Preparation of Bi2O3/Al Core-Shell Energetic Composite by Two-Step Ball Milling Method and Its Application in Solid Propellant
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
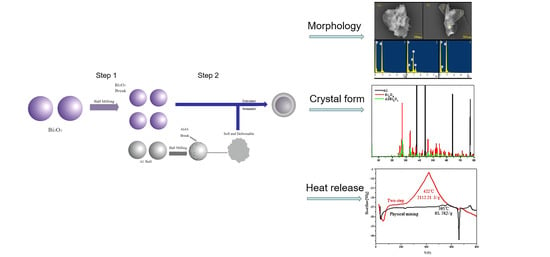
2.2. Two-Step Ball Milling Process
2.2.1. Ball Milling Process
2.2.2. Calculation of the Ratio of Al and Bi2O3
2.3. Instruments and Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Two-Step Ball Milling Parameters
3.1.1. Ball Milling of Bi2O3
3.1.2. The Preparation of Bi2O3/Al Core-Shell Energetic Composites
3.2. Morphology and Structure Characterization of Bi2O3/Al Core-Shell Energetic Composites
3.2.1. Ball Milling Effect and Sample Morphology
3.2.2. Changes in Lattice Structure
3.3. Properties of Solid Propellant Contained Bi2O3/Al Core-Shell Energetic Composite
3.3.1. Density and Density Specific Impulse of the Propellants
3.3.2. Explosion Heat of the Propellant
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, X.; Li, J.; Liu, X. Research Status and Development Trend of High-energy Chemical Propellant. Available online: http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=conference&id=6554186 (accessed on 18 May 2019).
- Wang, S.; Tan, H.; Jin, Y. Energy Level Analysis of NEPE Solid Propellant Containing Hexanitrohexaazaisowurtzitane. Fly. Missile 2002, 2, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, R.L.; Lee, R.S.; Tillotson, T.M.; Hrubesh, L.W.; Swansiger, R.W.; Foxet, G.A. Sol-Gel Manufactured Energetic Material. U.S. Patent 20,030,697,477, 5 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, A.; Obamedo, J.; Schoenitz, M.; Dreizin, E.L. Effect of composition on properties of reactive Al·Bi powders preparedby mechanical milling. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2015, 83, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Luss, D.; Martirosyan, K.S. The behavior of nanothermite reaction based on Bi2O3/Al. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 074311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valliappan, S.; Swiatkiewicz, J.; Puszynski, J.A. Reactivity of aluminum nanopowers with metal oxides. Power Technol. 2005, 156, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W. Preparation and Properties of High Density HTPE Propellant; Beijing Institute of Technology: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yermakov, A.Y.; Yurchikov, Y.Y.; Barinov, V.A. Magnetic properties of amorphous powders of y-co alloys produced by grinding. Phys. Metal. Metallogr. 1981, 52, 50–58. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, C.C.; Cavin, O.B.; McKamey, C.G.; Scarbrough, J.O. Preparation of amorphous Ni60-Nb40 by mechanical alloying. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1993, 43, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; An, C.; Luo, J.; Wang, J.Y. Preparation and Characterization of Nano-CL-20/AP Energetic Composite Particles. Energy Mater. 2018, 29, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, J.; Wang, X.; Han, Z.; Feng, B. Preparation and Microscopic Properties of Aluminum Powder/Teflon Mechanically Activated Energetic Materials. Meter. Rep. 2018, 32, 894–898. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Ma, M.; Zhang, W. Adhesion Characteristics of Metal Powder in High Energy Ball Milling Process. Therm. Process. Technol. 