Porous Waste Glass for Lead Removal in Packed Bed Columns and Reuse in Cement Conglomerates
Abstract
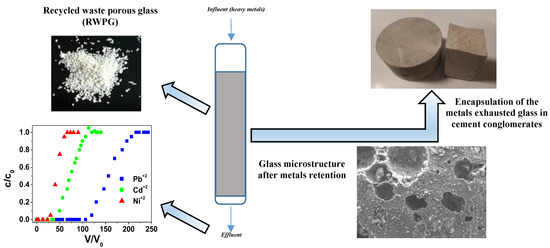
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.2. Column Tests
2.3. Applications of RWPG Beads After Sorption
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hermabessiere, L.; Dehaut, A.; Paul-Pont, I.; Lacroix, C.; Jezequel, R.; Soudant, P.; Duflos, G. Occurrence and effects of plastic additives on marine environments and organisms: A review. Chemosphere 2017, 182, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montes-Grajales, D.; Fennix-Agudelo, M.; Miranda-Castro, W. Occurrence of personal care products as emerging chemicals of concern in water resources: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basile, T.; Petrella, A.; Petrella, M.; Boghetich, G.; Petruzzelli, V.; Colasuonno, S.; Petruzzelli, D. Review of endocrine-disrupting-compound removal technologies in water and wastewater treatment plants: An EU perspective. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 8389–8401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Zeng, G.; Gong, J.; Liang, J.; Xu, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, M.; Liu, Y.; et al. Evaluation methods for assessing effectiveness of in situ remediation of soil and sediment contaminated with organic pollutants and heavy metals. Environ. Int. 2017, 105, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciniglia, C.; Mastrobuoni, F.; Scortichini, M.; Petriccione, M. Oxidative damage and cell-programmed death induced in Zea mays L. by allelochemical stress. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 926–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spasiano, D. Dark fermentation process as pretreatment for a sustainable denaturation of asbestos containing wastes. J. Hazards Mater. 2018, 349, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spasiano, D.; Luongo, V.; Race, M.; Petrella, A.; Fiore, S.; Apollonio, C.; Pirozzi, F.; Fratino, U.; Piccinni, A.F. Sustainable bio-hydrothermal sequencing treatment for asbestos-cement wastes. J. Hazards Mater. 2019, 364, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, V.V.; Wang, L.; Padhye, R. Electrospun nanofibre materials to filter air pollutants—A review. J. Ind. Text. 2018, 47, 2253–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyjoo, Y.; Sun, H.; Liu, J.; Pareek, V.K.; Wang, S. A review on photocatalysis for air treatment: From catalyst development to reactor design. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 310, 537–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, B.; Zhu, L.; Xing, B. Effects and mechanisms of biochar-microbe interactions in soil improvement and pollution remediation: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, E.; Gorgoglione, A.; Petrella, A.; Petruzzelli, V.; Gikas, P. Benzene removal in horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands treatment. Int. J. Environ. Agric. Biotechnol. 2015, 10, 14603–14614. [Google Scholar]
- Ciniglia, C.; Sansone, C.; Panzella, L.; Napolitano, A.; d’Ischia, M. Effects of walnut husk washing waters and their phenolic constituents on horticultural species. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 3299–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, A.; Petrella, M.; Boghetich, G.; Mastrorilli, P.; Petruzzelli, V.; Ranieri, E.; Petruzzelli, D. Laboratory scale unit for photocatalytic removal of organic micropollutants from water and wastewater. Methyl orange degradation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 2201–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, A.; Boghetich, G.; Petrella, M.; Mastrorilli, P.; Petruzzelli, V.; Petruzzelli, D. Photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes. Pilot plant investigation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 2566–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, A.; Mascolo, G.; Murgolo, S.; Petruzzelli, V.; Ranieri, E.; Spasiano, D.; Petruzzelli, D. Photocatalytic oxidation of organic micro-pollutants: Pilot plant investigation and mechanistic aspects of the degradation reaction. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2016, 203, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karak, T.; Bora, K.; Paul, R.K.; Das, S.; Khare, P.; Dutta, A.K.; Boruah, R.K. Paradigm shift of contamination risk of six heavy metals in tea (Camellia sinensis L.) growing soil: A new approach influenced by inorganic and organic amendments. J. Hazards Mater. 2017, 338, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.H.; Chen, L.J.; Yu, L.; Guo, Z.B.; Shan, C.Q.; Lin, J.Q.; Gu, Y.G.; Yang, Z.B.; Yang, Y.X.; Shao, J.R.; et al. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of human exposure to oral bioaccessibility of heavy metals via urban street dusts from different functional areas in Chengdu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, N.; Dino, G.A.; Ajmone-Marsan, F.; Lasagna, M.; Romè, C.; De Luca, D.A. Extractive waste management: A risk analysis approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 900–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, E.; Fratino, U.; Petrella, A.; Torretta, V.; Rada, E.C. Ailanthus Altissima and Phragmites Australis for chromium removal from a contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 15983–15989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, A.; Azari, A.; Rezakazemi, M.; Ansarpour, M. Removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewaters: A review. ChemBioEng Rev. 2017, 4, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Femina Carolin, C.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Saravanan, A.; Janet Joshiba, G.; Naushad, Mu. Efficient techniques for the removal of toxic heavy metals from aquatic environment: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2782–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruzzelli, D.; Petruzzelli, V.; Basile, T.; Petruzzelli, M.; Petrella, A.; Maggiore, M. Chemical and geochemical characterisation of a disused red brick factory area of central Italy. Chem. Ecol. 2011, 27 (Suppl. 1), 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habineza, A.; Zhai, J.; Ntakirutimana, T.; Qiu, F.P.; Li, X.; Wang, Q. Heavy metal removal from wastewaters by agricultural waste low-cost adsorbents: Hindrances of adsorption technology to the large scale industrial application—A review. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 78, 192–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.K. A review on the adsorption of heavy metals by clay minerals, with special focus on the past decade. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 438–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, N.; Imran, M.; Shaheen, M.R.; Ishaque, W.; Kamran, M.A.; Matloob, A.; Rehim, A.; Hussain, S. Phytoremediation strategies for soils contaminated with heavy metals: Modifications and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turan, M.; Mart, U.; Yüksel, B.; Celik, M.S. Lead removal in fixed-bed columns by zeolite and sepiolite. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthilkumar, R.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Thilakavathi, M.; Iyer, P.V.R.; Velan, M. Application of seaweeds for the removal of lead from aqueous solution. Biochem. Eng. J. 2007, 33, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaini, M.A.A.; Amano, Y.; Machida, M. Adsorption of heavy metals onto activated carbons derived from polyacrylonitrile fiber. J. Hazards Mater. 2010, 180, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, C.K.; Park, D.; Woo, S.H.; Park, J.M. Removal of cationic heavy metal from aqueous solution by activated carbon impregnated with anionic surfactants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawierucha, I.; Kozlowska, J.; Kozlowski, C.; Trochimczuk, A. Sorption of Pb (II), Cd (II) and Zn (II) performed with the use of carboxyphenylresorcinarene-impregnated Amberlite XAD-4 resin. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 52, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.C.; Loganathan, P.; Nguyen, T.V.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J.; Naidu, R. Simultaneous adsorption of Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn by an iron-coated Australian zeolite in batch and fixed-bed column studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Fu, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, A.; Shuang, C.; Gao, C. Synthesis and characterization of a novel magnetic cation exchange resin and its application for efficient removal of Cu2+ and Ni2+ from aqueous solutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, O.; Goodarzi, V.; Saeb, M.R.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Borja, R. Competitive removal of heavy metal ions from squid oil under isothermal condition by CR11 chelate ion exchanger. J. Hazards Mater. 2017, 334, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alinnor, I.J. Adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution by fly ash. Fuel 2007, 86, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Khatoon, A.; Mohd-Setapar, S.H.; Kumar, R.; Rafatullah, M. Chemically oxidized pineapple fruit peel for the biosorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 6432–6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, A.; Petruzzelli, V.; Basile, T.; Petrella, M.; Boghetich, G.; Petruzzelli, D. Recycled porous glass from municipal/industrial solid wastes sorting operations as a lead ion sorbent from wastewaters. React. Funct. Polym. 