Strain Dependence of Hysteretic Giant Magnetoimpedance Effect in Co-Based Amorphous Ribbon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Measurement Method
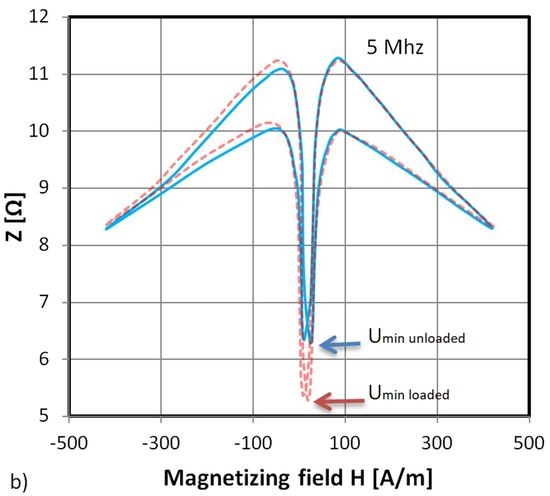
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panina, L.; Mohri, K.; Bushida, K.; Noda, M. Giant magneto-impedance and magneto-inductive effects in amorphous alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 76, 6198–6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Cai, B.; Xu, D. Giant magneto-impedance effect in amorphous magnetostrictive FeSiB thin films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2000, 213, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, T.; Nishibe, Y.; Yamadera, H.; Nonomura, Y.; Takeuchi, M.; Taga, Y. Giant magneto-impedance effect in layered thin films. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1997, 33, 4367–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panina, L.V.; Mohri, K. Magneto-impedance in multilayer films. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2000, 81, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukova, V.; Blanco, J.M.; Ipatov, M.; Gonzalez, J.; Churyukanova, M.; Zhukov, A. Engineering of magnetic softness and giant magnetoimpedance effect in Fe-rich microwires by stress-annealing. Scr. Mater. 2018, 142, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chobaomsup, V.; Jantaratana, P.; Boonyongmaneerat, Y. Effects of Current Pulsation on Magnetic Properties and Giant Magnetoimpedance of Electrodeposited NiFe Coatings on Cu Wires. Mater. Sci. Forum 2018, 928, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, M.; Kraus, L.; Ripka, P. Giant magnetoimpedance sensors. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2001, 4, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, E.P.; Rowe, H. An impedance magnetometer. Proceed. Phys. Soc. 1938, 50, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turney, G.L.; Cousins, G.E. A portable direct-reading magnetometer. J. Sci. Instrum. 1938, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobel, M.; Pirota, K.R. Giant magnetoimpedance: Concepts and recent progress. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 242, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corte-León, P.; Zhukova, V.; Ipatov, M.; Blanco, J.M.; Gonzalez, J.; Zhukov, A. Engineering of magnetic properties of Co-rich microwires by joule heating. Intermetallics 2019, 105, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, L. GMI modeling and material optimization. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2003, 106, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.P.; Uchiyama, T.; Mohri, K.; Kita, E.; Bushida, K. Sensitive stress-impedance micro sensor using amorphous magnetostrictive wire. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1997, 33, 3355–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejedor, M.; Hernando, B.; Sánchez, M.L.; Prida, V.M.; Vázquez, M. The torsional dependence of the magneto-impedance effect in current-annealed Co-rich amorphous wires. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1998, 31, 3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beato-López, J.J.; Vargas-Silva, G.; Pérez-Landazábal, J.I.; Gómez-Polo, C. Giant stress-impedance (GSI) sensor for diameter evaluation in cylindrical elements. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 269, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematov, M.G.; Salem, M.M.; Adam, A.; Ahmed, M.; Panina, L.V.; Morchenko, A.T. Effect of stress on magnetic properties of annealed glass-coated Co71Fe5B11Si10Cr3 amorphous microwires. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalca, I.; Ercuta, A.; Ionascu, C. The Villari effect in Fe–Cr–B amorphous ribbons. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2003, 106, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosenko, V.K.; Maslov, V.V.; Kirilchuk, V.V.; Kochkubey, A.P. Some industrial applications of amorphous and nanocrystalline alloys. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2008, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazda, P.; Nowicki, M.; Szewczyk, R. Influence of alloy composition on GMI effect in amorphous ribbons. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1996, 020012. [Google Scholar]
- Makhnovskiy, D.P.; Panina, L.V.; Mapps, D.J. Asymmetrical magnetoimpedance in as-cast CoFeSiB amorphous wires due to ac bias. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 77, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, M.H.; Yu, S.C.; Kim, C.G.; Vázquez, M. Origin of asymmetrical magnetoimpedance in a Co-based amorphous microwire due to dc bias current. Appl. Phys. Let. 2003, 83, 2871–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciureanu, P.; Khalil, I.; Melo, L.G.C.; Rudkowski, P.; Yelon, A. Stress-induced asymmetric magneto-impedance in melt-extracted Co-rich amorphous wires. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 249, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.H.