Impact of Process Parameters on the Diameter of Nanobubbles Generated by Electrolysis on Platinum-Coated Titanium Electrodes Using Box–Behnken Experimental Design
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Electrolysis
2.2. Experimental Plan
2.3. Size Distribution Density Measurement
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Power Model
2.6. Parity Plots
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sauter Diameters of Obtained Bubbles
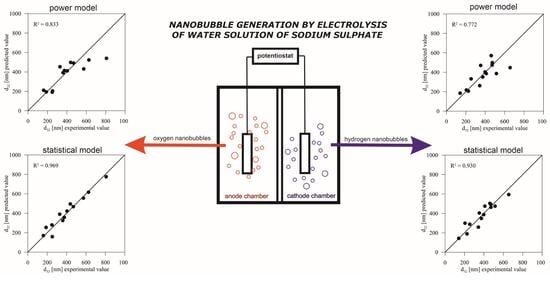
3.2. Statistical Model
3.3. Power Model
3.4. Comparison with Literature Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsuge, H. Micro- and Nanobubbles. Fundamentals and Applications; Pan Stanford Publishing: Boca Raton, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 9789814463119. [Google Scholar]
- Ulatowski, K.; Sobieszuk, P.; Mróz, A.; Ciach, T. Stability of nanobubbles generated in water using porous membrane system. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2019, 136, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, R.; Majumder, S.K. Microbubble generation and microbubble-aided transport process intensification-A state-of-the-art report. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2013, 64, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Ng, W.J.; Liu, Y. Principle and applications of microbubble and nanobubble technology for water treatment. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulatowski, K.; Sobieszuk, P. Gas nanobubble dispersions as the important agent in environmental processes—Generation methods review. Water Environ. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulatowski, K.; Sobieszuk, P. Influence of liquid flowrate on size of nanobubbles generated by porous-membrane modules. Chem. Process Eng. 2018, 39, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasaka, K.; Hirabayashi, A.; Nishino, T.; Fujioka, S.; Kobayashi, D. Development of microbubble aerator for waste water treatment using aerobic activated sludge. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 3172–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juwana, W.E.; Widyatama, A.; Dinaryanto, O.; Budhijanto, W. Indarto; Deendarlianto Hydrodynamic characteristics of the microbubble dissolution in liquid using orifice type microbubble generator. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019, 141, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessarabov, D.; Millet, P. Brief Historical Background of Water Electrolysis. In PEM Water Electrolysis; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 17–42. ISBN 9780128111451. [Google Scholar]
- Endo, T.; Tsuji, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Yanagida, Y.; Hatsuzawa, T. Design and fabrication of cell alignment device based on electrolytically-generated air bubbles, and its practical realization using polystyrene microbeads. Microchim. Acta 2009, 164, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrrell, J.W.G.; Attard, P. Images of nanobubbles on hydrophobic surfaces and their interactions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, R.T.; Arcadia, C.E.; Rosenstein, J.K. Probing the nucleation, growth, and evolution of hydrogen nanobubbles at single catalytic sites. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 283, 1773–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, S.R.; Edwards, M.A.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Luo, L.; White, H.S. Electrochemistry of single nanobubbles. Estimating the critical size of bubble-forming nuclei for gas-evolving electrode reactions. Faraday Discuss. 2016, 193, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Ranaweera, R.; Luo, L. Hydrogen Bubble Formation at Hydrogen-Insertion Electrodes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 15421–15426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Saihara, Y.; Ogumi, Z. Study of hydrogen nanobubbles in solution in the vicinity of a platinum wire electrode using double-potential step chronoamperometry. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 52, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Saihara, Y.; Maeda, M.; Kawamura, M.; Ogumi, Z. Concentration of hydrogen nanobubbles in electrolyzed water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 298, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, K.; Nagata, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Saihara, Y.; Ogumi, Z. Characteristics of hydrogen nanobubbles in solutions obtained with water electrolysis. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2007, 600, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, K.; Ioka, A.; Oku, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Saihara, Y.; Ogumi, Z. Concentration determination of oxygen nanobubbles in electrolyzed water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 329, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meegoda, J.N.; Aluthgun Hewage, S.; Batagoda, J.H. Stability of nanobubbles. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, K.; Takeda, H.; Rabolt, B.; Okaya, T.; Ogumi, Z.; Saihara, Y.; Noguchi, H. Hydrogen particles and supersaturation in alkaline water from an Alkali-Ion-Water electrolyzer. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2001, 506, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postnikov, A.V.; Uvarov, I.V.; Lokhanin, M.V.; Svetovoy, V.B. Highly energetic phenomena in water electrolysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Postnikov, A.V.; Uvarov, I.V.; Lokhanin, M.V.; Svetovoy, V.B. Electrically controlled cloud of bulk nanobubbles in water solutions. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Postnikov, A.V.; Uvarov, I.V.; Penkov, N.V.; Svetovoy, V.B. Collective behavior of bulk nanobubbles produced by alternating polarity electrolysis. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prokaznikov, A.; Tas, N.; Svetovoy, V. Surface assisted combustion of hydrogen-oxygen mixture in nanobubbles produced by electrolysis. Energies 2017, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Postnikov, A.V.; Uvarov, I.V.; Prokaznikov, A.V.; Svetovoy, V.B. Observation of spontaneous combustion of hydrogen and oxygen in microbubbles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 121604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Qiao, L. Understanding Combustion of H2/O2 Gases inside Nanobubbles Generated by Water Electrolysis Using Reactive Molecular Dynamic Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. A 2018, 122, 5261–5269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zeng, K. Evaluating the behavior of electrolytic gas bubbles and their effect on the cell voltage in alkaline water electrolysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 13825–13832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, P.; Bakshi, S.; Chatterjee, D. Study on the characteristics of hydrogen bubble formation and its transport during electrolysis of water. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 138, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scriven, L.E. On the dynamics of phase growth. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1959, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, K.; Yamanishi, Y.; Guan, C.; Yanase, S. Control of hydrogen bubble plume during electrolysis of water. J. Phys. Commun. 2019, 3, 035012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, R.; Fan, Y.; Anderson, T.J.; Zhang, B. Imaging Single Nanobubbles of H2 and O2 during the Overall Water Electrolysis with Single-Molecule Fluorescence Microscopy. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 3682–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetefeld, J.; McKenna, S.A.; Patel, T.R. Dynamic light scattering: A practical guide and applications in biomedical sciences. Biophys. Rev. 2016, 8, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calgaroto, S.; Wilberg, K.Q.; Rubio, J. On the nanobubbles interfacial properties and future applications in flotation. Miner. Eng. 2014, 60, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohorecki, R.; Moniuk, W.; Bielski, P.; Sobieszuk, P.; Da̧browiecki, G. Bubble diameter correlation via numerical experiment. Chem. Eng. J. 2005, 113, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Chen, G.; Yuan, Q.; Luo, L.; Gonthier, Y. Hydrodynamics and mass transfer characteristics in gas-liquid flow through a rectangular microchannel. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 2096–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, K.; Tuziuti, T.; Kanematsu, W. Mysteries of bulk nanobubbles (ultrafine bubbles); stability and radical formation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 48, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.X.; Fang, H.P.; Hu, J. Long lifetime of nanobubbles due to high inner density. Sci. China Ser. G Phys. Mech. Astron. 2008, 51, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Independent Variable | Independent Variable Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Salt concentration [mol/dm3] | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.19 |