2010, 70, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, A.; Spasiano, D.; Acquafredda, P.; De Vietro, N.; Ranieri, E.; Cosma, P.; Rizzi, V.; Petruzzelli, V.; Petruzzelli, D. Heavy metals retention (Pb (II), Cd (II), Ni (II)) from single and multimetal solutions by natural biosorbents from the olive oil milling operations. Process Saf. Environ. 2018, 114, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corinaldesi, V.; Gnappi, G.; Moriconi, G.; Montenero, A. Reuse of ground waste glass as aggregate for mortars. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, I. Reuse of waste glass in building brick production. Waste Manag. Res. 2009, 27, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amore, G.K.O.; Caniato, M.; Travan, A.; Turco, G.; Marsich, L.; Ferluga, A.; Schmid, C. Innovative thermal and acoustic insulation foam from recycled waste glass powder. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Azevedo, A.R.G.; Alexandre, J.; Zanelato, E.B.; Marvila, M.T. Influence of incorporation of glass waste on the rheological properties of adhesive mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 148, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.X.; Duan, Z.H.; Poon, C.S. Fresh properties of cement pastes or mortars incorporating waste glass powder and cullet. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 131, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.X.; Duan, Z.H.; Poon, C.S. Combined use of waste glass powder and cullet in architectural mortar. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2017, 82, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Liu, L.; Ji, R.; Wang, X. Integrated utilization of fly ash and waste glass for synthesis of foam/dense bi-layered insulation ceramic tile. Energy Build. 2018, 168, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, A.; Petrella, M.; Boghetich, G.; Petruzzelli, D.; Ayr, U.; Stefanizzi, P.; Calabrese, D.; Pace, L. Thermo-acoustic properties of cement-waste-glass mortars. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Constr. Mater. 2009, 162, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monich, P.R.; Romero, A.R.; Höllen, D.; Bernardo, E. Porous glass-ceramics from alkali activation and sinter-crystallization of mixtures of waste glass and residues from plasma processing of municipal solid waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 188, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; van Onna, D.V.; Spiesz, P.; Yu, Q.L.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Development of ultra-lightweight fibre reinforced concrete applying expanded waste glass. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Halim, S.H.; Shehata, A.M.A.; El-Shahat, M.F. Removal of lead ions from industrial waste water by different types of natural materials. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1678–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadir, T.; Bakan, G.; Altas, L.; Buyukgungor, H. The investigation of lead removal by biosorption: An application at storage battery industry wastewaters. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2007, 41, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razali, M.; Kim, J.F.; Attfield, M.; Budd, P.M.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M.; Szekely, G. Sustainable wastewater treatment and recycling in membrane manufacturing. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 5196–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, M.; Zou, S.; Yang, X.; Long, T.E.; He, Z. Efficient recovery of polyelectrolyte draw solutes in forward osmosis towards sustainable water treatment. Desalination 2017, 422, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulembier, O.; Mezzasalma, L.; Taton, D.; De Winter, J. Benzoic Acid-Organocatalyzed Ring-Opening (co) Polymerization (ORO (c) P) of L-Lactide and Ɛ-Caprolactone Under Solvent-Free Conditions: From Simplicity to Recyclability. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.F.; Szekely, G.; Schaepertoens, M.; Valtcheva, I.B.; Jimenez-Solomon, M.F.; Livingston, A.G. In situ solvent recovery by organic solvent nanofiltration. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2371–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasiano, D.; Luongo, V.; Petrella, A.; Alfè, M.; Pirozzi, F.; Fratino, U.; Piccinni, A.F. Preliminary study on the adoption of dark fermentation as pretreatment for a sustainable hydrothermal denaturation of cement-asbestos composites. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 166, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italian Organization for Standardization (UNI). Cement Composition, Specifications and Conformity Criteria for Common Cements. EN 197-1. Available online: http://store.uni.com/magento-1.4.0.1/index.php/en-197-1-2011.html (accessed on 14 September 2011).
