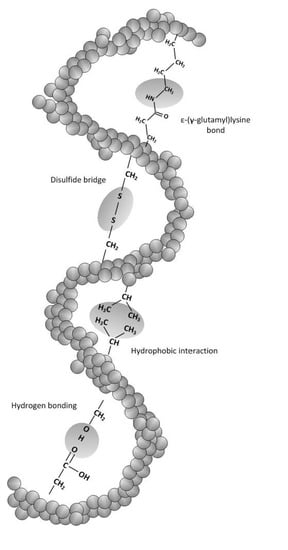
Determination and Quantification of Molecular Interactions in Protein Films: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Protein Films
2.1. Definition and Characteristics of Proteins
| Amino acid | β-lactoglobulin (Whey Protein) (mol%) | β-conglycinin (Soy Protein) (mol%) | γ-gliadins (Wheat Gluten) (mol%) | Whole Gliadins (Wheat Gluten) (per 100 g protein) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alanine | 5.4 | 4.0 | 2.3 | 28.6 |
| Arginine | 2.5 | 8.3 | 1.8 | 17.4 |
| Asparagine | 3.1 | 12.0 | 2.9 | – |
| Aspartic acid | 6.9 | – | – | 24.8 |
| Cysteine | 2.8 | 0.03 | – | 29.0 |
| Glutamic acid | 6.2 | 24.5 | 45.8 | 301.1 |
| Glutamine | 11.2 | – | – | – |
| Glycine | 0.9 | 3.5 | 1.4 | 26.8 |
| Histidine | 1.5 | 2.8 | 1.6 | 16.3 |
| Isoleucine | 6.3 | 4.5 | 4.4 | 38.0 |
| Leucine | 13.6 | 7.5 | 7.0 | 60.6 |
| Lysine | 10.5 | 6.1 | – | 5.0 |
| Methionine | 2.8 | 0.4 | 0.9. | 10.9 |
| Phenylalanine | 3.2 | 5.4 | 5.2 | 37.5 |
| Proline | 4.2 | 4.7 | 14.5 | 142.0 |
| Serine | 3.3 | 5.4 | 4.3 | 53.6 |
| Threonine | 4.4 | 3.3 | 1.7 | 21.3 |
| Tryptophan | 2.0 | – | – | 3.8 |
| Tyrosine | 3.6 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 16.0 |
| Valine | 5.4 | 4.1 | 3.8 | 41.6 |
2.2. Whey Protein
2.3. Soy Protein
2.4. Wheat Gluten
3. Cross-Linking in Protein Films

3.1. Thermal Cross-Linking
3.2. Enzymatic Cross-Linking
3.3. Irradiation
3.4. Chemical Cross-Linking
4. Methods to Determine the Degree of Cross-Linking in Protein Films
4.1. Structural Analysis of Solutions
4.1.1. Electrophoretic Analysis
4.1.2. Size Exclusion Chromatography
| Soluble fraction of film-forming solution | Molecular weight (kDa) | Responsible interactions |
|---|---|---|
| Native WPI/WPC | 40 | Native or intramolecular cross-linked |
| Heated WPI/WPC | 600–3800 | Disulfide bonds |
| γ-Irradiated WPI/WPC | 1000–2000 | Bityrosine bridges |
4.2. Structural Analysis of Solid Biofilms
4.2.1. Spectroscopic Techniques
| Whey protein film | Wavenumber (cm−1) | Responsible interactions |
|---|---|---|
| Native | 1621, 1634, 1692 | Intramolecular β-sheets |
| 1649 | α-helix | |
| 1606, 1663, 1677 | β-turns, side chain residues | |
| Heated | Elimination and diminishment of the native bands | |
| 1612 | Intermolecular β-sheets | |
| 1682 | Antiparallel β-sheets | |
4.2.2. X-ray Scattering Methods
5. Quantification of Degree of Cross-Linking in Protein Films
5.1. Swelling
5.2. Protein Solubility Study
| Type of Interaction | Specific Interaction | Reagents Capable of Breaking up the Interactions |
|---|---|---|
| Covalent | Disulfide bonding | Oxidizing or reducing agents, e.g., performic acid, DTT |
| Non-Covalent | Hydrogen bonding | Strong H-bonding agents, e.g., urea, diemethyl formamide, thiourea, SDS |
| Non-Covalent | Hydrophobic interaction | Ionic and nonionic detergents, e.g., SDS, thiourea, Triton, CHAPS sodium salts of long-chain fatty acids |
| Non-Covalent electrostatic | Acid hydrophilic basic hydrophilic | Acids, alkali or salt solution |
| State | Qualification | Quantification |
|---|---|---|
| Solution | SDS-Page Size exclusion chromatography X-ray scattering | – |
| Film | Spectroscopic techniques X-ray diffraction | Swelling protein solubility study |
6. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sängerlaub, S.; Gibis, D.; Kirchhoff, E.; Tittjung, M.; Schmid, M.; Müller, K. Compensation of pinhole defects in food packages by application of iron-based oxygen scavenging multilayer films. In Proceedings of the 5th international Symposium on Food Packaging, Berlin, Germany, 14–16 November 2012.
