PLA-PEG Nanoparticles Improve the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Rosiglitazone on Macrophages by Enhancing Drug Uptake Compared to Free Rosiglitazone
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. PLA-PEG Synthesis and Characterization
2.3. Nanoparticle Formulation and Characterization
2.4. Encapsulation Efficiency
2.5. Release Studies
2.6. In Vitro Studies on Cells: Toxicity, Internalization, and Anti-Inflammatory Potential
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nanoparticle Formulation
3.2. Encapsulation Efficiency
3.3. RSG Release from Nanoparticles
3.4. Cell Viability in the Presence of RSG Nanoparticles
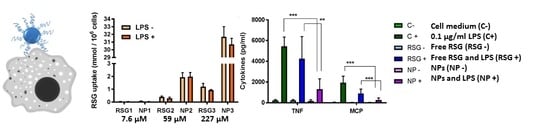
3.5. Inflammation Evaluation in RAW264.7 Cells
3.6. Free RSG and NP Uptake by RAW264.7 Cells
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adamson, P.D.; Dweck, M.R.; Newby, D.E. The vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque: In vivo identification and potential therapeutic avenues. Heart 2015, 101, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naghavi, M.; Falk, E.; Hecht, H.S.; Jamieson, M.J.; Kaul, S.; Berman, D.; Fayad, Z.; Budoff, M.J.; Rumberger, J.; Naqvi, T.Z.; et al. From vulnerable plaque to vulnerable patient—Part iii: Executive summary of the screening for heart attack prevention and education (shape) task force report. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 98, 2H–15H. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, K.J.; Tabas, I. Macrophages in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Cell 2011, 145, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowski, N.; Hillaireau, H.; Vergnaud, J.; Tsapis, N.; Pallardy, M.; Kerdine-Romer, S.; Fattal, E. Surface coating mediates the toxicity of polymeric nanoparticles towards human-like macrophages. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 482, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowski, N.; Hillaireau, H.; Vergnaud-Gauduchon, J.; Nicolas, V.; Tsapis, N.; Kerdine-Romer, S.; Fattal, E. Surface-modified biodegradable nanoparticles’ impact on cytotoxicity and inflammation response on a co-culture of lung epithelial cells and human-like macrophages. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, N.; Park, J.-H. Endocytosis and exocytosis of nanoparticles in mammalian cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 51–63. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura, Y.; Maeda, H. A new concept for macromolecular therapeutics in cancer-chemotherapy—Mechanism of tumoritropic accumulation of proteins and the antitumor agent smancs. Cancer Res. 1986, 46, 6387–6392. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Balkwill, F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bilati, U.; Allémann, E.; Doelker, E. Development of a nanoprecipitation method intended for the entrapment of hydrophilic drugs into nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 24, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaly, N.; Yameen, B.; Wu, J.; Farokhzad, O.C. Degradable controlled-release polymers and polymeric nanoparticles: Mechanisms of controlling drug release. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2602–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricote, M.; Huang, J.; Fajas, L.; Li, A.; Welch, J.; Najib, J.; Witztum, J.L.; Auwerx, J.; Palinski, W.; Glass, C.K. Expression of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (pparγ) in human atherosclerosis and regulation in macrophages by colony stimulating factors and oxidized low density lipoprotein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7614–7619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Ting, A.T.; Seed, B. Ppar-γ agonists inhibit production of monocyte inflammatory cytokines. Nature 1998, 391, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehrke, M.; Lazar, M.A. The many faces of pparγ. Cell 2005, 123, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.C.; Brown, K.K.; Silvestre, M.J.; Willson, T.M.; Palinski, W.; Glass, C.K. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma ligands inhibit development of atherosclerosis in ldl receptor-deficient mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobitz, A.; Zambanini, A.; Sowell, M.; Heise, M.; Louridas, B.; McMorn, S.; Semigran, M.; Koch, G. A retrospective evaluation of congestive heart failure and myocardial ischemia events in 14,237 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus enrolled in 42 short-term, double-blind, randomized clinical studies with rosiglitazone. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2008, 17, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobatto, M.E.; Fuster, V.; Fayad, Z.A.; Mulder, W.J. Perspectives and opportunities for nanomedicine in the management of atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 835–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schiener, M.; Hossann, M.; Viola, J.R.; Ortega-Gomez, A.; Weber, C.; Lauber, K.; Lindner, L.H.; Soehnlein, O. Nanomedicine-based strategies for treatment of atherosclerosis. Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Mascolo, D.; Lyon, C.J.; Aryal, S.; Ramirez, M.R.; Wang, J.; Candeloro, P.; Guindani, M.; Hsueh, W.A.; Decuzzi, P. Rosiglitazone-loaded nanospheres for modulating macrophage-specific inflammation in obesity. J. Control Release 2013, 170, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Langer, R. Preventing diet-induced obesity in mice by adipose tissue transformation and angiogenesis using targeted nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5552–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, V.; Mundra, V.; Mahato, R.I. Nanomedicines of hedgehog inhibitor and ppar-gamma agonist for treating liver fibrosis. