An Extremely Efficient Silylated Benzensulfonate Flame Retardant for Polycarbonate
Abstract
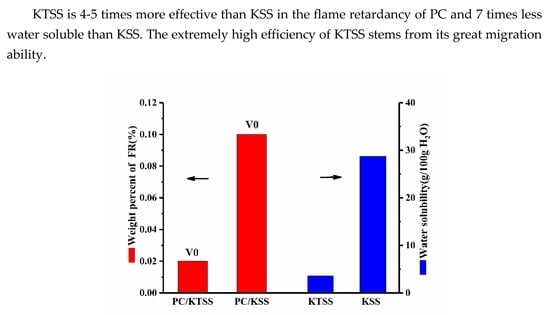
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Potassium 4-(Trimethylsilyl)benzenesulfonate (KTSS)
2.3. Preparation of Flame Retardant Polycarbonate (PC) Blends
2.4. Water Solubility
2.5. Measurements and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Water Solubility of KTSS
3.2. Thermal Stability of KTSS
3.3. Dispersion of KTSS in PC
3.4. Flammability
3.5. Cone Calorimeter Test (CONE) Analysis of Flame Retardant PC
3.6. Decomposition of KTSS
3.7. Thermal Gravimetric Analyses (TGA) Analysis of PC/KTSS
3.8. TGA-FTIR Analysis of PC/KTSS
3.9. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Analysis of Chars
3.10. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis of Chars
3.11. Mechanism of Flame Retardant
3.12. Physical Properties of PC/FR
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levchik, S.V.; Weil, E.D. Overview of recent developments in the flame retardancy of polycarbonates. Polym. Int. 2005, 54, 981–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lv, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q. Synergism of polysiloxane and zinc borate flame retardant polycarbonate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 2795–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.C.; Wang, Y.B.; Luo, Z.L.; Qi, T.Y. Design and application of highly efficient flame retardants for polycarbonate combining the advantages of cyclotriphosphazene and silicone oil. Polymers 2019, 11, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Yang, R. Flame retardancy, thermal and mechanical properties of sulfonate-containing polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (S-POSS)/polycarbonate composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 116, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Yin, H.; Cai, X. Synergistic effects between silicon-containing flame retardant and potassium-4-(phenylsulfonyl)benzenesulfonate (KSS) on flame retardancy and thermal degradation of PC. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 114, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Song, L.; Yuen, R.K.K.; Jiang, S.; Pan, H.; Hu, Y. Enhanced properties of the Incorporation of a novel reactive phosphorus- and sulfur-containing flame-retardant monomer into unsaturated polyester resin. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 15918–15926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazuhiko, I.; Shimomai, K. Flame-Retardent Polycarbonate Resin Composition and a molded Product Using the Same. U.S. Patent 6,342,550, 29 January 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Ouyang, X.; Ning, F.; Wang, J. Mechanistic study on flame retardance of polycarbonate with a small amount of potassium perfluorobutane sulfonate by TGA-FTIR/XPS. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouvertné, W. Flame Resistant Polycarbonates. U.S. Patent 3,775,367, 27 November 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Ballistreri, A.; Montaudo, G.; Scamporrino, E.; Puglisi, C.; Cucinella, S.J. Intumescent flame retardants for polymers. IV. The polycarbonate–aromatic sulfonates system. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1988, 26, 2113–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.D.; Deng, L.T.; Yin, H.Q.; Cai, X.F. Synergistic effect of organic silicon on the flame retardancy and thermal properties of polycarbonate/potassium-4-(phenylsulfonyl) benzenesulfonate systems. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 127, 2095–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Cai, X. Antagonistic flame retardancy between hexakis(4-nitrophenoxy) cyclotriphosphazene and potassium diphenylsulfone sulfonate in the PC system. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 126, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.Y.; Guo, J.W.; Xian, J.X.; Fu, S.Q. Novel sulfonate-containing halogen-free flame-retardants: Effect of ternary and quaternary sulfonates centered on adamantane on the properties of polycarbonate composites. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 39270–39278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.L.; Chen, C.K.; Chen, X.L. Effects of carbon fibers on the flammability and smoke emission characteristics of halogen-free thermoplastic polyurethane/ammonium polyphosphate. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 3762–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.Y.; Hamerton, I. Recent developments in the chemistry of halogen-free flame retardant polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 1661–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravadits, I.; Tóth, A.; Marosi, G.; Márton, A.; Szép, A. Organosilicon surface layer on polyolefins to achieve improved flame retardancy through an oxygen barrier effect. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2001, 74, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaux, E.; Rochery, M.; Bourbigot, S. Polyurethane/clay and polyurethane/POSS nanocomposites as flame retarded coating for polyester and cotton fabrics. Fire. Mater. 2002, 26, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, A.; Bertóti, I.; Blazsó, M.; Bánhegyi, G.; Szaplonczay, P. Oxidative damage and recovery of silicone rubber surfaces. I. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic study. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1994, 52, 1293–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serizawa, S.; Iji, M. Flame Retardant Resin Composition. U.S. Patent 6,001,921, 14 December 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeois, P.; Calas, R. Poly(trimethylsilyl)benzenes: Synthese, sulfonation. J. Organomet. Chem. 1975, 84, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arichem LLC. Material Safety Data Sheet. 2013, pp. 1–7. Available online: www.arichem.com/products/Flame_Retardants/KSS-MSDS.pdf (accessed on 3 July 2020).