- Buchner, N. Verpackung von Lebensmitteln; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1999. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, G.L. Food Packaging: Principles and Practice; Taylor & Francis/CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cuq, B.; Gontard, N.; Guilbert, S. Proteins as agricultural polymers for packaging production. Cereal Chem. 1998, 75, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krochta, J.M.; Baldwin, E.A.; Nisperos-Carriedo, M.O. Edible Coatings and Films to Improve Food Quality; Technomic Publ. Co.: Lancaster, PA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Krochta, J.M. Proteins as raw materials for films and coatings: definitions, current status, and opportunities. In Protein-Based Films and Coatings; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Gennadios, A. Protein-Based Films and Coatings; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gennadios, A.; Weller, C.L.; Testin, R.F. Modification of physical and barrier properties of edible wheat gluten-based films. Cereal Chem. 1993, 70, 426–429. [Google Scholar]
- Gennadios, A.; Brandenburg, A.H.; Weller, C.L.; Testin, R.F. Effect of pH on properties of wheat gluten and soy protein isolate films. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1993, 41, 1835–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Gago, M.B.; Nadaud, P.; Krochta, J.M. Water vapor permeability, solubility, and tensile properties of heat-denatured versus native whey protein films. J. Food Sci. 1999, 64, 1034–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sothornvit, R.; Krochta, J.M. Plasticizer effect on oxygen permeability of beta-lactoglobulin films. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 6298–6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sothornvit, R.; Krochta, J.M. Plasticizer effect on mechanical properties of beta-lactoglobulin films. J. Food Eng. 2001, 50, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micard, V.; Belamri, R.; Morel, M.H.; Guilbert, S. Properties of chemically and physically treated wheat gluten films. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 2948–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandenburg, A.H.; Weller, C.L.; Testin, R.F. Edible films and coatings from soy protein. J. Food Sci. 1993, 58, 1086–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Hinz, L.-V.; Wild, F.; Noller, K. Effects of hydrolysed whey proteins on the techno-functional characteristics of whey protein-based films. Materials 2013, 6, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugnicourt, E.; Schmid, M.; Nerney, O.M.; Wildner, J.; Smykala, L.; Lazzeri, A.; Cinelli, P. Processing and validation of whey-protein-coated films and laminates at semi-industrial scale as novel recyclable food packaging materials with excellent barrier properties. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 2013, 496207:1–496207:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Izquierdo, V.M.; Reid, D.S.; McHugh, T.H.; Berrios, J.De.J.; Krochta, J.M. Thermal transitions and extrusion of glycerol-plasticized whey protein mixtures. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, E169–E175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gennadios, A.; Weller, C.; Testin, R. Temperature effect on oxygen permeability of edible protein‐based films. J. Food Sci. 1993, 58, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Hammann, F.; Winkler, H. Technofunctional properties of films made from ethylene vinyl acetate/whey protein isolate compounds. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2014, 27, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Dallmann, K.; Bugnicourt, E.; Cordoni, D.; Wild, F.; Lazzeri, A.; Noller, K. Properties of whey protein coated films and laminates as novel recyclable food packaging materials with excellent barrier properties. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2012, 2012, 562381:1–562381:7. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, M.; Sängerlaub, S.; Wege, L.; Stäbler, A. Properties of transglutaminase crosslinked whey protein isolate coatings and cast films. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2014, 27, 799–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Müller, K.; Sängerlaub, S.; Stäbler, A.; Starck, V.; Ecker, F.; Noller, K. Mechanical and barrier properties of thermoplastic whey protein isolate/ethylene vinyl acetate blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Krimmel, B.; Grupa, U.; Noller, K. Effects of thermally induced denaturation on technological-functional properties of whey protein isolate-based films. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 5315–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinelli, P.; Schmid, M.; Bugnicourt, E.; Wildner, J.; Bazzichi, A.; Anguillesi, I.; Lazzeri, A. Whey protein layer applied on biodegradable packaging film to improve barrier properties while maintaining biodegradability. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 108, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsella, J.; Whitehead, D. Proteins in whey: Chemical, physical, and functional properties. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 1989, 33, 437–438. [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella, J.E. Functional properties of soy proteins. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1979, 56, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsella, J. Relationships between structure and functional properties of food proteins. Food Proteins 1982, 1, 51–103. [Google Scholar]
