Electrical Conduction Mechanism and Dielectric Properties of Spherical Shaped Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Synthesized by Co-Precipitation Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structure Analysis
2.2. Dielectric Properties
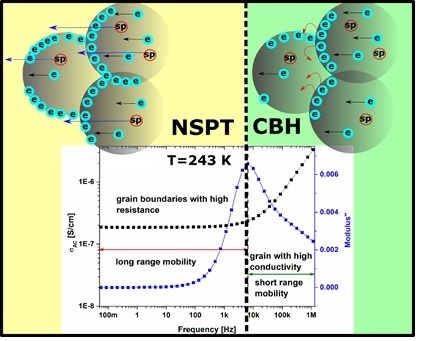
2.3. Electrical Conduction Mechanism
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
- Electrical conductivity of agglomerated and compressed Fe3O4 nanoparticles is associated with the structure of the sample, and can be described by Maxwell-Wagner model and Koop’s theory.
- In the low frequency region, electrical conductivity is associated with long-range mobility and grain boundaries with high resistance, whereas in high frequencies region, it is related to the short-range mobility, and grains with high conductivity.
- With increasing temperature, conductivity related to the grain boundaries can be observed within a wider frequency region, which is associated with the shift of peaks related to the electrical relaxation process.
- The maximum of the peaks observed on M”(f) plots is associated with a transition between long and short range mobility.
- Increasing the value of ε’ and ε” in the low frequency region is associated with grain boundaries polarization, according to the Maxwell-Wagner model; in the low-frequency region, charge carriers accumulate in grain boundaries, and the hopping process requires more energy.
- AC conductivity in Fe3O4 nanoparticles follows the Jonscher’s power law, characteristic for disordered solids; electrical conductivity is associated with two mechanisms described by correlated barrier hopping and non-overlapping small polaron tunneling models.
- CBH and NSPT models are valid for different temperature and frequency regions. For low temperatures and high frequencies, the conduction mechanism can be described by the CBH model, whereas for high temperatures and low frequencies, the NSPT model is more adequate.
- The value of hopping energy for the tunneling of small polarons decreases with increasing temperatures, and in higher temperatures WH < 0 eV; thus tunneling occurs spontaneously.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patil, R.P.; Delekar, S.D.; Mane, D.R.; Hankare, P.P. Synthesis, structural and magnetic properties of different metal ion substituted nanocrystalline zinc ferrite. Results Phys. 2013, 3, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, X.; Xu, T.; Nie, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, C. Synthesis and characterization of nanosized MnZn ferrites via a modified hydrothermal method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 439, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seetha Rama Raju, V. Synthesis of non-stoichiometric zinc ferrite for electromagnetic wave absorber applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2017, 224, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Hussain Gul, I.; Zarrar, M.; Anwar, H.; Khan Niazi, M.B.; Khan, A. Improved electrical properties of cadmium substituted cobalt ferrites nano-particles for microwave application. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 405, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, R. Novel applications of ferrites. Phys. Res. Int. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Xie, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, R. Synthesis of spherical Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles by co-precipitation in choline chloride/urea deep eutectic solvent. Mater. Lett. 2013, 112, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbarasu, M.; Anandan, M.; Chinnasamy, E.; Gopinath, V.; Balamurugan, K. Synthesis and characterization of polyethylene glycol (PEG) coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles by chemical co-precipitation method for biomedical applications. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 135, 536–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, L.C.; Seabra, A.B.; Pelegrino, M.T.; De Araujo, D.R.; Bernardes, J.S.; Haddad, P.S. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles dispersed in Pluronic F127 hydrogel: potential uses in topical applications. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14496–14503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimzadeh, I.; Aghazadeh, M.; Doroudi, T.; Ganjali, M.R.; Kolivand, P.H. Superparamagnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles coated with PEG/PEI for biomedical applications: A facile and scalable preparation route based on the cathodic electrochemical deposition method. Adv. Phys. Chem. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jin, C.; Yuan, G.; Han, J.; Wang, M.; Guo, R. Implantation of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles in Shells of Au@m-SiO2Yolk@Shell Nanocatalysts with Both Improved Recyclability and Catalytic Activity. Langmuir 2017, 33, 7486–7493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Chen, L. Superparamagnetic POT/Fe3O4 nanoparticle composites with supported Au nanoparticles as recyclable high-performance nanocatalysts. Mater. Today Chem. 2017, 5, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, M.T.; Ahmad, I.; Kanwal, M.; Ali, I. Effect of praseodymium ions on manganese based spinel ferrites. Chinese J. Phys. 2017, 55, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazirehpour, M.; Seyyed Ebrahimi, S.A. Effect of aspect ratio on dielectric, magnetic, percolative and microwave absorption properties of magnetite nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 638, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuraman, K.; Alagarsamy, S.; Banu, M.A.; Naidu, V. Synthesis of Nano sized Ce-Co Doped Zinc Ferrite and their Permittivity and Hysteresis Studies. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2011, 32, 975–8887. [Google Scholar]
