RH [%] | Pressure [hPa] | CO2 [ppm] | 1/CO2 [ppm−1] | δ13C(CO2) [‰] | CH4 [ppm] | 1/CH4 [ppm−1] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wind velocity [m/s] | 0.27 | |||||||||
| Temperature [°C] | 0.00 | −0.45 | ||||||||
| RH [%] | −0.35 | −0.19 | −0.17 | |||||||
| Pressure [hPa] | 0.38 | 0.42 | −0.36 | −0.01 | ||||||
| CO2 [ppm] | −0.40 | −0.35 | 0.30 | 0.24 | −0.45 | |||||
| 1/CO2 [ppm−1] | 0.40 | 0.35 | −0.30 | −0.24 | 0.45 | −1.00 | ||||
| δ13C(CO2) [‰] | 0.29 | 0.39 | −0.37 | −0.31 | 0.48 | −0.80 | 0.80 | |||
| CH4 [ppm] | −0.27 | −0.42 | 0.39 | 0.17 | −0.25 | 0.67 | −0.67 | −0.41 | ||
| 1/CH4 [ppm−1] | 0.27 | 0.42 | −0.39 | −0.17 | 0.25 | −0.67 | 0.67 | 0.41 | −1.00 | |
| δ13C(CH4) [‰] | 0.03 | 0.24 | −0.33 | −0.03 | 0.10 | −0.52 | 0.52 | 0.28 | −0.88 | 0.88 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Górka, M.; Bezyk, Y.; Sówka, I. Assessment of GHG Interactions in the Vicinity of the Municipal Waste Landfill Site—Case Study. Energies 2021, 14, 8259. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14248259
Górka M, Bezyk Y, Sówka I. Assessment of GHG Interactions in the Vicinity of the Municipal Waste Landfill Site—Case Study. Energies. 2021; 14(24):8259. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14248259
Chicago/Turabian StyleGórka, Maciej, Yaroslav Bezyk, and Izabela Sówka. 2021. "Assessment of GHG Interactions in the Vicinity of the Municipal Waste Landfill Site—Case Study" Energies 14, no. 24: 8259. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14248259
APA StyleGórka, M., Bezyk, Y., & Sówka, I. (2021). Assessment of GHG Interactions in the Vicinity of the Municipal Waste Landfill Site—Case Study. Energies, 14(24), 8259. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14248259