Removal of Chromates and Sulphates by Mg/Fe LDH and Heterostructured LDH/Halloysite Materials: Efficiency, Selectivity, and Stability of Adsorbents in Single- and Multi-Element Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of LDH and H-LDH Composites
2.3. Adsorption Experiments in Single- and Multi-Element Solutions
2.4. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Adsorbents
3.1.1. XRD Results
3.1.2. FTIR Results
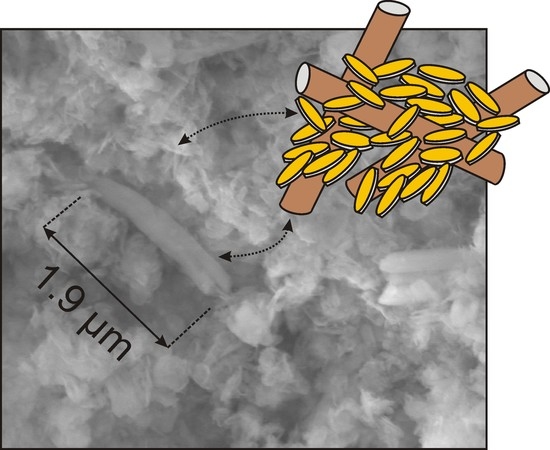
3.1.3. SEM Results
3.1.4. Chemical Composition and DTA Results
3.2. Adsorption in a Single Element System
3.3. Adsorption in a Multi-Element System
3.4. Solid State Analysis after Adsorption and Insight into Removal Mechanisms
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carolin, C.F.; Kumar, P.S.; Saravanan, A.; Joshiba, G.J.; Naushad, M. Efficient techniques for the removal of toxic heavy metals from aquatic environment: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2782–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Astruc, D. Nanomaterials for removal of toxic elements from water. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 356, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, M.; Zhang, S.; Pan, B.; Zhang, W.; Lv, L.; Zhang, Q. Heavy metal removal from water/wastewater by nanosized metal oxides: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 211, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.K. A review on the adsorption of heavy metals by clay minerals, with special focus on the past decade. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 438–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, K.; Gupta, S. Adsorption of a few heavy metals on natural and modified kaolinite and montmorillonite: A review. Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2008, 140, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzatahmadi, N.; Ayoko, G.A.; Millar, G.J.; Speight, R.; Yan, C.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Xi, Y. Clay-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron composite materials for the remediation of contaminated aqueous solutions: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 312, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, C.H.; Fiore, S.; Tong, D.S.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.S.; Ji, S.F.; Yu, W.H. Functional magnetic nanoparticle/clay mineral nanocomposites: Preparation, magnetism and versatile applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 127, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orolínová, Z.; Mockovčiaková, A. Structural study of bentonite/iron oxide composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 114, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, E.; Karapinar, N.; Donat, R. The removal of heavy metal cations by natural zeolites. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2004, 280, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Tan, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, X. Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution by oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, K.G.; Gupta, S.S. Adsorptive accumulation of Cd(II), Co(II), Cu(II), Pb(II), and Ni(II) from water on montmorillonite: Influence of acid activation. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2007, 310, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haggerty, G.M.; Bowman, R.S. Sorption of chromate and other inorganic anions by organo-zeolite sorption of chromate and other inorganic anions by organo-zeolite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusof, A.M.; Malek, N.A. Removal of Cr(VI) and As(V) from aqueous solutions by HDTMA-modified zeolite Y. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Bowman, R.S. Retention of inorganic oxyanions by organo-kaolinite. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3771–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Fan, M.; Yang, D.; He, H.; Liu, D.; Yuan, A.; Zhu, J.; Chen, T. Montmorillonite-supported magnetite nanoparticles for the removal of hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusik, J.; Wścisło, A. Enhanced heavy metal adsorption on functionalized nanotubular halloysite interlayer grafted with aminoalcohols. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 100, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janacek, D.; Kvitek, L.; Karlikova, M.; Pospiskova, K.; Safarik, I. Removal of silver nanoparticles with native and magnetically modified halloysite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 162, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maziarz, P.; Matusik, J.; Leiviskä, T.; Strączek, T.; Kapusta, C.; Marek Woch, W.; Tokarz, W.; Górniak, K. Toward highly effective and easily separable halloysite-containing adsorbents: The effect of iron oxide particles impregnation and new insight into As(V) removal mechanisms. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 210, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.-H.; Lim, T.-T.; Dong, Z. Application of layered double hydroxides for removal of oxyanions: A review. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1343–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, S.J.; Christy, A.G.; Génin, J.M.R.; Kameda, T.; Colombo, F. Nomenclature of the hydrotalcite supergroup: Natural layered double hydroxides. Mineral. Mag. 2012, 76, 1289–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, N.; Zhou, C.H.; Keeling, J.; Fiore, S.