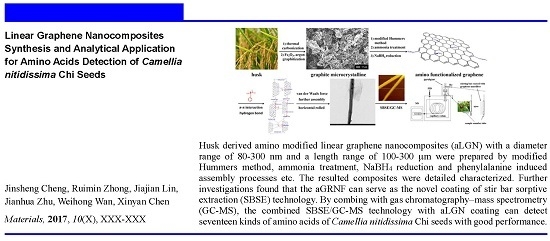
Linear Graphene Nanocomposite Synthesis and an Analytical Application for the Amino Acid Detection of Camellia nitidissima Chi Seeds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
3.1. Possible Mechanism for the aLGN Formation
3.2. aLGN Coating Based SBSE/GC-MS Detection for Camellia Nitidissima Chi Seeds
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Apparatus and Methods
4.3. aLGN Nanocomposites Synthesis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allen, M.J.; Tung, V.C.; Kaner, R.B. Honeycomb carbon: A review of graphene. Chem. Rev. 2009, 110, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diba, M.; Fam, D.W.H.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Shaffer, M.S. Electrophoretic deposition of graphene–related materials: A review of the fundamentals. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 82, 83–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Aksay, I.A. Graphene based electrochemical sensors and biosensors: A review. Electroanalsis 2010, 22, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.S.; Zhang, G.C.; Du, J.; Tang, L.H.; Xu, J.Y.; Li, J.H. New role of graphene oxide as active hydrogen donor in the recyclable palladium nanoparticles catalyzed ullmann reaction in environmental friendly ionic liquid/supercritical carbon dioxide system. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 3485–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Du, J. Facile synthesis of germanium-graphene nanocomposites and their application as anode materials for lithium ion batteries. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundeberg, M.B.; Gao, Y.; Woessner, A.; Tan, C.; Alonso–González, A.; Watanabe, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Hone, J.; Hillenbrand, R.; Koppens, F.H.L. Thermoelectric detection and imaging of propagating graphene plasmons. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ye, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, F.P.; Lu, X.P.; Xie, Y.Z.; Chen, S.H.; Tan, H.L.; Xu, F.G.; Song, Y.H. Hierarchical nanocomposites of Co3O4/polyaniline nanowire arrays/reduced graphene oxide sheets for amino acid detection. Sens. Actuator B: Chem. 2014, 203, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, Y.; Furukawa, K.; Matsuo, K.; Inoue, S.; Hayashi, K.; Hibino, H. On-chip graphene oxide aptasensor for multiple protein detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 866, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Wan, W.; Zhu, W. One-pot solvothermal synthesis of TiO2 nanobelt/graphene composites for selective renal cancer cells destruction. Chin. J. Chem. 2016, 34, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, M. Hydrothermal route for cutting graphene sheets into blue-luminescent graphene quantum dots. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abolhasani, M.M.; Shirvanimoghaddam, K.; Naebe, M. PVDF/graphene composite nanofibers with enhanced piezoelectric performance for development of robust nanogenerators. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 138, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.S.; Du, J.; Zhu, W.J. Facile synthesis of three-dimensional chitosan-graphene mesostructures for reactive black 5 removal. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Lu, W.; Li, Q.; Byun, J.H.; Oh, Y.; Chou, T.W. Graphene-based fibers: A Review. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 5113–5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, B.; Peng, L.; Xu, Z.; Gao, C. Wet-spinning of continuous montmorillonite-graphene fibers for fire-resistant lightweight conductors. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5214–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.Q.; Chen, Z.Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Tang, H.; Jiang, Y.S.; Wei, X.; Li, X.Y.; Qi, X.X. Isolation and characterization of polymorphic microsatellite loci in Camellia nitidissima Chi (Theaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2010, 97, 89–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luong, V.D.; Luu, H.T.; Nguyen, T.Q.T.; Nguyen, Q.D. Camellia luteopallida (Theaceae), a new species from Vietnam. Ann. Bot. Fen. 2016, 53, 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J. N.; Lin, H. Y.; Yang, N. S.; Li, Y.H.; Lee, M.W.; Chuang, C.H.; Ho, C.T.; Kuo, S.C.; Way, T.D. Chemical constituents and anti-cancer activity of yellow Camellias against MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9638–9644. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Z.C.; Qi, X.X.; Wei, X.; Chen, Z.Y.; Tang, H.; Chai, S.F. Nutrient composition in leaves of cultivated and wild Camellia Nitidissima. Pak. J. Bot. 2012, 44, 635–638. [Google Scholar]