2002, 1, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G. Research on Heat and Mass Transfer Process of Multiscale Brown Coal; Northeastern University: Boston, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, M.A.; Yan, J.H.; Deng, X.; Cheng, C.S.; Zavattieri, P. Three-dimensional digital image correlation to quantify deformation and crack-opening displacement in ductile aluminum under mixed-mode I/III loading. Opt. Eng. 2007, 46, 051003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mae, H.; Teng, X.; Bai, Y.; Wierzbicki, T. Comparison of ductile fracture properties of aluminum castings: Sand mold vs. metal mold. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2008, 45, 1430–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fredenburg, D.A.; Thadhani, N.N. Predicting the shock compression response of heterogeneous powder mixtures. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 223513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, M.; Chiang, Y.M.; Kosacki, I.; Lee, L.J.; Tuller, H.; Liu, Y. Solute Segregation and Grain-Boundary Impedance in High-Purity Stabilized Zirconia. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1996, 79, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Lu, D.; Jiang, Y. Study on the preparation of SiC/Al composite powder by high energy ball milling. Spec. Cast. Nonferrous Alloys 2011, 8, 749–753. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, D.; Jiang, H.; Liu, J. Diffraction Abnormal Fine Structure (DAFS) Spectra and Its Application. Adv. Phys. 1997, 3, 250–264. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, K.W.; Pantoya, M.L.; Levitas, V.I. Fast reactions with nanometre and micrometre aluminum:A study on oxidation versus fluorination. Combust. Flame 2008, 155, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitas, V.I.; Pantoya, M.L.; Watson, K.W. Melt-dispersion mechanism for fast reaction of aluminum particles: Extension for micron scale particles and fluorination. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 201917–201919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.; Lee, D.; Park, K.; Zachariah, M.R. Importance of Phase Change of Aluminum in Oxidation of Aluminum Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 14793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udhayabanu, V.; Singh, N.; Murty, B.S. Mechanical activation of aluminothermic reduction of NiO by high energy ball milling. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 497, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilip, J.J.; Reddy, B.S.; Das, S.; Das, K. In-situ Al-based bulk nanocomposites by solid-state aluminothermic reaction in Al-Ti-O system. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 475, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Dong, S.; Luo, P.; Yangli, A.; Liu, Q.; Xie, Z. Effect of Ni addition on the preparation of Al2O3-TiB2 composites using high-energy ball milling. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2014, 2, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Slycken, J.; Verleysen, P.; Degrieck, J.; Samek, L.; De Cooman, B.C. High-strain-rate behavior of low-alloy multiphase aluminumand silicon-based transformation-induced plasticity steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.Y.; Fei, W.D.; Wang, L.D.; Li, Z.J. An aluminum borate whisker-reinforced aluminum matrix composite with high plasticity. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 430, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Liu, W.; Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Hu, W. Effect of High Energy Ball Milling Process Parameters on Properties of Titanium Hydroxide Powder and Magnesium Powder. Powder Metall. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 21, 626–631. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, F.; Wang, C.; Zhu, H.; Yi, J. Energy performance and characteristic signal analysis of low-characteristic fuel-rich propellant containing 3,4-diaminofurazan. Solid State Rocket Technol. 2008, 31, 621–624. [Google Scholar]