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.A.; Yu, J.Q.; Cai, B.C. Giant magnetoimpedance and stress-impedance effects in multilayered FeSiB/Cu/FeSiB films with a meander structure. J. Mater. Res. 2003, 18, 868–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohri, K.; Uchiyama, T.; Shen, L.P.; Cai, C.M.; Panina, L.V. Sensitive micro magnetic sensor family utilizing magneto-impedance (MI) and stress-impedance (SI) effects for intelligent measurements and controls. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2001, 91, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobeno, A.F.; Zhukov, A.; Blanco, J.M.; Larin, V.; Gonzalez, J. Magnetoelastic sensor based on GMI of amorphous microwire. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2001, 91, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marusenkov, A. Possibilities of further improvement of 1s fluxgate variometers. Geosci. Instrum. Methods Data Syst. 2017, 6, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicki, M.; Szewczyk, R.; Charubin, T.; Marusenkov, A.; Nosenko, A.; Kyrylchuk, V. Modeling the Hysteresis Loop of Ultra-High Permeability Amorphous Alloy for Space Applications. Materials 2018, 11, 2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazda, P.; Kachniarz, M.; Szudarek, M. Test stand for investigating of giant magneto-impedance. In International Conference Automation; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Mao, X.H.; Chen, J.A.; Ding, W.; Gao, X.Y.; Zhou, Z.M. Stress-impedance effects in layered FeSiB/Cu/FeSiB films with a meander line structure. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 292, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnecker, J.P.; Tiberto, P.A.O.L.A.; Kurlyandskaia, G.V.; Sinnecker, E.H.C.P.; Vázquez, M.; Hernando, A. Hysteretic giant magneto impedance. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 84, 5814–5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipatov, M.; Zhukova, V.; Zhukov, A.; Gonzalez, J.; Zvezdin, A. Low-field hysteresis in the magnetoimpedance of amorphous microwires. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 134421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipatov, M.; Zhukova, V.; Gonzalez, J.; Zhukov, A. Magnetoimpedance hysteresis in amorphous microwires induced by core–shell interaction. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 122401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béron, F.; Valenzuela, L.A.; Knobel, M.; Melo, L.G.; Pirota, K.R. Hysteretic giant magnetoimpedance effect analyzed by first-order reversal curves. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 1601–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukova, V.; Blanco, J.M.; Ipatov, M.; Churyukanova, M.; Taskaev, S.; Zhukov, A. Tailoring of magnetoimpedance effect and magnetic softness of Fe-rich glass-coated microwires by stress-annealing. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabias, J.; Asfour, A.; Yonnet, J.-P. The Impact of Bending Stress on the Performance of Giant Magneto-Impedance (GMI) Magnetic Sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knobel, M.; Vázquez, M.; Kraus, L. Giant magnetoimpedance. Handb. Magn. Mater. 2003, 15, 497–563. [Google Scholar]
- Kraus, L.; Švec, P. Magnetoelastic hysteresis of amorphous ribbons. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 7220–7222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, R.C. Inverse compensation for hysteresis in magnetostrictive transducers. Math. Comput. Model. 2001, 33, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oppermann, K.; Arminger, B.R.; Zagar, B.G. Smart hysteresis compensation of a magneto-elastic force sensor based on Terfenol-D. In Proceeding of 2010 IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Austin, TX, USA, 3–6 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, K.I.; Muranaka, C.S.; Yamaguchi, M. A new hybrid device using magnetostrictive amorphous films and piezoelectric substrates. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1994, 30, 916–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurlyandskaya, G.V.; Vazquez, M.; Munoz, J.L.; Garcia, D.; McCord, J. Effect of induced magnetic anisotropy and domain structure features on magnetoimpedance in stress annealed Co-rich amorphous ribbons. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 196, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nowicki, M.; Gazda, P.; Szewczyk, R.; Marusenkov, A.; Nosenko, A.; Kyrylchuk, V. Strain Dependence of Hysteretic Giant Magnetoimpedance Effect in Co-Based Amorphous Ribbon. Materials 2019, 12, 2110. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12132110
Nowicki M, Gazda P, Szewczyk R, Marusenkov A, Nosenko A, Kyrylchuk V. Strain Dependence of Hysteretic Giant Magnetoimpedance Effect in Co-Based Amorphous Ribbon. Materials. 2019; 12(13):2110. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12132110
Chicago/Turabian StyleNowicki, Michał, Piotr Gazda, Roman Szewczyk, Andriy Marusenkov, Anton Nosenko, and Vasyl Kyrylchuk. 2019. "Strain Dependence of Hysteretic Giant Magnetoimpedance Effect in Co-Based Amorphous Ribbon" Materials 12, no. 13: 2110. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12132110
APA StyleNowicki, M., Gazda, P., Szewczyk, R., Marusenkov, A., Nosenko, A., & Kyrylchuk, V. (2019). Strain Dependence of Hysteretic Giant Magnetoimpedance Effect in Co-Based Amorphous Ribbon. Materials, 12(13), 2110. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12132110