Use of Biopolymers in Mucosally-Administered Vaccinations for Respiratory Disease
Abstract
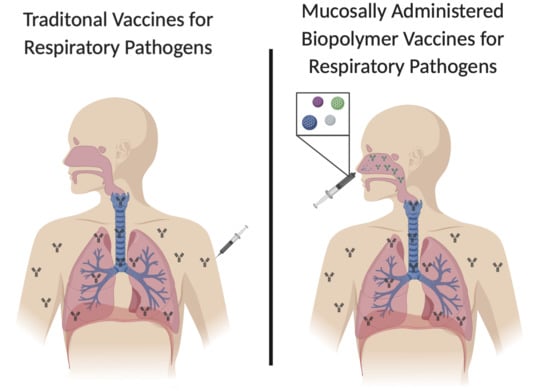
:1. Introduction
2. Chitosan
3. Starch
4. Alginate
5. Gellan
6. β-Glucans
7. Emulsan
8. Hyaluronic Acid
9. Conclusions/Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forum of International Respiratory Societies. The Global Impact of Respiratory Disease, 2nd ed.; European Respiratory Society: Sheffield, UK, 2017; pp. 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Naghavi, M.; Allen, C.; Barber, R.M.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Carter, A.; Casey, D.C.; Charlson, F.J.; Chen, A.Z.; Coates, M.M.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Life Expectancy, All-Cause Mortality, and Cause-Specific Mortality for 249 Causes of Death, 1980–2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1459–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, K.H.T.; Duclos, P.; Nelson, E.A.S.; Hutubessy, R.C.W. An Update of the Global Burden of Pertussis in Children Younger than 5 Years: A Modelling Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, W.W.; Weintraub, E.; Dhankhar, P.; Cheng, P.-Y.; Brammer, L.; Meltzer, M.I.; Bresee, J.S.; Shay, D.K. Estimates of US Influenza-Associated Deaths Made Using Four Different Methods. Influenza Other Respir Viruses 2009, 3, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skeiky, Y.A.W.; Sadoff, J.C. Advances in Tuberculosis Vaccine Strategies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyre, M.; Samaha, H.; Makonnen, Y.J.; Saad, A.; Abd-Elnabi, A.; Galal, S.; Ettel, T.; Dauphin, G.; Lubroth, J.; Roger, F.; et al. Avian Influenza Vaccination in Egypt: Limitations of the Current Strategy. J. Mol. Genet. Med. 2009, 3, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wendelboe, A.M.; Van Rie, A.; Salmaso, S.; Englund, J.A. Duration of Immunity Against Pertussis After Natural Infection or Vaccination. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2005, 24, S58–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, J.C.; Postic, B.; Brown, A.; Harrison, K.; Birgenheier, R.; Dowda, H. Influenza A/Philippines/2/82 Outbreak in a Nursing Home: Limitations of Influenza Vaccination in the Aged. Am. J. Infect. Control 1984, 12, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Sangiao, E.; Holban, A.M.; Gestal, M.C. Advanced Nanobiomaterials: Vaccines, Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases. Molecules 2016, 21, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbal-Gill, I.; Fisher, A.N.; Rappuoli, R.; Davis, S.S.; Illum, L. Stimulation of Mucosal and Systemic Antibody Responses against Bordetella Pertussis Filamentous Haemagglutinin and Recombinant Pertussis Toxin after Nasal Administration with Chitosan in Mice. Vaccine 1998, 16, 2039–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patria, M.F.; Tagliabue, C.; Longhi, B.; Esposito, S. Influenza Vaccination in Children at High Risk of Respiratory Disease. Adv. Vaccines 2013, 1, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, B.; Hägerström, H.; Fransén, N.; Edsman, K.; Björk, E. The Influence of Gellan Gum on the Transfer of Fluorescein Dextran across Rat Nasal Epithelium in Vivo. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2005, 59, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Bao, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, D.; Wu, W. Alkyl Polyglycoside, a Highly Promising Adjuvant in Intranasal Split Influenza Vaccines. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2017, 13, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdi, M.H.; Conway, B.R.; Smith, A.M. Development of Mucoadhesive Sprayable Gellan Gum Fluid Gels. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 488, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, P.; Sharma, S.; Garg, S. Permeability Issues in Nasal Drug Delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2002, 7, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Hirai, S.; Bawarshi, R. Nasal Absorption of Propranolol from Different Dosage Forms by Rats and Dogs. J. Pharm. Sci. 1980, 69, 1411–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacon, A.; Makin, J.; Sizer, P.J.; Jabbal-Gill, I.; Hinchcliffe, M.; Illum, L.; Chatfield, S.; Roberts, M. Carbohydrate Biopolymers Enhance Antibody Responses to Mucosally Delivered Vaccine Antigens. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 5764–5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, J.; Zhao, D.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, K. Polymer-Based Nanomaterials and Applications for Vaccines and Drugs. Polymers 2018, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Min, M.; Du, N.; Gu, Y.; Hode, T.; Naylor, M.; Chen, D.; Nordquist, R.E.; Chen, W.R. Chitin, Chitosan, and Glycated Chitosan Regulate Immune Responses: The Novel Adjuvants for Cancer Vaccine. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 387023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulescu, M.; Ficai, D.; Oprea, O.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E.; Holban, A.M. Antimicrobial Chitosan Based Formulations with Impact on Different Biomedical Applications. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2015, 16, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woggum, T.; Sirivongpaisal, P.; Wittaya, T. Properties and Characteristics of Dual-Modified Rice Starch Based Biodegradable Films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 67, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and Biomedical Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liakos, I.; Rizzello, L.; Scurr, D.J.; Pompa, P.P.; Bayer, I.S.; Athanassiou, A. All-Natural Composite Wound Dressing Films of Essential Oils Encapsulated in Sodium Alginate with Antimicrobial Properties. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 463, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, W.; Kim, Y.-C.; Hong, M.; Rejinold, S.; Park, K.; Yoon, I.; Yoo, S.; Lee, H.; Ahn, J. Microcrystalline Cellulose for Delivery of Recombinant Protein-Based Antigen against Erysipelas in Mice. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 7670505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmałek, T.; Froelich, A.; Tasarek, S. Application of Gellan Gum in Pharmacy and Medicine. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 466, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadpourdounighi, N.; Behfar, A.; Ezabadi, A.; Zolfagharian, H.; Heydari, M. Preparation of Chitosan Nanoparticles Containing Naja Naja Oxiana Snake Venom. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyer, A.M.; Hinchcliffe, M.; Watts, P.; Castile, J.; Jabbal-Gill, I.; Nankervis, R.; Smith, A.; Illum, L. Nasal Delivery of Insulin Using Novel Chitosan Based Formulations: A Comparative Study in Two Animal Models Between Simple Chitosan Formulations and Chitosan Nanoparticles. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehr, C.-M.; Bouwstra, J.A.; Schacht, E.H.; Junginger, H.E. In Vitro Evaluation of Mucoadhesive Properties of Chitosan and Some Other Natural Polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1992, 78, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeela, E.A.; O’Connor, D.; Jabbal-Gill, I.; Illum, L.; Davis, S.S.; Pizza, M.; Peppoloni, S.; Rappuoli, R.; Mills, K.H.G. A Mucosal Vaccine against Diphtheria: Formulation of Cross Reacting Material (CRM197) of Diphtheria Toxin with Chitosan Enhances Local and Systemic Antibody and Th2 Responses Following Nasal Delivery. Vaccine 2000, 19, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witschi, C.; Mrsny, R.J. In Vitro Evaluation of Microparticles and Polymer Gels for Use as Nasal Platforms for Protein Delivery. Pharm. Res. 1999, 16, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidi, M.; Romeijn, S.G.; Verhoef, J.C.; Junginger, H.E.; Bungener, L.; Huckriede, A.; Crommelin, D.J.A.; Jiskoot, W. N-Trimethyl