Reducing Yield Asymmetry between Tension and Compression by Fabricating ZK60/WE43 Bimetal Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Fabrication of ZK60/WE43 Composite Rods
2.2. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties
3. Results
3.1. Interface Microstructure
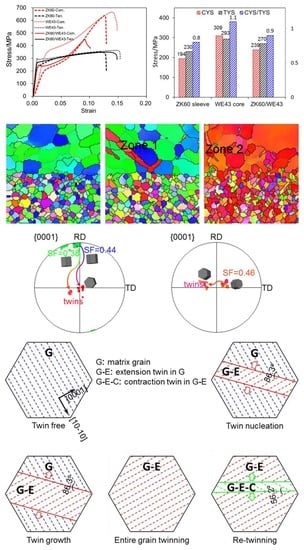
3.2. Yield Asymmetry between Tension and Compression
3.3. Evolution of Crystallographic Texture
4. Discussion
4.1. Deformation Mechanisms
4.2. Twinning Evolution of ZK60/WE43 Composites
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- In the ZK60 sleeve, a relatively high intensity of the crystallographic texture was present with most c-axes of the grains perpendicular to the ED. The predominant deformation mechanism was {10-12}<−1011> extension twinning in compression, while prismatic slip became a dominant deformation mode in tension along the ED. The different deformation modes were observed to be responsible for the plastic anisotropy of the extruded ZK60 sleeve.
- (2)
- In the WE43 core, the presence of yttrium resulted in fine-grained structure, texture weakening, solution strengthening, and second phase strengthening. In tension along the ED, the non-basal (prismatic) slip of <a> dislocations became prevalent. In compression, the extension twinning {10-12}<−1011> and basal <a> slip were activated. WE43 was relatively isotropic at room temperature since the activation stress was related to the combination of multiple deformation modes.
- (3)
- The yield tension-compression asymmetry between tension and compression for the ZK60/WE43 composite along the ED was effectively reduced with a compression-to-tension ratio of ~0.9. The strengths (CYS and TYS) of the composite samples lay in-between those of the constituents in the same direction.
- (4)
- EBSD results indicated the nucleation and growth of extension twinning and the presence of double twinning in a host of grains. The primary extension twins were observed to be merged together, covering the whole zones of grains with increasing strain. In the interface zone, the contraction twinning {10-11}<10-1-2> was also activated within the extension twin at a higher strain to form {10-12}-{10-11} double twins.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suh, B.-C.; Shim, M.-S.; Shin, K.S.; Kim, N.J. Current issues in magnesium sheet alloys: Where do we go from here? Scr. Mater. 2014, 84–85, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, J.; Al-Samman, T. Superior light metals by texture engineering: Optimized aluminum and magnesium alloys for automotive applications. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 818–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Stanford, N.; Davies, C.H.J.; Nie, J.; Birbilis, N. Magnesium extrusion alloys: A review of developments and prospects. Int. Mater. Rev. 2018, 64, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, P.A. Production, properties, and industrial uses of magnesium and its alloys. Int. Met. Rev. 2013, 23, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.; Chen, D.L.; Xu, S.; Luo, A.A. Strain-Controlled Low-Cycle Fatigue Properties of a Newly Developed Extruded Magnesium Alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2008, 39, 3014–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Miao, J.; Luo, A.A. A new magnesium sheet alloy and its multi-stage homogenization for simultaneously improved ductility and strength at room temperature. Scr. Mater. 2019, 171, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Jin, L.; Dong, J.; Wang, F.; Dong, S.; Ding, W.; Luo, A.A. Towards high ductility in magnesium alloys —The role of intergranular deformation. Int. J. Plast. 2019, 123, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Jin, L.; Dong, S.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, J. Asymmetry strain hardening behavior in Mg-3% Al-1% Zn and Mg-8% Gd-3% Y alloy tubes. Mater. Lett. 2013, 107, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xin, Y.; Chapuis, A.; Huang, X.; Xin, R.; Liu, Q. The different effects of twin boundary and grain boundary on reducingyield asymmetry between tension and compression of Mg alloys. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, W.; Xin, R.; Xu, J.; Song, B.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q. Effects of precipitate type on twin/slip activity in ZK60 alloys and yield asymmetry. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 792, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Cao, B.; Chen, W.; Duan, J.; Cui, G. Effects of Texture and Grain Size on the Yield Strength of ZK61 Alloy Rods Processed by Cyclic Extrusion and Compression. Materials 2017, 10, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, S.M.; Wang, C.H.; Diao, Y.D.; Wu, S.D.; Li, S.X. Influence of Grain Size and Texture on the Yield Asymmetry of Mg-3Al-1Zn Alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2011, 27, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.R.; Zhu, Y.M.; Liu, R.L.; Xu, S.W.; Davies, C.H.J.; Nie, J.F.; Birbilis, N. Achieving exceptionally high strength in Mg 3Al 1Zn-0.3Mn extrusions via suppressing intergranular deformation. Acta Mater. 2018, 160, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.Z.; Chen, D.L. Strain controlled cyclic deformation behavior of an extruded magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 496, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Dong, J.; Sun, J.; Luo, A.A. In-situ investigation on the microstructure evolution and plasticity of two magnesium alloys during three-point bending. Int. J. Plast. 2015, 72, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, M.R.; Keshavarz, Z.; Beer, A.G.; Atwell, D. Influence of grain size on the compressive deformation of wrought Mg-3Al-1Zn. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 5093–5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kadiri, H.; Barrett, C.D.; Wang, J.; Tomé, C.N. Why are {101−2} twins profuse in magnesium? Acta Mater. 2015, 85, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.; Jonas, J.J.; Luo, A.A.; Sachdev, A.K.; Godet, S. Influence of {10-12} extension twinning on the flow behavior of AZ31 Mg alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 445–446, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahedi, M.; McWilliams, B.A.; Moy, P.; Knezevic, M. Deformation twinning in rolled WE43-T5 rare earth magnesium alloy: Influence on strain hardening and texture evolution. Acta Mater. 2017, 131, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokdad, F.; Chen, D.L.; Li, D.Y. Single and double twin nucleation, growth, and interaction in an extruded magnesium alloy. Mater. Des. 2017, 119, 376–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokdad, F.; Chen, D.L.; Li, D.Y. Twin-twin interactions and contraction twin formation in an extruded magnesium alloy subjected to an alteration of compressive direction. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 737, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; El Kadiri, H.; Oppedal, A.L.; Baird, J.C.; Li, B.; Horstemeyer, M.F.; Vogel, S.C. Twinning effects in a rod-textured AM30 Magnesium alloy. Int. J. Plast. 2012, 29, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Bohlen, J.; Heinemann, F.; Letzig, D. Mechanical anisotropy and deep drawing behaviour of AZ31 and ZE10 magnesium alloy sheets. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnett, M.R.; Nave, M.D.; Ghaderi, A. Yield point elongation due to twinning in a magnesium alloy. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.E.; Robson, J.D.; Turski, M. Reducing yield asymmetry and anisotropy in wrought magnesium alloys—A comparative study. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 744, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Q. Suppressing theyield asymmetry between tension and compression of Mg alloy by hybrid extension twins structure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 567, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Valle, J.A.; Carreño, F.; Ruano, O.A. Influence of texture and grain size on work hardening and ductility in magnesium-based alloys processed by ECAP and rolling. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 4247–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.T.; Yin, D.L.; Liu, J.Q.; Tao, J.; Su, Y.L.; Zhao, X. Effect of grain size on mechanical property of Mg-3Al-1Zn alloy. Scr. Mater. 2008, 59, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, J.D. The effect of internal stresses due to precipitates on twin growth in magnesium. Acta Mater. 2016, 121, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, J.D.; Stanford, N.; Barnett, M.R. Effect of precipitate shape on slip and twinning in magnesium alloys. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 1945–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekumalla, S.; Seetharaman, S.; Almajid, A.; Gupta, M. Mechanical Properties of Magnesium-Rare Earth Alloy Systems: A Review. Metals 2014, 5, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bohlen, J.; Nürnberg, M.R.; Senn, J.W.; Letzig, D.; Agnew, S.R. The texture and anisotropy of magnesium-zinc-rare earth alloy sheets. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 2101–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Song, B.; Hou, D.; Pan, F. The yield asymmetry and precipitation behavior of pRE-twinned ZK60 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 652, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, M.R. A rationale for the strong dependence of mechanical twinning on grain size. Scr. Mater. 