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 1158–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davaa, E.; Park, J.S. Formulation parameters influencing the physicochemical characteristics of rosiglitazone-loaded cationic lipid emulsion. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kevadiya, B.D.; Woldstad, C.; Ottemann, B.M.; Dash, P.; Sajja, B.R.; Lamberty, B.; Morsey, B.; Kocher, T.; Dutta, R.; Bade, A.N.; et al. Multimodal theranostic nanoformulations permit magnetic resonance bioimaging of antiretroviral drug particle tissue-cell biodistribution. Theranostics 2018, 8, 256–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Gupta, A.; Jaiswal, A.; Dube, A.; Mishra, S.; Chaurasia, M.K. Design and development of amphotericin b bearing polycaprolactone microparticles for macrophage targeting. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2011, 7, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.M.; Shive, M.S. Biodegradation and biocompatibility of pla and plga microspheres. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 28, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmaso, S.; Caliceti, P. Stealth properties to improve therapeutic efficacy of drug nanocarriers. J. Drug Deliv. 2013, 2013, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurtig, M.; Shive, M.; Kapoor, M.; Mahomed, N.; Marshall, W. Disposition and ultimate fate of a pla-peg sustained release polymer after intra-articular injection. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2016, 24, S524–S525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival—Application to proliferation and cyto-toxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, E.; Sah, H. Recent trends in preparation of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles by mixing polymeric organic solution with antisolvent. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallwood, I.M. Handbook of organic solvent properties. In Handbook of Organic Solvent Properties; Wiley, Ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1996; p. vii. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Teply, B.A.; Sherifi, I.; Sung, J.; Luther, G.; Gu, F.X.; Levy-Nissenbaum, E.; Radovic-Moreno, A.F.; Langer, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Formulation of functionalized plga–peg nanoparticles for in vivo targeted drug delivery. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Kao, W.J. Drug release kinetics and transport mechanisms of non-degradable and degradable polymeric delivery systems. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Solvent Mixture | Size (nm) ± SD | Polydispersity Index ± SD | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DCM:acetone 1:1 | 123 ± 7 | 0.15 ± 0.06 | −17 ± 6 |
| DCM:ethyl acetate 1:1 | 130 ± 5 | 0.16 ± 0.05 | −18 ± 7 |
| Drug Amount | Size (nm) ± SD | Polydispersity Index ± SD | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RSG 4 mg | 115 ± 2 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | −20 ± 1 |
| RSG 7 mg | 111 ± 3 | 0.09 ± 0.02 | −21 ± 1 |
| RSG 10 mg | 115 ± 4 | 0.12 ± 0.02 | −15 ± 4 |
| Drug Amount | Size (nm) ± SD | Polydispersity Index ± SD | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RSG 4 mg | 79 ± 1 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | −23 ± 3 |
| RSG 7 mg | 81 ± 1 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | −17 ± 6 |
| RSG 10 mg | 82 ± 4 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | −28 ± 1 |
| Solvent Mixture | Emulsion-Evaporation | Nanoprecipitation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EE (%) | DL (%) | EE (%) | DL (%) | |
| Acetone/DCM 10 mg | 4.7 | 0.47 | ||
| ethyl acetate/DCM 10 mg | 5.7 | 0.56 | ||
| ACN 10 mg | 22 | 2.1 | ||
| ACN 7 mg | 30 | 2.0 | ||
| ACN 4 mg | 32 | 1.3 | ||
| Acetone 10 mg | 22 | 2.1 | ||
| Acetone 7 mg | 23 | 1.6 | ||
| Acetone 4 mg | 41 | 1.6 | ||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giacalone, G.; Tsapis, N.; Mousnier, L.; Chacun, H.; Fattal, E. PLA-PEG Nanoparticles Improve the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Rosiglitazone on Macrophages by Enhancing Drug Uptake Compared to Free Rosiglitazone. Materials 2018, 11, 1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101845
Giacalone G, Tsapis N, Mousnier L, Chacun H, Fattal E. PLA-PEG Nanoparticles Improve the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Rosiglitazone on Macrophages by Enhancing Drug Uptake Compared to Free Rosiglitazone. Materials. 2018; 11(10):1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101845
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiacalone, Giovanna, Nicolas Tsapis, Ludivine Mousnier, Hélène Chacun, and Elias Fattal. 2018. "PLA-PEG Nanoparticles Improve the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Rosiglitazone on Macrophages by Enhancing Drug Uptake Compared to Free Rosiglitazone" Materials 11, no. 10: 1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101845
APA StyleGiacalone, G., Tsapis, N., Mousnier, L., Chacun, H., & Fattal, E. (2018). PLA-PEG Nanoparticles Improve the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Rosiglitazone on Macrophages by Enhancing Drug Uptake Compared to Free Rosiglitazone. Materials, 11(10), 1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101845