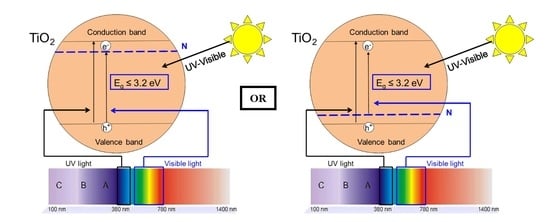
Highly Efficient Low-Temperature N-Doped TiO2 Catalysts for Visible Light Photocatalytic Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples Preparation
2.1.1. Pure TiO2 Powder Synthesis
2.1.2. N-Doped TiO2 Powder Synthesis
2.1.3. Urea-Doped TiO2 Powder Synthesis at a Large Scale
2.2. Sample Characterization
2.3. Photocatalytic Tests
3. Results
3.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) of TiO2 Samples
3.2. TEM Micrographs
3.3. Sample Textural Properties
3.4. Optical Properties
3.5. XPS Measurements
3.6. Photocatalytic Activity
3.6.1. Under UV/Visible Light
3.6.2. Under Low-Energy Light (λ > 390 nm)
3.7. Characterization of the Large-Scale Urea-Doped TiO2 Photocatalyst
4. Discussion
4.1. Crystallinity and Texture of TiO2 Based Samples
4.2. Photoactivity and N-Doping
4.3. Large-Scale Synthesis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoffmann, M.R.; Martin, S.T.; Choi, W.; Bahnemann, D.W. Environmental Applications of Semiconductor Photocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 69–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, A.; Le Hunte, S. An overview of semiconductor photocatalysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 1997, 108, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, A.; García-López, E.; Marcì, G.; Palmisano, L. A survey of photocatalytic materials for environmental remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 211–212, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauf, M.A.; Ashraf, S.S. Fundamental principles and application of heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of dyes in solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 151, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Hashimoto, K.; Watanabe, T. TiO2 Photocatalysis: Fundamentals and Applications; BKC, Inc.: Tokyo, Japan, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Carp, O. Photoinduced reactivity of titanium dioxide. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2004, 32, 33–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malengreaux, C.M.; Douven, S.; Poelman, D.; Heinrichs, B.; Bartlett, J.R. An ambient temperature aqueous sol–gel processing of efficient nanocrystalline doped TiO2-based photocatalysts for the degradation of organic pollutants. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2014, 71, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahy, J.G.; Leonard, G.L.-M.; Pirard, S.; Wicky, D.; Daniel, A.; Archambeau, C.; Liquet, D.; Heinrichs, B. Aqueous sol-gel synthesis and film deposition methods for the large-scale manufacture of coated steel with self-cleaning properties. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 81, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahy, J.G.; Lambert, S.D.; Leonard, G.L.-M.; Zubiaur, A.; Olu, P.-Y.; Mahmoud, A.; Boschini, F.; Heinrichs, B. Towards a large scale aqueous sol-gel synthesis of doped TiO2: Study of various metallic dopings for the photocatalytic degradation of p-nitrophenol. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2016, 329, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malengreaux, C.M.; Léonard, G.M.-L.; Pirard, S.L.; Cimieri, I.; Lambert, S.D.; Bartlett, J.R.; Heinrichs, B. How to modify the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 thin films through their roughness by using additives. A relation between kinetics, morphology and synthesis. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 243, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasseroul, L.; Pirard, S.L.; Lambert, S.D.; Páez, C.A.; Poelman, D.; Pirard, J.-P.; Heinrichs, B. Kinetic study of p-nitrophenol photodegradation with modified TiO2 xerogels. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 191, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.; Bard, A.J. An Improved Photocatalyst of TiO2/SiO2 Prepared by a Sol-Gel Synthesis. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 9882–9885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratzel, M. Sol-gel processed TiO2 films for photovoltaic applications. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2001, 22, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, C.J.; Scherer, G.W. Sol-Gel Science: The Physics and Chemistry of Sol-Gel Processing; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Kapusuz, D.; Park, J.; Ozturk, A. Effect of initial water content and calcination temperature on photocatalytic properties of TiO2 nanopowders synthesized by the sol-gel process. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 12788–12797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malengreaux, C.M.; Timmermans, A.; Pirard, S.L.; Lambert, S.D.; Pirard, J.