2008, 59, 696–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, M.R.; Wang, H.; Guo, T. An Orowan precipitate strengthening equation for mechanical twinning in Mg. Int. J. Plast. 2019, 112, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, N.; Barnett, M.R. Solute strengthening of prismatic slip, basal slip and twinning in Mg and Mg-Zn binary alloys. Int. J. Plast. 2013, 47, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Low, T.S.E.; Niezgoda, S.R.; Li, X.; Geng, Y.; Luo, A.A.; Tang, G. Abnormal texture development in magnesium alloy Mg-3Al-1Zn during large strain electroplastic rolling: Effect of pulsed electric current. Int. J. Plast. 2016, 87, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Luo, A.A.; Sutton, S.C.; Zeng, L.; Wang, S.; Zeng, X.; Li, D.; Ding, W. Twinning behavior and lattice rotation in a Mg-Gd-Y-Zr alloy under ballistic impact. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 650, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, J.J.; Wang, F.; Wu, P.D.; Whittington, W.R.; El Kadiri, H.; Agnew, S.R. Demonstration of alloying, thermal activation, and latent hardening effects on quasi-static and dynamic polycrystal plasticity of Mg alloy, WE43-T5, plate. Int. J. Plast. 2016, 81, 123–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, D.; Wynne, B.; Gao, J.; Huang, Y.; Rainforth, W.M. Basal slip mediated tension twin variant selection in magnesium WE43 alloy. Acta Mater. 2019, 170, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, N.; Marceau, R.K.W.; Barnett, M.R. The effect of high yttrium solute concentration on the twinning behaviour of magnesium alloys. Acta Mater. 2015, 82, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.N.; Li, H.X.; Luo, J.R.; Liu, Y.J.; Du, Q.; Zhang, J.S. Interfacial bonding mechanism and mechanical properties of novel AZ31/WE43 bimetal composites fabricated by insert molding method. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 729, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, B.; Tang, A.; Song, J.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, T.; Huang, G.; Pan, F. Enhanced stretch formability at room temperature for Mg-Al-Zn/Mg-Y laminated composite via porthole die extrusion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 731, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.N.; Liu, J.C.; Nie, X.Y.; Li, Y.; Li, H.X.; Du, Q.; Zhuang, L.Z.; Zhang, J.S. Interface formation in magnesium-magnesium bimetal composites fabricated by insert molding method. Mater. Des. 2016, 91, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, T.; Wu, R.; Hou, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, M. Effects of Annealing Process on the Interface of Alternate α/β Mg-Li Composite Sheets Prepared by Accumulative Roll Bonding. J. Mater. Proc. Technol. 2018, 254, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.N.; Xu, D.X.; Li, H.X.; Zhang, J.S.; Chen, D.L. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg/Mg bimetal composites fabricated by hot-pressing diffusion and co-extrusion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 764, 138194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Boehlert, C.J.; Wang, Q.D.; Yin, D.D.; Ding, W.J. In-situ analysis of the tensile deformation modes and anisotropy of extruded Mg-10Gd-3Y-0.5Zr (wt.%) at elevated temperatures. Int. J. Plast. 2016, 84, 255–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Agnew, S.R.; Wu, P.D. Modeling twinning and detwinning behavior of Mg alloy ZK60A during monotonic and cyclic loading. Int. J. Plast. 2015, 65, 61–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, K.; Xu, D.; Song, X.; Ma, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, D. Reducing Yield Asymmetry between Tension and Compression by Fabricating ZK60/WE43 Bimetal Composites. Materials 2020, 13, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010249
Zhao K, Xu D, Song X, Ma Y, Li H, Zhang J, Chen D. Reducing Yield Asymmetry between Tension and Compression by Fabricating ZK60/WE43 Bimetal Composites. Materials. 2020; 13(1):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010249
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Kangning, Dexing Xu, Xiao Song, Yingzhong Ma, Hongxiang Li, Jishan Zhang, and Daolun Chen. 2020. "Reducing Yield Asymmetry between Tension and Compression by Fabricating ZK60/WE43 Bimetal Composites" Materials 13, no. 1: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010249
APA StyleZhao, K., Xu, D., Song, X., Ma, Y., Li, H., Zhang, J., & Chen, D. (2020). Reducing Yield Asymmetry between Tension and Compression by Fabricating ZK60/WE43 Bimetal Composites. Materials, 13(1), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010249