Characteristics of Carrier Transport and Crystallographic Orientation Distribution of Transparent Conductive Al-Doped ZnO Polycrystalline Films Deposited by Radio-Frequency, Direct-Current, and Radio-Frequency-Superimposed Direct-Current Magnetron Sputtering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Hall Mobility and Carrier Concentration
2.2. Texture Evolution
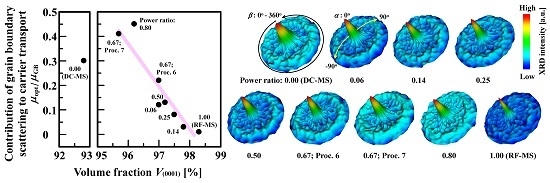
2.3. Correlation between Texture Evolution and Carrier Transport
3. Experimental Details
3.1. Film Deposition
3.2. Characterization
4. Summary
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Out-of-Plane Grazing-Incidence XRD Profiles Obtainable in AZO Films with (0001) and (10–11) Orientations


| Magnitude of Differences in Angle, (|ψD − ψ|) (deg) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Diffraction Peak | (0001) Orientation | Orientation |
| 0002 | 17.21 | 44.29 |
| 0004 | 36.28 | 25.22 |
| 74.12 | 12.52 | |
| 43.49 | 18.13 | |
| 19.00 | 4.97 | |
| 25.83 | ||
| 0.24 | 1.42 | |
| 19.08 | ||
| 15.87 | 3.89 | |
| 11.31 | ||
| 31.76 | 1.14 | |
| 10.76 | ||
| 61.71 | 12.11 | |
| 24.06 | 7.87 | |
| 10.61 | 17.21 | |
| 56.82 | 4.79 | |
| 40.34 | 8.96 | |
| 21.24 | ||
| 22.16 | ||
| 23.13 | 13.72 | |
| 18.32 | ||
| 38.48 | ||
| 6.16 | 5.30 | |
| 22.60 | ||
| 34.21 | ||
References
- Minami, T.; Sato, H.; Nanto, H.; Takata, S. Group III impurity doped zinc oxide thin films prepared by RF magnetron sputtering. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1985, 24, L781–L784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, T. New n-type transparent conducting oxides. MRS Bull. 2000, 25, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, K.; Manabw, H.; Umezu, N.; Mori, I.; Ushiro, T.; Nakabayashi, I. Film properties of ZnO:Al prepared by cosputtering of ZnO:Al and either Zn or Al targets. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1997, 15, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Park, K.C.; Ma, D.Y. Structural, electrical and optical properties of aluminum doped zinc oxide films prepared by radio frequency magnetron sputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 81, 7764–7772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addonizio, M.L.; Antonania, A.; Cantele, G.; Privato, C. Transport mechanisms of RF sputtered Al-doped ZnO films by H2 process gas dilution. Thin Solid Films 1999, 49, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kon, M.; Song, P.K.; Shigesato, Y.; Frach, P.; Mizukami, A.; Suzuki, K. Al-doped ZnO films deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering in mid-Frequency mode with dual cathodes. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 41, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Gordon, R.G. Textured aluminum-doped zinc oxide thin films from atmospheric pressure chemical-vapor deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 1992, 71, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramatsu, M.; Imaeda, K.; Horio, N.; Nawata, N. Transparent conducting ZnO thin films prepared by XeCl excimer laser ablation. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1998, 16, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Gilmore, C.M.; Horwitz, J.S.; Pique, A.; Murata, H.; Kushto, G.P.; Schlaf, R.; Kafafi, Z.H.; Chrisey, D.B. Transparent conducting aluminum-doped zinc oxide thin films for organic light-emitting devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 76, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agura, H.; Suzuki, A.; Matsushita, T.; Aoki, T.; Okuda, M. Low resistivity transparent conducting Al-doped ZnO films prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Thin Solid Films 2003, 445, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Cameron, D.C. Aluminum-doped zinc oxide transparent conductors deposited by the sol-gel process. Thin Solid Films 1994, 238, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musat, V.; Teixeira, B.; Fortunato, E.; Monteiro, R.C.C.; Vilarinho, P. Al-doped ZnO thin films by sol-gel method. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 180–181, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhouane, B.H.T. Structural and electrical properties of aluminum-doped zinc oxide films prepared by sol-gel process. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 25, 3301–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomoto, J.; Inaba, K.; Osada, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Makino, H.; Yamamoto, T. Highly (0001)-oriented Al-doped ZnO polycrystalline films on amorphous glass substrates. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 125302-1–125302-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomoto, J.; Makino, H.; Yamamoto, T. Carrier mobility of highly transparent conductive Al-doped ZnO polycrystalline films deposited by radio-frequency, direct-current, and radio-frequency-superimposed direct-current magnetron sputtering: Grain boundary effect and scattering in the grain bulk. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 045304-1–045304-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomoto, J.; Makino, H.; Yamamoto, T. High-Hall-mobility Al-doped ZnO films having textured polycrystalline structure with a well-defined (0001) orientation. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 320-1–320-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomoto, J.; Makino, H.; Yamamoto, T. Correlation between carrier transport and orientation evolution of polycrystalline transparent conductive Al-doped ZnO films. Thin Solid Films 2016, 620, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomoto, J.; Inaba, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Makino, H.; Yamamoto, T. Interface layer to tailor the texture and surface morphology of Al-doped ZnO polycrystalline films on glass substrates. J. Cryst. Growth 2017, 468, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, N.; Nishihara, T.; Goto, S.; Xu, J.; Ito, T. Control of preferred orientation for ZnOx films: Control of self-texture. J. Cryst. Growth 1993, 130, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.M.; Zakria, M.; Shakoor, R.I.; Raffi, M.; Ahmad, M. Mechanisms of composite-hydroxide-mediated approach for the synthesis of functional ZnO nanostructures and morphological dependent optical emissions. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2015, 6, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkholz, M.; Selle, B.; Fenske, F.; Fuhs, W. Structure-function relationship between preferred orientation of crystallites and electrical resistivity in thin polycrystalline ZnO:Al films. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 205414-1–205414-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardeniers, J.G.E.; Rittersma, Z.M.; Burger, G.J. Preferred orientation and piezoelectricity in sputtered ZnO films. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 83, 7844–7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, T.; Suzuki, S.; Miyata, T. Electrical Conduction Mechanism of Highly Transparent and Conductive ZnO Thin Films. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 2001, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellmer, K. Resistivity of polycrystalline zinc oxide films: Current status and physical limit. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2001, 34, 3097–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, J.Y.W. The electrical properties of polycrystalline silicon films. J. Appl. Phys. 1975, 46, 5247–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarkiewicz, T.; Zakrzewska, K.; Leja, E. Scattering of charge carriers in transparent and conducting thin oxide films with a non-parabolic conduction band. Thin Solid Films 1989, 174, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Avrutin, V.; Izyumskaya, N.; Özgür, Ü.; Yankovich, A.B.; Kvit, A.V.; Voyles, P.M.; Morkoç, H. Electron scattering mechanisms in GZO films grown on a-sapphire substrates by plasma-enhanced molecular beam epitaxy. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 103713-1–103713-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Jeong, J.-H.; Park, J.K.; Baik, Y.J.; Kim, I.H.; Seong, T.-Y.; Kim, W.M. Optical analysis of doped ZnO thin films using nonparabolic conduction-band parameters. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 123507-1–123507-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasako, T.; Song, H.; Makino, H.; Shirakata, S.; Yamamoto, T. Temperature dependence of electrical properties of Ga-doped ZnO films deposited by ion-plating with DC arc discharge. Thin Solid Films 2013, 528, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, H. Scattering by Ionized Impurities in Semiconductors. Phys. Rev. 1951, 83, 879–885. [Google Scholar]
