A Hybrid System for Magnetic Hyperthermia and Drug Delivery: SPION Functionalized by Curcumin Conjugate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Synthesis of Curcumin and Sodium Alginate Conjugate (AA-Cur)
2.1.2. Synthesis of Uncoated SPION and SPION Stabilized with Cationic Chitosan/AA-Cur Bilayer (SPION-CCh/AA-Cur)
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.2.2. Small Angle X-ray Scattering Measurements
2.2.3. Vibrating Scanning Magnetometry Measurements
2.2.4. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Measurements
2.2.5. Magnetic Heating
2.2.6. Other Methods
2.2.7. Biological Stud Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology and Chemical Characterization of Obtained Systems
3.2. Magnetic Properties of SPION-CCh-AA-Cur
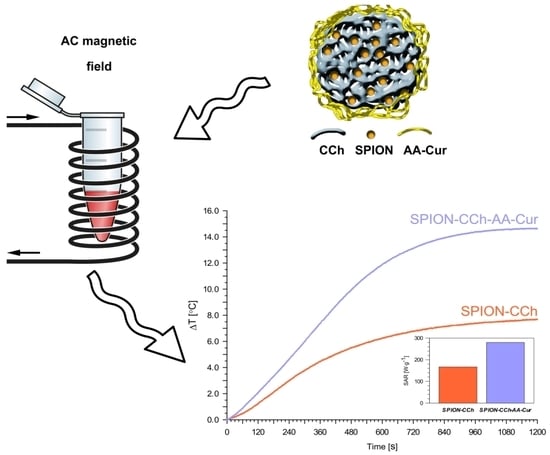
3.3. Magnetic Heating
3.4. Fluorescence Measurements
3.5. Biological Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, Y.L.; King, A.D. State of the art MRI in head and neck cancer. Clin. Radiol. 2018, 73, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hervault, A.; Thanh, N.T.K. Magnetic nanoparticle-based therapeutic agents for thermo-chemotherapy treatment of cancer. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 11553–11573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Gong, A.; Chen, B.; Zheng, J.; Chen, T.; Shen, Z.; Wu, A. Exploring a new SPION-based MRI contrast agent with excellent water-dispersibility, high specificity to cancer cells and strong MR imaging efficacy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerf. 2015, 126, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delli Pizzi, A.; Basilico, R.; Cianci, R.; Seccia, B.; Timpani, M.; Tavoletta, A.; Caposiena, D.; Faricelli, B.; Gabrielli, D.; Caulo, M. Rectal cancer MRI: Protocols, signs and future perspectives radiologists should consider in everyday clinical practice. Insights Imaging 2018, 9, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Guo, M.; Pang, H.; Qi, J.; Zhang, J.; Ge, Y. Treatment of malignant glioma using hyperthermia. Neural Regen. Res. 2013, 8, 2775–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier-Hauff, K.; Rothe, R.; Scholz, R.; Gneveckow, U.; Wust, P.; Thiesen, B.; Feussner, A.; Deimling, A.; Waldoefner, N.; Felix, R.; et al. Intracranial thermotherapy using magnetic nanoparticles combined with external beam radiotherapy: Results of a feasibility study on patients with glioblastoma multiforme. J. Neurooncol. 2007, 81, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier-Hauff, K.; Ulrich, F.; Nestler, D.; Niehoff, H.; Wust, P.; Thiesen, B.; Orawa, H.; Budach, V.; Jordan, A. Efficacy and safety of intratumoral thermotherapy using magnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles combined with external beam radiotherapy on patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J. Neurooncol. 2011, 103, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revia, R.A.; Zhang, M. Magnetite nanoparticles for cancer diagnosis, treatment, and treatment monitoring: Recent advances. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, D.G.; Saravanakumar, G.; Son, S.; Han, H.S.; Heo, R.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, J.H. Dextran sulfate-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as a contrast agent for atherosclerosis imaging. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, J.; Hyeon, T.; Park, H.; Messersmith, P.B.; Park, T.G. Bioinspired surface immobilization of hyaluronic acid on monodisperse magnetite nanocrystals for targeted cancer imaging. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 4154–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.L.; Qi, X.R.; Maitani, Y.; Nagai, T. Preparation and characterization of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles stabilized by alginate. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 333, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Z.T.; Wang, J.F.; Kuo, H.Y.; Shen, C.R.; Wang, J.J.; Yen, T.C. In situ preparation of high relaxivity iron oxide nanoparticles by coating with chitosan: A potential MRI contrast agent useful for cell tracking. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Nikles, D.E.; Brazel, C.S. Synthesis and characterization of multifunctional chitosan-Mnfe2o4 nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia and drug delivery. Materials 2010, 3, 4051–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kania, G.; Sternak, M.; Jasztal, A.; Chlopicki, S.; Błażejczyk, A.; Nasulewicz-Goldeman, A.; Wietrzyk, J.; Jasiński, K.; Skórka, T.; Zapotoczny, S.; et al. Uptake and bioreactivity of charged chitosan-coated superparamagnetic nanoparticles as promising contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szpak, A.; Kania, G.; Skórka, T.; Tokarz, W.; Zapotoczny, S.; Nowakowska, M. Stable aqueous dispersion of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles protected by charged chitosan derivatives. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczyńska, A.; Guzdek, K.; Derszniak, K.; Karewicz, A.; Lewandowska-ŁAńcucka, J.; Mateuszuk, Ł.; Skórka, T.; Banasik, T.; Jasiński, K.; Kapusta, C.; et al. Novel nanostructural contrast for magnetic resonance imaging of endothelial inflammation: Targeting SPIONs to vascular endothelium. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 72586–72595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, A.; Wu, R.; Zhou, M.; Wang, P. Mechanism of the anti-inflammatory effect of curcumin: PPAR-γ activation. PPAR Res. 2007, 2007, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adiwidjaja, J.; McLachlan, A.J.; Boddy, A.V. Curcumin as a clinically-promising anti-cancer agent: pharmacokinetics and drug interactions. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2017, 13, 953–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorasitthiyanukarn, F.N.; Muangnoi, C.; Ratnatilaka Na Bhuket, P.; Rojsitthisak, P.; Rojsitthisak, P. Chitosan/alginate nanoparticles as a promising approach for oral delivery of curcumin diglutaric acid for cancer treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 93, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marjaneh, R.M.; Rahmani, F.; Hassanian, S.M.; Rezaei, N.; Hashemzehi, M.; Bahrami, A.; Ariakia, F.; Fiuji, H.; Sahebkar, A.; Avan, A.; et al. Phytosomal curcumin inhibits tumor growth in colitis-associated colorectal cancer. J. Cell Physiol 2018, 233, 6785–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karewicz, A.; Bielska, D.; Loboda, A.; Gzyl-Malcher, B.; Bednar, J.; Jozkowicz, A.; Dulak, J.; Nowakowska, M. Curcumin-containing liposomes stabilized by thin layers of chitosan derivatives. Colloids Surf. B Biointerf. 2013, 109, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raveendran, R.; Bhuvaneshwar, G.S.; Sharma, C.P. Hemocompatible curcumin-dextran micelles as pH sensitive pro-drugs for enhanced therapeutic efficacy in cancer cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.; Tian, F.; Dahmani, F.Z.; Yang, H.; Yue, D.; He, S.; Zhou, J.; Yao, J. Curcumin-carboxymethyl chitosan (CNC) conjugate and CNC/LHR mixed polymeric micelles as new approaches to improve the oral absorption of P-gp substrate drugs. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 3424–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadavalli, T.; Ramasamy, S.; Chandrasekaran, G.; Michael, I.; Therese, H.A.; Chennakesavulu, R. Dual responsive PNIPAM-chitosan targeted magnetic nanopolymers for targeted drug delivery. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 380, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczerba, W.; Costo, R.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S.; Del Puerto Morales, M.; Thünemann, A.F. SAXS analysis of single-and multi-core iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2017, 50, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orthaber, D.; Bergmann, A.; Glatter, O. SAXS experiments on absolute scale with Kratky systems using water as a secondary standard. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2000, 33, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breßler, I.; Kohlbrecher, J.; Thünemann, A.F. SASfit: A tool for small-angle scattering data analysis using a library of analytical expressions. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2015, 48, 1587–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skumiel, A.; Hornowski, T.; Józefczak, A.; Koralewski, M.; Leszczyński, B. Uses and limitation of different thermometers for measuring heating efficiency of magnetic fluids. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 100, 1308–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrón, V.; Torrent, J.; De Grave, E. Hydromaghemite, an intermediate in the hydrothermal transformation of 2-line ferrihydrite into hematite. Am. Mineral. 2003, 88, 1679–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Church, J.S.; Woodhead, A.L. Infrared and Raman spectroscopic studies on iron oxide magnetic nano-particles and their surface modifications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Grant, J.; Piquette-Miller, M.; Allen, C. Synthesis and physicochemical and dynamic mechanical properties of a water-soluble chitosan derivative as a biomaterial. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 2845–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passaglia, E.; Bertoldo, M.; Coiai, S.; Augier, S.; Savi, S.; Ciardelli, F. Nanostructured polyolefins/clay composites: Role of the molecular interaction at the interface. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2008, 19, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, R.; Zamora-Mora, V.; Sibaja-Ballestero, M.; Vega-Baudrit, J.; López, D.; Mijangos, C. Influence of iron oxide nanoparticles on the rheological properties of hybrid chitosan ferrogels. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2009, 339, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Chang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wei, Z.; Kang, J.; Sang, L.; Dong, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, H.; Qi, M. Preparation and characterization of PVPI-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles as an MRI contrast agent. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 340, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.; Tojeira, A.; Vaz, D.C.; Mendes, A.; Bártolo, P. Preparation and characterization of films based on alginate and aloe vera. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2011, 16, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimmo, T.; Marzadori, C.; Montecchio, D.; Gessa, C. Characterisation of Ca- and Al-pectate gels by thermal analysis and FT-IR spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 2510–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tong, L.; Chu, J.; Xiao, K.; Zhou, Z.; Dong, W.; Chu, X. Preparation, characterization and properties of alginate/poly(γ-glutamic acid) composite microparticles. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurado-López, B.; Vieira, R.S.; Rabelo, R.B.; Beppu, M.M.; Casado, J.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E. Formation of complexes between functionalized chitosan membranes and copper: A study by angle resolved XPS. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 185, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Z.; Yang, W.S.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Q.M.; Ye, H. Preparation and characterization of carboxyl-group functionalized superparamagnetic nanoparticles and the potential for bio-applications. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2007, 18, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslick, K.S.; Fang, M.; Hyeon, T. Sonochemical synthesis of iron colloids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 11960–11961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Xie, S.; Li, X. Preparation of polylysine-modified superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 374, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibeigi, S.; Vaezi, M.R. Phase transformation of iron oxide nanoparticles by varying the molar ratio of Fe2+:Fe3+. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2008, 31, 1591–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darezereshki, E.; Bakhtiari, F.; Alizadeh, M.; Behrad Vakylabad, A.; Ranjbar, M. Direct thermal decomposition synthesis and characterization of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2012, 15, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournus, F.; Bonet, E. Magnetic susceptibility curves of a nanoparticle assembly, I: Theoretical model and analytical expressions for a single magnetic anisotropy energy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeun, M.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, K.H.; Paek, S.H.; Bae, S. Physical Contribution of Néel and Brown Relaxation to Interpreting Intracellular Hyperthermia Characteristics Using Superparamagnetic Nanofluids. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 5719–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, S.; Kitaguchi, R.; Takeda, R.; Yamada, T.; Takemura, Y. Rotation of Magnetization Derived from Brownian Relaxation in Magnetic Fluids of Different Viscosity Evaluated by Dynamic Hysteresis Measurements over a Wide Frequency Range. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemati, Z.; Alonso, J.; Khurshid, H.; Phan, M.H.; Srikanth, H. Core/shell iron/iron oxide nanoparticles: are they promising for magnetic hyperthermia? RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 38697–38702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loo, G.; Saelens, X.; Van Gurp, M.; MacFarlane, M.; Martin, S.J.; Vandenabeele, P. The role of mitochondrial factors in apoptosis: A Russian roulette with more than one bullet. Cell Death Differ. 2002, 9, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Presa, P.; Luengo, Y.; Multigner, M.; Costo, R.; Morales, M.P.; Rivero, G.; Hernando, A. Study of heating efficiency as a function of concentration, size, and applied field in γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 25602–25610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kekalo, K.; Baker, I.; Meyers, R. Magnetic Nanoparticles with High Specific Absorption Rate at Low Alternating Magnetic Field. Nano Life 2015, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, M.; Guerrini, A.; Cauteruccio, S.; Thakare, P.; Dova, D.; Orsini, F.; Arosio, P.; Carrara, C.; Sangregorio, C.; Lascialfari, A.; Maggioni, D.; Licandro, E. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles functionalized by peptide nucleic acids. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 15500–15512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barick, K.C.; Hassan, P.A. Glycine passivated Fe3O4 nanoparticles for thermal therapy. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2012, 369, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abenojar, E.C.; Wickramasinghe, S.; Bas-Concepcion, J.; Samia, A.C.S. Structural effects on the magnetic hyperthermia properties of iron oxide nanoparticles. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2016, 26, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculaes, D.; Lak, A.; Anyfantis, G.C.; Marras, S.; Laslett, O.; Avugadda, S.K.; Cassani, M.; Serantes, D.; Hovorka, O.; Chantrell, R.; Pellegrino, T. Asymmetric Assembling of Iron Oxide Nanocubes for Improving Magnetic Hyperthermia Performance. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 12121–12133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, R.; Yan, Y.Y.; Roberts, C. Study of the effect of dipole interactions on hyperthermia heating the cluster composed of superparamagnetic nanoparticles. AIP Adv. 2015, 5, 127232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nemati, Z.; Alonso, J.; Martinez, L.M.; Khurshid, H.; Garaio, E.; Garcia, J.A.; Phan, M.H.; Srikanth, H. Enhanced Magnetic Hyperthermia in Iron Oxide Nano-Octopods: Size and Anisotropy Effects. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 8370–8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ye, X.; Oh, S.J.; Kikkawa, J.M.; Kagan, C.R.; Murray, C.B. Bistable magnetoresistance switching in exchange-coupled CoFe2O4-Fe3O4 binary nanocrystal superlattices by self-assembly and thermal annealing. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 1478–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serantes, D.; Simeonidis, K.; Angelakeris, M.; Chubykalo-Fesenko, O.; Marciello, M.; Del Puerto Morales, M.; Baldomir, D.; Martinez-Boubeta, C. Multiplying magnetic hyperthermia response by nanoparticle assembling. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 5927–5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.H.; Lima, E.; Mansilla, M.V.; Zysler, R.D.; Troiani, H.; Pisciotti, M.L.M.; Locatelli, C.; Benech, J.C.; Oddone, N.; Zoldan, V.C.; Winter, E.; Pasa, A.A.; Creczynski-Pasa, T.B. Superparamagnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles mPEG350- and mPEG2000-coated: Cell uptake and biocompatibility evaluation. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, B.; Wan, Y.; Wang, X.; Zha, Q.; Liu, H.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, S. Synthesis and characterization of N-(2-hydroxy)propyl-3-trimethyl ammonium chitosan chloride for potential application in gene delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerf. 2012, 91, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kania, G.; Kwolek, U.; Nakai, K.; Yusa, S.; Bednar, J.; Wójcik, T.; Chłopicki, S.; Skórka, T.; Szuwarzyński, M.; Szczubiałka, K.; Kepczynski, M.; Nowakowska, M. Stable polymersomes based on ionic–zwitterionic block copolymers modified with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 5523–5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Sample | dmax [nm] | PDI | ζ [mV] |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPION-CCh | 108 ± 4 | 0.26 | +34 ± 6 |
| SPION-CCh-AA-Cur | 58 ± 9 | 0.21 | −35 ± 6 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lachowicz, D.; Kaczyńska, A.; Wirecka, R.; Kmita, A.; Szczerba, W.; Bodzoń-Kułakowska, A.; Sikora, M.; Karewicz, A.; Zapotoczny, S. A Hybrid System for Magnetic Hyperthermia and Drug Delivery: SPION Functionalized by Curcumin Conjugate. Materials 2018, 11, 2388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122388
Lachowicz D, Kaczyńska A, Wirecka R, Kmita A, Szczerba W, Bodzoń-Kułakowska A, Sikora M, Karewicz A, Zapotoczny S. A Hybrid System for Magnetic Hyperthermia and Drug Delivery: SPION Functionalized by Curcumin Conjugate. Materials. 2018; 11(12):2388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122388
Chicago/Turabian StyleLachowicz, Dorota, Agnieszka Kaczyńska, Roma Wirecka, Angelika Kmita, Wojciech Szczerba, Anna Bodzoń-Kułakowska, Marcin Sikora, Anna Karewicz, and Szczepan Zapotoczny. 2018. "A Hybrid System for Magnetic Hyperthermia and Drug Delivery: SPION Functionalized by Curcumin Conjugate" Materials 11, no. 12: 2388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122388
APA StyleLachowicz, D., Kaczyńska, A., Wirecka, R., Kmita, A., Szczerba, W., Bodzoń-Kułakowska, A., Sikora, M., Karewicz, A., & Zapotoczny, S. (2018). A Hybrid System for Magnetic Hyperthermia and Drug Delivery: SPION Functionalized by Curcumin Conjugate. Materials, 11(12), 2388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122388