Wood Sawdust/Natural Rubber Ecocomposites Cross-Linked by Electron Beam Irradiation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Experimental Installation and Sample Irradiation
2.4. Laboratory Tests
2.4.1. Mechanical Characteristics
2.4.2. Rubber-Filler Interactions
2.4.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.4.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical and Mechanical Characteristics
3.2. Gel Fraction and Crosslink Density of the Blends
3.3. The Water Uptake
3.4. Rubber-Fiber Interactions
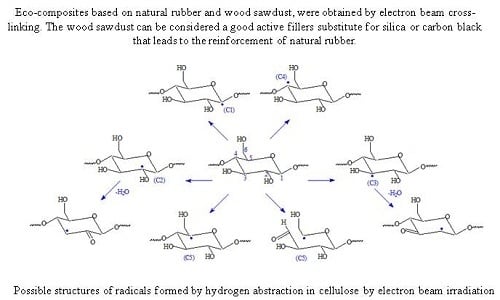
3.5. The Effect of Electron Beam Radiation on NR/Wood Sawdust Composites
3.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manaila, E.; Craciun, G.; Stelescu, M.D.; Ighigeanu, D.; Ficai, M. Radiation vulcanization of natural rubber with polyfunctional monomers. Polym. Bull. 2014, 71, 57–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelescu, M.D. Characteristics of silicone rubber blends. Leather Footwear J. 2010, 10, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Stelescu, M.D.; Manaila, E.; Craciun, G. Vulcanization of ethylene-propylene–terpolymer-based rubber mixtures by radiation processing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 128, 2325–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, L.; Rodriguez, A.; Marcos-Fernandez, A.; Chamorro, C. A new interpretation of the crosslinking mechanism of NR with dicumyl peroxide. Kautsch. Gummi Kunstst. 1998, 51, 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, L.; Rodriguez, A.; Valentin, J.L.; Marcos-Fernandez, A.; Posadas, P. Conventional and efficient crosslinking of natural rubber: Effect of heterogeneities on the physical properties. Kautsch. Gummi Kunstst. 2005, 58, 638–643. [Google Scholar]
- Ikarashi, Y.; Toyoda, K.; Ohasawa, N.; Uchima, T.; Tsuchiya, T.; Kaniwa, M.A.; Sato, M.; Takahashi, M.; Nakamura, A. Comparative studies by cell culture and in vivo implantation test on the toxicity of natural rubber latex materials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1992, 26, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dluzneski, P.R. Peroxide vulcanization of elastomers. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2001, 74, 451–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez Grima, M.M. Novel Co-agents for Improved Properties in Peroxide Cure of Saturated Elastomers. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Stelescu, M.D.; Manaila, E.; Craciun, G.; Zuga, N. Crosslinking and grafting ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer with accelerated electrons in the presence of polyfunctional monomers. Polym. Bull. 2012, 68, 263–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelescu, M.D.; Manaila, E.; Craciun, G.; Dumitrascu, M. New green polymeric composites based on Hemp and Natural Rubber Processed by Electron Beam Irradiation. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans: Silica, Some Silicates, Coal Dust and Para-Aramid Fibrils; World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, World Health Organization: Lyon, France, 1997; Volume 68, Available online: http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Monographs/vol68/index.php (accessed on 18 September 2014).
- Beliczky, L.S.; Fajen, J. Rubber industry. In Encyclopaedia of Occupational Health and Safety, 4th ed.; Stellman, J.M., Ed.; International Labor Office: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998; Volume 80, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Manaila, E.; Stelescu, M.D.; Doroftei, F. Polymeric composites based on natural rubber and hemp fibers. Iran. Polym. J. 2015, 24, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristaldi, G.; Latteri, A.; Recca, G.; Cicala, G. Composites Based on Natural Fibre Fabrics. In Woven Fabric Engineering; Dubrovski, P.D., Ed.; Sciyo: Rijeka, Croatia, 2010; pp. 318–342. Available online: http://www.intechopen.com (accessed on 2 June 2014).
