Injectable Hydrogels Based on Pluronic/Water Systems Filled with Alginate Microparticles for Biomedical Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparation
2.2. Particle Size Distribution
2.3. Rheological Characterization
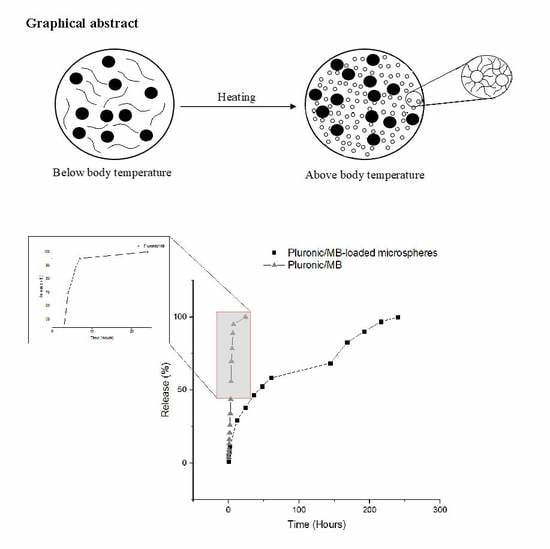
2.4. Drug Release
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Particle size distribution (PSD)
3.2. Rheological Characterization
3.2.1. Pluronic/Water Systems
3.2.2. Pluronic/Water System Filled with Alginate Microparticles
3.3. Drug Release
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sivashanmugam, A.; Kumar, R.A.; Priya, M.V.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. An overview of injectable polymeric hydrogels for tissue engineering. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 72, 543–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, D.R.; Crompton, K.E.; Horne, M.K.; Finkelstein, D.I.; Forsythe, J.S. Neural tissue engineering of the CNS using hydrogels. J. Biomater. Res. Part B: Appl. Biomater. 2008, 87, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.B.; Zhang, F.; Lineaweaver, W.C. Luminal fillers in nerve conduits for peripheral nerve repair. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2006, 57, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, F.; Chen, M.B.; Lineaweaver, W.C. Conduit luminal additives for peripheral nerve repair. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2009, 87, 199–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terenghi, G. Peripheral nerve regeneration and neurotrophic factors. J. Anat. 1999, 194, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.; Johnston, T.P. Kinetics of sol-to-gel transition for poloxamer polyols. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1991, 43, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, W.; Geng, J.; Chitgupi, U.; Unsal, H.; Federizon, J.; Rzayev, J.; Sukumaran, D.K.; Alexandridis, P.; Lovell, J.F. Therapeutic surfactant-stripped frozen micelles. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Goel, S.; Sun, B.; Chitgupi, U.; Geng, J.; Sun, H.; Barnhart, T.E.; Cai, W.; Xia, J. Surfactant-Stripped Frozen Pheophytin Micelles for Multimodal Gut Imaging. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 8524–8530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, A.S. Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Bures, P.; Leobandung, W.; Ichikawa, H. Hydrogels in pharmaceutical formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 50, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidian, H.; Park, K. Hydrogels. In Fundamentals and Applications of Controlled Release Drug Delivery, 1st ed.; Siepmann, J., Siegel, R.A., Rathbone, M.J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 75–105. [Google Scholar]
- Willerth, V.; Sakiyama-Elbert, S.E. Approaches to neural tissue engineering using scaffolds for drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Damodaran, G.; Nikolskaya, N.; Gorman, A.M.; Windebank, A.; Pandit, A. The effect of laminin peptide gradient in enzymatically cross-linked collagen scaffolds on neurite growth. J. Biomater. Res. Part A 2010, 92, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, A.J.; Cook, M.J. Polymer-based drug delivery devices for neurological disorders. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2009, 8, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jollivet, C.; Aubert-Pouessel, A.; Clavreul, A.; Venier-Julienne, M.-C.; Remy, S.; Montero-Menei, C.N.; Benoit, J.-P.; Menei, P. Striatal implantation of GDNF releasing biodegradable microspheres promotes recovery of motor function in a partial model of Parkinson’s disease. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Moore, M.J.; Zhang, X.; Klassen, H.; Langer, R.; Young, M. Intravitreal injections of GDNF-loaded biodegradable microspheres are neuroprotective in a rat model of glaucoma. Mol. Vis. 2007, 13, 1783–1792. [Google Scholar]