- Italian Organization for Standardization (UNI). Methods of Testing Cement-Part 1: Determination of Strength. EN 196-1. Available online: http://store.uni.com/magento-1.4.0.1/index.php/en-196-1-2016.html (accessed on 27 April 2016).
- Italian Organization for Standardization (UNI). Characterization of Waste-Compliance Test for Leaching of Granular Waste Materials and Sludges. EN 12457-2. Available online: http://store.uni.com/magento-1.4.0.1/index.php/en-12457-2-2002.html (accessed on 18 September 2002).
- Gustafsson, S.E. Transient plane source techniques for thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity measurements of solid materials. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1991, 62, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, A.; Petruzzelli, V.; Ranieri, E.; Catalucci, V.; Petruzzelli, D. Sorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Ni(II) from single- and multimetal solutions by recycled waste porous glass. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2016, 203, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglezakis, V.J.; Grigoropoulou, H. Effects of operating conditions on the removal of heavy metals by zeolite in fixed bed reactors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 112, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvidović, N.V.; Perić, J.; Trgo, M. Column performance in lead removal from aqueous solutions by fixed bed of natural zeolite–clinoptilolite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 49, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, A.; Petrella, M.; Boghetich, G.; Basile, T.; Petruzzelli, V.; Petruzzelli, D. Heavy metals retention on recycled waste glass from solid wastes sorting operations: A comparative study among different metal species. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karein, S.M.M.; Joshaghani, A.; Ramezanianpour, A.A.; Isapour, S.; Karakouzian, M. Effects of the mechanical milling method on transport properties of self-compacting concrete containing perlite powder as a supplementary cementitious material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 172, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różycka, A.; Pichór, W. Effect of perlite waste addition on the properties of autoclaved aerated concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 120, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, A.; Spasiano, D.; Rizzi, V.; Cosma, P.; Race, M.; De Vietro, N. Lead Ion Sorption by Perlite and Reuse of the Exhausted Material in the Construction Field. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liuzzi, S.; Rubino, C.; Stefanizzi, P.; Petrella, A.; Boghetich, A.; Casavola, C.; Pappalettera, G. Hygrothermal properties of clayey plasters with olive fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 158, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mundo, R.; Petrella, A.; Notarnicola, M. Surface and bulk hydrophobic cement composites by tyre rubber addition. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 172, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, A.; Spasiano, D.; Liuzzi, S.; Ayr, U.; Cosma, P.; Rizzi, V.; Petrella, M.; Di Mundo, R. Use of cellulose fibers from wheat straw for sustainable cement mortars. J. Sustain. Cem. Based Mater. 2018, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, L.; Bellezze, T.; Belli, A.; Bignozzi, M.C.; Bolzoni, F.; Brenna, A.; Cabrini, M.; Candamano, S.; Cappai, M.; Caputo, D.; et al. Binders alternative to Portland cement and waste management for sustainable construction-part 1. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2018, 16, 186–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coppola, L.; Bellezze, T.; Belli, A.; Bignozzi, M.C.; Bolzoni, F.; Brenna, A.; Cabrini, M.; Candamano, S.; Cappai, M.; Caputo, D.; et al. Binders alternative to Portland cement and waste management for sustainable construction-part 2. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2018, 16, 207–221. [Google Scholar]