- Begum, K.; Islam, M.A. Natural fiber as a substitute to synthetic fiber in Polymer Composites: A Review. Res. J. Eng. Sci. 2013, 2, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Nora’asheera, M.N. Composites From Polypropylene (PP) Reinforced With Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunch (OPEFB) Fibre. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Malaysia Pahang, Pahang, Malaysia, May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fakhrul, T.; Mahbub, R.; Islam, M.A. Properties of wood sawdust and wheat Flour Reinforced Polypropylene Composites. J. Mod. Sci. Technol. 2013, 1, 135–148. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.Y.; Feng, X.Q.; Lauke, B.; Mai, Y.W. Effects of particle size, particle/matrix interface adhesion and particle loading on mechanical properties of particulate–polymer composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2008, 39, 933–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmarkar, A.; Chauhan, S.S.; Modak, J.M.; Chanda, M. Mechanical properties of wood–fiber reinforced polypropylene composites: Effect of a novel compatibilizer with isocyanate functional group. Compos. Part A Appl. S 2007, 38, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.R.; Hasan, M.; Huque, M.M.; Islam, M.N. Physico-Mechanical Properties of Jute Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene Composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2010, 29, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.R.; Islam, M.N.; Huque, M.M. Influence of fiber treatment on the mechanical and Morphological Properties of Sawdust Reinforced Polypropylene Composites. J. Polym. Environ. 2010, 18, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleland, M.R. Industrial Applications of Electron Accelerators—Ion Beam Applications. In Presented at the CERN Accelerator School/Small Accelerator Course, Zeegse, The Netherlands, 24 May–2 June 2005; Available online: http://cas.web.cern.ch/cas/Holland/PDF-lectures/Cleland/School-2.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2016).
- Arroyo, M.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A.; Herrero, B. Organo-montmorillonite as substitute of carbon black in natural rubber compounds. Polymer 2003, 44, 2447–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenal, J.M.; Chazeau, L.; Guy, L.; Bomal, Y.; Gauthier, C. Molecular weight between physical entanglements in natural rubber: A critical parameter during strain-induced crystallization. Polymer 2007, 48, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, G. Swelling of filler-reinforced vulcanizates. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1963, 7, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, L.; Ulahannan, J.; Joseph, R. Effect of curing temperature, fibre loading and bonding agent on the equilibrium swelling of isora-natural rubber composites. Compos. Interface 2006, 13, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Liu, M.; Jia, D.; Zhou, Y. Synthesis of natural rubber-g-maleic anhydride and its use as a compatibilizer in natural rubber/short nylon fiber composites. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2013, 31, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Nizami, S.S.; Raza, N.Z.; Mahmood, K. Effect of micro-sized marble sludge on physical properties of natural rubber composites. Chem. Ind. Chem. Eng. Q. 2013, 19, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, H.; Shuhelmy, S.; Edgham, M.R. The effect of a silane coupling agent on curing characteristics and mechanical properties of bamboo fibre filled NR composites. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohls, D.J.; Beauage, G. Rational design of reinforced rubber. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2002, 6, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Nizami, S.S.; Riza, N.Z. Reinforcement of natural rubber hybrid composites based on marble sludge/Silica and marble sludge/rice husk derived silica. J. Adv. Res. 2014, 5, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, K. Hybrid composites prepared from Industrial waste: Mechanical and swelling behavior. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukle, S.; Gravitis, J.; Putnina, A.; Stikute, A. The effect of steam explosion treatment on technical hemp fibres. In Proceedings of the 8th International Scientific and Practical Conference, Rezekne, Latvia, 20–22 June 2011; Volume 1, pp. 230–237.