Chitosan (TMC) Nanoparticles Loaded with Influenza Subunit Antigen for Intranasal Vaccination: Biological Properties and Immunogenicity in a Mouse Model. Vaccine 2007, 25, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, A.; Sánchez, A.; Janes, K.; Behrens, I.; Kissel, T.; Jato, J.L.V.; Alonso, M.J. Low Molecular Weight Chitosan Nanoparticles as New Carriers for Nasal Vaccine Delivery in Mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 57, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, K.; Nishimura, S.; Nishi, N.; Numata, F.; Tone, Y.; Tokura, S.; Azuma, I. Adjuvant Activity of Chitin Derivatives in Mice and Guinea-Pigs. Vaccine 1985, 3, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, J.; Une, T.; Ishihara, C.; Nishimura, K.; Tokura, S.; Mizukoshi, N.; Azuma, I. Stimulation of Non-Specific Host Resistance against Sendai Virus and Escherichia Coli Infections by Chitin Derivatives in Mice. Vaccine 1987, 5, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.H.; Barnard, A.; Watkins, J.; Redhead, K. Cell-Mediated Immunity to Bordetella Pertussis: Role of Th1 Cells in Bacterial Clearance in a Murine Respiratory Infection Model. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rowe, J.; Macaubas, C.; Monger, T.M.; Holt, B.J.; Harvey, J.; Poolman, J.T.; Sly, P.D.; Holt, P.G. Antigen-Specific Responses to Diphtheria-Tetanus-Acellular Pertussis Vaccine in Human Infants Are Initially Th2 Polarized. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 3873–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Illum, L.; Jabbal-Gill, I.; Hinchcliffe, M.; Fisher, A.N.; Davis, S.S. Chitosan as a Novel Nasal Delivery System for Vaccines. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 51, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Maharjan, S.; Sindurakar, P.; Cho, K.-H.; Choi, Y.-J.; Cho, C.-S. Needle-Free Immunization with Chitosan-Based Systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, F.; Heuking, S.; Junginger, H.E.; Borchard, G. Progress in Chitosan-Based Vaccine Delivery Systems. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2010, 20, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Fan, Y.-T.; Zhou, T.-J.; Gong, J.-H.; Cui, L.-H.; Cho, K.-H.; Choi, Y.-J.; Jiang, H.-L.; Cho, C.-S. Chemical Modification of Chitosan for Efficient Vaccine Delivery. Molecules 2018, 23, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán, J.I.; Vázquez, A.; Cyras, V.P. Bio-Nanocomposites Based on Derivatized Potato Starch and Cellulose, Preparation and Characterization. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 7196–7203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Mendieta, S.A.; Guillén, D.; Espitia, C.; Hernández-Pando, R.; Sanchez, S.; Rodríguez-Sanoja, R. A Novel Antigen-Carrier System: The Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Acr Protein Carried by Raw Starch Microparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 474, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laakso, T.; Artursson, P.; Sjöholm, I. Biodegradable Microspheres IV: Factors Affecting the Distribution and Degradation of Polyacryl Starch Microparticles. J. Pharm. Sci. 1986, 75, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degling, L.; Stjärnkvist, P. Biodegradable Microspheres XVIII: The Adjuvant Effect of Polyacryl Starch Microparticles with Conjugated Human Serum Albumin. Vaccine 1995, 13, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikingsson, L.D.; Sjöholm, I. Polyacryl Starch Microparticles as Adjuvant in Oral Immunisation, Inducing Mucosal and Systemic Immune Responses in Mice. Vaccine 2002, 20, 3355–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larhed, A.; Stertman, L.; Edvardsson, E.; Sjöholm, I. Starch Microparticles as Oral Vaccine Adjuvant: Antigen-Dependent Uptake in Mouse Intestinal Mucosa. J. Drug Target. 