| Test No. | Metal Specie | Solution | Flow Rate (Lh−1) | Influent Concentration (mgL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pb+2 | single | 0.2 | 2 |
| 2 | Cd+2 | single | 0.2 | 2 |
| 3 | Ni+2 | single | 0.2 | 2 |
| 4 | Pb+2 | binary | 0.2 | 2 |
| Cd+2 | binary | 0.2 | 2 | |
| 5 | Pb+2 | binary | 0.2 | 2 |
| Ni+2 | binary | 0.2 | 2 | |
| 6 | Pb+2 | ternary | 0.2 | 2 |
| Cd+2 | ternary | 0.2 | 2 | |
| Ni+2 | ternary | 0.2 | 2 | |
| 7 | Pb+2 | ternary | 0.2 | 3 |
| 8 | Pb+2 | ternary | 0.2 | 4 |
| 9 | Pb+2 | ternary | 0.2 | 5 |
| Cd+2 | ternary | 0.2 | 5 | |
| Ni+2 | ternary | 0.2 | 5 | |
| 10 | Pb+2 | ternary | 0.15 | 2 |
| 11 | Pb+2 | ternary | 0.3 | 2 |
| 12 | Pb+2 | ternary | 0.4 | 2 |
| Test No. | Metal | Solution | qexp (mg·g−1) | BV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pb+2 | single | 1.45 ± 0.1 | 160 ± 8 |
| 2 | Cd+2 | single | 0.85 ± 0.05 | 80 ± 4 |
| 3 | Ni+2 | single | 0.5 ± 0.05 | 40 ± 2 |
| Test No. | Metal | Solution | qexp (mg·g−1) | BV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | Pb+2 | binary | 1.05 ± 0.1 | 110 ± 6 |
| Cd+2 | 0.5 ± 0.05 | 50 ± 3 | ||
| 5 | Pb+2 | binary | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 115 ± 6 |
| Ni+2 | 0.3 ± 0.0 | 30 ± 2 |
| Test No. | Metal Specie | Solution | Influent Concentration (mgL−1) | qexp (mg·g−1) | BV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | Pb+2 | ternary | 2 | 1.0 ± 0.05 | 106 ± 5 |
| Cd+2 | ternary | 2 | 0.45 ± 0.0 | 40 ± 2 | |
| Ni+2 | ternary | 2 | 0.25 ± 0.0 | 20 ± 1 | |
| 7 | Pb+2 | ternary | 3 | 1.2 ± 0.05 | 83 ± 4 |
| 8 | Pb+2 | ternary | 4 | 1.4 ± 0.05 | 65 ± 3 |
| 9 | Pb+2 | ternary | 5 | 1.5 ± 0.05 | 50 ± 3 |
| Cd+2 | ternary | 5 | 0.9 ± 0.05 | 16 ± 1 | |
| Ni+2 | ternary | 5 | 0.50 ± 0.0 | 7 ± 0.5 |
| Test No. | Metal Specie | Solution | Flow Rate (Lh−1) | qexp (mg·g−1) | BV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | Pb+2 | ternary | 0.15 | 1.2 ± 0.05 | 150 ± 7 |
| 7 | Pb+2 | ternary | 0.2 | 1.0 ± 0.05 | 106 ± 5 |
| 11 | Pb+2 | ternary | 0.3 | 0.9 ± 0.05 | 78 ± 4 |
| 12 | Pb+2 | ternary | 0.4 | 0.8 ± 0.05 | 67 ± 3 |
| Element | Wt.% | Wt.% Sigma |
|---|---|---|
| Na | 11.6 | 0.25 |
| Al | 3.5 | 0.1 |
| Si | 66.0 | 0.5 |
| Ca | 9.8 | 0.15 |
| Ni | 1.5 | 0.1 |
| Cd | 2.4 | 0.2 |
| Pb | 5.2 | 0.3 |
| Total: | 100.00 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petrella, A.; Spasiano, D.; Race, M.; Rizzi, V.; Cosma, P.; Liuzzi, S.; De Vietro, N. Porous Waste Glass for Lead Removal in Packed Bed Columns and Reuse in Cement Conglomerates. Materials 2019, 12, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12010094
Petrella A, Spasiano D, Race M, Rizzi V, Cosma P, Liuzzi S, De Vietro N. Porous Waste Glass for Lead Removal in Packed Bed Columns and Reuse in Cement Conglomerates. Materials. 2019; 12(1):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12010094
Chicago/Turabian StylePetrella, Andrea, Danilo Spasiano, Marco Race, Vito Rizzi, Pinalysa Cosma, Stefania Liuzzi, and Nicoletta De Vietro. 2019. "Porous Waste Glass for Lead Removal in Packed Bed Columns and Reuse in Cement Conglomerates" Materials 12, no. 1: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12010094
APA StylePetrella, A., Spasiano, D., Race, M., Rizzi, V., Cosma, P., Liuzzi, S., & De Vietro, N. (2019). Porous Waste Glass for Lead Removal in Packed Bed Columns and Reuse in Cement Conglomerates. Materials, 12(1), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12010094