- Belitz, H.-D.G.W.; Schieberle, P. Lehrbuch der Lebensmittelchemie: Mit 634 Tabellen; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Cheftel, J.; Cuq, J.; Lorient, D. Amino acids, peptides, and proteins. Food Chem. 1985, 2, 246–369. [Google Scholar]
- Panyam, D.; Kilara, A. Enhancing the functionality of food proteins by enzymatic modification. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1996, 7, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Muñoz, P.; Villalobos, R.; Chiralt, A. Effect of thermal treatments on functional properties of edible films made from wheat gluten fractions. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciannamea, E.M.; Stefani, P.M.; Ruseckaite, R.A. Physical and mechanical properties of compression molded and solution casting soybean protein concentrate based films. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 38, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, J.R.; Dangaran, K.; Schmidt, W.F. Blends of cysteine-containing proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 5393–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Were, L.; Hettiarachchy, N.; Coleman, M. Properties of cysteine‐added soy protein‐wheat gluten films. J. Food Sci. 1999, 64, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez‐Gago, M.; Nadaud, P.; Krochta, J. Water vapor permeability, solubility, and tensile properties of heat‐denatured versus native whey protein films. J. Food Sci. 1999, 64, 1034–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Izquierdo, V.M.; Krochta, J.M. Thermoplastic processing of proteins for film formation—A review. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, R30–R39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damodaran, S. Amino acids, peptides, and proteins. Food Sci. Technol. 1996, 321–430. [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella, J.; Whitehead, D.; Brady, J.; Bringe, N.; Fox, P. Milk proteins: Possible relationships of structure and function. In Developments in Dairy Chemistry. 4. Functional Milk Proteins; Elsevier Applied Science: London, UK, 1989; pp. 55–95. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.-G.; Yang, X.-Q.; Ahmad, I.; Min, W.; Zhu, J.-H.; Yuan, D.-B. Soybean β-conglycinin constituent subunits: Isolation, solubility and amino acid composition. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzel, M.R. Manufacture and use of dairy protein fractions. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 996S–1002S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lasztity, R. The Chemistry of Cereal Proteins, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis: Oxon, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Foegeding, E.A.; Mleko, S.W. Whey protein products. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jovanovic, S.; Barac, M.; Macej, O. Whey proteins-properties and possibility of application. Mljekarstvo 2005, 55, 215–233. [Google Scholar]
- Yada, R.Y. Proteins in Food Processing; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- De Wit, J. Thermal stability and functionality of whey proteins. J. Dairy Sci. 1990, 73, 3602–3612. [Google Scholar]
- Dybing, S.; Smith, D. Relation of chemistry and processing precedures to whey protein functionality: A review. Cult. Dairy Prod. J. 1991, 26, 4–12. [Google Scholar]
- Belitz, H.-D.; Grosch, W.; Schieberle, P. Food Chemistry: With 634 Tables; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer, W.H.; Norton, R.S.; Nichol, L.W.; McKenzie, G.H. Thermodenaturation of bovine beta-leactoglobulin kinetics and introduction of beta-structure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1971, 243, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Töpel, A. Chemie und Physik der Milch: Naturstoff-Rohstoff-Lebensmittel; Behr: Hamburg, Germany, 2004. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- De Wit, J.N. Lecturer’s Handbook on Whey and Whey Products; European Whey Products Association: Brüssel, Belgium, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Morr, C.; Ha, E. Whey protein concentrates and isolates: Processing and functional properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1993, 33, 431–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laboratory, E.M.B. Protein Data Bank in Europe 2014. Available online: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbe (accessed on 23 June 2014).