-P.; Poelman, D.; Heinrichs, B. Optimized deposition of TiO2 thin films produced by a non-aqueous sol–gel method and quantification of their photocatalytic activity. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 195–196, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, U. Chemical modification of titanium alkoxides for sol–gel processing. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 3701–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, K.M.S.; El-Khatib, R.M.; Ali, T.T.; Mahmoud, H.A.; Elsamahy, A.A. Titania nanoparticles by acidic peptization of xerogel formed by hydrolysis of titanium(IV) isopropoxide under atmospheric humidity conditions. Powder Technol. 2013, 245, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahshid, S.; Askari, M.; Ghamsari, M.S. Synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles by hydrolysis and peptization of titanium isopropoxide solution. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 189, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braconnier, B.; Páez, C.A.; Lambert, S.D.; Alié, C.; Henrist, C.; Poelman, D.; Pirard, J.-P.; Cloots, R.; Heinrichs, B. Ag- and SiO2-doped porous TiO2 with enhanced thermal stability. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 122, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, A.; Marcì, G.; Palmisano, L.; Schiavello, M.; Uosaki, K.; Ikeda, S.; Ohtani, B. Preparation of polycrystalline Tio2 photocatalysts impregnated with various transition metal ions: Characterization and photocatalytic activity for the degradation of 4-nitrophenol. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggieri, F.; Di, D. Electrospun Cu-, W- and Fe-doped TiO2 nanofibres for photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine 6G. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2013, 15, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Burda, C. Chemically synthesized nitrogen-doped metal oxide nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. 2007, 339, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaez, M.; Nolan, N.T.; Pillai, S.C.; Seery, M.K.; Falaras, P.; Kontos, A.G.; Dunlop, P.S.M.; Hamilton, J.W.J.; Byrne, J.A.; O’Shea, K.; et al. A review on the visible light active titanium dioxide photocatalysts for environmental applications. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 125, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Valentin, C.; Pacchioni, G. Trends in non-metal doping of anatase TiO2: B, C, N and F. Catal. Today 2013, 206, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Valentin, C.; Pacchioni, G.; Selloni, A.; Livraghi, S.; Cozzi, V.R. Characterization of Paramagnetic Species in N-Doped TiO2 Powders by EPR Spectroscopy and DFT Calculations. J. Phys. Chem. B Lett. 2005, 109, 11414–11419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, P. Electrochimica Acta Construction of N, S codoped TiO2 NCs decorated TiO2 nano-tube array photoelectrode and its enhanced visible light photocatalytic mechanism. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 103, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, A.; Sivakumar, S.; Ramasamy, A.K.; Balasubramanian, V. Photocatalytic degradation of triazine dyes over N-doped TiO2 in solar radiation. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2013, 39, 2287–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Dashora, A.; Jaiswal, R.; Fernandes, R.; Yadav, M.; Kothari, D.C.; Ahuja, B.L.; Miotello, A. Experimental and Theoretical Investigations on the Activity and Stability of Substitutional and Interstitial Boron in TiO2 Photocatalyst. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 18581–18590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwase, M.; Yamada, K.; Kurisaki, T.; Prieto-mahaney, O.O.; Ohtani, B.; Wakita, H. Visible-light photocatalysis with phosphorus-doped titanium (IV) oxide particles prepared using a phosphide compound. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 132–133, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodson, C.J.; Heinrichs, B.; Tasseroul, L.; Bied, C.; Mahy, J.G.; Wong Chi Man, M.; Lambert, S.D. Efficient P- and Ag-doped titania for the photocatalytic degradation of waste water organic pollutants. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 682, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Hyeon, T.; Lee, H. Visible Light-Induced Degradation of Carbon Tetrachloride on. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 966–970. [Google Scholar]
- Granados, G.O.; Páez, C.A.M.; Martínez, F.O.; Páez-Mozo, E.A. Photocatalytic degradation of phenol on TiO2 and TiO2/Pt sensitized with metallophthalocyanines. Catal. Today 2005, 107–108, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z. An N-doped anatase/rutile TiO2 hybrid from low-temperature direct nitridization: Enhanced photoactivity under UV-/visible-light. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.W.; Rouquerol, J.; Bergeret, H.J.G.; Gallezot, P.; Vaarkamp, M.; Koningsberger, D.C.; Datye, A.K.; Niemantsverdriet, J.W.; Butz, T.; Engelhardt, G.; et al. Handbook of Heterogenous Catalysis; Weitkamp, J., Ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 1997; pp. 428–582. [Google Scholar]