2004, 12, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarei, F.; Dounighi, N.M.; Zolfagharian, H.; Khaki, P.; Bidhendi, S.M. Alginate Nanoparticles as a Promising Adjuvant and Vaccine Delivery System. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 75, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowersock, T.L.; Hogenesch, H.; Suckow, M.; Porter, R.E.; Jackson, R.; Park, H.; Park, K. Oral Vaccination with Alginate Microsphere Systems. J. Control. Release 1996, 39, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otterlei, M.; Ostgaard, K.; Skjåk-Braek, G.; Smidsrød, O.; Soon-Shiong, P.; Espevik, T. Induction of Cytokine Production from Human Monocytes Stimulated with Alginate. J. Immunother. 1991, 10, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujihara, M.; Nagumo, T. An Influence of the Structure of Alginate on the Chemotactic Activity of Macrophages and the Antitumor Activity. Carbohydr. Res. 1993, 243, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelatto, M.C.; Guimond, P.; Bowersock, T.L.; HogenEsch, H. Induction of Systemic and Mucosal Immune Response in Cattle by Intranasal Administration of Pig Serum Albumin in Alginate Microparticles. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2001, 83, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Dünnhaupt, S. Chitosan-Based Drug Delivery Systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, O.; Cordeiro-da-Silva, A.; Tavares, J.; Santarém, N.; de Sousa, A.; Borchard, G.; Junginger, H.E. Immune Response by Nasal Delivery of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen and Codelivery of a CpG ODN in Alginate Coated Chitosan Nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, O.; Tavares, J.; de Sousa, A.; Borchard, G.; Junginger, H.E.; Cordeiro-da-Silva, A. Evaluation of the Immune Response Following a Short Oral Vaccination Schedule with Hepatitis B Antigen Encapsulated into Alginate-Coated Chitosan Nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 32, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, S.M.; Free, S.J. The Structure and Synthesis of the Fungal Cell Wall. Bioessays 2006, 28, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Ostroff, G.R.; Lee, C.K.; Specht, C.A.; Levitz, S.M. Characterization and Optimization of the Glucan Particle-Based Vaccine Platform. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 1585–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.J.; Doni, A.; Hummelshøj, T.; Honoré, C.; Bastone, A.; Mantovani, A.; Thielens, N.M.; Garred, P. Synergy between Ficolin-2 and Pentraxin 3 Boosts Innate Immune Recognition and Complement Deposition. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 28263–28275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, G.D.; Taylor, P.R.; Reid, D.M.; Willment, J.A.; Williams, D.L.; Martinez-Pomares, L.; Wong, S.Y.C.; Gordon, S. Dectin-1 Is A Major β-Glucan Receptor On Macrophages. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, N.; Asakawa, A.; Inui, A.; Masuda, Y.; Nanba, H. Enhancement of Cytotoxicity of NK Cells by D-Fraction, a Polysaccharide from Grifola Frondosa. Oncol. Rep. 2005, 13, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Ostroff, G.R.; Lee, C.K.; Wang, J.P.; Specht, C.A.; Levitz, S.M. Distinct Patterns of Dendritic Cell Cytokine Release Stimulated by Fungal -Glucans and Toll-Like Receptor Agonists. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 1774–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Ostroff, G.R.; Lee, C.K.; Specht, C.A.; Levitz, S.M. Robust Stimulation of Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses Following Vaccination with Antigen-Loaded β-Glucan Particles. mBio 2010, 1, e00164-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smet, R.; Demoor, T.; Verschuere, S.; Dullaers, M.; Ostroff, G.R.; Leclercq, G.; Allais, L.; Pilette, C.; Dierendonck, M.; De Geest, B.G.; et al. β-Glucan Microparticles Are Good Candidates for Mucosal Antigen Delivery in Oral Vaccination. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutnick, D.L.; Shabtai, Y. Exopolysaccharide bioemulsifiers in biosurfactants and biotechnology. In Exopolysaccharide Bioemulsifiers; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1987; Volume 25, pp. 211–246. [Google Scholar]
