Digital Light Processing of Zirconia Suspensions Containing Photocurable Monomer/Camphor Vehicle for Dental Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Starting Materials
2.2. Zirconia Suspensions Preparation
2.3. Optimization of DLP Process for 4Y-PSZ
2.4. Manufacturing of 4Y-PSZ Disks
2.5. Characterization of 4Y-PSZ Disks
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of 4Y-PSZ Powders for DLP Process
3.2. Effect of Camphor Addition on Viscosity of 4Y-PSZ Suspensions
3.3. Effect of Dispersant Content on Viscosities of 4Y-PSZ Suspensions
3.4. Effect of Solid Loading on Viscosities of 4Y-PSZ Suspensions
3.5. Photopolymerization Behavior of 4Y-PSZ Suspensions with Camphor/HDDA Vehicle
3.6. Microstructures of As-Manufactured 4Y-PSZ Disks
3.7. Effect of Sintering Temperature on Densification Behavior of 4Y-PSZ Disks
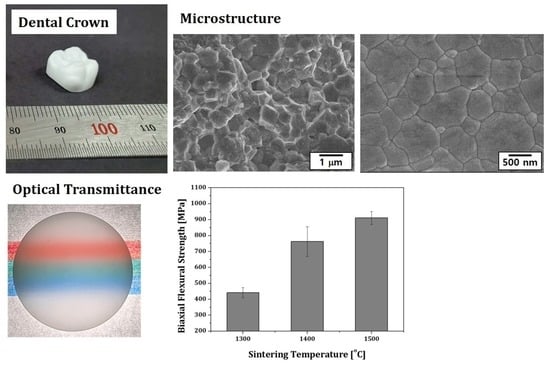
3.8. Microstructures of Sintered 4Y-PSZ Disks
3.9. Crystalline Phases of Sintered 4Y-PSZ
3.10. Mechanical Properties of Sintered 4Y-PSZ
3.11. Optical Properties of 4Y-PSZ
3.12. Usefulness of Present Approach for Dental Applications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manicone, P.F.; Iommetti, P.R.; Raffaelli, L. An overview of zirconia ceramics: Basic properties and clinical applications. J. Dent. 2007, 35, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denry, I.; Kell, J. State of the art of zirconia for dental applications. Dent. Mater. 2008, 24, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Nakamura, T.; Matsumura, H.; Ban, S.J.; Kobayashi, T. Current status of zirconia restoration. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2013, 57, 236–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Lawn, B.R. Novel zirconia materials in dentistry. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.R.; Kaizer, M.R.; Zhao, M.; Guo, B.; Song, Y.F.; Zhang, Y. Graded ultra-translucent zirconia (5Y-PSZ) for strength and functionalities. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Reveron, H.; Spies, B.C.; Van Meerbeek, B.; Chevalier, J. Trade-off between fracture resistance and translucency of zirconia and lithium-disilicate glass ceramics for monolithic restorations. Acta Biomater. 2019, 91, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, Y.R.; Elia, C.N.; Monteiro, S.N.; Santos, H.E.S.D.; Santos, C.D. Modeling of the influence of chemical composition, sintering temperature, density, and thickness in the light transmittance of four zirconia dental prostheses. Materials 2019, 12, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galante, R.; Figueiredo-Pina, C.G.; Serro, A.P. Additive manufacturing of ceramics for dental applications: A review. Dent. Mater. 2019, 35, 825–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanlar, L.N.; Rios, A.S.; Tahmaseb, A.; Zandinejad, A. Additive manufacturing of zirconia ceramic and its application in clinical dentistry: A review. Dent. J. 2021, 9, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, X.; Wade-Zhu, J.; Binner, J.; Bai, J. A comprehensive study of dense zirconia components fabricated by additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 43, 101994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakeri, S.; Vippola, M.; Levänen, E. A comprehensive review of the photopolymerization of ceramic resins used in stereolithography. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 35, 101177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Camargo, I.L.; Morais, M.N.; Fortulan, C.A.; Branciforti, M.C. A review on the rheological behavior and formulations of ceramic suspensions for vat photopolymerization. Ceram. Inter. 2021, 47, 11906–11921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harianawala, H.H.; Kheur, M.G.; Apte, S.K.; Kale, B.B.; Sethi, T.S.; Kheur, S.M. Comparative analysis of transmittance for different types of commercially available zirconia and lithium disilicate materials. J Adv. Prosthodont. 2014, 6, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manziuc, M.M.; Gasparik, C.; Negucioiu, M.; Constantiniuc, M.; Burde, A.; Vlas, I.; Dudea, D. Optical properties of translucent zirconia: A review of the literature. EBT J. 2019, 3, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrer, W.; Schwentenwein, M.; Lube, T.; Danzer, R. Fractography of zirconia-specimens made using additive manufacturing (LCM) technology. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 4331–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.J.; Kang, J.H.; Sakthiabirami, K.; Lim, H.P.; Yun, K.D.; Yim, E.K.; Oh, G.J.; Yang, H.S.; Lee, K.K.; Park, S.W. Evaluation of cure depth and geometrical overgrowth depending on zirconia volume fraction using digital light processing. J. Nanosci. Nanotechno. 2019, 19, 2154–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.J.; Kang, J.H.; Fisher, J.G.; Park, S.W. Effect of the volume fraction of zirconia suspensions on the microstructure and physical properties of products produced by additive manufacturing. Dent. Mater. 2019, 35, e91–e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Tang, W.; Li, S.; Duan, W.; Dou, R. Partially stabilized zirconia moulds fabricated by stereolithographic additive manufacturing via digital light processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 770, 138537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Zhao, W.; Xing, B.; Sing, Y.; Gao, S.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Z. Effects of exposure time and printing angle on the curing characteristics and flexural strength of ceramic samples fabricated via digital light processing. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 24379–24384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Z.; Lu, Y.; Lou, Y.; Yu, P.; Sun, M.; Tan, X.; Zhang, J.; Yue, L.; Yu, H. Determination of hardness and fracture toughness of Y-TZP manufactured by digital light processing through the indentation technique. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6612840. [Google Scholar]