- Cho, S.Y.; Rhee, C. Mechanical properties and water vapor permeability of edible films made from fractionated soy proteins with ultrafiltration. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 37, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Liu, D.; Zhang, L. Advances in proteinous biomaterials. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2008, 2, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunte, L.; Gennadios, A.; Cuppett, S.; Hanna, M.; Weller, C.L. Cast films from soy protein isolates and fractions 1. Cereal Chem. 1997, 74, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwabuchi, S.; Yamauchi, F. Electrophoretic analysis of whey proteins present in soybean globulin fractions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1987, 35, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermansson, A. Physico-chemical aspects of soy proteins structure formation. J. Texture Stud. 1978, 9, 33–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Utsumi, S.; Inaba, H.; Kitamura, K.; Harada, K. Differences in subunit composition of glycinin among soybean cultivars. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1981, 29, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utsumi, S.; Kinsella, J.E. Forces involved in soy protein gelation: effects of various reagents on the formation, hardness and solubility of heat‐induced gels made from 7S, 11S, and soy isolate. J. Food Sci. 1985, 50, 1278–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasztity, R. Recent results in the investigation of the structure of the gluten complex. Food Nahrung 1986, 30, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagrain, B.; Goderis, B.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. Molecular basis of processing wheat gluten toward biobased materials. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shewry, P.; Tatham, A. Disulphide bonds in wheat gluten proteins. J. Cereal Sci. 1997, 25, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrigley, C.; Bietz, J.; Pomeranz, Y. Proteins and amino acids. In Wheat: Chemistry and Technology, 3rd ed.; American Association of Cereal Chemists: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1988; Volume I, pp. 159–275. [Google Scholar]
- Wieser, H. Chemistry of gluten proteins. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avena-Bustillos, R.J.; Krochta, J.M. Water vapor permeability of caseinate-based edible films as affected by pH, calcium crosslinking and lipid content. J. Food Sci. 1993, 58, 904–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kester, J.J.; Richardson, T. Modification of whey proteins to improve functionality. J. Dairy Sci. 1984, 67, 2757–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeek, C.J.R.; van den Berg, L.E. Extrusion processing and properties of protein-based thermoplastics. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2010, 295, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K.; Cheftel, J.C. Sulfhydryl group/disulfide bond interchange reactions during heat-induced gelation of whey protein isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1989, 37, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsella, J.E.; Morr, C.V. Milk proteins: Physicochemical and functional properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1984, 21, 197–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Gago, M.B.; Krochta, J.M. Denaturation time and temperature effects on solubility, tensile properties, and oxygen permeability of whey protein edible films. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Murphy, P.A.; Johnson, L.A.; Fratzke, A.R.; Reuber, M.A. Pilot-plant fractionation of soybean glycinin and β-conglycinin. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1999, 76, 285–293. [Google Scholar]
- German, B.; Damodaran, S.; Kinsella, J.E. Thermal dissociation and association behavior of soy proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1982, 30, 807–811. [Google Scholar]
- Subirade, M.; Kelly, I.; Guéguen, J.; Pézolet, M. Molecular basis of film formation from a soybean protein: Comparison between the conformation of glycinin in aqueous solution and in films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1998, 23, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Renkema, J.M.; van Vliet, T. Heat-induced gel formation by soy proteins at neutral pH. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 1569–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuchell, Y.M.; Krochta, J.M. Enzymatic treatments and thermal effects on edible soy protein films. J. Food Sci. 1994, 59, 1332–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, J.; Bottomley, R.; Timms, M.; Booth, M. The effect of heat on wheat gluten and the involvement of sulphydryl-disulphide interchange reactions. J. Cereal Sci. 1983, 1, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; MacRitchie, F. Changes in proteins induced by heating gluten dispersions at high temperature. J. Cereal Sci. 2004, 39, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gällstedt, M.; Mattozzi, A.; Johansson, E.; Hedenqvist, M.S. Transport and tensile properties of compression-molded wheat gluten films. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 2020–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pommet, M.; Redl, A.; Morel, M.H.; Domenek, S.; Guilbert, S. Thermoplastic processing of protein-based bioplastics: Chemical engineering aspects of mixing, extrusion and hot molding. Macromol. Symp. 2003, 197, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sothornvit, R.; Olsen, C.W.; McHugh, T.H.; Krochta, J.M. Formation conditions, water-vapor permeability, and solubility of compression-molded whey protein films. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 1985–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, G.A.H.; Koppelman, S.J. Transglutaminase catalyzed reactions: Impact on food applications. J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 2798–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Rinzema, A.; Tramper, J.; Bol, J. Microbial transglutaminase—A review of its production and application in food processing. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1995, 44, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, A.S.; Puhl, C.; Kadla, J.F.; Khan, S.A. Enzymatic cross-linking of β-lactoglobulin: Conformational properties using FTIR spectroscopy. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1707–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, V.D.; Clare, D.A.; Catignani, G.L.; Swaisgood, H.E. Cross-linking and rheological changes of whey proteins treated with microbial transglutaminase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, M. Properties of cast films made from different ratios of whey protein isolate, hydrolysed whey protein isolate and glycerol. Materials 2013, 6, 3254–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, M.; Hettiarachchy, N.S. Properties of films produced by cross-linking whey proteins and 11S globulin using transglutaminase. J. Food Sci. 1998, 63, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.-H.; Wang, B.; Field, P.D.; Aglan, H.A. Characteristics of edible films made from dairy proteins and zein hydrolysate cross-linked with transglutaminase. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 39, 287–294. [Google Scholar]
- Motoki, M.; Nio, N.; Takinami, K. Functional properties of heterologous polymer prepared by transglutaminase between milk casein and soybean globulin. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1987, 51, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoki, M.; Seguro, K. Transglutaminase and its use for food processing. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1998, 9, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, M.; Hettiarachchy, N.S. Biopolymers produced by cross-linking soybean 11S globulin with whey proteins using transglutaminase. J. Food Sci. 1997, 62, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-S.; Zhao, M.-M.; Yang, X.-Q.; Jiang, Y.-M.; Chun, C. Gelation behavior of wheat gluten by heat treatment followed by transglutaminase cross-linking reaction. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.S.; Lai, H.M. Physicochemical properties of wheat flour dough modified by microbial transglutaminase. J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabato, S.; Ouattara, B.; Yu, H.; D’aprano, G.; Le Tien, C.; Mateescu, M.; Lacroix, M. Mechanical and barrier properties of cross-linked soy and whey protein based films. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.C.; Song, K.B. Effect of ascorbic acid and protein concentration on the molecular weight profile of bovine serum albumin and β-lactoglobulin by γ-irradiation. Food Res. Int. 1999, 32, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brault, D.; D’Aprano, G.; Lacroix, M. Formation of free-standing sterilized edible films from irradiated caseinates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 2964–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, K.; Delsignore, M.; Lin, S. Protein damage and degradation by oxygen radicals. II. Modification of amino acids. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 9902–9907. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.A.; Sala, G.; Olieman, C.; de Kruif, K.G. Molecular mass distributions of heat-induced β-lactoglobulin aggregates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 2949–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.W.S.; Camirand, W.M.; Pavlath, A.E. Structures and functionalities of milk proteins. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1996, 36, 807–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köksel, H.; Sapirstein, H.; Celik, S.; Bushuk, W. Effects of gamma-irradiation of wheat on gluten proteins. J. Cereal Sci. 1998, 28, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, M.; Song, K. Effect of gamma-irradiation on the physicochemical properties of gluten films. Food Chem. 2005, 92, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, W.F.; Sullivan, P.D. The effect of radiation on collagen I. Electron-spin resonance spectra of 2537-Å-irradiated collagen. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biophys. Incl. Photosynth. 1966, 120, 222–228. [Google Scholar]
