Identification of Specific Hydroxyapatite {001} Binding Heptapeptide by Phage Display and Its Nucleation Effect
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
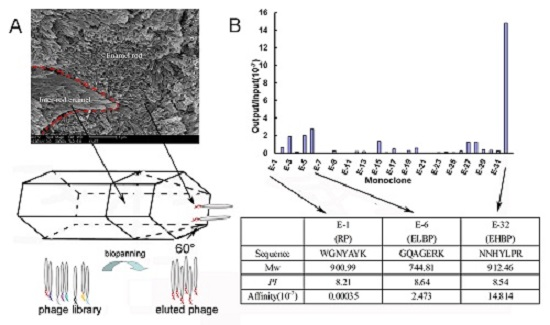
2.1. Identification of Enamel Binding Peptides
2.2. Binding Specificity of EHBP to Enamel Surface
2.3. Characterization of the Deposits of in Vitro Mineralization
2.4. Kinetic Study of in Vitro Induced Mineralization
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ehrlich, H. Biocomposites and mineralized tissues. In Biological Materials of Marine Origin; Gorb, S.N., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 91–210. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, F.A.; Müller, L.; Caillard, D.; Conforto, E. Preferred growth orientation of biomimetic apatite crystals. J. Cryst. Growth 2007, 304, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, P.; Wilcock, C.J.; Miller, C.A.; Moorehead, R.; Hatton, P.V. Process optimisation to control the physico-chemical characteristics of biomimetic nanoscale hydroxyapatites prepared using wet chemical precipitation. Materials 2015, 8, 2297–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capanema, N.S.; Mansur, A.A.; Carvalho, S.M.; Silva, A.R.; Ciminelli, V.S.; Mansur, H.S. Niobium-doped hydroxyapatite bioceramics: Synthesis, characterization and in vitro cytocompatibility. Materials 2015, 8, 4191–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakasam, M.; Locs, J.; Salma-Ancane, K.; Loca, D.; Largeteau, A.; Berzina-Cimdina, L. Fabrication, properties and applications of dense hydroxyapatite: A review. J. Funct. Biomater. 2015, 6, 1099–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyde, A. Microstructure of enamel. In Dental Enamel (Ciba Foundation Symposium 205); Chadwick, D.J., Cardew, G., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 18–31. [Google Scholar]
- O’Yang, J.; Liao, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Jalkanen, J.; Lajoie, G.; Karttunen, M.; Goldberg, H.A.; Hunter, G.K. Matrix gla protein inhibits ectopic calcification by a direct interaction with hydroxyapatite crystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 18406–18412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, W.; Sahai, N. A potential mechanism for amino acid-controlled crystal growth of hydroxyapatite. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 9157–9167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Zhang, H.; Yin, J.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Yao, F. Hydroxyapatite crystal formation in the presence of polysaccharide. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiba, K.; Motozuka, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ogawa, N.; Otsuka, Y.; Ohnuma, K.; Kataoka, T.; Tagaya, M. Effect of cationic surfactant micelles on hydroxyapatite nanocrystal formation: An investigation into the inorganic–organic interfacial interactions. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 1463–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, K.I.; Park, S.P.; Lee, J.H.; Jung, H.S. Aspartic acid-assisted synthesis of multifunctional strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite microspheres. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Cölfen, H. On the biophysical regulation of mineral growth: Standing out from the crowd. J. Struct. Biol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navrotsky, A. Energetic cues to pathways to biomineralization: Precursors, clusters, and nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 12096–12101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdemir, D.; Lee, A.Y.; Myerson, A.S. Nucleation of crystals from solution: Classical and two-step model. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onuma, K.; Atsue, I. Cluster growth model for hydroxyapatie. Chem. Mater. 1998, 10, 3346–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nudelman, F.; Pieterse, K.; George, A.; Bomans, P.H.H.; Friedrich, H.; Brylka, L.J.; Hilbers, P.A.J.; de With, G.; Sommerdijk, N.A.J.M. The role of prenucelation clusters in surface-induced calcium phosphate crystallization. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 1010–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Cölfen, H.; Yu, S.-H. Biomimetic mineralization/synthesis of mesoscale order in hybrid inorganic–organic materials via nanoparticle self-assembly. MRS Bull. 2005, 30, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.-Q.; Hoheisel, T.N.; Sai, H.; Li, Z.; Carloni, J.D.; Wang, S.; Youngman, R.E.; Baker, S.P.; Gruner, S.M.; Wiesner, U.; et al. Formation of periodically-ordered calcium phosphate nanostructures by block copolymer-directed self-assembly. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Dahl, T.; Veis, A.; George, A. Nucleation of apatite crystals in vitro by self-assembled dentin matrix protein 1. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gower, L.B. Biomimetic model systems for investigating the amorphous precursor pathway and its role in biomineralization. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 4551–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassett, D.C.; Marelli, B.; Nazhat, S.N.; Barralet, J.E. Stabilization of amorphous calcium carbonate with nanofibrillar biopolymers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 3460–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Azaïs, T.; Robin, M.; Vallée, A.; Catania, C.; Legriel, P.; Pehau-Arnaudet, G.; Babonneau, F.; Giraud-Guille, M.; Nassif, N. The predominant role of collagen in the nucleation, growth, structure and orientation of bone apatite. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, H.; Hanke, T.; Born, R.; Fischer, C.; Frolov, A.; Langrock, T.; Hoffmann, R.; Schwarzenbolz, U.; Henle, T.; Simon, P.; et al. Mineralization of biomimetically carboxymethylated collagen fibrills in a model dual membrane diffusion system. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 326, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, H.; Hanke, T.; Frolov, A.; Langrock, T.; Hoffmann, R.; Fischer, C.; Schwarzenbolz, U.; Henle, T.; Born, R.; Worch, H. Modification of collagen in vitro with respect to N-Carboxymethyllysine. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2009, 44, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, H.; Hanke, T.; Simon, P.; Born, R.; Fischer, C.; Frolov, A.; Langrock, T.; Hoffmann, R.; Schwarzenbolz, U.; Henle, T.; et al. Carboxymethylation of collagen with respect to Ca-phosphate phases formation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Mater. 2010, 92, 542–551. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, C.; Arribart, H.; Guille, M.M.G. Biomimetism and bioinspiration as tools for the design of innovative materials and systems. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, H. Chitin and collagen as universal and alternative templates in biomineralization. Int. Geol. Rev. 2010, 52, 661–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiourvas, D.; Tsetsekou, A.; Kammenou, M.I.; Boukos, N. Biomimetic synthesis of ribbon-like hydroxyapatite employing poly (l-arginine). Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 58, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarikaya, M.; Tamerler, C.; Jen, A.K.; Schulten, K.; Baneyx, F. Molecular biomimetics: Nanotechnology through biology. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamerler, C.; Duman, M.; Oren, E.E.; Gungormus, M.; Xiong, X.; Kacar, T.; Parviz, B.A.; Sarikaya, M. Materials specificity and directed assembly of a gold-binding peptide. Small 2006, 2, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, C.R.; Tamerler, C.; Sarikaya, M. Adsorption, diffusion, and self-assembly of an engineered gold-binding peptide on Au(111) investigated by atomic force microscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2009, 48, 5174–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Liu, Y.; Wei, W.; Mao, J. GEPIs-HA hybrid: A novel biomaterial for tooth repair. Med. Hypotheses 2008, 71, 591–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, G.R.; Wuthier, R.E. Fourier transform infrared characterization of mineral phases formed during induction of mineralization by collagenase-released matrix vesicles in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 13718–13724. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.L.; Rosi, N.L. Peptide-based methods for the preparation of nanostructured inorganic materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2010, 49, 1924–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gungormus, M.; Fong, H.; Kim, W.; Evans, J.S.; Tamerler, C.; Sarikaya, M. Regulation of in vitro Calcium Phosphate Mineralization by Combinatorially Selected Hydroxyapatite-Binding Peptides. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gungormus, M.; Branco, M.; Fong, H.; Schneider, J.P.; Tamerler, C.; Sarikaya, M. Self assembled bi-functional peptide hydrogels with biomineralization-directing peptides. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 7266–7274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, M.D.; Stanley, S.K.; Amis, E.J.; Becker, M.L. Identification of a highly specific hydroxyapatite-binding peptide using phage display. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 1830–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segvich, S.J.; Smith, H.C.; Kohn, D.H. The adsorption of preferential binding peptides to apatite-based materials. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Buchko, G.W.; Shaw, W.J.; De Yoreo, J.J.; Tarasevich, B.J. Sequence-defined energetic shifts control the disassembly kinetics and microstructure of amelogenin adsorbed onto hydroxyapatite (100). Langmuir 2015, 31, 10451–10460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addadi, L.; Weiner, S. Interactions between acidic proteins and crystals: Stereochemical requirements in biomineralization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 4110–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradian-Oldak, J. Amelogenins: Assembly, processing and control of crystal morphology. Matrix Biol. 2001, 20, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grohe, B.; O’Young, J.; Ionescu, D.A.; Lajoie, G.; Rogers, K.A.; Karttunen, M.; Goldberg, H.A.; Hunter, G.K. Control of calcium oxalate crystal growth by face-specific adsorption of an osteopontin phosphopeptide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 14946–14951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, F.Z.; Ge, J. New observations of the hierarchical structure of human enamel, from nanoscale to microscale. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2007, 1, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Tao, J.; Yu, X.; Fu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, X.; Xu, G.; Tang, R. Anisotropic demineralization and oriented assembly of hydroxyapatite crystals in enamel: Smart structures of biominerals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 7162–7165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Mao, J.; Zhou, B.; Wei, W.; Gong, S. Peptide aptamers against titanium-based implants identified through phage display. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartgerink, J.D.; Beniash, E.; Stupp, S.I. Self-assembly and mineralization of peptide-amphiphile nanofibers. Science 2001, 294, 1684–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutsopoulos, S. Synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite crystals: A review study on the analytical methods. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 62, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, N.P.; West, P.; Torzilli, P.A.; Mendelsohn, R. FTIR microscopic imaging of collagen and proteoglycan in bovine cartilage. Biopolymers 2001, 62, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daculsi, G.; Kerebel, B. High-resolution electron microscope study of human enamel crystallites: Size, shape, and growth. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1978, 65, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamid, J.; Sharir, A.; Addadi, L.; Weiner, S. Amorphous calcium phosphate is a major component of the forming fin bones of zebrafish: Indications for an amorphous precursor phase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12748–12753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beniash, E.; Metzler, R.A.; Lam, R.S.; Gilbert, P.U. Transient amorphous calcium phosphate in forming enamel. J. Struct. Biol. 2009, 166, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisawa, R.; Wada, Y.; Nodasaka, Y.; Kuboki, Y. Acidic amino acid-rich sequences as binding sites of osteonectin to hydroxyapatite crystals. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1292, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iline-Vul, T.; Matlahov, I.; Grinblat, J.; Keinan-Adamsky, K.; Goobes, G. Changes to the disordered phase and apatite crystallite morphology during mineralization by an acidic mineral binding peptide from osteonectin. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 2656–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matlahov, I.; Iline-Vul, T.; Abayev, M.; Lee, E.M.; Nadav-Tsubery, M.; Keinan-Adamsky, K.; Grey, J.J.; Goobes, G. Interfacial mineral–peptide properties of a mineral binding peptide from osteonectin and bone-like apatite. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 5562–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavafoghi Johromi, M.; Yao, G.; Cerruti, M. The importance of amino acid interactions in the crystallization of hydroxyapatite. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20120906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavafoghi Johromi, M.; Cerruti, M. Amino acid/ion aggregate formation and their role in hydroxyapatite precipitation. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, I.S.; Rashid, N.; Hing, K.A. Surface charge and the effect of excess calcium ions on the hydroxyapatite surface. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6818–6826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Xu, Z.; Cui, Q.; Sahai, N. Predicting the structure-activity relationship of hydroxyapatite binding peptides by enhanced-sampling molecular simulation. Langmuir 2016, 32, 7009–7022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarbrough, D.K.; Hagerman, E.; Eckert, R.; He, J.; Choi, H.; Cao, N.; Le, K.; Hedger, J.; Qi, F.; Anderson, M.; et al. Specific binding and mineralization of calcified surfaces by small peptides. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2010, 86, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, J.; Shi, X.; Wu, Y.-B.; Gong, S.-Q. Identification of Specific Hydroxyapatite {001} Binding Heptapeptide by Phage Display and Its Nucleation Effect. Materials 2016, 9, 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9080700
Mao J, Shi X, Wu Y-B, Gong S-Q. Identification of Specific Hydroxyapatite {001} Binding Heptapeptide by Phage Display and Its Nucleation Effect. Materials. 2016; 9(8):700. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9080700
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Jing, Xin Shi, Ya-Bo Wu, and Shi-Qiang Gong. 2016. "Identification of Specific Hydroxyapatite {001} Binding Heptapeptide by Phage Display and Its Nucleation Effect" Materials 9, no. 8: 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9080700
APA StyleMao, J., Shi, X., Wu, Y. -B., & Gong, S. -Q. (2016). Identification of Specific Hydroxyapatite {001} Binding Heptapeptide by Phage Display and Its Nucleation Effect. Materials, 9(8), 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9080700