- Berdahl, B.J.; Carle, G.C.; Oyama, V.I. Automatic amino acid analyzer. Anal. Biochem. 1971, 88, 332–333. [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira, J.M.F. Stir-bar sorptive extraction: 15 years making sample preparation more environment-friendly. Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 71, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; He, M.; Wu, X.; Chen, B.B.; Hu, B. Graphene oxide/polyethyleneglycol composite coated stir bar for sorptive extraction of fluoroquinolones from chicken muscle and liver. J. Chromat. A 2015, 1418, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltussen, E.; Sandra, P.; David, F.; Cramers, C. Stir bar sorptive extraction (SBSE), a novel extraction technique for aqueous samples: Theory and principles. J. Microcol. Sep. 1999, 11, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, X.; Hu, B. Preparation of sol–gel polyethylene glycol-polydimethylsiloxane-poly (vinyl alcohol)-coated sorptive bar for the determination of organic sulfur compounds in water. J. Chromat. A 2008, 1202, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.B.; Cheng, J.S.; Ma, Q.; Feng, Y.Q.; Li, J.H. Graphene-polymer composite: extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water samples by stir rod sorptive extraction. Anal. Meth. 2011, 3, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.S.; Tang, L.H.; Li, J.H. Palladium nanoparticles-decorated graphene nanosheets as highly regioselective catalyst for cyclotrimerization reaction. J. Nanosci. Nanotech. 2011, 11, 5159–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Samulski, E.T. Synthesis of water soluble graphene. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1679–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.L.; Cheng, J.S.; Li, J.H.; Wang, Y.S. Graphene as a novel matrix for the analysis of small molecules by MALDI–TOF MS. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6208–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.S.; Yang, W.; Xiao, D.; Sheng, X.H.; Yang, X.; Shuai, Z.G.; Luo, Y.; Yao, J.N. Single crystalline submicrotubes from small organic molecules. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 6430–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.H.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, J.E.; Choi, E.Y.; Kim, S.O. Peptide/graphene hybrid assembly into core/shell nanowires. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2060–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, Q.; Geng, Z.; Tang, G. Extraction-separation and determination of amino acid in seeds of Rubia Cordifolia L. J. Shanxi Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 1996, 12, 118–119. [Google Scholar]
- Ochiai, N.; Sasamoto, K.; David, F.; Sandra, P. Solvent-assisted stir bar sorptive extraction by using swollen polydimethylsiloxane for enhanced recovery of polar solutes in aqueous samples: Application to aroma compounds in beer and pesticides in wine. J. Chromat. A 2016, 1455, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Xing, S.; Liu, S.; Wu, H.; Wang, S.; Zang, X.; Ma, W. GC-MS analysis of volatile components of mango (Mangifera indica L. var Zihua) fruits. Food Sci. 2010, 31, 220–223. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, S.; Dong, L.; Wu, C. Use of a novel sol–gel Dibenzo8-Crown-6 solid-phase microextraction fiber and a new derivatizing reagent for determination of aliphatic amines in lake water and human urine. Chromatographia 2003, 58, 615–621. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.S.; Wan, W.H.; Chen, X.Y.; Zheng, Q.X. Preparation and structural characterization of graphene by rice husk. Transact. CSAE 2015, 31, 88–294. [Google Scholar]
- Hummers, W.; Offeman, R. Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 339–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Entry | Amino Acids (Retention Time/min) | Relative Content 2 (mg/g Dry Wet) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | Ala (13.06) Gly (13.65) Thr 3 (14.07) Ser (14.52) Val 3 (15.64) Leu 3 (17.65) Ile 3 (17.91) Cys (18.59) Pro (21.14) Met 3 (24.39) Asp (26.90) Phe 3 (27.21) Glu (30.31) Lys 3 (30.64) Tyr (34.55) His (35.16) Arg (37.61) EAAs Total | 4.9 3.7 2.1 4.3 4.1 6.6 3.2 0.6 4.8 0.5 7.0 4.2 7.5 5.1 1.7 1.5 5.0 25.8 66.8 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, J.; Zhong, R.; Lin, J.; Zhu, J.; Wan, W.; Chen, X. Linear Graphene Nanocomposite Synthesis and an Analytical Application for the Amino Acid Detection of Camellia nitidissima Chi Seeds. Materials 2017, 10, 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10040443
Cheng J, Zhong R, Lin J, Zhu J, Wan W, Chen X. Linear Graphene Nanocomposite Synthesis and an Analytical Application for the Amino Acid Detection of Camellia nitidissima Chi Seeds. Materials. 2017; 10(4):443. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10040443
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Jinsheng, Ruimin Zhong, Jiajian Lin, Jianhua Zhu, Weihong Wan, and Xinyan Chen. 2017. "Linear Graphene Nanocomposite Synthesis and an Analytical Application for the Amino Acid Detection of Camellia nitidissima Chi Seeds" Materials 10, no. 4: 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10040443
APA StyleCheng, J., Zhong, R., Lin, J., Zhu, J., Wan, W., & Chen, X. (2017). Linear Graphene Nanocomposite Synthesis and an Analytical Application for the Amino Acid Detection of Camellia nitidissima Chi Seeds. Materials, 10(4), 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10040443