An Optimal Integrated Control Scheme for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator-Based Wind Turbines under Asymmetrical Grid Fault Conditions
Abstract
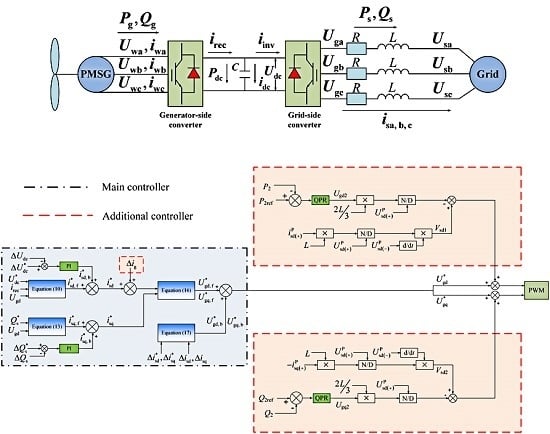
:1. Introduction
2. Design of Main Controller
2.1. Introduction of Differential Flatness-Based Theory
- (a)
- Generation of the predicted reference trajectory: the desired reference state trajectory should be generated according to the flat output signals and then the corresponding controlled input trajectory is produced as the feedforward control variables;
- (b)
- Feedback compensation for tracking error: feedback compensation is used to adjust the tracking error caused by system uncertainty or external disturbances.
2.2. Differential Flatness-Based Description of PMSG Grid-Side System
2.3. Design of Differential Flatness-Based Controller for Grid-Side Voltage Source Converter
3. Design of the Additional Controller
3.1. Compensation Controller to Restrain the Second Harmonic Oscillations of Transmission Power
3.2. Control Strategy to Reduce DC-Link Overvoltage
4. Simulation Results
4.1. Simulation Model Description
4.2. Cases Studies
4.2.1. Case 1: Single-Phase-to-Ground Short-Circuit Grid Fault
4.2.2. Case 2: Phase-to-Phase Short-Circuit Grid Fault
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, P.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Liu, C.; Hu, T.; Wang, W.W. The impact of LVRT characteristics on the stability of Northwest China grid with large scale wind power. In Proceedings of the 2013 2nd IET Renewable Power Generation Conference (RPG 2013), Beijing, China, 9–11 September 2013.
- Yao, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, Z.; Liu, A. Coordinated control of a DFIG-based wind-power generation system with SGSC under distorted grid voltage conditions. Energies 2013, 6, 2541–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, O.; Yazdani, A. A control strategy for power regulation in a direct-drive WECS with flexible drive-train. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2014, 5, 1156–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Jeung, Y.; Lee, D.; Kim, H. LVRT scheme of PMSG wind power systems based on feedback linearization. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 2376–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iov, F.; Hansen, A.D.; Sørensen, P.; Cutululis, N.A. Mapping of Grid Faults and Grid Codes; Risø National Laboratory: Roskilde, Denmark, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Freire, N.M.A.; Marques Cardoso, A.J. A fault-tolerant direct controlled PMSG drive for wind energy conversion systems. IEEE Trans Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, S.Y.; Li, G.J.; Peng, L.; Sun, Y.Z.; Lie, T.T. A nonlinear control for enhancing HVDC light transmission system stability. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2007, 29, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.H.; Shi, X.C.; Fu, C.; Wang, Y. A high-performance nonlinear control strategy of three-phase VSC systems. Proc. CSEE 2014, 34, 863–871. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, Y.A.-R.I.; El-Saadany, E.F. A control scheme for PWM voltage-source distributed-generation inverters for fast load-voltage regulation and effective mitigation of unbalanced voltage disturbances. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 2072–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.D.; Wai, R.-J.; Liao, Y. Design of backstepping power control for grid-side converter of voltage source converter-based high-voltage DC wind power generation system. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2013, 7, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Liang, H. Dual-PI rotor current control of doubly-fed induction wind generators under unbalanced grid voltage. In Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference (APPEEC), Wuhan, China, 25–28 March 2011.
- Ng, C.H.; Ran, L.; Bumby, J. Unbalanced-grid-fault ride-through control for a wind turbine inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2008, 44, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moawwad, A.; El Moursi, M.S.; Xiao, W.D. A novel transient control strategy for VSC-HVDC connecting offshore wind power plant. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2014, 5, 1056–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Williams, B.W. Compensation of network voltage unbalance using doubly fed induction generator-based wind farms. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2009, 3, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Hu, J.B. Sliding-mode-based direct power control of grid-connected wind-turbine-driven doubly fed induction generators under unbalanced grid voltage conditions. IEEE Trans Energy Convers. 2012, 27, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Huang, S.D.; Zheng, L.; Xu, Q.; Huang, K.Y. Sliding model SVM-DPC for grid-side converter of D-PMSG under asymmetrical faults. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Beijing, China, 20–23 August 2011.
- Wessels, C.; Gebhardt, F.; Fuchs, F.W. Fault ride-through of a DFIG wind turbine using a dynamic voltage restorer during symmetrical and asymmetrical grid faults. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalakshmi, M.; Latha, S.; Ranjithpandi, S. Sliding mode control for PMSG based dynamic voltage restorer. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Energy Efficient Technologies for Sustainability (ICEETS), Nagercoil, India, 10–12 April 2013.