- Mazen, S.A.; Abu-Elsaad, N.I. Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of the lithium ferrite obtained by ball milling and heat treatment. Appl. Nanosci. 2015, 5, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, R.J.; Joshi, U.S.; Caltun, O.F. Microstructural and Electrical Properties of Barium Strontium Titanate and Nickel Zinc Ferrite Composites. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2015, 10, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, R.A.; Murty, B.S.; Murthy, V.R.K. Maxwell-Wagner polarization in grain boundary segregated NiCuZn ferrite. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2014, 14, 1727–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, I.; Naseem, S.; Naeem Ashiq, M.; Khan, M.A.; Niaz, S.; Rana, M.U. Structural and dielectric properties of doped ferrite nanomaterials suitable for microwave and biomedical applications. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2015, 25, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, D.K.; Choudhary, R.N.P.; Samantaray, B.K. Studies of dielectric relaxation and AC conductivity behavior of plasticized polymer nanocomposite electrolytes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2008, 3, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurram, A.A.; Rakha, S.A.; Zhou, P.; Shafi, M.; Munir, A. Correlation of electrical conductivity, dielectric properties, microwave absorption, and matrix properties of composites filled with graphene nanoplatelets and carbon nanotubes. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhoe, B.M.; Hassan, M.K.; Wiggins, J.S.; Mauritz, K.A. Universal power law behavior of the AC conductivity versus frequency of agglomerate morphologies in conductive carbon nanotube-reinforced epoxy networks. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2016, 54, 1918–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megdiche, M.; Perrin-Pellegrino, C.; Gargouri, M. Conduction mechanism study by overlapping large-polaron tunnelling model in SrNiP2O7 ceramic compound. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 584, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladhar, A.; Arous, M.; Kaddami, H.; Raihane, M.; Kallel, A.; Graça, M.P.F.; Costa, L.C. AC and DC electrical conductivity in natural rubber/nanofibrillated cellulose nanocomposites. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 209, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellakkat, M.; Hundekal, D. Electrical conductivity and supercapacitor properties of polyaniline/chitosan/nickel oxide honeycomb nanocomposite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, O.G.; Salman, Y.A.K.; Saleem, S.A. Electrical conductivity and dielectric characteristics of in situ prepared PVA/HgS nanocomposite films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 3591–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahouli, A.; Sylvestre, A.; Jomni, F.; Yangui, B.; Legrand, J. Experimental and theoretical study of AC electrical conduction mechanisms of semicrystalline parylene C thin films. J. Phys. Chem. A 2012, 116, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Samaha, F.S.H.; Ismail, M.I.M. AC conductivity of nanoparticles CoxFe1−xFe2O4 (x = 0, 0.25 and 1) ferrites. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2014, 19, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velhal, N.B.; Patil, N.D.; Shelke, A.R.; Deshpande, N.G.; Puri, V.R. Structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of nickel substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: Effect of nickel concentration. AIP Adv. 2015, 5, 097166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, A.; Priyadharsini, P.; Chandrasekaran, G. Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of nanocrystalline zinc ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 3917–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, R.K.; Muduli, R.; Kar, S.K.; Behera, D. Dielectric relaxation and conduction mechanism of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 615, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.S.; Singh, G.P. Structural, magnetic and dielectric study of Cu substituted NiZn ferrite nanorod. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 401, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.H.; Yusoff, A.N. Complex impedance and dielectric properties of an Mg-Zn ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 1996, 233, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhan, N.; Gheisari, K.; Shoushtari, M.Z. Dielectric Properties of Nanocrystalline Zn-Doped Lithium Ferrites Synthesized by Microwave-Induced Glycine-Nitrate Process. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2016, 29, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, B.; Singh, L.; Annapu Reddy, V.; Jeong, D.Y.; Dabra, N.; Hundal, J.S. AC impedance spectroscopy, conductivity and optical studies of Sr doped bismuth ferrite nanocomposites. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 4120–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, V.; Cheruku, R.; Vijayan, L.; Govindaraj, G. Ce-substituted lithium ferrite: Preparation and electrical relaxation studies. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belal Hossen, M.; Akther Hossain, A.K.M. Complex impedance and electric modulus studies of magnetic ceramic Ni0.27Cu0.10Zn0.63Fe2O4. J. Adv. Ceram. 2015, 4, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melagiriyappa, E.; Jayanna, H.S.; Chougule, B.K. Dielectric behavior and ac electrical conductivity study of Sm3+ substituted Mg-Zn ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 112, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, A.; Afsar, M.F.; Sher, F.; Rafiq, M.A. Temperature and composition dependent density of states extracted using overlapping large polaron tunnelling model in MnxCo1−xFe2O4 (x = 0.25, 0.5, 0.75) nanoparticles. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2017, 509, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolte, J.; Salame, P.H.; Daryapurkar, A.S.; Gopalan, P. Impedance and AC conductivity study of nano crystalline, fine grained multiferroic bismuth ferrite (BiFeO3), synthesized by microwave sintering. AIP Adv. 2015, 5, 097164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T.; Vargas, M.; Ramana, C.V. Structural characteristics, electrical conduction and dielectric properties of gadolinium substituted cobalt ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 617, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batoo, K.; Ansari, M. Low temperature-fired Ni-Cu-Zn ferrite nanoparticles through auto-combustion method for multilayer chip inductor applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.A.; Khan, M.N.I.; Chowdhury, F.U.Z.; Akhter, S.; Uddin, M.M. Structural Properties, Impedance Spectroscopy and Dielectric Spin Relaxation of Ni-Zn Ferrite Synthesized by Double Sintering Technique. J. Sci. Res. 2015, 7, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvejić, Ž.; Rapajić, S.; Rakić, S.; Jankov, S.; Skuban, S.; Srdić, V.V. Conductivity and dielectric behaviour of indium substituted zinc ferrites prepared by coprecipitation method. Phys. Scr. 2015, 90, 095802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaoui, S.; Dahman, H.; Ben Mansour, N.; El Mir, L. Structural, optical and electrical properties of Cu2SnS3 nanoparticles synthesized by simple solvothermal technique. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2014, 26, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinger, M. More features, more tools, more CrysTBox. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2017, 50, 1226–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinger, M.; Jäger, A. Crystallographic Tool Box (CrysTBox): Automated tools for transmission electron microscopists and crystallographers. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2015, 48, 2012–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| T (K) | 2θ (degree) | D (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| 303 | 35.55 | 9.01 |
| 373 | 35.53 | 8.89 |
| 473 | 35.56 | 9.07 |
| 573 | 35.57 | 9.44 |
| Plane | Theoretical d-Spacing (nm) | d-Spacing (nm) (SAED Pattern) | d-Spacing (nm) (XRD at 303 K) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 220 | 0.296 | 0.296 | 0.296 |
| 311 | 0.253 | 0.257 | 0.252 |
| 400 | 0.210 | 0.213 | 0.209 |
| 422 | 0.171 | 0.172 | 0.171 |
| 511 | 0.161 | 0.163 | 0.161 |
| 440 | 0.148 | 0.149 | 0.148 |
| 533 | 0.128 | 0.129 | 0.128 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radoń, A.; Łukowiec, D.; Kremzer, M.; Mikuła, J.; Włodarczyk, P. Electrical Conduction Mechanism and Dielectric Properties of Spherical Shaped Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Synthesized by Co-Precipitation Method. Materials 2018, 11, 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050735
Radoń A, Łukowiec D, Kremzer M, Mikuła J, Włodarczyk P. Electrical Conduction Mechanism and Dielectric Properties of Spherical Shaped Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Synthesized by Co-Precipitation Method. Materials. 2018; 11(5):735. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050735
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadoń, Adrian, Dariusz Łukowiec, Marek Kremzer, Jarosław Mikuła, and Patryk Włodarczyk. 2018. "Electrical Conduction Mechanism and Dielectric Properties of Spherical Shaped Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Synthesized by Co-Precipitation Method" Materials 11, no. 5: 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050735
APA StyleRadoń, A., Łukowiec, D., Kremzer, M., Mikuła, J., & Włodarczyk, P. (2018). Electrical Conduction Mechanism and Dielectric Properties of Spherical Shaped Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Synthesized by Co-Precipitation Method. Materials, 11(5), 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050735