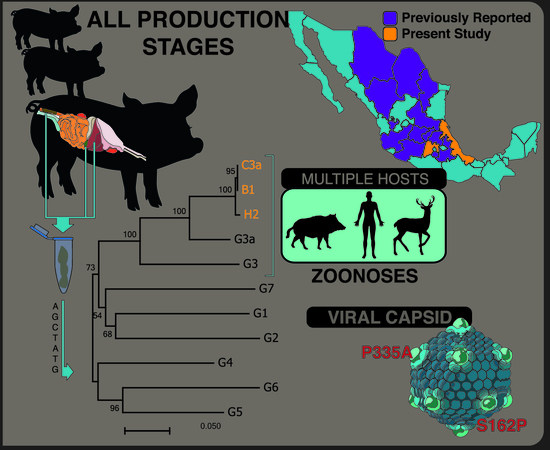
Phylogenetic Analysis and Characterization of the Complete Hepatitis E Virus Genome (Zoonotic Genotype 3) in Swine Samples from Mexico
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Molecular Detection of HEV
2.3. HEV Sequencing
2.4. Computer Sequence Analysis
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Detection of Hepatitis E
3.2. HEV Sequencing
- (i)
- Bile sample B1. We were able to assemble one complete hepatitis E virus genome, denoted MXCDg3a_B1c|_2016 with a coverage of 354.62. This genome is 7241 nucleotides (nt) long, excluding the poli-A tail (12 nt) at the 3’ termini. The genome consisted of 5’ UTR of 27 nt (1–27); three open reading frames—ORF1 of 5120 nt (27–5147), ORF2 of 1979 nt (5185–7164), ORF3 of 365 nt (5147–5512)—and a 3’ UTR of 77 nt (7164–7241), followed by the poli-A tail (Figure 1). This sequence had been deposited at GenBank under accession no. MG833836.
- (ii)
- Liver sample H2 was denoted MXCDg3a_H2cons|_2016; a partial sequence was obtained of 1473 nt covering the 3’ end (5766–7239) with a coverage of 6.30. The GenBank accession number is MH003296.
- (iii)
- Feces sample C3A was identified as MXCDg3a_C3Acons|_2016; a partial sequence of 4777 nt was obtained covering the 3’ end (2464–7241) with a coverage of 18.35; GenBank no. MG980615.
3.3. Complete Genome Characterization
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics Approval
References and Note
- Bouquet, J.; Cherel, P.; Pavio, N. Genetic characterization and codon usage bias of full-length hepatitis e virus sequences shed new lights on genotypic distribution, host restriction and genome evolution. Infect. Genet. Evolut. 2012, 12, 1842–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrendt, P.; Steinmann, E.; Manns, M.P.; Wedemeyer, H. The impact of hepatitis e in the liver transplant setting. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 1418–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Available online: http://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-e (accessed on 3 July 2017).
- Anang, S.; Subramani, C.; Nair, V.P.; Kaul, S.; Kaushik, N.; Sharma, C.; Tiwari, A.; Ranjith-Kumar, C.T.; Surjit, M. Identification of critical residues in hepatitis e virus macro domain involved in its interaction with viral methyltransferase and orf3 proteins. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Mori, Y.; Miyazaki, N.; Cheng, R.H.; Yoshimura, M.; Unno, H.; Shima, R.; Moriishi, K.; Tsukihara, T.; Li, T.C.; et al. Biological and immunological characteristics of hepatitis e virus-like particles based on the crystal structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12986–12991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guu, T.S.; Liu, Z.; Ye, Q.; Mata, D.A.; Li, K.; Yin, C.; Zhang, J.; Tao, Y.J. Structure of the hepatitis e virus-like particle suggests mechanisms for virus assembly and receptor binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12992–12997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, H. Culture systems for hepatitis e virus. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montpellier, C.; Wychowski, C.; Sayed, I.M.; Meunier, J.C.; Saliou, J.M.; Ankavay, M.; Bull, A.; Pillez, A.; Abravanel, F.; Helle, F.; et al. Hepatitis e virus lifecycle and identification of 3 forms of the orf2 capsid protein. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Ying, D.; Lhomme, S.; Tang, Z.; Walker, C.M.; Xia, N. Origin, antigenicity, and function of a secreted form of orf2 in hepatitis e virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4773–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Behloul, N.; Wen, J.; Zhang, J.; Meng, J. Role of asparagine at position 562 in dimerization and immunogenicity of the hepatitis e virus capsid protein. Infect. Genet. Evolut. 2016, 37, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.; Heller, B.; Capuccino, J.M.; Song, B.; Nimgaonkar, I.; Hrebikova, G.; Contreras, J.E.; Ploss, A. Hepatitis e virus orf3 is a functional ion channel required for release of infectious particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.-C.; Chijiwa, K.; Sera, N.; Ishibashi, T.; Etoh, Y.; Shinohara, Y.; Kurata, Y.; Ishida, M.; Sakamoto, S.; Takeda, N.; et al. Hepatitis e virus transmission from wild boar meat. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1958–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renou, C.; Afonso, A.-M.R.; Pavio, N. Foodborne transmission of hepatitis e virus from raw pork liver sausage, france. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1945–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riveiro-Barciela, M.; Minguez, B.; Girones, R.; Rodriguez-Frias, F.; Quer, J.; Buti, M. Phylogenetic demonstration of hepatitis e infection transmitted by pork meat ingestion. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 49, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, N.; Khan, M.S.U.; Hossain, M.B.; Sazzad, H.M.S.; Rahman, M.Z.; Ahmed, F.; Zeidner, N.S. Serological evidence of hepatitis e virus infection in pigs and jaundice among pig handlers in bangladesh. Zoonoses Public Health 2017, 64, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Wiseman, B.; Elvinger, F.; Guenette, D.; Toth, T.; Engle, R.; Emerson, S.; Purcell, R. Prevalence of antibodies to hepatitis e virus in veterinarians working with swine and in normal blood donors in the united states and other countries. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.T.; Shao, P.L.; Chang, L.Y.; Xia, N.S.; Chen, P.J.; Lu, C.Y.; Huang, L.M. Seroprevalence of hepatitis e virus infection among swine farmers and the general population in rural taiwan. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.J. Hepatitis e virus: Animal reservoirs and zoonotic risk. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, J.A.; Moturi, E.; Spiegel, P.; Schilperoord, M.; Burton, W.; Kassim, N.H.; Mohamed, A.; Ochieng, M.; Nderitu, L.; Navarro-Colorado, C.; et al. Hepatitis e outbreak, dadaab refugee camp, Kenya, 2012. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1010–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisano, M.B.; Lugo, B.C.; Poma, R.; Cristobal, H.A.; Raskovsky, V.; Martinez Wassaf, M.G.; Rajal, V.B.; Re, V.E. Environmental hepatitis e virus detection supported by serological evidence in the northwest of argentina. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 112, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.J.; Cao, N.X.; Xie, R.H.; Ding, C.X.; Chen, E.F.; Zhu, H.P.; Sun, J.M.; Shang, X.P.; Wang, X.X.; Miao, Z.P. Epidemiological investigation of a tap water-mediated hepatitis e virus genotype 4 outbreak in Zhejiang province, China. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 3387–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echevarria, J.M.; Gonzalez, J.E.; Lewis-Ximenez, L.L.; Dos Santos, D.R.; Munne, M.S.; Pinto, M.A.; Pujol, F.H.; Rodriguez-Lay, L.A. Hepatitis e virus infection in latin America: A review. J. Med. Virol. 2013, 85, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Teng, J.L.; Cao, K.Y.; Wernery, U.; Schountz, T.; Chiu, T.H.; Tsang, A.K.; Wong, P.C.; Wong, E.Y.; et al. New hepatitis e virus genotype in bactrian camels, Xinjiang, China, 2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 2219–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Hernandez, M.E.; Cruz-Rivera, M.; Sanchez-Betancourt, J.I.; Rico-Chavez, O.; Vergara-Castaneda, A.; Trujillo, M.E.; Sarmiento-Silva, R.E. Seroprevalence of anti-hepatitis e virus antibodies in domestic pigs in Mexico. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino-Ramos, T.; Martin-Acebes, M.A.; Casal, J.; Saiz, J.C.; Loza-Rubio, E. Prevalence of hepatitis e virus (hev) antibodies in mexican pigs. Food Environ. Virol. 2016, 8, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panduro, A.; Escobedo Melendez, G.; Fierro, N.A.; Ruiz Madrigal, B.; Zepeda-Carrillo, E.A.; Roman, S. [epidemiology of viral hepatitis in Mexico]. Salud Publica de Mexico 2011, 53 (Suppl. 1), S37–S45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cannon, R.; Roe, R.T. Livestock Disease Surveys: A Field Manual for Veterinarians; Australian Government Publishing Service: Canberra, Australia, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Cantu-Martinez, M.A.; Roig-Sagues, A.X.; Cedillo-Rosales, S.; Zamora-Avila, D.E.; Avalos-Ramirez, R. [molecular detection of hepatitis e virus in pig livers destined for human consumption in the state of nuevo leon, Mexico]. Salud Publica de Mexico 2013, 55, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rio, D.C.; Ares, M.; Hannon, G.J.; Nilsen, T.W. Purification of rna using trizol (tri reagent). Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2010, 2010, pdb.prot5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Deus, N.; Seminati, C.; Pina, S.; Mateu, E.; Martin, M.; Segales, J. Detection of hepatitis e virus in liver, mesenteric lymph node, serum, bile and faeces of naturally infected pigs affected by different pathological conditions. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 119, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Haqshenas, G.; Guenette, D.; Halbur, P.; Schommer, S.; Pierson, F.; Toth, T.; Meng, X. Detection by reverse transcription-pcr and genetic characterization of field isolates of swine hepatitis e virus from pigs in different geographic regions of the united states. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1326–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. Cd-hit: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics (Oxf. Engl.) 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushnell, B. Bbmap Short Read Aligner. University of California, Berkeley, California. Available online: http://sourceforge.net/projects/bbmap (accessed on 1 February 2018).