- Jiang, Y.; Hao, Z.; Luo, H.; Shao, Z.; Yu, Q.; Sun, M.; Ke, Y.; Chen, Y. Synergistic effects of boron-doped silicone resin and a layered double hydroxide modified with sodium dodecyl benzenesulfonate for enhancing the flame retardancy of polycarbonate. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 11078–11086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, Y.; Yao, Q.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Cao, W.H. On the origin of alkali-catalyzed aromatization of phenols. Polymers 2019, 11, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, Y.; Yao, Q.; Cao, W.H.; Zhao, Y.Y. Base promoted Intumescence of phenols. Polymers 2020, 12, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montejo, M.; Urena, F.; Márquez, F.; González, J.J.L. The vibrational spectra of (CH3)3SiX (S=H, F, Br) molecules, revisited transferable scale factor sets for methylsilane derivatives. Spectrochim. Acta A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2005, 62, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nodera, A.; Kanai, T. Thermal decomposition behavior and flame retardancy of polycarbonate containing organic metal salts: Effect of salt composition. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 94, 2131–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, B.N.; Wilkie, C.A. A TGA/FTIR and mass spectral study on the thermal degradation of bisphenol A polycarbonate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2004, 86, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Factor, A. Mechanisms of thermal and photodegradations of bisphenol A polycarbonate. Adv. Chem. Ser. 1996, 249, 59–76. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, D.; Jung, H.T.; Kwon, G.; Yoon, Y.; Lee, M.; Bae, I.; Joo, B.J.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.A.; Lee, J.; et al. Dynamics and mechanism of flame retardants in polymer matrixes: Experiment and simulation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 8571–8578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, H.; Zhou, J. The thermal degradation of bisphenol: A polycarbonate containing methylphenyl–silicone additive. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis. 2007, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iji, M.; Serizawa, S.; Kiuchi, Y. New environmentally conscious flame-retarding plastics for electronics products. In Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Environmentally Conscious Design and Inverse Manufacturing, Tokyo, Japan, 1–3 February 1999; pp. 245–249. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Weiss, R.A. The effect of tosylate salts and zinc sulfonated polystyrene ionomer on the thermal stability of bisphenol A polycarbonate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2004, 84, 295–304. [Google Scholar]
- Oba, K.; Ishida, Y.; Ito, Y.; Ohtani, H.; Tsuge, S. Characterization of branching and/or cross-linking structures in polycarbonate by reactive pyrolysis-gas chromatography in the presence of organic alkali. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 8173–8183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Sample compound (KTSS) is available from the authors. |