| Ball Milling Time/h | Ball Milling Speed/r·min−1 | Ball-to-Material Ratio | Dmax/μm | Dmin/μm | Daverage/μm | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 350 | 10:1 | 7.64 | 0.45 | 2.46 | 0.34 |
| 2 | 350 | 10:1 | 6.84 | 0.37 | 1.96 | |
| 3 | 350 | 10:1 | 3.79 | 0.26 | 1.51 | |
| 5 | 350 | 10:1 | 4.40 | 0.32 | 1.54 | |
| 7 | 350 | 10:1 | 5.06 | 0.32 | 1.56 | |
| 9 | 350 | 10:1 | 6.24 | 0.33 | 1.94 | |
| 3 | 250 | 10:1 | 6.66 | 0.33 | 1.67 | 0.06 |
| 3 | 300 | 10:1 | 6.31 | 0.28 | 1.55 | |
| 3 | 350 | 10:1 | 3.79 | 0.26 | 1.51 | |
| 3 | 400 | 10:1 | 5.04 | 0.20 | 1.52 | |
| 3 | 450 | 10:1 | 6.38 | 0.22 | 1.63 | |
| 3 | 350 | 5:1 | 6.66 | 0.30 | 1.64 | 0.14 |
| 3 | 350 | 10:1 | 3.79 | 0.26 | 1.51 | |
| 3 | 350 | 15:1 | 3.28 | 0.22 | 1.21 | |
| 3 | 350 | 20:1 | 3.65 | 0.22 | 1.39 | |
| 3 | 350 | 25:1 | 4.38 | 0.23 | 1.45 |
| Ball Milling Time/h | Dmax/μm | Dmin/μm | Daverage/μm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.83 | 0.34 | 0.99 |
| 2 | 3.52 | 0.13 | 0.40 |
| 3 | 3.43 | 0.10 | 0.35 |
| Sample | Density/g·cm−3 |
|---|---|
| Al | 2.5587 ± 0.0132 |
| Bi2O3 | 8.7963 ± 0.0161 |
| Physical mixing | 7.1880 ± 0.0147 |
| Step ball mill | 8.0030 ± 0.0129 |
| Bi2O (%) | AP (%) | OB | ρ (g/cm3) | ISP (s) | ISR (g·s/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 62 | 0.596 | 1.778 | 269.2 | 478.6 |
| 2 | 60 | 0.585 | 1.804 | 266.7 | 481.1 |
| 4 | 58 | 0.575 | 1.830 | 264.2 | 483.5 |
| 6 | 56 | 0.564 | 1.857 | 261.7 | 486.0 |
| 8 | 54 | 0.553 | 1.885 | 259.1 | 488.5 |
| 10 | 52 | 0.542 | 1.914 | 256.5 | 491.0 |
| 12 | 50 | 0.531 | 1.944 | 253.9 | 493.5 |
| 15 | 47 | 0.514 | 1.991 | 249.8 | 497.3 |
| 17 | 45 | 0.503 | 2.023 | 247.1 | 499.8 |
| 19 | 43 | 0.491 | 2.056 | 244.3 | 502.3 |
| 20 | 42 | 0.485 | 2.073 | 242.9 | 503.5 |
| 21 | 41 | 0.480 | 2.091 | 241.4 | 504.7 |
| 23 | 39 | 0.468 | 2.126 | 238.5 | 507.0 |
| 25 | 37 | 0.456 | 2.163 | 235.2 | 508.8 |
| 26 | 36 | 0.450 | 2.182 | 233.4 | 509.3 |
| Content of Bi2O3/Al Composite in HTPE Propellant/wt% | Explosive Heat/MJ·kg−1 |
|---|---|
| 0 | 4.29 |
| 5 | 4.39 |
| 7.5 | 4.45 |
| 10 | 4.91 |
| 18 | 5.03 |
| 21 | 5.20 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, M.; Yao, Q.; Yang, H.; Guo, T.; Du, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; Luo, Y. Preparation of Bi2O3/Al Core-Shell Energetic Composite by Two-Step Ball Milling Method and Its Application in Solid Propellant. Materials 2019, 12, 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12111879
Xia M, Yao Q, Yang H, Guo T, Du X, Zhang Y, Li G, Luo Y. Preparation of Bi2O3/Al Core-Shell Energetic Composite by Two-Step Ball Milling Method and Its Application in Solid Propellant. Materials. 2019; 12(11):1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12111879
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Min, Qifa Yao, Huilian Yang, Tao Guo, Xiuxin Du, Yanjie Zhang, Guoping Li, and Yunjun Luo. 2019. "Preparation of Bi2O3/Al Core-Shell Energetic Composite by Two-Step Ball Milling Method and Its Application in Solid Propellant" Materials 12, no. 11: 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12111879
APA StyleXia, M., Yao, Q., Yang, H., Guo, T., Du, X., Zhang, Y., Li, G., & Luo, Y. (2019). Preparation of Bi2O3/Al Core-Shell Energetic Composite by Two-Step Ball Milling Method and Its Application in Solid Propellant. Materials, 12(11), 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12111879