- Zhao, J.; Ghebremeskel, G.N. A review of some of the factors affecting fracture and fatigue in SBR and BR vulcanizates. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2001, 74, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaught, A.D. Nomenclature of Carbohydrates (Recommendations 1996); The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 1996; Volume 68. [Google Scholar]
- Desmet, G. Functionalization of Cotton-Cellulose via High Energy Irradiation Initiated Grafting and Cyclodextrin Immobilization. Master’s Thesis, Department of Textiles, Faculty of Engineering University of Ghent, Ghent, Belgium, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rees, D.A. Outline Studies in Biology—Polysaccharide Shapes; Chapman and Hall Ltd.: London, UK, 1977; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Harmsen, P.F.H.; Huijgen, W.J.J.; Bermudez Lopez, L.M.; Bakker, R.R.C. Literature Review of Physical and Chemical Pretreatment Processes for Lignocellulosic Biomass. In Food and Biobased Reasearch, Wageningen UR, Biosynergy; Energy Research Centre of the Netherlands—ECN-E: Petten, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Henricson, K. Wood structure and fibers. In Educational Material during the Course “An Introduction to Chemical Pulping Technology”; Lappeenranta of Technology, Elenia Oy ja Ensto Finland Oy: Lappeenranta, Finland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.O.; Choi, H.Y. Morphology and surface properties of natural fiber treated with electron beam. In Microscopy: Science, Technology, Applications and Education; Méndez-Vilas, A., Díaz, J., Eds.; FORMATEX Research Center: Extremadura, Spain, 2010; pp. 1880–1887. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd Edeerozev, A.M.; Akil, H.M.; Azhar, A.B.; Zainal Ariffin, M.I. Chemical modification of kenaf fibers. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 2023–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, M.; Francis, B.; Varughese, K.T.; Thomas, S. The effects of silane coupling agents on the viscoelastic properties of rubber biocomposites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2006, 291, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.G.; Choi, S.S.; Park, W.H.; Cho, D. Characterization of surface modified flax fibers and their biocomposites with PHB. Macromol. Symp. 2003, 197, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgacem, M.N.; Bataille, P.; Sapieha, S. Effect of corona modification on the mechanical properties of polypropylene/cellulose composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1994, 53, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henniges, U.; Hasani, M.; Potthast, A.; Westman, G.; Rosenau, T. Electron beam irradiation of cellulosic Materials—Opportunities and Limitations. Materials 2013, 6, 1584–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, J.; Methot, M.; Jordan, B. The effects of ionizing radiation on the cellulose of wood-free paper. Cellulose 2006, 13, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wencka, M.; Wichlacz, K.; Kasprzyk, H.; Lijewski, S.; Hoffmann, S.K. Free radicals and their electron spin relaxation in cellobiose. X-band and W-band ESR and electron spin echo studies. Cellulose 2007, 14, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wach, R.A.; Mitomo, H.; Yoshii, F. ESR investigation on gamma-irradiated methylcellulose and hydroxyethylcellulose in dry state and in aqueous solution. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2004, 261, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, A.; Bertini, S.; Gastaldi, G.; Iannaccone, N.; Macciantelli, D.; Torri, G.; Vismara, E. Electron beam irradiated textile cellulose fibres: ESR studies and derivatisation with glycidyl methacrylate (GMA). Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 1787–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, S.; Chakraborty, R.; Bhattacharya, P. Optimization of biodegradation of natural fiber (Chorchorus capsularis): HDPE composite using response surface methodology. Iran. Polym. J. 2013, 22, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Idrus, M.A.M.; Hamdan, S.; Rahman, M.R.; Islam, M.S. Treated tropical wood sawdust-Polypropylene Polymer Composite: Mechanical and Morphological Study. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 2, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, P.; Gao, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhang, L. Nanocomposites of poly (lactic acid) reinforced with cellulose nanofibrils. BioResources 2010, 5, 1811–1823. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.; Cao, J.; Wang, X. Investigation of the interfacial compatibility of PEG and thermally modified wood flour/polypropylene composites using the stress relaxation approach. BioResurces 2013, 8, 2064–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Cao, J.; Wang, X. Properties of PEG/thermally modified wood flour/polypropylene (PP) composites. For. Stud. China 2012, 14, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, K.A.; Bhardwaj, Y.K.; Chaudhari, C.V.; Kumar, V.; Goel, N.K.; Sabharwal, S. Radiation processed ethylene vinyl acetate-multiple walled carbon nanotube nano-composites: Effect of MWNT addition on the gel content and crosslinking density. eXPRESS Polym. Lett. 2009, 3, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlesby, A.; Pinner, S.H. Analysis of the solubility behaviour of irradiated polyethylene and other polymers. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1959, 249, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifa, J.; Yunus, W.M.Z.W.; Dahlan, K.Z.H.M.; Ahmad, M.H. Preparation and properties of radiation crosslinked natural rubber/clay nanocomposites. Polym. Test. 2005, 24, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagorski, Z.P. EB-crosslinking of elastomers, how does it compare withb radiation crosslinking of other polymers? Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2004, 71, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, M.J.; Anandjiwala, R.D.; Thomas, S. Chapter 10: Lignocellulosic fiber reinforced rubber composites. In Natural Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites: From Macro to Nanoscale; Jacob, M., Thomas, S., Eds.; Old City Publishing, Inc.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2009; pp. 255–258. [Google Scholar]
- Dumitrescu, L.; Matei, A.; Manciulea, I. Composites acrylic copolymers-wood waste. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference Advanced Composite Materials Engineering (COMAT 2012), Brasov, Romania, 18–20 October 2012; pp. 597–600.