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L.; Jin, G.C.; Zhu, T.T.; Tong, D.S.; Yu, W.H. Tracked changes of dolomite into Ca-Mg-Al layered double hydroxide. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 159, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bai, Z.; Zhao, D.; Chai, Y.; Guo, M.; Zhang, J. New synthetic route to Mg–Al–CO3 layered double hydroxide using magnesite. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 1228–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosni, K.; Srasra, E. Using kaolinitic clay for preparation of a hydrotalcite-like compound. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2011, 2, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muriithi, G.N.; Petrik, L.F.; Gitari, W.M.; Doucet, F.J. Synthesis and characterization of hydrotalcite from South African Coal fly ash. Powder Technol. 2017, 312, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, Y.; Ohmichi, T.; Kamegawa, T.; Mori, K.; Yamashita, H. A novel conversion process for waste slag: Synthesis of a hydrotalcite-like compound and zeolite from blast furnace slag and evaluation of adsorption capacities. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, Y.; Yamashita, H. Synthesis of Ca-based layered double hydroxide from blast furnace slag and its catalytic applications. ISIJ Int. 2015, 55, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, R.; López-Delgado, A.; Padilla, I.; Yates, M. Hydrotalcite-like compounds: A way to recover a hazardous waste in the aluminium tertiary industry. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 95, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galindo, R.; López-Delgado, A.; Padilla, I.; Yates, M. Synthesis and characterisation of hydrotalcites produced by an aluminium hazardous waste: A comparison between the use of ammonia and the use of triethanolamine. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 115, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heraldy, E.; Wijaya, K.; Santosa, S.J. Mg_Al hydrotalcite-like synthesized from brine water for eosin yellow removal. Indones. J. Chem. 2011, 11, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Daud, M.; McKay, G.; Shehzad, F.; Al-Harthi, M.A. Recent progress in layered double hydroxides (LDH)-containing hybrids as adsorbents for water remediation. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 143, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.-Q.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J.-Q.; Wei, F. Hierarchical nanocomposites derived from nanocarbons and layered double hydroxides—Properties, synthesis, and applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 675–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yu, Y.; Huang, P.-P.; Liu, H.; Cao, C.-Y.; Song, W.-G. Core–shell structured MgAl-LDO@Al-MS hexagonal nanocomposite: An all inorganic acid–base bifunctional nanoreactor for one-pot cascade reactions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Zhang, H.; Fan, T.; Chen, J.; Duan, X. Nearly monodispersed core-shell structural Fe3O4@DFUR-LDH submicro particles for magnetically controlled drug delivery and release. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 908–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Avilés, A.; Aranda, P.; Ruiz-Hitzky, E. Layered double hydroxide/sepiolite heterostructured materials. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 130, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Shi, Z. Synthesis and characterization of a novel Mg–Al hydrotalcite-loaded kaolin clay and its adsorption properties for phosphate in aqueous solution. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 637, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Shi, Z.; Li, B.; Yang, L.; Luo, L.; Yang, X. Adsorption of Cr(VI) and Phosphate on Mg–Al hydrotalcite supported kaolin clay prepared by ultrasound-assisted coprecipitation method using batch and Fixed-Bed Systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 7746–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusik, J.; Gaweł, A.; Bielańska, E.; Osuch, W.; Bahranowski, K. The effect of structural order on nanotubes derived from kaolin-group minerals. Clays Clay Miner. 2009, 57, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavani, F.; Trifirò, A.V. Hydrotalcite-type anionic clays: Preparation, properties and application. Catal. Today 1991, 11, 171–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.; Peng, L.; Liao, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Shahzad, A.; Ifthikar, J.; Zhao, M.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z. Selective removal of heavy metals by hydrotalcites as adsorbents in diverse wastewater: Different intercalated anions with different mechanisms. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 1112–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantino, V.R.L.; Pinnavaia, T.J. Basic properties of Mg2+1−xAl3+x layered double hydroxides Intercalated by carbonate, hydroxide, chloride, and sulfate anions. Inorg. Chem. 1995, 34, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilhan, S.; Izotova, S.G.; Komlev, A.A. Synthesis and characterization of MgFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared by hydrothermal decomposition of co-precipitated magnesium and iron hydroxides. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, J.; Evans, D.G.; Duan, X. Stoichiometric synthesis of pure MFe2O4 (M) Mg, Co, and Ni) spinel ferrites from tailored layered double hydroxide (hydrotalcite-like) precursors. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 1597–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cosimo, J.I.; Díez, V.K.; Xu, M.; Iglesia, E.; Apesteguía, C.R. Structure and surface and catalytic properties of Mg-Al basic oxides. J. Catal. 1998, 178, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloprogge, J.T.; Frost, R.L. Fourier transform infrared and raman spectroscopic study of the local structure of Mg-, Ni-, and Co-hydrotalcites. J. Solid State Chem. 1999, 146, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahami, A.; Beall, G.W. Structural and morphological characterization of Mg0.8Al0.2(OH)2Cl0.2 hydrotalcite produced by mechanochemistry method. J. Solid State Chem. 2016, 233, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.; Chin, Y.P.; Ahn, J.Y.; Wei-Haas, M.; McAdams, B.; Hwang, I. Reciprocal influences of dissolved organic matter and nanosized zero-valent iron in aqueous media. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rives, V. Characterization of layered double hydroxides and their decomposition products. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2002, 75, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanezaki, E. Thermal behavior of the hydrotalcite-like layered structure of Mg and Al-layered double hydroxides with interlayer carbonate by means of in situ powder HTXRD and DTA/TG. Solid State Ion. 1998, 106, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, M.; Huber, R.; Adok-Sipiczki, M.; Nardin, C.; Szilagyi, I. Ion specific effects on the stability of layered double hydroxide colloids. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 4024–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chitrakar, R.; Tezuka, S.; Sonoda, A.; Sakane, K.; Ooi, K.; Hirotsu, T. Adsorption of phosphate from seawater on calcined MgMn-layered double hydroxides. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2005, 290, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tezuka, S.; Chitrakar, R.; Sonoda, A.; Ooi, K.; Tomida, T. Studies on selective adsorbents for oxo-anions. Nitrate ion-exchange properties of layered double hydroxides with different metal atoms. Green Chem. 2004, 6, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezuka, S.; Chitrakar, R.; Sonoda, A.; Ooi, K.; Tomida, T. Studies on selective adsorbents for oxo-anions. NO−3 adsorptive properties of Ni-Fe layered double hydroxide in seawater. Adsorption 2005, 11, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.-H.; Lim, T.-T. Influences of co-existing species on the sorption of toxic oxyanions from aqueous solution by nanocrystalline Mg/Al layered double hydroxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 180, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laipan, M.; Fu, H.; Zhu, R.; Sun, L.; Steel, R.M.; Ye, S.; Zhu, J.; He, H. Calcined Mg/Al-LDH for acidic wastewater treatment: Simultaneous neutralization and contaminant removal. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 153, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forano, C. Environmental remediation involving layered double hydroxides. In Clay Surfaces: Fundamentals and Applications; Wypych, F., Satyanarayana, K.G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 426–458. [Google Scholar]
- Chubar, N.; Gilmour, R.; Gerda, V.; Micusik, M.; Omastova, M.; Heister, K.; Man, P.; Fraissard, J.; Zaitsev, V. Layered double hydroxides as the next generation inorganic anion exchangers: Synthetic methods versus applicability. Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2017, 245, 62–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| mg/L | Cr-CW | Cr-RW | S-CW | S-RW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr(VI) | 59.7 | 33.9 | 0.09 | 0.01 |
| S(VI) | 66.9 | 46.8 | 474.1 | 337.5 |
| Cl− | 750.0 | >30,000 | 750.0 | >30,000 |
| Na+ | 76.7 | 10,710 | 89.9 | 11,072 |
| K+ | 41.6 | 36.8 | 349.2 | 280.0 |
| Ca2+ | 133.7 | 117.5 | 127.4 | 115.8 |
| Mg2+ | 16.7 | 6.9 | 16.4 | 6.7 |
| Fetotal | 0.33 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.49 |
| Zn2+ | 116.7 | 9.21 | 108.1 | 9.52 |
| pH | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matusik, J.; Rybka, K. Removal of Chromates and Sulphates by Mg/Fe LDH and Heterostructured LDH/Halloysite Materials: Efficiency, Selectivity, and Stability of Adsorbents in Single- and Multi-Element Systems. Materials 2019, 12, 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091373
Matusik J, Rybka K. Removal of Chromates and Sulphates by Mg/Fe LDH and Heterostructured LDH/Halloysite Materials: Efficiency, Selectivity, and Stability of Adsorbents in Single- and Multi-Element Systems. Materials. 2019; 12(9):1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091373
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatusik, Jakub, and Karolina Rybka. 2019. "Removal of Chromates and Sulphates by Mg/Fe LDH and Heterostructured LDH/Halloysite Materials: Efficiency, Selectivity, and Stability of Adsorbents in Single- and Multi-Element Systems" Materials 12, no. 9: 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091373
APA StyleMatusik, J., & Rybka, K. (2019). Removal of Chromates and Sulphates by Mg/Fe LDH and Heterostructured LDH/Halloysite Materials: Efficiency, Selectivity, and Stability of Adsorbents in Single- and Multi-Element Systems. Materials, 12(9), 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091373