- Fujimori, E. Ultraviolet light‐induced change in collagen macromolecules. Biopolymers 1965, 3, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gennadios, A.; Rhim, J.; Handa, A.; Weller, C.; Hanna, M. Ultraviolet radiation affects physical and molecular properties of soy protein films. J. Food Sci. 1998, 63, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wihodo, M.; Moraru, C.I. Physical and chemical methods used to enhance the structure and mechanical properties of protein films. A review. J. Food Eng. 2012, 114, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustunol, Z.; Mert, B. Water solubility, mechanical, barrier, and thermal properties of cross-linked whey protein isolate-based films. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitford, D. Proteins: Structure and Function; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Monahan, F.J.; German, J.B.; Kinsella, J.E. Effect of pH and temperature on protein unfolding and thiol/disulfide interchange reactions during heat-induced gelation of whey proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Tien, C.; Letendre, M.; Ispas-Szabo, P.; Mateescu, M.A.; Delmas-Patterson, G.; Yu, H.L.; Lacroix, M. Development of biodegradable films from whey proteins by cross-linking and entrapment in cellulose. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 5566–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildirim, M.; Hettiarachchy, N.S.; Kalapathy, U. Properties of biopolymers from cross-linking whey protein isolate and soybean 11S globulin. J. Food Sci. 1996, 61, 1129–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roefs, S.; Dekruif, K.G. A model for the denautartion and aggregation of beta-lactoglobulin. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 226, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.A.M.; van Mil, P. Heat-induced aggregation of beta-lactoglobulin: Role of the free thiol group and disulfide bonds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 2942–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangavajhyala, N.; Ghorpade, V.; Hanna, M. Solubility and molecular properties of heat-cured soy protein films. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 4204–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Weller, C.; Gennadios, A.; Zeece, M.; Testin, R. Physical and molecular properties of wheat gluten films cast from heated film‐forming solutions. J. Food Sci. 1999, 64, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, S.; Chander, R.; Sharma, A. Antioxidant properties of Maillard reaction products obtained by gamma-irradiation of whey proteins. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redl, A.; Morel, M.H.; Bonicel, J.; Vergnes, B.; Guilbert, S. Extrusion of wheat gluten plasticized with glycerol: Influence of process conditions on flow behavior, rheological properties, and molecular size distribution. Cereal Chem. 1999, 76, 361–370. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Damodaran, S. Heat-induced conformational changes in whey protein isolate and its relation to foaming properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, R.; Fujita, Y.; Kitabatake, N. Effects of heating at neutral and acid pH on the structure of β-lactoglobulin A revealed by differential scanning calorimetry and circular dichroism spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gen. Subj. 2006, 1760, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.L.; Holt, C.; McNulty, D.; Clarke, D.T.; Brownlow, S.; Jones, G.R. Effect of temperature on the secondary structure of beta-lactoglobulin at pH 6.7, as determined by CD and IR spectroscopy: A test of the molten globule hypothesis. Biochem. J. 1997, 324, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kelly, S.M.; Jess, T.J.; Price, N.C. How to study proteins by circular dichroism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Proteins Proteomics 2005, 1751, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.; Mantsch, H.H. The use and misuse of FTIR spectroscopy in the determination of protein structure. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 30, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, A.; Strumia, M.C.; Alvarez Igarzabal, C.I. Cross-linked soy protein as material for biodegradable films: Synthesis, characterization and biodegradation. J. Food Eng. 2011, 106, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, E.; Elliott, A. The structure of synthetic polypeptides. II. Investigation with polarized infra-red spectroscopy. Proc. R. Soc. Lon. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1951, 205, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, F.; Xue, W.; Lee, L. FTIR spectra studies on the secondary structures of 7S and 11S globulins from soybean proteins using AOT reverse micellar extraction. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, T.; Subirade, M.; Pézolet, M. Molecular description of the formation and structure of plasticized globular protein films. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 3209–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangavel, C.; Barbot, J.; Popineau, Y.; Guéguen, J. Evolution of wheat gliadins conformation during film formation: A Fourier transform infrared study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georget, D.M.; Belton, P.S. Effects of temperature and water content on the secondary structure of wheat gluten studied by FTIR spectroscopy. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panick, G.; Malessa, R.; Winter, R. Differences between the pressure-and temperature-induced denaturation and aggregation of β-lactoglobulin A, B, and AB monitored by FT-IR spectroscopy and small-angle X-ray scattering. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 6512–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belloque, J.; Smith, G.M. Thermal denaturation of β-lactoglobulin. A 1H NMR study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hardin, C.C.; Foegeding, E.A. NMR studies of thermal denaturation and cation-mediated aggregation of β-lactoglobulin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 2411–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, H.; Ragona, L.; Varani, L.; Musco, G.; Consonni, R.; Zetta, L.; Monaco, H.L. Partially folded structure of monomeric bovine β-lactoglobulin. FEBS Lett. 1996, 381, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavanagh, G.M.; Clark, A.H.; Ross-Murphy, S.B. Heat-induced gelation of globular proteins: Part 3. Molecular studies on low pH β-lactoglobulin gels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2000, 28, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, H.; Vorwerg, W.; Schmid, M. Synthesis of hydrophobic whey protein isolate by acylation with fatty acids. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 62, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lent, L.; Vanasupa, L.; Tong, P. Whey protein edible film structures determined by atomic force microscope. J. Food Sci. 1998, 63, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, M.; Le, T.; Ouattara, B.; Yu, H.; Letendre, M.; Sabato, S.; Mateescu, M.; Patterson, G. Use of γ-irradiation to produce films from whey, casein and soya proteins: Structure and functionals characteristics. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2002, 63, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, M.; Ikura, T.; Semisotnov, G.V.; Kihara, H.; Amemiya, Y.; Kuwajima, K. Kinetic refolding of β-lactoglobulin. Studies by synchrotron X-ray scattering, and circular dichroism, absorption and fluorescence spectroscopy. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 275, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, L. New evidences of glass transitions and microstructures of soy protein plasticized with glycerol. Macromol. Biosci. 2005, 5, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, N.H.; Miles, M.J.; Popineau, Y.; Harries, J.; Shewry, P.; Tatham, A.S. Small angle X-ray scattering of wheat seed-storage proteins: α-, γ- and ω-gliadins and the high molecular weight (HMW) subunits of glutenin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1999, 1430, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuktaite, R.; Plivelic, T.S.; Cerenius, Y.; Hedenqvist, M.S.; Gällstedt, M.; Marttila, S.; Ignell, R.; Popineau, Y.; Tranquet, O.; Shewry, P.R. Structure and morphology of wheat gluten films: From polymeric protein aggregates toward superstructure arrangements. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1438–1448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Rodler, N.; Miesbauer, O.; Rojahn, M.; Vogel, T.; Dörfler, R.; Kucukpinar, E.; Langowski, H.-C. Adhesion and barrier performance of novel barrier adhesives used in multilayered high-barrier laminates. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 2405–2436. [Google Scholar]
- Cluff, E.; Gladding, E.; Pariser, R. A new method for measuring the degree of crosslinking in elastomers. J. Polym. Sci. 1960, 45, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigi, A.; Cojazzi, G.; Panzavolta, S.; Roveri, N.; Rubini, K. Stabilization of gelatin films by crosslinking with genipin. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4827–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Hsieh, F.-H. Protein–protein interactions during high-moisture extrusion for fibrous meat analogues and comparison of protein solubility methods using different solvent systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 2681–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhim, J.W.; Gennadios, A.; Handa, A.; Weller, C.L.; Hanna, M.A. Solubility, tensile, and color properties of modified soy protein isolate films. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 4937–4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.S.; Hsieh, F.-H. Protein-protein interactions in high moisture-extruded meat analogs and heat-induced soy protein gels. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2007, 84, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lee, T.-C. Effect of extrusion temperature on solubility and molecular weight distribution of wheat flour proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compton, S.J.; Jones, C.G. Mechanism of dye response and interference in the Bradford protein assay. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 151, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floris, R.; Bodnar, I.; Weinbreck, F.; Alting, A.C. Dynamic rearrangement of disulfide bridges influences solubility of whey protein coatings. Int. Dairy J. 2008, 18, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hammann, F.; Schmid, M. Determination and Quantification of Molecular Interactions in Protein Films: A Review. Materials 2014, 7, 7975-7996. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7127975
Hammann F, Schmid M. Determination and Quantification of Molecular Interactions in Protein Films: A Review. Materials. 2014; 7(12):7975-7996. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7127975
Chicago/Turabian StyleHammann, Felicia, and Markus Schmid. 2014. "Determination and Quantification of Molecular Interactions in Protein Films: A Review" Materials 7, no. 12: 7975-7996. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7127975
APA StyleHammann, F., & Schmid, M. (2014). Determination and Quantification of Molecular Interactions in Protein Films: A Review. Materials, 7(12), 7975-7996. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7127975