- Gorkovenko, A.; Zhang, J.; Gross, R.A.; Allen, A.L.; Kaplan, D.L. Bioengineering of emulsifier structure: Emulsan variants. Can. J. Microbiol. 1997, 43, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, G.D.; Gordon, S. Fungal β-Glucans and Mammalian Immunity. Immunity 2003, 19, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Kasko, A.M. Carbohydrate-Based Polymers for Immune Modulation. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castro, G.R.; Panilaitis, B.; Bora, E.; Kaplan, D.L. Controlled Release Biopolymers for Enhancing the Immune Response. Mol. Pharm. 2007, 4, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Briones, M.; O’Hagan, D.T. A Novel Bioadhesive Intranasal Delivery System for Inactivated Influenza Vaccines. J. Control. Release 2001, 70, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, L.; Sharma, A.; Yadav, A.K.; Mishra, N. Recent Advances on Biodegradable Polymeric Carrier-Based Mucosal Immunization: An Overview. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Sahdev, P.; Ochyl, L.J.; Akerberg, J.J.; Moon, J.J. Cationic Liposome-Hyaluronic Acid Hybrid Nanoparticles for Intranasal Vaccination with Subunit Antigens. J. Control. Release 2015, 208, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernasconi, V.; Norling, K.; Bally, M.; Höök, F.; Lycke, N.Y. Mucosal Vaccine Development Based on Liposome Technology. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 5482087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheul, R.J.; Slütter, B.; Bal, S.M.; Bouwstra, J.A.; Jiskoot, W.; Hennink, W.E. Covalently Stabilized Trimethyl Chitosan-Hyaluronic Acid Nanoparticles for Nasal and Intradermal Vaccination. J. Control. Release 2011, 156, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Biopolymer | Applications | Advantages for Vaccine Design | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan | Hydrogels, dressings, drug delivery systems, gene delivery | Biocompatibility, degradability, mucoadhesive, mucosal absorption, stimulation of immune response, antimicrobial | [18,19,20] |
| Starch | Scaffolds, drug delivery systems, tissue repair | Biocompatibility, immune modulation, biodegradability | [18,21] |
| Alginate | Coatings and dressings, drug delivery, pharmaceutical excipient, packaging | Biocompatibility, immunomodulation, vaccine enhancer, tumor suppressor | [22,23] |
| Cellulose | Pharmaceutical excipient, packaging, drug delivery, coatings | Low price, abundant in nature, vaccine adjuvant, easy protein binding | [18,24] |
| Gellan | Food industry, multifunctional additive in pharmacy, regenerative medicine, gene delivery | Antigen delivery, mucosal delivery, immune response stimulation | [17,25] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dedloff, M.R.; Effler, C.S.; Holban, A.M.; Gestal, M.C. Use of Biopolymers in Mucosally-Administered Vaccinations for Respiratory Disease. Materials 2019, 12, 2445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12152445
Dedloff MR, Effler CS, Holban AM, Gestal MC. Use of Biopolymers in Mucosally-Administered Vaccinations for Respiratory Disease. Materials. 2019; 12(15):2445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12152445
Chicago/Turabian StyleDedloff, Margaret R., Callie S. Effler, Alina Maria Holban, and Monica C. Gestal. 2019. "Use of Biopolymers in Mucosally-Administered Vaccinations for Respiratory Disease" Materials 12, no. 15: 2445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12152445
APA StyleDedloff, M. R., Effler, C. S., Holban, A. M., & Gestal, M. C. (2019). Use of Biopolymers in Mucosally-Administered Vaccinations for Respiratory Disease. Materials, 12(15), 2445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12152445