- Houari, A.; Renaudineau, H.; Martin, J.-P.; Pierfederici, S.; Meibody-Tabar, F. Flatness-based control of three-phase inverter with output LC filter. IEEE Trans Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 2890–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimene, M.; Payman, A.; Dakyo, B. Flatness-based control of a variable-speed wind-energy system connected to the grid. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Ecological Vehicles and Renewable Energies, Monte-Carlo Monaco, Monaco, 25–27 March 2014.
- Aldwaihi, H.A.; Delaleau, E. Maximum power point tracker of a wind generator based on the flatness-based control. In Proceedings of the Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 17–22 September 2011.
- Thounthong, P.; Pierfederici, S.; Davat, B. Analysis of differential flatness-based control for a fuel cell hybrid power source. IEEE Trans Energy Convers. 2010, 25, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenmeyer, V.; Delaleau, E. Exact feedforward linearization based on differential flatness. Int. J. Control 2003, 76, 537–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Chung, I.; Moon, S. Tuning of the PI controller parameters of a PMSG wind turbine to improve control performance under various wind speeds. Energies 2015, 8, 1406–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Kim, C.; Park, J.; Kang, D.; Kim, J. Circulating current control in MMC under the unbalanced voltage. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2013, 28, 1952–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumper, J.F.; Hagenmeyer, V.; Kuehl, S.; Kennel, R. Deadbeat control for electrical drives: A robust and performant design based on differential flatness. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 4585–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Chen, W.J.; Liserre, M.; Blaabjerg, F. Power controllability of a three-phase converter with an unbalanced AC source. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 1591–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trilla, L.; Gomis-Bellmunt, O.; Junyent-Ferre, A.; Mata, M.; Sanchez Navarro, J.; Sudria-Andreu, A. Modeling and validation of DFIG 3-MW wind turbine using field test data of balanced and unbalance voltage sags. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2011, 2, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Chen, C.; Lai, J.; Moon, S. Admittance compensation in current loop control for a grid-tie LCL fuel cell inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2008, 23, 1716–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, A.; Chen, Y.D.; Shuai, Z.K.; Tu, C.M. An improved reactive current detection and power control method for single-phase photovoltaic grid-connected DG system. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2013, 28, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlader, A.M.; Urasaki, N.; Yona, A.; Senjyu, T.; Saber, A.Y. Design and implement a digital H∞ robust controller for a MW-class PMSG-based grid-interactive wind energy conversion system. Energies 2013, 6, 2084–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.Y.; Kim, M.K.; Choi, J.W. Hybrid intelligent control method to improve the frequency support capability of wind energy conversion systems. Energies 2015, 8, 11430–11451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, M.; Rodriguez, P.; Vazquez, S.; Luna, A.; Carrasco, J.M.; Teodorescu, R. Decoupled double synchronous reference frame current controller for unbalanced grid voltage conditions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Raleigh, NC, USA, 15–20 September 2012.
- Song, H.-S.; Nam, K. Dual current control scheme for PWM converter under unbalanced input voltage conditions. IEEE Trans Ind. Electron. 1999, 46, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


















| Name | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Blade radius | 58 | m |
| Cut-in speed | 4 | m/s |
| Rated wind speed | 12 | m/s |
| Cut-out speed | 25 | m/s |
| Rated power | 5.2 | MVA |
| Rated speed | 12.24 | r/min |
| Air density | 1.225 | kg/m3 |
| Cp | 0.466 | - |
| Name | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Rated voltage | 3 | kV |
| Rated power | 5.3 | MVA |
| Number of poles | 49 | - |
| Rated frequency | 10 | Hz |
| d-axis reactance | 11 | mH |
| q-axis reactance | 11 | mH |
| Leakage reactance | 1 | mH |
| Name | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Rated DC-link voltage | 4.8 | kV |
| DC-link capacitor | 8000 | µF |
| Pulse-width-modulation (PWM) converter switching frequency | 4000 | Hz |
| Inductance at the AC side of grid-side converter | 0.0008 | H |
| Resistance at the AC side of grid-side converter Transmission inductance | 0.002 | Ω |
| 1.5 | H | |
| Transmission resistance | 0.1 | Ω |
| Ratio of the step-up transformer | 3/35 | kV |
| Rated capacity of the step-up transformer | 50 | MVA |
| Frequency of grid-side and transmission system | 50 | Hz |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Liu, C.; Li, G. An Optimal Integrated Control Scheme for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator-Based Wind Turbines under Asymmetrical Grid Fault Conditions. Energies 2016, 9, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9040307
Wang D, Liu C, Li G. An Optimal Integrated Control Scheme for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator-Based Wind Turbines under Asymmetrical Grid Fault Conditions. Energies. 2016; 9(4):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9040307
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Dan, Chongru Liu, and Gengyin Li. 2016. "An Optimal Integrated Control Scheme for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator-Based Wind Turbines under Asymmetrical Grid Fault Conditions" Energies 9, no. 4: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9040307
APA StyleWang, D., Liu, C., & Li, G. (2016). An Optimal Integrated Control Scheme for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator-Based Wind Turbines under Asymmetrical Grid Fault Conditions. Energies, 9(4), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9040307