- Péan, J.-M.; Menei, P.; Morel, O.; Montero-Menei, C.N.; Benoit, J.-P. Intraseptal implantation of NGF-releasing microspheres promote the survival of axotomized cholinergic neurons. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2097–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arica, B.; Kaş, H.S.; Moghdam, A.; Akalan, N.; Hincal, A.A. Carbidopa/levodopa-loaded biodegradable microspheres: In vivo evaluation on experimental Parkinsonism in rats. J. Control. Release 2005, 102, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnavi, S.; Di Blasio, L.; Tonda-Turo, C.; Macardi, A.; Primo, L.; Ciardelli, G.; Gambarotta, G.; Geuna, S.; Perroteau, I. Gelatin based hydrogels as delivery systems for vascular endothelial growth factor release in peripheral nerve tissue engineering. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2014, 11, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonda-Turo, C.; Gnavi, S.; Ruini, F.; Gambarotta, G.; Gioffredi, E.; Chiono, V.; Perroteau, I.; Ciardelli, G. Development and characterisation of novel agar and gelatin injectable hydrogel as filler for peripheral nerve guidance channel. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2014, 11, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Marra, K.G. Injectable, Biodegradable Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications. Materials 2010, 3, 1746–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Cong, S.; Wang, P.; Ma, J.; Liu, H.; Ning, P. Novel green micelles Pluronic F-127 coating performance on nano zero-valent iron: Enhanced reactivity and innovative kinetics. Sep. Purif. Tech. 2017, 174, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.E.; Gallardo, V.; Clares, B.; García, M.B.; Ruiz, M.A. Study and description of hydrogels and organogels as vehicles for cosmetic active ingredients. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2009, 60, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serieye, S.; Méducin, F.; Milošević, I.; Fu, L.; Guillot, S. Interface tuning and stabilization of monoglyceride mesophase dispersions: Food emulsifiers and mixtures efficiency. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 2017, 496, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Mosqueda, L.M.; Ramírez, P.; Trujillo-Cayado, L.A.; Santos, J.; Muñoz, J. Development of eco-friendly submicron emulsions stabilized by a bio-derived gum. Colloids Surf. B 2014, 123, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, K.C.; Damitz, R.; Chauhan, A. Relating emulsion stability to interfacial properties for pharmaceutical emulsions stabilized by Pluronic F68 surfactant. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 521, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, P.; Muñoz, J.; Fainerman, V.B.; Aksenenko, E.V.; Mucic, N.; Miller, R. Dynamic interfacial tension of triblock copolymers solutions at the water-hexane interface. Colloids Surf. A 2011, 391, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.J.; Aswal, V.K.; Goyal, P.S.; Bahadur, P. Micellar structure of an ethylene oxide−propylene oxide block copolymer: A small-angle neutron scattering study. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 8452–8458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pragatheeswaran, A.M.; Chen, S.B. The influence of poly (acrylic acid) on micellization and gelation characteristics of aqueous Pluronic F127 copolymer system. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2016, 294, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipton, A.J. Dunn, In situ gelling systems. In Sustained-Release Injectable Products, 1st ed.; Senior, J., Radomsky, M.L., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 241–278. [Google Scholar]
- Hollister, L.E. Site-specific drug delivery to CNS: Old and new. Neurobiol. Aging 1989, 10, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandridis, P.; Hatton, T.A. Poly (ethylene oxide)- poly (propylene oxide)- poly (ethylene oxide) block copolymer surfactants in aqueous solutions and at interfaces: Thermodynamics, structure, dynamics, and modeling. Colloids Surf. A 1995, 96, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanka, G.; Hoffmann, H.; Ulbricht, W. Phase diagrams and aggregation behavior of poly (oxyethylene)-poly (oxypropylene)-poly (oxyethylene) triblock copolymers in aqueous solutions. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 4145–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, B.K.; Wang, Q.; Sun, W.; Li, L. Micellization to gelation of a triblock copolymer in water: Thermoreversibility and scaling. J. Polym. Sci. B 2004, 42, 2014–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K.; Bhatia, S.R. Effect of anti-inflammatories on Pluronic F127: Micellar assembly, gelation and partitioning. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 278, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Ruiter, R.; Royon, L.; Snoeijer, J.H.; Brunet, P. Drop spreading and gelation of thermoresponsive polymers. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 3096–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calero, N.; Santos, J.; Echevarría, C.; Muñoz, J.; Cidade, M.T. Time-dependent behavior in analyte-, temperature-, and shear-sensitive Pluronic PE9400/water systems. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2018, 296, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, C.C.; de Bruyn, J.R. Gelation and long-time relaxation of aqueous solutions of Pluronic F127. J. Rheol. 2019, 63, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-Y.; Xu, J.; Zheng, L.-Q.; Li, X.-W. Preparation of temperature-sensitive microemulsion-based gels formed from a triblock copolymer. Colloids Surf. A 2007, 307, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-R.; Sung, K.C.; Vong, W.-J. In situ gelling of alginate/pluronic solutions for ophthalmic delivery of pilocarpine. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 2358–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Y.; Gao, F.; Sha, X.; Fang, X. Pluronic-based functional polymeric mixed micelles for co-delivery of doxorubicin and paclitaxel to multidrug resistant tumor. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 488, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Cai, C.; Lin, J.; Chen, T. Dual-drug delivery system based on hydrogel/micelle composites. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2606–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Parvathy, J.; Nair, A.S. A novel composite matrix based on polymeric micelle and hydrogel as a drug carrier for the controlled release of dual drugs. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Uchida, Y.; Takami, T.; Ito, T.; Anzai, R.; Sonotaki, S.; Murakami, Y. Dual drug release from hydrogels covalently containing polymeric micelles that possess different drug release properties. Colloids Surf. B 2017, 153, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, R.A.; Kim, H.-W. Core–shell designed scaffolds for drug delivery and tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2015, 21, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambhia, K.J.; Ma, P.X. Controlled drug release for tissue engineering. J. Control. Release 2015, 219, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Zou, A.; Li, W.; Yao, C.; Shaofei, X. DDSolver: An add-in program for modeling and comparison of drug dissolution profiles. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, P.I.P.; Sousa, A.I.; Ferreira, I.M.M.; Novo, C.M.M.; Borges, J.P. Towards the development of multifunctional chitosan-based iron oxide nanoparticles: Optimization and modelling of doxorubicin release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 153, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, P.I.P.; Sousa, A.I.; Silva, J.C.; Ferreira, I.M.M.; Novo, C.M.M.; Borges, J.P. Chitosan-based nanoparticles as drug delivery systems for doxorubicin: Optimization and modelling. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cidade, M.T.; Ramos, D.J.; Santos, J.; Carrelo, H.; Calero, N.; Borges, J.P. Injectable Hydrogels Based on Pluronic/Water Systems Filled with Alginate Microparticles for Biomedical Applications. Materials 2019, 12, 1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071083
Cidade MT, Ramos DJ, Santos J, Carrelo H, Calero N, Borges JP. Injectable Hydrogels Based on Pluronic/Water Systems Filled with Alginate Microparticles for Biomedical Applications. Materials. 2019; 12(7):1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071083
Chicago/Turabian StyleCidade, M. T., D. J. Ramos, J. Santos, H. Carrelo, N. Calero, and J. P. Borges. 2019. "Injectable Hydrogels Based on Pluronic/Water Systems Filled with Alginate Microparticles for Biomedical Applications" Materials 12, no. 7: 1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071083
APA StyleCidade, M. T., Ramos, D. J., Santos, J., Carrelo, H., Calero, N., & Borges, J. P. (2019). Injectable Hydrogels Based on Pluronic/Water Systems Filled with Alginate Microparticles for Biomedical Applications. Materials, 12(7), 1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071083