Antimicrobial Silver Multilayer Coating for Prevention of Bacterial Colonization of Orthopedic Implants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Implant Items
SML Coating
2.2. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity
2.2.1. QualiScreen® Tests
2.2.2. Agar Immersion Test
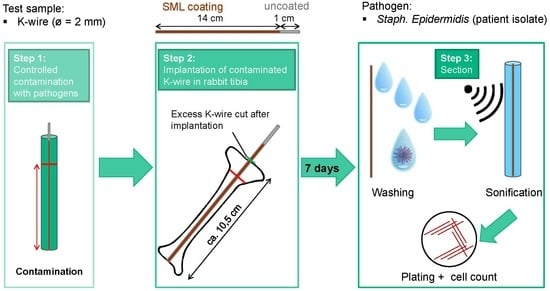
2.3. In Vivo Study Design
2.3.1. Pilot Studies
2.3.2. Main Study
2.4. Bacteria
2.4.1. Bacterial Strains
2.4.2. Bacteria Cultivation and Pre-Incubation of Implants
2.5. Surgery
2.6. Sample Collection for Silver Measurement
2.7. Evaluation Methods
2.7.1. Clinical Assessment for Infection
2.7.2. Microbiological Assessment for Infection
2.7.3. Histological Evaluation
2.7.4. Silver Levels
2.7.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity
3.2. In Vivo Experiments
3.2.1. Clinical Assessment
3.2.2. Microbiological Assessment for Infection
3.2.3. Histological Evaluation
3.2.4. Blood and Urine Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Joint Registry for England, Wales, Northern Ireland and the Isle of Man. 15th Annual Report 2018; National Joint Registry for England: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Australian Orthopaedic Association. Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry: Annual Report 2019; Australian Orthopaedic Association: Adelaide, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Trauma Register, D.G.U. Jahresbericht 2019; Endoprothesenregister Deutschland (EPRD): Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerli, W. Clinical presentation and treatment of orthopaedic implant-associated infection. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 276, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärrholm, J.; Garellick, G.; Rogmark, C.; Herberts, P. Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register: Annual Report 2017; Sahlgrenska University Hospital: Gothenburg, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cochran, A.R.; Ong, K.L.; Lau, E.; Mont, M.A.; Malkani, A.L. Risk of Reinfection After Treatment of Infected Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2016, 31, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasch, R.; Merk, S.; Assmann, G.; Lahm, A.; Napp, M.; Merk, H.; Flessa, S. Comparative Analysis of Direct Hospital Care Costs between Aseptic and Two-Stage Septic Knee Revision. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klouche, S.; Sariali, E.; Mamoudy, P. Total hip arthroplasty revision due to infection: A cost analysis approach. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2010, 96, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hernandez-Vaquero, D.; Fernandez-Fairen, M.; Torres, A.; Menzie, A.M.; Fernandez-Carreira, J.M.; Murcia-Mazon, A.; Guerado, E.; Merzthal, L. Treatment of periprosthetic infections: An economic analysis. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 821650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciola, C.R.; Campoccia, D.; Ehrlich, G.D.; Montanaro, L. Biofilm-based implant infections in orthopaedics. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 830, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanaro, L.; Speziale, P.; Campoccia, D.; Ravaioli, S.; Cangini, I.; Pietrocola, G.; Giannini, S.; Arciola, C.R. Scenery of Staphylococcus implant infections in orthopedics. Future Microbiol. 2011, 6, 1329–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dapunt, U.; Radzuweit-Mihaljevic, S.; Lehner, B.; Haensch, G.M.; Ewerbeck, V. Bacterial Infection and Implant Loosening in Hip and Knee Arthroplasty: Evaluation of 209 Cases. Materials 2016, 9, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmerli, W.; Trampuz, A.; Ochsner, P.E. Prosthetic-Joint Infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stefánsdóttir, A.; Johansson, D.; Knutson, K.; Lidgren, L.; Robertsson, O. Microbiology of the infected knee arthroplasty: Report from the Swedish Knee Arthroplasty Register on 426 surgically revised cases. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 41, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wafa, H.; Grimer, R.J.; Reddy, K.; Jeys, L.; Abudu, A.; Carter, S.R.; Tillman, R.M. Retrospective evaluation of the incidence of early periprosthetic infection with silver-treated endoprostheses in high-risk patients: Case-control study. Bone Jt. J. 2015, 97, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerli, W. Bone and Joint Infections: From Microbiology to Diagnostics and Treatment; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sendi, P.; Zumstein, M.A.; Zimmerli, W. Protheseninfektionen—Eine Übersichtsarbeit für die Praxis. Praxis 2011, 100, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Renz, N.; Trampuz, A. Management of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Hip Pelvis 2018, 30, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, K.K.; Wood, S.; Tarity, T.D. Low-Virulence Organisms and Periprosthetic Joint Infection-Biofilm Considerations of These Organisms. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2018, 11, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasso, M.; Schiavone Panni, A. Low-grade periprosthetic knee infection: Diagnosis and management. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2015, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hischebeth, G.T.; Randau, T.M.; Ploeger, M.M.; Friedrich, M.J.; Kaup, E.; Jacobs, C.; Molitor, E.; Hoerauf, A.; Gravius, S.; Wimmer, M.D. Staphylococcus aureus versus Staphylococcus epidermidis in periprosthetic joint infection-Outcome analysis of methicillin-resistant versus methicillin-susceptible strains. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 93, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busscher, H.J.; van der Mei, H.C.; Subbiahdoss, G.; Jutte, P.C.; van den Dungen, J.J.A.M.; Zaat, S.A.J.; Schultz, M.J.; Grainger, D.W. Biomaterial-associated infection: Locating the finish line in the race for the surface. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cristina, M.L.; Sartini, M.; Schinca, E.; Ottria, G.; Spagnolo, A.M. Operating room environment and surgical site infections in arthroplasty procedures. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2016, 57, E142. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, A.; Namba, Y.; Matsuura, M.; Horisawa, A. Airborne contamination in an operating suite: Report of a five-year survey. J. Hyg. 1984, 93, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elek, S.D.; Conen, P.E. The Virulence of Staphylococcus pyogenes for Man.: A Study of the Problems of Wound Infection. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1957, 38, 573–586. [Google Scholar]
- Berríos-Torres, S.I.; Umscheid, C.A.; Bratzler, D.W.; Leas, B.; Stone, E.C.; Kelz, R.R.; Reinke, C.E.; Morgan, S.; Solomkin, J.S.; Mazuski, J.E.; et al. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Guideline for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection, 2017. JAMA Surg. 2017, 152, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhardi, V.J.; Bichara, D.A.; Kwok, S.J.J.; Freiberg, A.A.; Rubash, H.; Malchau, H.; Yun, S.H.; Muratoglu, O.K.; Oral, E. A fully functional drug-eluting joint implant. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alt, V.; Kirchhof, K.; Seim, F.; Hrubesch, I.; Lips, K.S.; Mannel, H.; Domann, E.; Schnettler, R. Rifampicin-fosfomycin coating for cementless endoprostheses: Antimicrobial effects against methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 4518–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coraça-Huber, D.C.; Putzer, D.; Fille, M.; Hausdorfer, J.; Nogler, M.; Kühn, K.