- Ridley, B.K. Reconciliation of the Conwell-Weisskopf and Brooks-Herring formulae for charged-impurity scattering in semiconductors: Third-body interference. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 1977, 10, 1589–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, D.; Queisser, H.J. Electron scattering by ionized impurities in semiconductors. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1981, 53, 745–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, B.K. Quantum Processes in Semiconductors, 2nd ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1988; pp. 141–151. [Google Scholar]
- Minami, T.; Sato, H.; Ohashi, K.; Tomofuji, T.; Takata, S. Conduction mechanism of highly conductive and transparent zinc oxide thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering. J. Cryst. Growth 1992, 117, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, N.; Hüpkes, J.; Rau, U. Field Emission at Grain Boundaries: Modeling the Conductivity in Highly Doped Polycrystalline Semiconductors. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2016, 5, 024009-1–024009-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Joubert, D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 1758–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellmer, K.; Bikowski, A. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Doping of ZnO and ZnO Alloys. J. Phys. D 2016, 49, 413002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegard, L. Die Konstitution der Mischkristalle und die Raumerfüllung der Atome. Z. Phys. 1921, 5, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Inaba, K. Introduction to XRD analysis of modern functional thin films using a 2-dimensional detector-(1)GI-XRD. Rigaku J. 2016, 32, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Perrière, J.; Hebert, C.; Jedrecy, N.; Seiler, W.; Zanellato, O.; Portier, X.; Perez-Casero, R.; Millon, E.; Nistor, M. On the relevance of large scale pulsed-laser deposition: Evidence of structural heterogeneities in ZnO thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 123502-1–123502-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, Y.; Yodogawa, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Shibata, N.; Ikuhara, Y. Dopant-segregation-controlled ZnO single-grain-boundary varistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 152112-1–152112-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikowski, A.; Ellmer, K. A comparative study of electronic and structural properties of polycrystalline and epitaxial magnetron-sputtered ZnO:Al and Zn1-xMgxO:Al Films-Origin of the grain barrier traps. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 63709-1–63709-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Oka, N.; Kusayanagi, M.; Nakatomi, S.; Shigesato, Y. Origin of carrier scattering in polycrystalline Al-doped ZnO films. Appl. Phys. Express 2014, 7, 105802-1–105802-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Uehara, K.; Okada, A.; Reddy, S.L.; Endo, T. High resolution X-ray diffraction analyses of (La,Sr)MnO3/ZnO/Sapphire(0001) double heteroepitaxial films. Adv. Mater. Phys. Chem. 2013, 3, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J., II; Bae, J.; Wang, Z.L.; Snyder, R.L. Room-temperature, texture-controlled growth of ZnO thin films and their application for growing aligned ZnO nanowire arrays. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 085609-1–085609-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariosa, D.; Elhordoy, F.; Dalchiele, E.A.; Marotti, R.E.; Stari, C. Texture vs. morphology in ZnO nano-rods: On the x-ray diffraction characterization of electrochemically grown samples. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 124901-1–124901-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, M.; Magalhães, S.; Soares, M.R.; Soares, M.J.; Rino, L.; Alves, E.; Lorenz, K.; Correia, M.R.; Lourenço, A.C.; Monteiro, T. Disorder induced violet/blue luminescence in rf-deposited ZnO films. Phys. Status Solidi C 2013, 10, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, L.; Navarrete-Astorga, E.; Pereyra, C.J.; Cuevas, A.; Romero, R.; Ariosa, D.; Henríquez, R.; Muñoz, E.; Marotti, R.E.; Martín, F.; et al. The Effect of a Sputtered Al-Doped ZnO Seed Layer on the Morphological, Structural and Optical Properties of Electrochemically Grown ZnO Nanorod Arrays. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, D392–D400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Inaba, K. X-ray thin-film measurement techniques VIII. Detectors and series summary. Rigaku J. 2012, 28, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Als-Nielsen, J.; Jacquemain, D.; Kjaer, K.; Leveiller, F.; Lahav, M.; Leiserowitz, L. Principles and applications of grazing incidence X-ray and neutron scattering from ordered molecular monolayers at the air-water interface. Phys. Rep. 1994, 246, 251–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkholz, M. Chaps. 4: Grazing Incidence Configurations. In Thin Film Analysis by X-ray Scattering; Birkholz, M., Ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2006; pp. 143–182. [Google Scholar]
