Effects of Tungsten Addition on the Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Fe-3.5B Alloy in Liquid Zinc
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Preparation of Samples
2.2. Immersion Test
2.3. Material Characterization
3. Results
3.1. As-Cast Microstructure and Phase Identification
3.2. Corrosion Rate and Morphology of the Corrosion Layer
3.3. Element Distribution in the Corrosion Layer
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of W Addition on the Microstructure of the Fe-3.5B Alloy
4.2. Effect of W Addition on the Corrosion Resistance of the Fe-3.5B Alloy
4.3. Corrosion Mechanism of Fe-3.5B-xW Alloys
- (1)
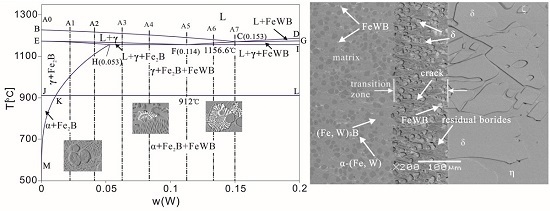
- Corrosion of the α-(Fe, W) matrix. As the metal matrix comes into contact with liquid zinc, the α-(Fe, W) phase is the first victim of corrosion. A succession of Γ, Γ1, δ, ζ, and η-Zn compounds are generated. In this paper, the existences of δ, ζ, and η-Zn phases are confirmed by XRD; however, the Γ phase is too thin to be detected.
- (2)
- Formation of cracks along the reticular borides. Numerous Fe-Zn compounds and the refined reticular borides can act as a barrier and impede the diffusion of liquid zinc. Hence, it is difficult for zinc atoms to find the defects through which they can diffuse in the completeness of the boride net structure. Due to the different coefficients of thermal expansion of the Fe-Zn compounds a lot of micro-cracks are initiated in the reticular borides and the diffusion channels for zinc atoms are formed.
- (3)
- Formation of the transition region. The Zn atoms diffuse along the cracks to the α-(Fe, W) wrapped by the reticular borides, and the δ phase is generated. As the content of Zn is not high, the borides still maintain a relatively intact reticular structure. This leads to a transition region consisting of the uncorroded boride and δ compounds. Meanwhile, the cracks become very obvious.
- (4)
- Spalling of the reticular borides. The cracks are further propagated along the borides and the corrosion products are transported by thermo-stress and the flow of liquid zinc. Eventually, the borides are spalled off.
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The morphology of the borides in the Fe-3.5B-xW alloys is different, several types exist, such as the reticular borides (Fe, W)2B, the rod borides (Fe, W)3B, and the white borides FeWB with their flower-like shape. Furthermore, the network structure of the eutectic borides is refined significantly by W inclusion.
- (2)
- The alloy with a 11 wt % W addition exhibits the best corrosion resistance to liquid zinc at 520 °C. The corrosion of the α-(Fe, W) phase occurs preferentially. As W addition increases, the corrosion resistance of the α-(Fe, W) phase is improved. The W addition can also improve the stability of the borides.
- (3)
- Micro-cracks are initiated along the boride grain boundaries, and result in the fracture-spalling of the borides.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giorgi, M.L.; Durighello, P.; Nicolle, R.; Guillot, J.B. Dissolution kinetics of iron in liquid zinc. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 5803–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marder, A.R. The metallurgy of zinc-coated steel. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2000, 45, 191–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.R.B.; van Ooij, W.J. High-temperature batch hot-dip galvanizing. Part 1. General description of coatings formed at 560 °C. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1997, 89, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Lin, J.P.; Wang, Y.L.; Chen, G.L. The corrosion of intermetallic alloys in liquid zinc. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 428, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Lin, J.P.; Wang, Y.L.; Chen, G.L. The corrosion of Fe3Al alloy in liquid zinc. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 1340–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Mei, X.; Jun, S. Materials resistance to liquid zinc corrosion on surface of sink roll. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2007, 14, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, B.G.; Hwang, S.Y.; Kim, M.C.; Kim, K.Y. Reaction of WC-Co coating with molten zinc in a zinc pot of a continuous galvanizing line. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 39, 5803–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K. Wear of cobalt-based alloys sliding in molten zinc. Wear 2003, 255, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Barbero, E.; Xu, J.; Burris, M.; Chang, K.M. Liquid metal corrosion of 316L, Fe3Al, and FeCrSi in molten Zn-Al baths. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 2049–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.G.; Xiao, Q.; Kuang, J.C.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Xing, J.D. Effect of rare and titanium additions on the microstructures and properties of low carbon Fe-B cast steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 466, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xing, J.; Fu, H.; Yi, D.; Zhi, X. Effects of boron concentration on the corrosion resistance of Fe-B alloys immersed in 460 °C molten zinc bath. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 2208–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xing, J.; Liu, G.; Yi, D.; Fu, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Effect of chromium concentration on microstructure and properties of Fe-3.5B alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 6800–6808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, K. Effect of chromium on microstructure and properties of high boron white cast iron. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2008, 39, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xing, J.; Yi, D.; Fu, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhu, B. Effects of chromium addition on corrosion resistance of Fe-3.5B alloy in liquid zinc. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 4902–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xing, J.; Fu, H.; Yi, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, B.; Gao, Y. Microstructure and interface characteristics of Fe-B alloy in liquid 0.25 wt % Al-Zn at various bath temperatures. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 132, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xing, J.; Fu, H.; Yi, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, B.; Ma, S. Interfacial morphology and corrosion resistance of Fe-B cast steel containing chromium and nickel in liquid zinc. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 2826–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xing, J.; Fu, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J. Microstructure and crystallography of borides and secondary precipitation in 18 wt % Cr-4 wt % Ni-1 wt % Mo-3.5 wt % B-0.27 wt % C steel. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinz, H.P.; Nigg, B.; Hoffmann, A. The corrosion behaviour of refractory metals against molten and evaporated zinc. In Proceedings of the 17th Plansee Seminar 2009, Reutte, Austria, 25–29 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.F.; Xing, J.D.; Lv, L.L. Effect of tungsten addition on the toughness and hardness of Fe2B in wear-resistant Fe-B-C cast alloy. Mater. Charact. 2013, 75, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draley, J.E.; Weeks, J.R. Corrosion by Liquid Metal; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1970; p. 251. [Google Scholar]
- Rompaey, T.V.; Kumar, K.C.H.; Wollants, P.J. Thermodynamic optimization of the B-Fe system. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 334, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, P. A thermodynamic evaluation of the C-Cr-Fe-W system. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1988, 19, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duschanek, H.; Rogl, P. Critical assessment and thermodynamic calculation of the binary system boron-tungsten (B-W). J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 1995, 16, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliţanu, N. Nanostructure formation and soft magnetic properties evolution in Fe91 − xWxB9 amorphous alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 2002, 90, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leithe-Jasper, A.; Klesnar, H.; Rogl, P.; Komai, M.; Ken-lchi, T. Reinvestigation of isothermal sections in M (M = Mo, W)-Fe-B ternary systems at 1323 K. J. Jpn. Inst. Met. 2000, 64, 154–162. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Xing, J.; Fu, H.; He, Y.; Bai, Y.; Li, Y.; Bai, Y. Interface characteristics and corrosion behaviour of oriented bulk Fe2B alloy in liquid zinc. Corros. Sci. 2014, 78, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsipas, D.N.; Triantafyllidis, G.K.; Kiplagat, J.K.; Psillaki, P. Degradation behaviour of boronized carbon and high alloy steels in molten aluminium and zinc. Mater. Lett. 1998, 37, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xing, J.; Ma, S.; et al. Effect of Fe2B orientation on erosion–corrosion behavior of Fe-3.5 wt % B steel in flowing zinc. Corros. Sci. 2015, 98, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Samples | B | C | Si | W | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0 | 3.50 | 0.10–0.15 | 0.43–0.51 | 0 | Balance |
| A1 | 3.50 | 0.10–0.15 | 0.43–0.51 | 2 | Balance |
| A2 | 3.50 | 0.10–0.15 | 0.43–0.51 | 4 | Balance |
| A3 | 3.50 | 0.10–0.15 | 0.43–0.51 | 6 | Balance |
| A4 | 3.50 | 0.10–0.15 | 0.43–0.51 | 8 | Balance |
| A5 | 3.50 | 0.10–0.15 | 0.43–0.51 | 11 | Balance |
| A6 | 3.50 | 0.10–0.15 | 0.43–0.51 | 13 | Balance |
| A7 | 3.50 | 0.10–0.15 | 0.43–0.51 | 15 | Balance |
| Sample | Phase | Fe | W | B | Ratio of Fe and B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0 | α-Fe | 100.00 | - | - | - |
| Fe2B | 67.90 | - | 32.10 | 2:1 | |
| A7 | α-(Fe, W) | 98.97 | 1.03 | - | - |
| (Fe, W)3B | 75.56 | 3.11 | 21.33 | 3:1 | |
| FeWB | 34.05 | 32.28 | 33.67 | 1:1 |
| Number | Fe | W | B | Zn | Phase | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt % | at % | wt % | at % | wt % | at % | wt % | at % | ||
| 1 | 81.97 | 73.93 | 11.35 | 3.11 | 4.58 | 21.34 | 2.10 | 1.62 | (Fe, W)3B |
| 2 | 42.19 | 37.93 | 32.48 | 8.87 | 8.70 | 40.42 | 16.63 | 12.77 | FeBZnx |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Yin, F.; Ouyang, X.; Li, Z. Effects of Tungsten Addition on the Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Fe-3.5B Alloy in Liquid Zinc. Materials 2017, 10, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10040399
Liu X, Wang M, Yin F, Ouyang X, Li Z. Effects of Tungsten Addition on the Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Fe-3.5B Alloy in Liquid Zinc. Materials. 2017; 10(4):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10040399
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xin, Mengmeng Wang, Fucheng Yin, Xuemei Ouyang, and Zhi Li. 2017. "Effects of Tungsten Addition on the Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Fe-3.5B Alloy in Liquid Zinc" Materials 10, no. 4: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10040399
APA StyleLiu, X., Wang, M., Yin, F., Ouyang, X., & Li, Z. (2017). Effects of Tungsten Addition on the Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Fe-3.5B Alloy in Liquid Zinc. Materials, 10(4), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10040399