-D. Gentamicin palmitate as a new antibiotic formulation for mixing with bone tissue and local release. Cell Tissue Bank. 2014, 15, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Su, B.; Chinnaraj, S.; Jana, S.; Bowen, L.; Charlton, S.; Duan, P.; Jakubovics, N.S.; Chen, J. Nanostructured titanium surfaces exhibit recalcitrance towards Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campoccia, D.; Montanaro, L.; Arciola, C.R. A review of the biomaterials technologies for infection-resistant surfaces. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8533–8554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alt, V. Antimicrobial coated implants in trauma and orthopaedics-A clinical review and risk-benefit analysis. Injury 2017, 48, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardes, J.; Ahrens, H.; Gebert, C.; Streitbuerger, A.; Buerger, H.; Erren, M.; Gunsel, A.; Wedemeyer, C.; Saxler, G.; Winkelmann, W.; et al. Lack of toxicological side-effects in silver-coated megaprostheses in humans. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 2869–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bus, M.P.A.; van de Sande, M.A.J.; Fiocco, M.; Schaap, G.R.; Bramer, J.A.M.; Dijkstra, P.D.S. What Are the Long-term Results of MUTARS(R) Modular Endoprostheses for Reconstruction of Tumor Resection of the Distal Femur and Proximal Tibia? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2017, 475, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hardes, J.; Henrichs, M.P.; Hauschild, G.; Nottrott, M.; Guder, W.; Streitbuerger, A. Silver-Coated Megaprosthesis of the Proximal Tibia in Patients with Sarcoma. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 2208–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hardes, J.; von Eiff, C.; Streitbuerger, A.; Balke, M.; Budny, T.; Henrichs, M.P.; Hauschild, G.; Ahrens, H. Reduction of periprosthetic infection with silver-coated megaprostheses in patients with bone sarcoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 101, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donati, F.; Di Giacomo, G.; D’Adamio, S.; Ziranu, A.; Careri, S.; Rosa, M.; Maccauro, G. Silver-Coated Hip Megaprosthesis in Oncological Limb Savage Surgery. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 9079041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zajonz, D.; Birke, U.; Ghanem, M.; Prietzel, T.; Josten, C.; Roth, A.; Fakler, J.K.M. Silver-coated modular Megaendoprostheses in salvage revision arthroplasty after periimplant infection with extensive bone loss–A pilot study of 34 patients. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Accentus Medical. How Agluna Works. Available online: http://www.accentus-medical.com/products-agluna.asp (accessed on 18 March 2020).
- Schmidt-Braekling, T.; Streitbuerger, A.; Gosheger, G.; Boettner, F.; Nottrott, M.; Ahrens, H.; Dieckmann, R.; Guder, W.; Andreou, D.; Hauschild, G.; et al. Silver-coated megaprostheses: Review of the literature. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2017, 27, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scoccianti, G.; Frenos, F.; Beltrami, G.; Campanacci, D.A.; Capanna, R. Levels of silver ions in body fluids and clinical results in silver-coated megaprostheses after tumour, trauma or failed arthroplasty. Injury 2016, 47 (Suppl. 4), S11–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, T.; Miyamoto, H.; Yonekura, Y.; Tsukamoto, M.; Ando, Y.; Noda, I.; Sonohata, M.; Mawatari, M. Silver oxide-containing hydroxyapatite coating has in vivo antibacterial activity in the rat tibia. J. Orthop. Res. 2013, 31, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PMDA. PMDA_Products Approved in FY 2015 New Medical Devices. Available online: https://www.pmda.go.jp/english/review-services/reviews/approved-information/devices/0001.html (accessed on 18 March 2020).
