Reactive Infiltration and Microstructural Characteristics of Sn-V Active Solder Alloys on Porous Graphite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Materials
2.2. Wetting Experiment
2.3. Microstructural Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spreading Characteristics
3.2. Reactive Infiltrating
3.3. Effects of Porosity
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- V concentrations have a minor influence on the final apparent contact angles of Sn-V alloys on porous graphite and a trace doping of 0.5 wt.% V obviously improved the wettability of liquid Sn on porous graphite.
- (2)
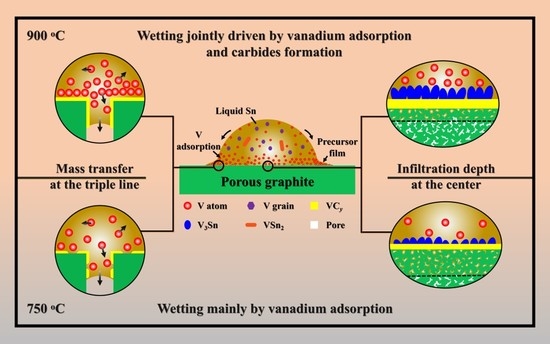
- Sn-V alloys approximately started to spread on porous graphite at 650 °C and reached the quasi-equilibrium state at 900 °C. The spreading kinetics of Sn-V alloys on porous graphite at 750–900 °C was well described by the classical chemical reaction-controlled model. However, thermodynamic analysis and associated microstructural characterization evidenced that, besides the formation of vanadium carbides, the adsorption of active V element at the three-phase contact line considerably contributed to the spreading and infiltrating of Sn-V alloys on porous graphite.
- (3)
- The formation of continuous phase of vanadium carbides resulted in the closure of pores, and hence stopped the infiltration of Sn-V alloys in porous graphite substrate. Consequently, the infiltration depth of Sn-V alloys in porous graphite decreased by the accelerated carbides formation at increased wetting temperature.
- (4)
- The difference in mass transfer at the three-phase contact line was accountable for the difference in wetting behaviors between porous graphite and CVD diamond. The presence of pores in graphite substrate impeded the stacking of active V atoms at the wetting three-phase contact line, which was responsible for the difference in the wettability of Sn-V alloy on porous graphite and polycrystalline CVD diamond.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chu, K.; Jia, C.; Guo, H.; Li, W. On the thermal conductivity of Cu–Zr/diamond composites. Mater. Des. 2013, 45, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.C.; Sung, M. The brazing of diamond. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2009, 27, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalegno, V.; Salvo, M.; Ferraris, M. Surface modification of carbon/carbon composites to improve their wettability by copper. Carbon 2012, 50, 2296–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.-P.; Chen, B.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, H.-S.; Ye, L. Joining of Cf/SiC composite with a Cu–Au–Pd–V brazing filler and interfacial reactions. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 34, 1481–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morscher, G.N.; Shpargel, T.P.; Asthana, R. Active metal brazing of titanium to high-conductivity carbon-based sandwich structures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 498, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Liu, C.; He, Y. Effect of brazing temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of graphite/copper joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 594, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-W.; Mendez, P.; Eagar, T. Strain energy distribution in ceramic-to-metal joints. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Ge, C. Brazing of doped graphite to Cu using stress relief interlayers. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 2662–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Feng, J. Active brazing carbon/carbon composite to TC4 with Cu and Mo composite interlayers. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 525, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Li, H.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, L. Brazing of C/C composites to Ti6Al4V using graphene nanoplatelets reinforced TiCuZrNi brazing alloy. Mater. Lett. 2016, 18, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Yang, M.; He, P.; Huang, C.; Pan, F.; Huang, Y. Effect of in situ synthesized TiB whisker on microstructure and mechanical properties of carbon–carbon composite and TiBw/Ti–6Al–4V composite joint. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4553–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, G.; Li, M.; Lin, J.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, A.; Zhong, Z.; Qi, J.; Feng, J. Three-dimensional graphene-reinforced Cu foam interlayer for brazing C/C composites and Nb. Carbon 2017, 118, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Shi, W. Interface reaction in ultrasonic vibration-assisted brazing of aluminum to graphite using Sn–Ag–Ti solder foil. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 221, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, L.C.; Hsieh, M.J.; Chen, T.Y.; Cheng, S.Y.; Chen, C.W. Active soldering of aluminum-graphite composite to aluminum using Sn3.5Ag4Ti0.5Cu active filler. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2016, 107, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, D.A.; Nicholas, M. The wetting of carbon by copper and copper alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 1970, 5, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devincent, S.M.; Michal, G.M. Reaction layer formation at the graphite/copper-chromium alloy interface. Metall. Trans. A 1993, 24, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Shen, P.; Lin, Q.; Qiu, F.; Jiang, Q. Wetting of porous graphite by Cu–Ti alloys at 1373K. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 124, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Yamaki, T.; Miyoshi, N.; Shinozaki, N.; Ogawa, T. Wettability of Cu-Ti Alloys on Graphite in Different Placement States of Copper and Titanium at 1373 K (1100 °C). Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2015, 46, 2262–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Shen, P.; Lin, Q.; Qiu, F.; Jiang, Q. Effect of Cr on the wetting in Cu/graphite system. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 6276–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Hu, S.; Song, X.; Zhao, Y.; Bian, H.; Jin, C. Wetting Behaviors and Interfacial Characteristics of Sn0.3Ag0.7Cu Alloys Containing Ti or Cr on Graphite. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2018, 29, 5823–5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Hu, S.P.; Song, X.G.; Li, J.X.; Cao, J.; Feng, J.C.; Wang, G.D. Wettability and bonding of graphite by Sn0.3Ag0.7Cu-Ti alloys. Carbon 2017, 121, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liao, X.; Lin, Q.; Mu, D.; Huang, H.; Xu, X.; Huang, H. Reactive wetting of binary SnCr alloy on polycrystalline chemical vapour deposited diamond at relatively low temperatures. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2019, 92, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Mu, D.; Fu, W.; Huang, H.; Huang, H. Low-temperature wetting mechanisms of polycrystalline chemical vapour deposition (CVD) diamond by Sn-Ti solder alloys. Mater. Des. 2019, 182, 108039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, J.; Lin, Q.; Wu, Y.; Mu, D. Interfacial microstructures and mechanical integrity of synthetic diamond brazed by a low-temperature Cu-Sn-Cr filler alloy. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2019, 97, 107440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.-P.; Chen, B.; Mao, W.; Li, X.-H. Joining of Cf/SiC Composite With Pd-Co-V Brazing Filler. Weld. World 2012, 56, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, T.; Suzumura, A. Reaction products at brazed interface between Ag–Cu–V filler metal and diamond (111). J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 6409–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; He, Q.; Lin, Q.; Mu, D.; Huang, H.; Huang, H. Reactive Wetting of Sn-V Solder Alloys on Polycrystalline CVD Diamond. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 504, 144508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, D.; Feng, K.; Lin, Q.; Huang, H. Low-temperature wetting of sapphire using Sn–Ti active solder alloys. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 22175–22182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gremillard, L.; Saiz, E.; Radmilovic, V.R.; Tomsia, A.P. Role of titanium on the reactive spreading of lead-free solders on alumina. J. Mater. Res. 2006, 21, 3222–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eustathopoulos, N. Progress in understanding and modeling reactive wetting of metals on ceramics. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2005, 9, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiz, E.; Tomsia, A.P. Kinetics of high-temperature spreading. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2005, 9, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, A.; Drevet, B.; Eustathopoulos, N. Kinetics of diffusion-limited spreading of sessile drops in reactive wetting. Scr. Mater. 1997, 36, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dezellus, O.; Hodaj, F.; Eustathopoulos, N. Chemical reaction-limited spreading: The triple line velocity versus contact angle relation. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 4741–4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, R.; Ju, C.; Zhong, W.; Lin, Q. Improved wetting of Al2O3 by molten Sn with Ti addition at 973–1273 K. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 739, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, K.A. Chemical Kinetics: The Study of Reaction Rates in Solution; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Bougiouri, V.; Voytovych, R.; Dezellus, O.; Eustathopoulos, N. Wetting and reactivity in Ni-Si/C system: Experiments versus model predictions. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 2016–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Cao, R. Characteristics of spreading dynamics for adsorption wetting at high temperatures. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2015, 99, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougiouri, V.; Voytovych, R.; Rojo-Calderon, N.; Narciso, J.; Eustathopoulos, N. The role of the chemical reaction in the infiltration of porous carbon by NiSi alloys. Scr. Mater. 2006, 54, 1875–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczak, N.; Sobczak, J.; Rohatgi, P.K.; Ksiazek, M.; Radziwill, W.; Morgiel, J. Interaction between Ti or Cr containing copper alloys and porous graphite substrate. In Proceedings of the International Conference High Temp. Capillarity, Cracow, Poland, 29 June–2 July 1997; pp. 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Washburn, E.W. The dynamics of capillary flow. Phys. Rev. 1921, 17, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Behrendt, D.R. Reactive melt infiltration of silicon-molybdenum alloys into microporous carbon preforms. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1995, 194, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voytovych, R.; Bougiouri, V.; Calderon, N.R.; Narciso, J.; Eustathopoulos, N. Reactive infiltration of porous graphite by NiSi alloys. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 2237–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezellus, O.; Eustathopoulos, N. Fundamental issues of reactive wetting by liquid metals. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 4256–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, P.; Zheng, X.H.; Lin, Q.L.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, Q.C. Wetting of Polycrystalline α-Al2O3 by Molten Zr55Cu30Al10Ni5 metallic glass alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2009, 40, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Qiu, F.; Sui, R. Characteristics of precursor film in the wetting of Zr-based alloys on ZrC substrate at 1253 K. Thin Solid Films. 2014, 558, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, A.P. Precursor film of tin-based active solder wetting on ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 1993, 28, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko, E. Apparent contact angles for reactive wetting of smooth, rough, and heterogeneous surfaces calculated from the variational principles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 537, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Liao, X.; Lin, Q.; Mu, D.; Lu, J.; Huang, H.; Huang, H. Reactive Infiltration and Microstructural Characteristics of Sn-V Active Solder Alloys on Porous Graphite. Materials 2020, 13, 1532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071532
Zhang Y, Liao X, Lin Q, Mu D, Lu J, Huang H, Huang H. Reactive Infiltration and Microstructural Characteristics of Sn-V Active Solder Alloys on Porous Graphite. Materials. 2020; 13(7):1532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071532
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yubin, Xinjiang Liao, Qiaoli Lin, Dekui Mu, Jing Lu, Hui Huang, and Han Huang. 2020. "Reactive Infiltration and Microstructural Characteristics of Sn-V Active Solder Alloys on Porous Graphite" Materials 13, no. 7: 1532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071532
APA StyleZhang, Y., Liao, X., Lin, Q., Mu, D., Lu, J., Huang, H., & Huang, H. (2020). Reactive Infiltration and Microstructural Characteristics of Sn-V Active Solder Alloys on Porous Graphite. Materials, 13(7), 1532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071532