| Sample. | UL94(3.2 mm) | LOI/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| t1/t2(s) | D/I 1 | Rating | ||
| PC | 1.17/12.90 | Y/Y | V-2 | 25.9 |
| PC/0.02%KTSS | 0.65/6.33 | N/N | V-0 | 34.4 |
| PC/0.06%KTSS | 0.97/4.23 | N/N | V-0 | 37.1 |
| PC/0.1%KTSS | 0.92/3.78 | N/N | V-0 | 38.6 |
| PC/0.02%KSS | 0.93/8.47 | Y/Y | V-2 | 30.3 |
| PC/0.06%KSS | 0.95/7.31 | Y/Y | V-2 | 35.8 |
| PC/0.1%KSS | 0.72/4.42 | N/N | V-0 | 34.4 |
| PC/0.06%KBS | 0.94/6.91 | Y/Y | V-2 | |
| PC/0.1%KBS | 1.69/6.10 | Y/Y | V-2 | |
| Sample | TTI (s) | PHRR (kW/m2) | THR (MJ/m2) | tPHRR (s) | Char (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | 161 | 361.7 | 120.4 | 303 | 4.2 |
| PC/0.02%KTSS | 128 | 344.6 | 126.9 | 177 | 2.6 |
| PC/0.06%KTSS | 114 | 349.2 | 124.8 | 159 | 1.1 |
| PC/0.1%KTSS | 93 | 332.1 | 132.5 | 140 | 0.8 |
| PC/0.02%KSS | 145 | 406.6 | 125.5 | 293 | 2.6 |
| PC/0.06%KSS | 128 | 348.8 | 123.7 | 263 | 2.3 |
| PC/0.1%KSS | 130 | 319.6 | 125.0 | 273 | 2.6 |
| Sample | T5wt% (°C) | T10wt% (°C) | T50wt% (°C) | Tmax (°C) | Residues at 800 °C (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | 482 | 498 | 533 | 531 | 24.5 |
| PC/0.02%KTSS | 449 | 461 | 497 | 496 | 21.1 |
| PC/0.06%KTSS | 448 | 460 | 499 | 499 | 21.8 |
| PC/0.1%KTSS | 442 | 454 | 490 | 491 | 18.8 |
| Ignition Time | Surface Composition (wt%) | Weight Ratio | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | C | S | K | Si | K/S | K/Si | |
| 0 s | 23.00 | 58.90 | 1.75 | 0.32 | 16.04 | 0.18 | 0.020 |
| 5 s | 24.31 | 40.41 | 4.94 | 0.86 | 29.47 | 0.17 | 0.029 |
| 10 s | 23.16 | 59.28 | 1.57 | 2.29 | 13.73 | 1.46 | 0.17 |
| Sample | Tensile Modules/103 MPa | Tensile Strength/MPa | Elongation at Break/% | HDT/°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | 1.95 ± 0.11 | 62.4 ± 2.1 | 65.1 ± 3.1 | 124.1 |
| PC/0.02%KTSS | 1.93 ± 0.09 | 66.3 ± 2.0 | 64.6 ± 5.2 | 124.5 |
| PC/0.06%KTSS | 2.04 ± 0.10 | 71.0 ± 1.0 | 67.9 ± 6.7 | 124.7 |
| PC/0.10%KTSS | 1.98 ± 0.10 | 68.8 ± 2.1 | 67.1 ± 5.2 | 125.9 |
| PC/0.02%KSS | 1.89 ± 0.08 | 67.1 ± 2.9 | 64.1 ± 5.1 | 121.8 |
| PC/0.06%KSS | 1.86 ± 0.10 | 66.4 ± 4.4 | 70.4 ± 7.2 | 123.3 |
| PC/0.10%KSS | 1.81 ± 0.05 | 66.3 ± 1.3 | 64.5 ± 4.9 | 125.6 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, X.; Yao, Q.; Cao, W.; Tang, T. An Extremely Efficient Silylated Benzensulfonate Flame Retardant for Polycarbonate. Materials 2020, 13, 3550. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13163550
Lu X, Yao Q, Cao W, Tang T. An Extremely Efficient Silylated Benzensulfonate Flame Retardant for Polycarbonate. Materials. 2020; 13(16):3550. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13163550
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Xiaodong, Qiang Yao, Weihong Cao, and Tianbo Tang. 2020. "An Extremely Efficient Silylated Benzensulfonate Flame Retardant for Polycarbonate" Materials 13, no. 16: 3550. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13163550
APA StyleLu, X., Yao, Q., Cao, W., & Tang, T. (2020). An Extremely Efficient Silylated Benzensulfonate Flame Retardant for Polycarbonate. Materials, 13(16), 3550. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13163550