- Eto, S.; Kawano, S.; Someya, S.; Miyamoto, H.; Sonohata, M.; Mawatari, M. First Clinical Experience with Thermal-Sprayed Silver Oxide-Containing Hydroxyapatite Coating Implant. J. Arthroplast. 2016, 31, 1498–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holinka, J.; Pilz, M.; Hirschl, A.M.; Graninger, W.; Windhager, R.; Presterl, E. Differential bacterial load on components of total knee prosthesis in patients with prosthetic joint infection. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2012, 35, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerativitayanan, P.; Tatullo, M.; Khariton, M.; Joshi, P.; Perniconi, B.; Gaharwar, A.K. Nanoengineered Osteoinductive and Elastomeric Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, M.; Pearce, H.; Cross, L.; Tatullo, M.; Gaharwar, A.K. Advances in Nanotechnology for the Treatment of Osteoporosis. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2016, 14, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalilpour, P.; Lampe, K.; Wagener, M.; Stigler, B.; Heiss, C.; Ullrich, M.S.; Domann, E.; Schnettler, R.; Alt, V. Ag/SiO(x)C(y) plasma polymer coating for antimicrobial protection of fracture fixation devices. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 94, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alt, V.; Heiss, C.; Rupp, M. Treatment of a Recurrent Periprosthetic Joint Infection with an Intramedullary Knee Arthrodesis System with Low-Amount Metallic Silver Coating. J. Bone Jt. Infect. 2019, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alt, V.; Bitschnau, A.; Osterling, J.; Sewing, A.; Meyer, C.; Kraus, R.; Meissner, S.A.; Wenisch, S.; Domann, E.; Schnettler, R. The effects of combined gentamicin-hydroxyapatite coating for cementless joint prostheses on the reduction of infection rates in a rabbit infection prophylaxis model. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 4627–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucke, M.; Schmidmaier, G.; Sadoni, S.; Wildemann, B.; Schiller, R.; Haas, N.P.; Raschke, M. Gentamicin coating of metallic implants reduces implant-related osteomyelitis in rats. Bone 2003, 32, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reizner, W.; Hunter, J.G.; O’Malley, N.T.; Southgate, R.D.; Schwarz, E.M.; Kates, S.L. A systematic review of animal models for Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis. Eur. Cells Mater. 2015, 196–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, J.; Hovy, L.; Lindenmaier, H.-L.; Zeller, R.; Schwiesau, J.; Thomas, P.; Grupp, T.M. Präklinische Ergebnisse beschichteter Knieimplantate für Allergiker. Orthopade 2010, 39, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grupp, T.M.; Giurea, A.; Miehlke, R.K.; Hintner, M.; Gaisser, M.; Schilling, C.; Schwiesau, J.; Kaddick, C. Biotribology of a new bearing material combination in a rotating hinge knee articulation. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 7054–7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechert, T.; Steinrücke, P.; Guggenbichler, J.P. A new method for screening anti-infective biomaterials. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 1053–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruenke, J.; Roschke, I.; Agarwal, S.; Riemann, T.; Greiner, A. Quantitative Comparison of the Antimicrobial Efficiency of Leaching versus Nonleaching Polymer Materials. Macromol. Biosci. 2016, 16, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, R.D. Modification of the Brown and Brenn gram stain for the differential staining of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria in tissue sections. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1966, 46, 472–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, K.A.; Eighmy, J.; Fikes, J.D.; Halpern, W.G.; Hukkanen, R.R.; Long, G.G.; Meseck, E.K.; Patrick, D.J.; Thibodeau, M.S.; Wood, C.E.; et al. Use of Severity Grades to Characterize Histopathologic Changes. Toxicol. Pathol. 2018, 46, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klopfleisch, R. Multiparametric and semiquantitative scoring systems for the evaluation of mouse model histopathology—A systematic review. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Austrian Standards. Water Quality—Application of Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS). Part. 2: Determination of Selected Elements Including Uranium Isotopes; Austrian Standards: Wien, Austria, 2016; EN ISO 17294-2:2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.Y.H.; Monk, I.R.; da Silva, A.G.; Seemann, T.; Chua, K.Y.L.; Kearns, A.; Hill, R.; Woodford, N.; Bartels, M.D.; Strommenger, B.; et al. Global spread of three multidrug-resistant lineages of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heilmann, C.; Ziebuhr, W.; Becker, K. Are coagulase-negative staphylococci virulent? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathbone, C.R.; Cross, J.D.; Brown, K.V.; Murray, C.K.; Wenke, J.C. Effect of various concentrations of antibiotics on osteogenic cell viability and activity. J. Orthop. Res. 2011, 29, 1070–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauksch, L.; Hartmann, S.; Rohnke, M.; Szalay, G.; Alt, V.; Schnettler, R.; Lips, K.S. Biocompatibility of silver nanoparticles and silver ions in primary human mesenchymal stem cells and osteoblasts. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilz, M.; Staats, K.; Tobudic, S.; Assadian, O.; Presterl, E.; Windhager, R.; Holinka, J. Zirconium Nitride Coating Reduced Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilm Formation on Orthopaedic Implant Surfaces: An In Vitro Study. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2019, 477, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claro, T.; O’Reilly, M.; Daniels, S.; Humphreys, H. Surface microbial contamination in hospitals: A pilot study on methods of sampling and the use of proposed microbiologic standards. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2015, 43, 1000–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, E.; Parnell, P.; Couturier, J.; Barbut, F.; Le Bozec, A.; Arnoldo, L.; Madia, A.; Brusaferro, S.; Wilcox, M.H. Environmental contamination by bacteria in hospital washrooms according to hand-drying method: A multi-centre study. J. Hosp. Infect. 2018, 100, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]











| Group | Implant | Contamination | Animals | Time of Implantation Post Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Test item (SML item) K-wire (Titanium/AS®) + SML | 2 × 104 CFU MSSE RKI 10-00621 | 12 | 7 days |
| 2 | Blank item K-wire (Titanium/AS®) | 2 × 104 CFU MSSE RKI 10-00621 | 12 | 7 days |
| 3 | Negative control: Test item (SML item) K-wire (Titanium/AS®) + SML | Without contamination | 3 | 7 days |
| Type | Response | Mean | Difference from Log (Implantation) | p-Value Mann–Whitney Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| blank | Log(Implantation) | 4.376 | ||
| Log(K-wire) | 2.670 | −1.706 | 0.007 | |
| Log(rinsing sol.) | 3.393 | −0.983 | 0.069 | |
| Log(BMstd) | 2.649 | −1.727 | 0.112 | |
| SML | Log(Implantation) | 4.336 | ||
| Log(K-wire) | 1.073 | −3.263 | 0.000 | |
| Log(rinsing sol.) | 1.797 | −2.539 | 0.000 | |
| Log(BMstd) | 2.148 | −2.188 | 0.001 |
| Type | Difference | p-Value Mann–Whitney Test |
|---|---|---|
| Log(K-Wire) Blank vs. SML | 1.597 | 0.022 |
| Log(rinsing sol.) Blank vs. SML | 1.596 | 0.012 |
| Log(BMstd) Blank vs. SML | 0.501 | 0.362 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fabritius, M.; Al-Munajjed, A.A.; Freytag, C.; Jülke, H.; Zehe, M.; Lemarchand, T.; Arts, J.J.; Schumann, D.; Alt, V.; Sternberg, K. Antimicrobial Silver Multilayer Coating for Prevention of Bacterial Colonization of Orthopedic Implants. Materials 2020, 13, 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061415
Fabritius M, Al-Munajjed AA, Freytag C, Jülke H, Zehe M, Lemarchand T, Arts JJ, Schumann D, Alt V, Sternberg K. Antimicrobial Silver Multilayer Coating for Prevention of Bacterial Colonization of Orthopedic Implants. Materials. 2020; 13(6):1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061415
Chicago/Turabian StyleFabritius, Martin, Amir Andreas Al-Munajjed, Christiane Freytag, Henriette Jülke, Markus Zehe, Thomas Lemarchand, Jacobus J. Arts, Detlef Schumann, Volker Alt, and Katrin Sternberg. 2020. "Antimicrobial Silver Multilayer Coating for Prevention of Bacterial Colonization of Orthopedic Implants" Materials 13, no. 6: 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061415
APA StyleFabritius, M., Al-Munajjed, A. A., Freytag, C., Jülke, H., Zehe, M., Lemarchand, T., Arts, J. J., Schumann, D., Alt, V., & Sternberg, K. (2020). Antimicrobial Silver Multilayer Coating for Prevention of Bacterial Colonization of Orthopedic Implants. Materials, 13(6), 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061415