- Komissarenko, D.A.; Sokolov, P.S.; Evstigneeva, A.D.; Shmeleva, I.A.; Dosovitsky, A.E. Rheological and curing behavior of acrylate-based suspensions for the DLP 3D printing of complex zirconia parts. Materials 2018, 11, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoliquido, O.; Colombo, P.; Ortona, A. Additive manufacturing of ceramic components by digital light processing: A comparison between the “bottom-up” and the “top-down” approaches. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 2140–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, J.; Duan, Y.; Bai, H.; Li, J.; Jiang, D. Dispersion and properties of zirconia suspensions for stereolithography. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2020, 17, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borlaf, M.; Serra-Capdevila, A.; Colominas, C.; Graule, T. Development of UV-curable ZrO2 slurries for additive manufacturing (LCMDLP) technology. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 3797–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.P.; Hsu, H.J.; Lee, S.Y. Development of mask-less projection slurry stereolithography for the fabrication of zirconia dental coping. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2014, 15, 2413–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Jiang, C.P. Printing system using dynamic mask projection for fabricating zirconia dental implants. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2015, 30, 1498–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Maeng, W.Y.; Koh, Y.H.; Kim, H.E. Digital light processing of zirconia prostheses with high strength and translucency for dental applications. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 28211–28218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Liu, W.; Wu, Z.; An, D.; Huang, M.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Q.; Ji, X.; Wu, S.; Xie, Z. Fabrication of complex-shaped zirconia ceramic parts via a DLP-stereolithography-based 3D printing method. Ceram. Inter. 2018, 44, 3412–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liua, W.; He, R.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Song, X.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, L.; Wu, S. Fabrication of dense zirconia-toughened alumina ceramics through a stereolithography-based additive manufacturing. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Lee, J.B.; Maeng, W.Y.; Koh, Y.H.; Kim, H.E. Photocurable ceramic slurry using solid camphor as novel diluent for conventional digital light processing (DLP) process. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 4358–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Lee, J.W.; Yang, S.Y.; Lee, H.; Koh, Y.H.; Kim, H.E. Dual-scale porous biphasic calcium phosphate gyroid scaffolds using ceramic suspensions containing polymer microsphere porogen for digital light processing. Ceram. Inter. 2021, 47, 11285–11293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomeckova, V.; Halloran, J.W. Porous ceramics by photopolymerization with terpene–acrylate vehicles. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 95, 3763–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ASTM E112-13; Standard Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- ISO 6872; Dentistry-Ceramic Materials. International Organization of Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- Miura, D.; Ishida, Y.; Miyasaka, T.; Aoki, H.; Shinya, A. Reliability of different bending test methods for dental press ceramics. Materials 2020, 13, 5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM C1372-2015; Standard Test Method for Vickers Indentation Hardness of Advanced Ceramics. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- Johnston, W.M. Review of translucency determinations and applications to dental materials. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2014, 26, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagawa, Y.; Powers, J.M.; O’Brien, W.J. Optical properties of direct restorative materials. J. Dent. Res. 1981, 60, 890–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragain, J.C. A review of color science in dentistry: Colorimetry and color space. J. Dent. Oral. Disord. Ther. 2016, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichi, A.; Sedda, M.; Fonzar, R.F.; Carrabba, M.; Ferrari, M. Comparison of contrast ratio, translucency parameter, and flexural strength of traditional and “augmented translucency” zirconia for CEREC CAD/CAM System. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2016, 28, S31–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Westland, S. Tooth color and whitening—Digital technologies. J. Dent. 2018, 74, S42–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, M.L.; Halloran, J.W. Scattering of ultraviolet radiation in turbid suspensions. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 81, 2538–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halloran, J.W. Ceramic stereolithography: Additive manufacturing for ceramics by photopolymerization. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2016, 46, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordia, R.K.; Kang, S.J.L.; Olevsky, E.A. Current understanding and future research directions at the onset of the next century of sintering science and technology. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 2314–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.H.; Vardhaman, S.; Reddy, N.; Zhang, Y. Composition, processing, and properties of biphasic zirconia bioceramics: Relationship to competing strength and optical properties. Ceram. Inter. 2022, 48, 17095–17103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.G.; Kang, J.-H.; Joe, K.-B.; Sakthiabirami, K.; Jang, K.-J.; Jun, M.-J.; Oh, G.-J.; Park, C.; Park, S.-W. Evaluation of Physical Properties of Zirconia Suspension with Added Silane Coupling Agent for Additive Manufacturing Processes. Materials 2022, 15, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, W.A.; Kang, J.-H.; Yoon, H.-I. Optimized Zirconia 3D Printing Using Digital Light Processing with Continuous Film Supply and Recyclable Slurry System. Materials 2021, 14, 3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.K. Criteria for clinical translucency evaluation of direct esthetic restorative materials. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2016, 41, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahmiri, R.; Standard, O.C.; Hart, J.N.; Sorrell, C.C. Optical properties of zirconia ceramics for esthetic dental restorations: A systematic review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 119, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, T.A.; Abdulmajeed, A.A.; Donovan, T.E.; Ritter, A.V.; Vallittu, P.K.; Narhi, T.O.; Lassila, L.V. Optical properties and light irradiance of monolithic zirconia at variable thicknesses. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, N.; Isler, S. Microstructural, physical, and optical characterization of high-translucency zirconia ceramics. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 123, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzolatto, G.; Borba, M. Optical properties of new zirconia-based dental ceramics: Literature review. Ceramics 2021, 67, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Xu, Y.; Bai, W.; Lin, H. Dental zirconia fabricated by stereolithography: Accuracy, translucency and mechanical properties in different build orientations. Ceram. Inter. 2021, 47, 28837–28847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Role | Material (Supplier) | Weight [g] |
|---|---|---|
| Zirconia Powder | Yttria-stabilized zirconia (Zpex4) (Tosoh Co., Tokyo, Japan) | 71.85 |
| Photocurable Monomer | 1,6-hexanediol diacrylate (HDDA) (Sartomer, PA, USA) | 6.5 |
| Diluent | Camphor (C10H16O) (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) | 3.5 |
| Dispersant | Solution of a structured acrylate copolymer with pigment-affinic groups (DISPERBYK-2001) (BYK-Chemie GmbH, Wesel, Germany) | 2.87 |
| Photo Initiator | Diphenyl(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl) phosphine oxide (TPO) (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) | 1.13 |
| Refs. | [21] | [23] | [24] | [27] | Present Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solid Loading | 75 wt% | 42 vol% | 44 vol% | 50 vol% | 48 vol% |
| Viscosities [Pa·s] | 1.6 | 4.88 | ~2 | ~3.5 | ~1.40 |
| Sintering Temperatures [°C] | 1300 | 1400 | 1500 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grain Size [nm] | 130 ± 8.9 | 275 ± 32.3 | 543 ± 94.4 |
| Refs. | [10] | [24] | [25] | [26] | [27] |
| Flexural strength [MPa] | 1042 | 741 | 539 | 539.1 | 831 |
| Hardness | 12.59 GPa | n/a | 13.02 GPa | 1556 Hv | n/a |
| Refs. | [28] | [29] | [46] | [47] | Present Study |
| Flexural strength [MPa] | n/a | 530.25 | 433 | n/a | 911 |
| Hardness | 13.0597 Hv | 17.76 GPa | 1848 Hv | 12.59 GPa | 1371 Hv |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.-Y.; Koh, Y.-H.; Kim, H.-E. Digital Light Processing of Zirconia Suspensions Containing Photocurable Monomer/Camphor Vehicle for Dental Applications. Materials 2023, 16, 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16010402
Yang S-Y, Koh Y-H, Kim H-E. Digital Light Processing of Zirconia Suspensions Containing Photocurable Monomer/Camphor Vehicle for Dental Applications. Materials. 2023; 16(1):402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16010402
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Seo-Young, Young-Hag Koh, and Hyoun-Ee Kim. 2023. "Digital Light Processing of Zirconia Suspensions Containing Photocurable Monomer/Camphor Vehicle for Dental Applications" Materials 16, no. 1: 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16010402
APA StyleYang, S. -Y., Koh, Y. -H., & Kim, H. -E. (2023). Digital Light Processing of Zirconia Suspensions Containing Photocurable Monomer/Camphor Vehicle for Dental Applications. Materials, 16(1), 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16010402