Sol-Gel Derived Active Material for Yb Thin-Disk Lasers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. X-Ray Diffraction
2.2. Raman Spectroscopy
2.3. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
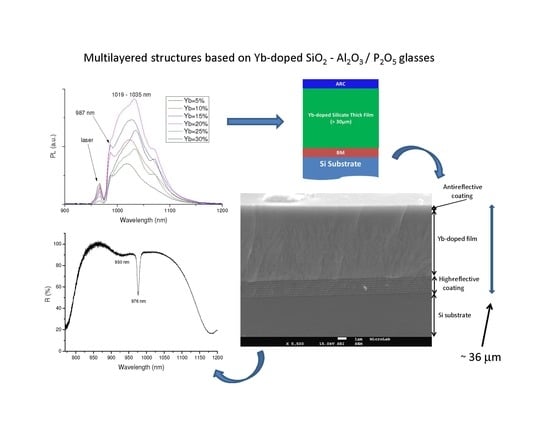
2.4. Photoluminescence Spectroscopy
2.5. Active Disk
2.5.1. TMM Simulations
2.5.2. Active Disk Structure
2.5.3. Active Disk Properties
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Preparation
4.1.1. Bulk Sample Preparation
4.1.2. Film Deposition
4.1.3. Active Disk Preparation
4.2. Sample Characterization
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heckl, O.H.; Kleinbauer, J.; Bauer, D.; Weiler, S.; Metzger, T.; Sutter, D.H. Ultrafast Thin-Disk Lasers. In Ultrashort Pulse Laser Technology—Laser Sources and Applications; Nolte, S., Schrempel, F., Dausinger, F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 195, pp. 93–115. ISBN 978-3-319-17659-8. [Google Scholar]
- Giesen, A.; Speiser, J. Fifteen Years of Work on Thin-Disk Lasers: Results and Scaling Laws. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2007, 13, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TRUMPF. Disk Lasers. Available online: http://www.trumpf-laser.com/en/products/solid-state-lasers/disk-lasers.html (accessed on 5 July 2017).
- BOEING. Boeing Thin Disk Laser Exceeds Performance Requirements During Testing. Available online: http://boeing.mediaroom.com/Boeing-Thin-Disk-Laser-Exceeds-Performance-Requirements-During-Testing (accessed on 5 July 2017).
- Giesen, A.; Hugel, H.; Voss, A.; Wittig, K.; Brauch, U.; Opower, H. Scalable concept for diode-pumped high-power solid-state lasers. Appl. Phys. B 1994, 58, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, G.; Shang, J.; Wang, H.; Qi, L.; Zhu, C.; Guo, F. A multi-pass pumping scheme for thin disk lasers with good anti-disturbance ability. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 4605–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchese, S.V.; Baer, C.R.E.; Peters, R.; Kränkel, C.; Engqvist, A.G.; Golling, M.; Maas, D.J.H.C.; Petermann, K.; Südmeyer, T.; Huber, G.; et al. Efficient femtosecond high power Yb:Lu2O3 thin disk laser. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 16966–16971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, R.; Kränkel, C.; Petermann, K.; Huber, G. Broadly tunable high-power Yb:Lu2O3 thin disk laser with 80% slope efficiency. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 7075–7082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francini, R.; Giovenale, F.; Grassano, U.M.; Laporta, P.; Taccheo, S. Spectroscopy of Er and Er-Yb-doped phosphate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2000, 13, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.C.; Almeida, R.M. Rare earth-doped photonic crystals via sol-gel. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2009, 20, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.G.; Almeida, R.M. Simultaneous broadening and enhancement of the 1.5 micron photoluminescence peak of Er3+ ions embedded in a 1-D photonic crystal microcavity. Appl. Phys. B 2010, 98, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.G.; Almeida, R.M. Elimination of porosity in heavily rare-earth doped sol–gel derived silicate glass films. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2012, 61, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.; Santos, L.F.; Almeida, R.M. Sol-gel derived Yb:YAG polycrystalline ceramics for laser applications. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 83, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, T.V.; Santos, L.F.; Gonçalves, M.C.; Almeida, R.M. Heavily Yb-doped silicate glass thick films. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 81, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, R.N.; Subalakshmi, G. Near-infrared down-conversion in Yb3+:TiO2 for solar cell applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschotta, R.; Nilsson, J.; Barber, P.R.; Caplen, J.E.; Tropper, A.C.; Hanna, D.C. Lifetime quenching in Yb-doped fibers. Opt. Commun. 1997, 136, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinoski, M.; Kaczkan, M.; Piramidowicz, R.; Frukacz, Z.; Sarnecki, J. Cooperative emission in Yb3+: YAG planar epitaxial waveguides. J. Lumin. 2011, 94–95, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RP Photonics Encyclopedia. Available online: http://www.rp-photonics.com/ytterbium_doped_gain_media.html (accessed on 5 July 2017).
- Matarrelli, M.; Montagna, M.; Zampedri, L.; Chiasera, A.; Ferrari, M.; Righini, G.C.; Fortes, L.M.; Gonçalves, M.C.; Santos, L.F.; Almeida, R.M. Self-absorption and Radiation trapping in Er3+-doped TeO2-based glasses. Europhys. Lett. 2005, 71, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouhia, C.; Kasap, S.O. Excitation diffusion in GeGaSe and GeGaS glasses heavily doped with Er3+. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 7709–7714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, J.; Wilson, A. Scherrer after Sixty Years: A Survey and Some New Results in the Determination of Crystallite Size. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1978, 11, 102–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| YbO1.5 (mol%) | τ (μs) | σ × τ (μs) |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 1043 | 1126 |
| 5 | 782 | 1718 |
| 7 | 763 | 1528 |
| 10 | 735 | 5931 |
| 13 | 828 | 5845 |
| 15 | 586 | 4173 |
| 20 | 485 | 4039 |
| 30 | 542 | 4652 |
| YbO1.5 (mol%) | τ (μs) | σ × τ (μs) |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 624 | 5509 |
| 10 | 614 | 8586 |
| 15 | 525 | 9648 |
| 20 | 511 | 11699 |
| 25 | 528 | 6349 |
| 30 | 482 | 7762 |
| SiO2 | PO2.5 | AlO1.5 | YbO1.5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 81 | 16 | − | 3 |
| 79 | 16 | − | 5 |
| 77 | 16 | − | 7 |
| 75 | 15 | − | 10 |
| 73 | 14 | − | 13 |
| 71 | 14 | − | 15 |
| 67 | 13 | − | 20 |
| 58 | 12 | − | 30 |
| 79 | − | 16 | 5 |
| 75 | − | 15 | 10 |
| 71 | − | 14 | 15 |
| 67 | − | 13 | 20 |
| 63 | − | 12 | 25 |
| 58 | − | 12 | 30 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almeida, R.M.; Ribeiro, T.; Santos, L.F. Sol-Gel Derived Active Material for Yb Thin-Disk Lasers. Materials 2017, 10, 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10091020
Almeida RM, Ribeiro T, Santos LF. Sol-Gel Derived Active Material for Yb Thin-Disk Lasers. Materials. 2017; 10(9):1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10091020
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmeida, Rui M., Tiago Ribeiro, and Luís F. Santos. 2017. "Sol-Gel Derived Active Material for Yb Thin-Disk Lasers" Materials 10, no. 9: 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10091020
APA StyleAlmeida, R. M., Ribeiro, T., & Santos, L. F. (2017). Sol-Gel Derived Active Material for Yb Thin-Disk Lasers. Materials, 10(9), 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10091020