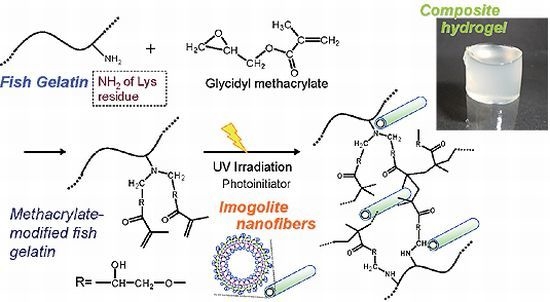
Preparation and Mechanical Properties of Photo-Crosslinked Fish Gelatin/Imogolite Nanofiber Composite Hydrogel
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Methacrylate-Modified Fish Gelatin (FG-GMA)
2.3. Synthesis of Imogolite
2.4. Preparation of Gelatin/Imogolite Composite Hydrogel by Photoirradiation
2.5. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Methacrylate-Modified Fish Gelatin (FG-GMA)

3.2. Preparation of Gelatin/Imogolite Composite Hydrogel by Photoirradiation

3.3. Electron Microscopic Observation of Lyophylized Gelatin/Imogolite Composite Gel


3.4. Physical Properties of Gelatin/Imogolite Composite Hydrogel



4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Elsdale, T.; Bard, J. Collagen substrata for studies on cell behavior. J. Cell Biol. 1972, 54, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schor, S.L. Cell proliferation and migration on collagen substrata in vitro. J. Cell Sci. 1980, 41, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Strom, S.C.; Michalopoulos, G. Collagen as a substrate for cell growth and differentiation. Methods Enzymol. 1982, 82, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wallace, D.G.; Rosenblatt, J. Collagen gel systems for sustained delivery and tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 1631–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.-W.; Tabata, Y.; Ikada, Y. Fabrication of porous gelatin scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, K.; Suzuki, S.; Tabata, Y.; Ikada, Y.; Nishimura, Y. Accelerated tissue regeneration through incorporation of basic fibroblast growth factor-impregnated gelatin microspheres into artificial dermis. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, A.; Mase, A.; Takizawa, Y.; Shinkai, M.; Honda, H.; Hata, K.-I.; Ueda, M.; Kobayashi, T. Transglutaminase-mediated gelatin matrices incorporating cell adhesion factors as a biomaterial for tissue engineering. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2003, 95, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.-H.; Liu, B.-S.; Chang, C.-J.; Hsu, S.-H.; Chen, Y.-S. Preparation of networks of gelatin and genipin as degradable biomaterials. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2004, 83, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Pérez-Mateos, M.; Gópez-Estaca, J.; López-Caballero, E.; Giménez, B.; Montero, P. Fish gelatin: A renewable material for developing active biodegradable films. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.A.; Bhat, R. Fish gelatin: Properties, challenges, and prospects as an alternative to mammalian gelatins. Food Hydrocolloids 2009, 23, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, K.; Liu, H.; Guo, S.; Kumar, D.N.T.; Wang, Q. Preparation of fish gelatin and fish gelatin/poly(L-lactide) nanofibers by electrospinning. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haug, I.J.; Draget, K.I.; Smidsrød, O. Physical and rheological properties of fish gelatin compared to mammalian gelatin. Food Hydrocolloids 2004, 18, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigi, A.; Cojazzi, G.; Panzavolta, S.; Rubini, K.; Roveri, N. Mechanical and thermal properties of gelatin films at different degrees of glutaraldehyde crosslinking. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigi, A.; Cojazzi, G.; Panzavolta, S.; Roveri, N.; Rubini, K. Stabilization of gelatin films by crosslinking with genipin. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4827–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, R.; Karim, A.A. Ultraviolet irradiation improves gel strength of fish gelatin. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 1160–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, B.-S.; Avena-Bustillos, R.J.; Shey, J.; Yee, E.; Bechtel, P.J.; Imam, S.H.; Glenn, G.M.; Orts, W.J. Rheological and mechanical properties of cross-linked fish gelatins. Polymer 2006, 47, 6379–6386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Uyama, H. Biocompatible hydrogel formation of gelatin from cold water fish via enzymatic networking. Polym. J. 2007, 39, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunoki, S.; Nagai, N.; Suzuki, T.; Munekata, M. Novel biomaterial from reinforced salmon collagen gel prepared by fibril formation and cross-linking. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2004, 98, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolodziejska, I.; Piotrowska, B. The water vapour permeability, mechanical properties and solubility of fish gelatin-chitosan films modified with transglutaminase or 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide (EDC) and plasticized with glycerol. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallgatter, A.M.; Kim, J.H.; Fricton, J.; Hu, W.S. Mechanical properties and cytocompatibility of biomimetic hydroxyapatite-gelatin nanocomposites. J. Mater. Res. 2006, 21, 3090–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-F.; Lee, S.-C. Effect of hydrotalcite on the swelling and mechanical behaviors for the hybrid nanocomposite hydrogels based on gelatin and hydrotalcite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 100, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y. Gelatin-clay nanocomposites of improved properties. Polymer 2007, 48, 5369–5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.Z.; Wang, Y.L.; Luo, H.L.; Cheng, G.X.; Yao, K.D. Carbon fiber-reinforced gelatin composites. I. Preparation and mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 75, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.P.; Li, P.; Ma, Y.L.; Yao, K.D. Gelatin/montmorillonite hybrid nanocomposite. I. Preparation and properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, N.; Uchiumi, D.; Niikura, A.; Someya, Y.; Shibata, M. Polypeptide/layered silicate nanocomposites using fish-based collagen peptide: Effect of crosslinking and chain extension of the collagen peptide. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 106, 4024–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.K.; Bera, T.; Saxena, P.S.; Maurya, A.K.; Garbyal, R.S.; Vajtai, R.; Ramachandrarao, P.; Srivastava, A. MWCNTs as reinforcing agent to the hap–gel nanocomposite for artificial bone grafting. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 93, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.P.; Katsuyama, Y.; Kurokawa, T.; Osada, Y. Double-network hydrogels with extremely high mechanical strength. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1155–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, Y.; Ito, K. The polyrotaxane gel: A topological gel by figure-of-eight cross-links. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, K.; Takehisa, T. Nanocomposite hydrogels: A unique organic–inorganic network structure with extraordinary mechanical, optical, and swelling/de-swelling properties. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1120–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, T.; Matsunaga, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ito, C.; Yoshida, R.; Suzuki, S.; Sasaki, N.; Shibayama, M.; Chung, U.-I. Design and fabrication of a high-strength hydrogel with ideally homogeneous network structure from tetrahedron-like macromonomers. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 5379–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cradwick, P.D.G.; Farmer, V.C.; Russell, J.D.; Masson, C.R.; Wada, K.; Yoshinaga, N. Imogolite, a hydrated aluminium silicate of tubular structure. Nat. Phys. Sci. 1972, 240, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, A.; Teramoto, N.; Chen, G.; Miura, Y.; Shibata, M. Preparation and characterization of complex gel of type I collagen and aluminosilicate containing imogolite nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 118, 2284–2290. [Google Scholar]
- Shikinaka, K.; Koizumi, Y.; Osada, Y.; Shigehara, K. Reinforcement of hydrogel by addition of fiber-like nanofiller. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 1212–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Otsuka, H.; Wada, S.-I.; Sohn, D.; Takahara, A. Preparation and properties of [poly(methyl methacrylate)/imogolite] hybrid via surface modification using phosphoric acid ester. Polymer 2005, 46, 12386–12392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Otsuka, H.; Wada, S.-I.; Sohn, D.; Takahara, A. Transparent polymer nanohybrid prepared by in situ synthesis of aluminosilicate nanofibers in poly(vinyl alcohol) solution. Soft Matter 2005, 1, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yah, W.O.; Yamamoto, K.; Jiravanichanun, N.; Otsuka, H.; Takahara, A. Imogolite reinforced nanocomposites: Multifaceted green materials. Materials 2010, 3, 1709–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, W.; Rong, J.; Zhou, C. Novel polymer nanocomposite hydrogel with natural clay nanotubes. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2012, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Elisseeff, J.; McIntosh, W.; Anseth, K.; Riley, S.; Ragan, P.; Langer, R. Photoencapsulation of chondrocytes in poly(ethylene oxide)-based semi-interpenetrating networks. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 51, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, A.I.; Akintoye, S.O.; Nicoll, S.B. Photo-crosslinked alginate hydrogels support enhanced matrix accumulation by nucleus pulposus cells in vivo. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2009, 17, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Inukai, K.; Maeda, M. Synthesis of imogolite from inorganic solution influence of solution concentration on forming precursor for the synthesis of large quantities of imogolite. J. Vac. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 49, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qian, L.; Shu, T.; Tong, Z. Rheology characterization of sol-gel transition in aqueous alginate solutions induced by calcium cations through in situ release. Polymer 2003, 44, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourchid, A.; Lécolier, E.; van Damme, H.; Levitz, P. On viscoelastic, birefringent, and swelling properties of laponite clay suspensions: Revisited phase diagram. Langmuir 1998, 14, 4718–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paineau, E.; Michot, L.J.; Bihannic, I.; Baravian, C. Aqueous suspensions of natural swelling clay minerals. 2. Rheological characterization. Langmuir 2011, 27, 7806–7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labanda, J.; Llorens, J. Rheology of Laponite colloidal dispersions modified by sodium polyacrylates. Colloids Surface A 2004, 249, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Teramoto, N.; Hayashi, A.; Yamanaka, K.; Sakiyama, A.; Nakano, A.; Shibata, M. Preparation and Mechanical Properties of Photo-Crosslinked Fish Gelatin/Imogolite Nanofiber Composite Hydrogel. Materials 2012, 5, 2573-2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5122573
Teramoto N, Hayashi A, Yamanaka K, Sakiyama A, Nakano A, Shibata M. Preparation and Mechanical Properties of Photo-Crosslinked Fish Gelatin/Imogolite Nanofiber Composite Hydrogel. Materials. 2012; 5(12):2573-2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5122573
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeramoto, Naozumi, Akihiko Hayashi, Kaori Yamanaka, Asako Sakiyama, Asuka Nakano, and Mitsuhiro Shibata. 2012. "Preparation and Mechanical Properties of Photo-Crosslinked Fish Gelatin/Imogolite Nanofiber Composite Hydrogel" Materials 5, no. 12: 2573-2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5122573
APA StyleTeramoto, N., Hayashi, A., Yamanaka, K., Sakiyama, A., Nakano, A., & Shibata, M. (2012). Preparation and Mechanical Properties of Photo-Crosslinked Fish Gelatin/Imogolite Nanofiber Composite Hydrogel. Materials, 5(12), 2573-2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5122573