- Birkholz, M. A thin film approach to protein crystallography. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2010, 268, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeone, D.; Baldinozzi, G.; Gosset, D.; Caer, S.L.; Bérar, J.-F. Grazing incidence X-ray diffraction for the study of polycrystalline layers. Thin Solid Films 2013, 530, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Koganezawa, T.; Kikuchi, M.; Ackermann, C.V.; Ackermann, J.; Brisset, H.; Hirosawa, I.; Yoshimoto, N. Crystal structure of oligothiophene thin films characterized by two-dimensional grazing incidence X-ray diffraction. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 53, 01AD01-1–01AD01-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiefer, S.; Huth, M.; Dobrinevski, A.; Nickel, B. Determination of the Crystal Structure of Substrate-Induced Pentacene Polymorphs in Fiber Structured Thin Films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 10316–10317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakudate, T.; Saito, Y.; Yoshimoto, N. Polymorphism in pentacene thin films on SiO2 substrate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 081903-1–081903-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Hosokai, T.; Koganezawa, T.; Yoshimoto, N. In Situ Real-Time X-Ray Diffraction during Thin Film Growth of Pentacene. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2012, 566, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannsfeld, S.C.B.; Tang, M.L.; Bao, Z. Thin Film Structure of Triisopropylsilylethynyl-Functionalized Pentacene and Tetraceno[2,3-b]thiophene from Grazing Incidence X-Ray Diffraction. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Process Number | PDC (W) | PRF (W) | Total Power, (PRF + PDC) (W) | Power Ratio, PRF/(PRF + PDC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proc. 1 | 200 | 0 | 200 | 0.00 |
| Proc. 2 | 150 | 10 | 160 | 0.06 |
| Proc. 3 | 25 | 175 | 0.14 | |
| Proc. 4 | 50 | 200 | 0.25 | |
| Proc. 5 | 100 | 100 | 200 | 0.50 |
| Proc. 6 | 200 | 300 | 0.67 | |
| Proc. 7 | 50 | 100 | 150 | 0.67 |
| Proc. 8 | 200 | 250 | 0.80 | |
| Proc. 9 | 0 | 200 | 200 | 1.00 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nomoto, J.; Inaba, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Watanabe, T.; Makino, H.; Yamamoto, T. Characteristics of Carrier Transport and Crystallographic Orientation Distribution of Transparent Conductive Al-Doped ZnO Polycrystalline Films Deposited by Radio-Frequency, Direct-Current, and Radio-Frequency-Superimposed Direct-Current Magnetron Sputtering. Materials 2017, 10, 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10080916
Nomoto J, Inaba K, Kobayashi S, Watanabe T, Makino H, Yamamoto T. Characteristics of Carrier Transport and Crystallographic Orientation Distribution of Transparent Conductive Al-Doped ZnO Polycrystalline Films Deposited by Radio-Frequency, Direct-Current, and Radio-Frequency-Superimposed Direct-Current Magnetron Sputtering. Materials. 2017; 10(8):916. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10080916
Chicago/Turabian StyleNomoto, Junichi, Katsuhiko Inaba, Shintaro Kobayashi, Takeshi Watanabe, Hisao Makino, and Tetsuya Yamamoto. 2017. "Characteristics of Carrier Transport and Crystallographic Orientation Distribution of Transparent Conductive Al-Doped ZnO Polycrystalline Films Deposited by Radio-Frequency, Direct-Current, and Radio-Frequency-Superimposed Direct-Current Magnetron Sputtering" Materials 10, no. 8: 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10080916
APA StyleNomoto, J., Inaba, K., Kobayashi, S., Watanabe, T., Makino, H., & Yamamoto, T. (2017). Characteristics of Carrier Transport and Crystallographic Orientation Distribution of Transparent Conductive Al-Doped ZnO Polycrystalline Films Deposited by Radio-Frequency, Direct-Current, and Radio-Frequency-Superimposed Direct-Current Magnetron Sputtering. Materials, 10(8), 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10080916