- Ali, A.M.M.; Subban, R.H.Y.; Bahron, H.; Winie, T.; Latif, F.; Yahya, M.Z.A. Grafted natural rubber based polymer electrolytes: ATR-FTIR and conductivity studies. Ionics 2008, 14, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Rahaman, M.S.; Al-Jubayer, A.; Islam, J.M.M. Modification of jute fibers by radiation-induced graft copolymerization and their applications. In Cellulose-Based Graft Copolymers: Structure and Chemistry; Thakur, V.K., Ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2015; pp. 209–235. [Google Scholar]
- Bodirlau, R.; Teaca, C.A. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and thermal analysis of lignocellulose fillers treated with organic anhydrides. Rom. J. Phys. 2009, 54, 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.Y.; Marchessault, R.H. Infrared spectra of crystalline polysaccharides. I. Hydrogen bonds in native celluloses. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. 1959, 37, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, A.L.; Ismail, H. Tensile properties, water uptake and thermal properties of polypropylene/waste pulverized tire/kenaf (PP/WPT/KNF) composites. BioResources 2013, 8, 806–817. [Google Scholar]
- Ciolacu, D.; Ciolacu, F.; Popa, V.I. Amorphous cellulose-structure and characterization. Cell. Chem. Technol. 2011, 45, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Bodîrlău, R.; Teacă, C.A.; Spiridon, I. Preparation and characterization of composites comprising modified hardwood and wood polymers/poly(vinyl chloride). BioResources 2009, 4, 1285–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Stuart, B. Infrared Spectroscopy: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Sydney, Australia, 2004; pp. 72–74. [Google Scholar]
- Nallasamy, P.; Mohan, S. Vibrational spectra of cis-1,4-polyisoprene. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2004, 29, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Premalal, H.G.B.; Ismail, H.; Baharin, A. Comparison of the mechanical properties of rice husk powder filled polypropylene composites with talc filled polypropylene composites. Polym. Test 2002, 21, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]























| Amount of Wood Sawdust (phr) | Vrf | Vro/Vrf |
|---|---|---|
| 75 kGy | ||
| 10 | 0.0542 | 0.6602 |
| 20 | 0.0579 | 0.6182 |
| 150 kGy | ||
| 10 | 0.0823 | 0.9924 |
| 20 | 0.0920 | 0.8875 |
| 300 kGy | ||
| 10 | 0.1364 | 0.7164 |
| 20 | 0.1402 | 0.6968 |
| 600 kGy | ||
| 10 | 0.1736 | 1.0388 |
| 20 | 0.1778 | 1.0141 |
| Wood Sawdust (phr) | p0/q0 |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0.2054 |
| 10 | 0.2305 |
| 20 | 0.1963 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manaila, E.; Stelescu, M.D.; Craciun, G.; Ighigeanu, D. Wood Sawdust/Natural Rubber Ecocomposites Cross-Linked by Electron Beam Irradiation. Materials 2016, 9, 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9070503
Manaila E, Stelescu MD, Craciun G, Ighigeanu D. Wood Sawdust/Natural Rubber Ecocomposites Cross-Linked by Electron Beam Irradiation. Materials. 2016; 9(7):503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9070503
Chicago/Turabian StyleManaila, Elena, Maria Daniela Stelescu, Gabriela Craciun, and Daniel Ighigeanu. 2016. "Wood Sawdust/Natural Rubber Ecocomposites Cross-Linked by Electron Beam Irradiation" Materials 9, no. 7: 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9070503
APA StyleManaila, E., Stelescu, M. D., Craciun, G., & Ighigeanu, D. (2016). Wood Sawdust/Natural Rubber Ecocomposites Cross-Linked by Electron Beam Irradiation. Materials, 9(7), 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9070503