- Doebelin, N.; Kleeberg, R. Profex: A graphical user interface for the Rietveld refinement program BGMN. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2015, 48, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, I.C.; Finney, R.J.; Flann, R.C.A.; Frost, M.T.; Wilson, B.W. Quantitative Analysis of High-alumina Refractories Using X-ray Powder Diffraction Data and the Rietveld Method. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1991, 74, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecloux, A. Exploitation des isothermes d’adsorption et de désorption d’azote pour l’étude de la texture des solides poreux. Mém. Soc. R. Sci. Liège 1971, 4, 169–209. [Google Scholar]
- KUBELKA, P. Ein Beitrag zur Optik der Farban striche. Z. Tech. Phys. 1931, 12, 593–603. [Google Scholar]
- Kubelka, P. New contributions to the optics of intensely light-scattering materials. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1948, 38, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Páez, C.A.; Poelman, D.; Pirard, J.P.; Heinrichs, B. Unpredictable photocatalytic ability of H2-reduced rutile-TiO2 xerogel in the degradation of dye-pollutants under UV and visible light irradiation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 94, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo Morales, A.; Sánchez Mora, E.; Pal, U. Use of diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for optical characterization of un-supported nanostructures. Rev. Mex. Fis. 2007, 53, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Bryson, C.E. Surface potential control in XPS. Surf. Sci. 1987, 189/190, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, D.A. High-Resolution X-Ray Photoemission Spectrum of the Valence Bands of Gold. Phys. Rev. B 1972, 5, 4709–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páez, C.A.; Liquet, D.Y.; Calberg, C.; Lambert, S.D.; Willems, I.; Germeau, A.; Pirard, J.P.; Heinrichs, B. Study of photocatalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide over ramsdellite-MnO2 by O2-pressure monitoring. Catal. Commun. 2011, 15, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.D.; Alie, C.; Pirard, J.P.; Heinrichs, B. Study of textural properties and nucleation phenomenon in Pd/SiO2, Ag/SiO2 and Cu/SiO2 cogelled xerogel catalysts. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2004, 342, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azouani, R.; Tieng, S.; Chhor, K.; Bocquet, J.F.; Eloy, P.; Gaigneaux, E.M.; Klementiev, K.; Kanaev, A.V. TiO2 doping by hydroxyurea at the nucleation stage: Towards a new photocatalyst in the visible spectral range. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittencourt, C.; Rutar, M.; Umek, P.; Mrzel, A.; Vozel, K.; Arcon, D.; Henzler, K.; Krüger, P.; Guttmann, P. Molecular nitrogen in N-doped TiO2 nanoribbons. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 23350–23356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, A.; Augugliaro, V.; Palmisano, L.; Pantaleo, G.; Savinov, E. Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of nitrophenols. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2003, 155, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augugliaro, V.; Palmisano, L.; Schiavello, M.; Sclafani, A.; Marchese, L.; Martra, G.; Miano, F. Photocatalytic degradation of nitrophenols in aqueous titanium dioxide dispersion. Appl. Catal. 1991, 69, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, B.; Anderson, M. Peptization Process in the Sol-Gel Preparation of Porous Anatase (TiO2). Chem. Mater. 1995, 7, 1772–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, G.G.; Lewis, R.J. Hawley Scondensed Chemcal Dictionary; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Mei, S.; Ferreira, J.M.F.; Norby, P.; Quaresmâ, S. Fabrication of rutile rod-like particle by hydrothermal method: An insight into HNO3 peptization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 283, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malengreaux, C.M.; Pirard, S.L.; Léonard, G.; Mahy, J.G.; Klobes, B.; Herlitschke, M.; Heinrichs, B.; Bartlett, J.R. Study of the photocatalytic activity of Fe3+, Cr3+, La3+ and Eu3+ single- doped and co-doped TiO2 catalysts produced by aqueous sol-gel processing. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 691, 726–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.X.; Zhao, Y.; Burda, C. Synthesis and Characterization of Nitrogen-Doped Group IVB Visible-Light-Photoactive Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3995–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Qiu, X.; Burda, C. The Effects of Sintering on the Photocatalytic Activity of N-Doped TiO2 Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 2629–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gole, J.L.; Stout, J.D.; Burda, C.; Lou, Y.; Chen, X. Highly Efficient Formation of Visible Light Tunable TiO2 - x N x Photocatalysts and Their Transformation at the Nanoscale. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Burda, C. Photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes by nitrogen-doped TiO2 nanocatalysts. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, B.; Prieto-Mahaney, O.O.; Li, D.; Abe, R. What is Degussa (Evonik) P25? Crystalline composition analysis, reconstruction from isolated pure particles and photocatalytic activity test. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2010, 216, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamarik, T.A.; Elmore, A.R. Final report of the safety assessment of Urea. Int. J. Toxicil. 2004, 24, 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Koirala, R.; Pratsinis, S.E.; Baiker, A. Synthesis of catalytic materials in flames: Opportunities and challenges. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3053–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Sample | Phase Distribution | dXRD | SBET | VDR | dBET | dTEM | Eg,direct | Eg,indirect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (nm) | (m2g−1) | (cm3g−1) | (nm) | (nm) | (eV) | (eV) | |
| ±5 | ±1 | ±5 | ±0.01 | ±1 | ±1 | ±0.01 | ±0.01 | |
| TiO2 pure A | Am[25%] + A[65%] + B[10%] | 4 | 205 | 0.11 | 8 | 5 | 3.35 | 3.06 |
| TiO2/U1 | Am[30%] + A[65% ]+ B[5%] | 5 | 235 | 0.15 | 7 | 6 | 3.25 | 2.97 |
| TiO2/U2 | Am[30%] + A[65%] + B[5%] | 4 | 255 | 0.16 | 6 | 6 | 3.24 | 2.97 |
| TiO2/U4 | Am[30%] + A[65%] + B[5%] | 4 | 260 | 0.16 | 6 | 7 | 3.27 | 3.04 |
| TiO2/U10 | Am[25%] + A[70%] + B[5%] | 4 | 270 | 0.16 | 6 | 5 | 3.36 | 3.05 |
| TiO2 pure B | Am[15%] + A[75%] + B[10%] | 4 | 195 | 0.10 | 8 | 5 | 3.42 | 3.12 |
| TiO2/EtDN1 | Am[20%] + A[65%] + B[5%] + R[10%] | 7 | 225 | 0.13 | 7 | 6 | 3.30 | 2.94 |
| TiO2/EtDN2 | Am[15%] + A[60%] + B[5%] + R[20%] | 4 | 240 | 0.13 | 6 | 6 | 3.39 | 2.99 |
| TiO2/EtDN4 | Am[15%] + A[45%] + B[5%] + R[35%] | 5 a–8 b | 195 | 0.11 | 8 | 7 | 3.30 | 2.94 |
| TiO2/EtDN10 | Am[35%] + A[20%] + B[5%] + R[40%] | 8 | 185 | 0.11 | 8 | 5 | 3.43 | 2.96 |
| TiO2/Et3N28 | Am[25%] + A[70%] + B[5%] | 4 | 230 | 0.13 | 7 | 5 | -c | -c |
| TiO2/Et3N42 | Am[20%] + A[75%] + B[5%] | 4 | 275 | 0.16 | 6 | 6 | -c | -c |
| TiO2/U2-LS | Am[30%] + A[65%] + B[5%] | 6 | 245 | 0.15 | 6 | 7 | -d | -d |
| Sample | DPNP8 under UV/Visible | DPNP8 under UV/Visible | DPNP24 under Visible | DPNP24 under Visible | N/Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (% g·m−2) | (%) | (% g·m−2) | (mol/mol) | |
| ±3 | ±0.02 | ±3 | ±0.02 | ||
| TiO2 pure A | 47 | 0.23 | 28 | 0.14 | 0.07 |
| TiO2/U1 | 43 | 0.18 | 42 | 0.18 | 0.06 |
| TiO2/U2 | 44 | 0.17 | 41 | 0.16 | 0.09 |
| TiO2/U4 | 45 | 0.17 | 41 | 0.16 | 0.08 |
| TiO2/U10 | 44 | 0.16 | 38 | 0.14 | 0.08 |
| TiO2 pure B | 50 | 0.26 | 20 | 0.10 | 0.08 |
| TiO2/EtDN1 | 38 | 0.17 | 31 | 0.14 | 0.08 |
| TiO2/EtDN2 | 39 | 0.16 | 31 | 0.13 | 0.12 |
| TiO2/EtDN4 | 45 | 0.23 | 33 | 0.17 | 0.11 |
| TiO2/EtDN10 | 25 | 0.14 | 28 | 0.15 | 0.06 |
| TiO2/Et3N28 | 43 | 0.19 | 43 | 0.19 | 0.32 |
| TiO2/Et3N42 | 49 | 0.18 | 69 | 0.25 | 0.13 |
| TiO2/U2-LS | 46 | 0.19 | 43 | 0.18 | -a |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahy, J.G.; Cerfontaine, V.; Poelman, D.; Devred, F.; Gaigneaux, E.M.; Heinrichs, B.; Lambert, S.D. Highly Efficient Low-Temperature N-Doped TiO2 Catalysts for Visible Light Photocatalytic Applications. Materials 2018, 11, 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040584
Mahy JG, Cerfontaine V, Poelman D, Devred F, Gaigneaux EM, Heinrichs B, Lambert SD. Highly Efficient Low-Temperature N-Doped TiO2 Catalysts for Visible Light Photocatalytic Applications. Materials. 2018; 11(4):584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040584
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahy, Julien G., Vincent Cerfontaine, Dirk Poelman, François Devred, Eric M. Gaigneaux, Benoît Heinrichs, and Stéphanie D. Lambert. 2018. "Highly Efficient Low-Temperature N-Doped TiO2 Catalysts for Visible Light Photocatalytic Applications" Materials 11, no. 4: 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040584
APA StyleMahy, J. G., Cerfontaine, V., Poelman, D., Devred, F., Gaigneaux, E. M., Heinrichs, B., & Lambert, S. D. (2018). Highly Efficient Low-Temperature N-Doped TiO2 Catalysts for Visible Light Photocatalytic Applications. Materials, 11(4), 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040584