| Current density [mA/cm2] | 20.0 | 30.0 | 40.0 |
| Time of electrolysis [min] | 10.0 | 20.0 | 30.0 |
| No. | Salt Concentration [mol/dm3] | Current Density [mA/cm2] | Electrolysis Time [min] | Sauter Diameter of Bubbles [nm] | |
| Hydrogen | Oxygen | ||||
| 1 | 0.01 | 30.0 | 10.0 | 343 | 161 |
| 2 | 0.01 | 40.0 | 20.0 | 226 | 188 |
| 3 | 0.10 | 20.0 | 30.0 | 374 | 404 |
| 4 | 0.10 | 40.0 | 10.0 | 352 | 574 |
| 5 | 0.19 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 398 | 469 |
| 6 | 0.10 | 30.0 | 20.0 | 515 | 376 |
| 7 | 0.19 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 471 | 626 |
| 8 | 0.19 | 30.0 | 10.0 | 462 | 808 |
| 9 | 0.19 | 40.0 | 20.0 | 656 | 439 |
| 10 | 0.10 | 30.0 | 20.0 | 515 | 375 |
| 11 | 0.10 | 20.0 | 10.0 | 472 | 329 |
| 12 | 0.10 | 40.0 | 30.0 | 255 | 361 |
| 13 | 0.01 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 205 | 253 |
| 14 | 0.01 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 141 | 249 |
| 15 | 0.10 | 30.0 | 20.0 | 410 | 376 |
| Variable Effect | Oxygen | Hydrogen | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reg. Coeff. | p-Value | Reg. Coeff. | p-Value | |
| Constant term | −1013.58 | 0.0727 | 717.515 | 0.262 |
| Salt concentration (L) | 8364.75 | 0.00753 | −2280.24 | 0.395 |
| Salt concentration (Q) | −2518.49 | 0.558 | −4427.45 | 0.424 |
| Current density (L) | 56.2611 | 0.0661 | −27.1527 | 0.414 |
| Current density (Q) | −0.477370 | 0.221 | 0.185045 | 0.687 |
| Time of electrolysis (L) | 3.68073 | 0.827 | 31.8921 | 0.177 |
| Time of electrolysis (Q) | 0.622724 | 0.108 | −1.03834 | 0.0499 |
| Salt concentration (L) and current density (L) | −106.152 | 0.0636 | 121.755 | 0.0846 |
| Salt concentration (L) and time of electrolysis (L) | −118.471 | 0.0155 | 38.4533 | 0.399 |
| Current density (L) and time of electrolysis (L) | −0.720128 | 0.0591 | 0.000671525 | 0.999 |
| Variable Effect | Oxygen | Hydrogen | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reg. Coeff. | p-Value | Reg. Coeff. | p-Value | |
| Constant term | −436.428 | 0.0523 | 351.990 | 0.0355 |
| Salt concentration (L) | 7115.80 | 0.000970 | - | - |
| Salt concentration (Q) | - | - | −6569.47 | 0.0764 |
| Current density (L) | 23.4847 | 0.0118 | −11.8771 | 0.00595 |
| Current density (Q) | - | - | - | - |
| Time of electrolysis (L) | - | - | 33.5349 | 0.0339 |
| Time of electrolysis (Q) | 0.657205 | 0.00683 | −0.982773 | 0.0157 |
| Salt concentration (L) and current density (L) | −86.5119 | 0.0569 | 89.0190 | 0.00255 |
| Salt concentration (L) and time of electrolysis (L) | −115.824 | 0.00522 | - | - |
| Current density (L) and time of electrolysis (L) | −0.655809 | 0.0224 | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ulatowski, K.; Jeżak, R.; Sobieszuk, P. Impact of Process Parameters on the Diameter of Nanobubbles Generated by Electrolysis on Platinum-Coated Titanium Electrodes Using Box–Behnken Experimental Design. Energies 2021, 14, 2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14092542
Ulatowski K, Jeżak R, Sobieszuk P. Impact of Process Parameters on the Diameter of Nanobubbles Generated by Electrolysis on Platinum-Coated Titanium Electrodes Using Box–Behnken Experimental Design. Energies. 2021; 14(9):2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14092542
Chicago/Turabian StyleUlatowski, Karol, Radosław Jeżak, and Paweł Sobieszuk. 2021. "Impact of Process Parameters on the Diameter of Nanobubbles Generated by Electrolysis on Platinum-Coated Titanium Electrodes Using Box–Behnken Experimental Design" Energies 14, no. 9: 2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14092542
APA StyleUlatowski, K., Jeżak, R., & Sobieszuk, P. (2021). Impact of Process Parameters on the Diameter of Nanobubbles Generated by Electrolysis on Platinum-Coated Titanium Electrodes Using Box–Behnken Experimental Design. Energies, 14(9), 2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14092542