Intermolecular RNA Recombination Occurs at Different Frequencies in Alternate Forms of Brome Mosaic Virus RNA Replication Compartments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Yeast Methods
2.2. Plasmids
2.3. Plasmid Construction
2.4. Induction of Transcription and Screening for Ura+ Cells
2.5. Identification of Intermolecular RNA Recombinants by Northern Blotting
2.6. Expected Intermolecular RNA Recombination Frequency
2.7. RNA Recombination after One Yeast Generation
2.8. Cell Fractionation
2.9. RT-PCR Cloning and Sequencing of Intermolecular RNA Recombinants
2.10. Electron Microscopy
2.11. Western Blotting
3. Results
3.1. The RNA3 Recruitment Element Is Not a Preferred Recombination Site
3.2. RNA3 Recruitment into Replication Compartments Through a Transposed Recruitment Element
3.3. Intramolecular RNA Recombination Occurs at High Frequency
3.4. Recruitment into Replication Compartments Is Necessary for Intermolecular RNA Recombination
3.5. Regulating the Levels of Proteins 1a and 2apol Modulates the Type of Replication Compartments
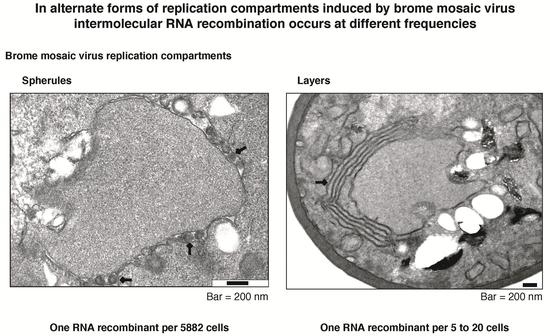
3.6. Intermolecular RNA Recombination Occurs at Higher Frequency in Layers Than in Spherules
3.7. The Template Recruitment Element Is Required for Intermolecular RNA Recombination in Layers
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kushner, D.B.; Lindenbach, B.D.; Grdzelishvili, V.Z.; Noueiry, A.O.; Paul, S.M.; Ahlquist, P. Systematic, genome-wide identification of host genes affecting replication of a positive-strand RNA virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15764–15769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panavas, T.; Serviene, E.; Brasher, J.; Nagy, P.D. Yeast genome-wide screen reveals dissimilar sets of host genes affecting replication of RNA viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 7326–7331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, C.; Prasanth, K.R.; Nagy, P.D. The glycolytic pyruvate kinase is recruited directly into the viral replicase complex to generate ATP for RNA synthesis. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 639–652.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.B.; Jovel, J.; Udomporn, P.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, W.X.; Gasciolli, V.; Vaucheret, H.; Ding, S.W. The 21-nucleotide, but not 22-nucleotide, viral secondary small interfering RNAs direct potent antiviral defense by two cooperative Argonautes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Ruiz, H.; Carbonell, A.; Hoyer, J.S.; Fahlgren, N.; Gilbert, K.B.; Takeda, A.; Giampetruzzi, A.; Garcia Ruiz, M.T.; McGinn, M.G.; Lowery, N.; et al. Roles and programming of arabidopsis argonaute proteins during turnip mosaic virus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolondam, B.; Rao, P.; Sztuba-Solinska, J.; Weber, P.H.; Dzianott, A.; Johns, M.A.; Bujarski, J.J. Co-infection with two strains of brome mosaic bromovirus reveals common RNA recombination sites in different hosts. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.J.; Rao, A.L. Emergence of distinct brome mosaic virus recombinants is determined by the polarity of the inoculum RNA. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5204–5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sztuba-Solinska, J.; Urbanowicz, A.; Figlerowicz, M.; Bujarski, J.J. RNA-RNA recombination in plant virus replication and evolution. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2010, 49, 415–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sztuba-Solinska, J.; Dzianott, A.; Bujarski, J.J. Recombination of 5′ subgenomic RNA3a with genomic RNA3 of brome mosaic bromovirus in vitro and in vivo. Virology 2011, 410, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Ruiz, H.; Ahlquist, P. Inducible yeast system for viral RNA recombination reveals requirement for an rna replication signal on both parental RNAs. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 8316–8328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, A.L.; Cheng Kao, C. The brome mosaic virus 3′ untranslated sequence regulates RNA replication, recombination, and virion assembly. Virus Res. 2015, 206, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaag, H.M.; Nagy, P.D. Silencing of Nicotiana Benthamiana Xrn4p exoribonuclease promotes tombusvirus RNA accumulation and recombination. Virology 2009, 386, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.P.; Serviene, E.; Nagy, P.D. Suppression of viral RNA recombination by a host exoribonuclease. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 2631–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wierzchoslawski, R.; Dzianott, A.; Kunimalayan, S.; Bujarski, J.J. A transcriptionally active subgenomic promoter supports homologous crossovers in a plus-strand RNA virus. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 6769–6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzianott, A.; Sztuba-Solinska, J.; Bujarski, J.J. Mutations in the antiviral RNAi defense pathway modify Brome Mosaic Virus RNA recombinant profiles. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2012, 25, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaag, H.M.; Lu, Q.; Schmitt, M.E.; Nagy, P.D. Role of RNase MRP in viral RNA degradation and RNA recombination. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serviene, E.; Shapka, N.; Cheng, C.P.; Panavas, T.; Phuangrat, B.; Baker, J.; Nagy, P.D. Genome-wide screen identifies host genes affecting viral RNA recombination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10545–10550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, P.D. The roles of host factors in tombusvirus RNA recombination. Adv. Virus Res. 2011, 81, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagy, P.D.; Zhang, C.; Simon, A.E. Dissecting RNA recombination in vitro: Role of RNA sequences and the viral replicase. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 2392–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, A.; Zhang, J.; Ollwerther, A.; Wang, X.; Ahlquist, P. Host ESCRT proteins are required for bromovirus RNA replication compartment assembly and function. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalev, N.; de Castro Martin, I.F.; Pogany, J.; Barajas, D.; Pathak, K.; Risco, C.; Nagy, P.D. Role of viral RNA and co-opted cellular ESCRT-I and ESCRT-III factors in formation of tombusvirus spherules harboring the tombusvirus replicase. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 3611–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertel, K.J.; Benefield, D.; Castano-Diez, D.; Pennington, J.G.; Horswill, M.; den Boon, J.A.; Otegui, M.S.; Ahlquist, P. Cryo-electron tomography reveals novel features of a viral RNA replication compartment. Elife 2017, 6, e25940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Brey, I.; Bartenschlager, R. Membranous replication factories induced by plus-strand RNA viruses. Viruses 2014, 6, 2826–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den Boon, J.A.; Diaz, A.; Ahlquist, P. Cytoplasmic viral replication complexes. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 8, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, R.; Thompson, C.; Ahlquist, P. Regeneration of a functional RNA virus genome by recombination between deletion mutants and requirement for cowpea chlorotic mottle virus 3a and coat genes for systemic infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 1820–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, M.L.; Ahlquist, P. A brome mosaic virus intergenic RNA3 replication signal functions with viral replication protein 1a to dramatically stabilize RNA in vivo. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 2622–2632. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, M.; Chen, J.; Janda, M.; Sullivan, M.; den Boon, J.; Ahlquist, P. A positive-strand RNA virus replication complex parallels form and function of retrovirus capsids. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, M.; Ahlquist, P. RNA-dependent replication, transcription, and persistence of brome mosaic virus RNA replicons in S. Cerevisiae. Cell 1993, 72, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Janda, M.; Krol, M.A.; Ahlquist, P. In vivo DNA expression of functional brome mosaic virus RNA replicons in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 7781–7790. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krol, M.A.; Olson, N.H.; Tate, J.; Johnson, J.E.; Baker, T.S.; Ahlquist, P. RNA-controlled polymorphism in the in vivo assembly of 180-subunit and 120-subunit virions from a single capsid protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 13650–13655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Westler, W.M.; den Boon, J.A.; Wang, X.; Diaz, A.; Steinberg, H.A.; Ahlquist, P. An amphipathic alpha-helix controls multiple roles of brome mosaic virus protein 1a in RNA replication complex assembly and function. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Fuchs, S.; Zhang, J.; Wellford, S.; Schuldiner, M.; Wang, X. An unrecognized function for COPII components in recruiting the viral replication protein BMV 1a to the perinuclear ER. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 3597–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chukkapalli, V.; Nchoutmboube, J.A.; Li, J.; Randall, G.; Belov, G.A.; Wang, X. Positive-strand RNA viruses stimulate host phosphatidylcholine synthesis at viral replication sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1064–E1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, A.; Wang, X.; Ahlquist, P. Membrane-shaping host reticulon proteins play crucial roles in viral RNA replication compartment formation and function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16291–16296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamunusinghe, D.; Seo, J.K.; Rao, A.L. Subcellular localization and rearrangement of endoplasmic reticulum by brome mosaic virus capsid protein. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 2953–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Basu, K.; Mui, J.; Vali, H.; Zheng, H.; Laliberte, J.F. Ultrastructural characterization of turnip mosaic virus-induced cellular rearrangements reveals membrane-bound viral particles accumulating in vacuoles. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 12441–12456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, M.; Chen, J.; Lee, W.M.; Janda, M.; Ahlquist, P. Alternate, virus-induced membrane rearrangements support positive-strand RNA virus genome replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11263–11268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doerflinger, S.Y.; Cortese, M.; Romero-Brey, I.; Menne, Z.; Tubiana, T.; Schenk, C.; White, P.A.; Bartenschlager, R.; Bressanelli, S.; Hansman, G.S.; et al. Membrane alterations induced by nonstructural proteins of human norovirus. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belov, G.A.; Nair, V.; Hansen, B.T.; Hoyt, F.H.; Fischer, E.R.; Ehrenfeld, E. Complex dynamic development of poliovirus membranous replication complexes. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, H.; Fukuda, Y.; Murata, K.; Kimura, A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J. Bacteriol. 1983, 153, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sikorski, R.S.; Hieter, P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Genetics 1989, 122, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, W. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratoty Manual; Cold Sprong Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dye, B.T.; Hao, L.; Ahlquist, P. High-throughput isolation of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae RNA. Biotechniques 2005, 38, 868–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Noueiry, A.; Ahlquist, P. Brome mosaic virus protein 1a recruits viral RNA2 to RNA replication through a 5′ proximal RNA2 signal. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 3207–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Nikolaitchik, O.; Singh, J.; Wright, A.; Bencsics, C.E.; Coffin, J.M.; Ni, N.; Lockett, S.; Pathak, V.K.; Hu, W.S. High efficiency of HIV-1 genomic RNA packaging and heterozygote formation revealed by single virion analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13535–13540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaitchik, O.A.; Dilley, K.A.; Fu, W.; Gorelick, R.J.; Tai, S.H.; Soheilian, F.; Ptak, R.G.; Nagashima, K.; Pathak, V.K.; Hu, W.S. Dimeric RNA recognition regulates HIV-1 genome packaging. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Noueiry, A.; Ahlquist, P. An alternate pathway for recruiting template RNA to the brome mosaic virus RNA replication complex. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 2568–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, M.; Kroner, P.; Ahlquist, P.; Meshi, T. Biological activities of hybrid RNAs generated by 3′-end exchanges between tobacco mosaic and brome mosaic viruses. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 3451–3459. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Kao, C. Factors regulating template switch in vitro by viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerases: Implications for RNA-RNA recombination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4972–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.S.; Temin, H.M. Genetic consequences of packaging two RNA genomes in one retroviral particle: Pseudodiploidy and high rate of genetic recombination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 1556–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon-Loriere, E.; Rossolillo, P.; Negroni, M. RNA structures, genomic organization and selection of recombinant HIV. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaag, H.M.; Pogany, J.; Nagy, P.D. A host Ca2+/Mn2+ ion pump is a factor in the emergence of viral RNA recombinants. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 7, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, T.C.; Kirkegaard, K. The polymerase in its labyrinth: Mechanisms and implications of RNA recombination. Trends Genet. 1991, 7, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, D.; Bienz, K. Recombination of poliovirus RNA proceeds in mixed replication complexes originating from distinct replication start sites. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 10960–10971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia-Ruiz, H.; Diaz, A.; Ahlquist, P. Intermolecular RNA Recombination Occurs at Different Frequencies in Alternate Forms of Brome Mosaic Virus RNA Replication Compartments. Viruses 2018, 10, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10030131
Garcia-Ruiz H, Diaz A, Ahlquist P. Intermolecular RNA Recombination Occurs at Different Frequencies in Alternate Forms of Brome Mosaic Virus RNA Replication Compartments. Viruses. 2018; 10(3):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10030131
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia-Ruiz, Hernan, Arturo Diaz, and Paul Ahlquist. 2018. "Intermolecular RNA Recombination Occurs at Different Frequencies in Alternate Forms of Brome Mosaic Virus RNA Replication Compartments" Viruses 10, no. 3: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10030131
APA StyleGarcia-Ruiz, H., Diaz, A., & Ahlquist, P. (2018). Intermolecular RNA Recombination Occurs at Different Frequencies in Alternate Forms of Brome Mosaic Virus RNA Replication Compartments. Viruses, 10(3), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10030131