- Narasimhan, V.; Danecek, P.; Scally, A.; Xue, Y.; Tyler-Smith, C.; Durbin, R. Bcftools/roh: A hidden markov model approach for detecting autozygosity from next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics (Oxf. Engl.) 2016, 32, 1749–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The sequence alignment/map format and samtools. Bioinformatics (Oxf. Engl.) 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okonechnikov, K.; Conesa, A.; Garcia-Alcalde, F. Qualimap 2: Advanced multi-sample quality control for high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics (Oxf. Engl.) 2016, 32, 292–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Schwartz, S.; Wagner, L.; Miller, W. A greedy algorithm for aligning DNA sequences. J. Comput. Biol. 2000, 7, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. Mega7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evolut. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotomayor-González, A.; Trujillo-Ortega, M.E.; Taboada-Ramírez, B.I.; Sandoval-Jaime, C.; Sarmiento-Silva, R.E. National Autonomous University of Mexico, Mexico. Phylogenetic analysis of hev orfs 1-3 aminoacid sequences. Cd-hit 4.6.8 was used to eliminate sequences with >98% similarity (−c.98), leaving a total of 100 reference sequences. Following this, alignment of the consensus and reference sequences was performed with clustal w (default parameters) and verified manually using mega7, 2018.
- Gardinali, N.R.; Barry, A.F.; Otonel, R.A.; Alfieri, A.F.; Alfieri, A.A. Hepatitis e virus in liver and bile samples from slaughtered pigs of Brazil. Memorias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz 2012, 107, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas, M.; Cortés, R.; Pina, S.; Peralta, B.; Allepuz, A.; Cortey, M.; Casal, J.; Martín, M. Longitudinal study of hepatitis e virus infection in Spanish farrow-to-finish swine herds. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 148, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, M.; Kaur, S.; Deka, D.; Singh, R.; Gill, J.P.S. Seroepidemiology and molecular characterization of hepatitis e virus infection in swine and occupationally exposed workers in Punjab, India. Zoonoses Public Health 2017, 64, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Gracia, M.T.; Mateos, M.L.; Galiana, C.; Fernandez-Barredo, S.; Garcia, A.; Gomez, M.T.; Moreira, V. Autochthonous hepatitis e infection in a slaughterhouse worker. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 77, 893–896. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prpic, J.; Cerni, S.; Skoric, D.; Keros, T.; Brnic, D.; Cvetnic, Z.; Jemersic, L. Distribution and molecular characterization of hepatitis e virus in domestic animals and wildlife in Croatia. Food Environ. Virol. 2015, 7, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, R.; She, R.; Mao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Du, F.; Liu, C.; Liu, J.; Cheng, M.; Zhu, R.; et al. Fatal disease associated with swine hepatitis e virus and porcine circovirus 2 co-infection in four weaned pigs in China. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, J.; Zhao, Y.; She, R.; Xiao, P.; Tian, J.; Chen, J. One case of swine hepatitis e virus and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus co-infection in weaned pigs. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erker, J.C.; Desai, S.M.; Schlauder, G.G.; Dawson, G.J.; Mushahwar, I.K. A hepatitis e virus variant from the united states: Molecular characterization and transmission in cynomolgus macaques. J. General Virol. 1999, 80 Pt 3, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forero, J.E.; Gutierrez-Vergara, C.; Parra Suescun, J.; Correa, G.; Rodriguez, B.; Gutierrez, L.A.; Diaz, F.J.; Lopez-Herrera, A. Phylogenetic analysis of hepatitis e virus strains isolated from slaughter-age pigs in colombia. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 49, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munne, M.S.; Altabert, N.R.; Otegui, M.L.; Vladimirsky, S.N.; Moreiro, R.; Espul, M.P.; Espul, C.; Manzur, A.; Soto, S.S.; Brajterman, L.S.; et al. Updating the knowledge of hepatitis e: New variants and higher prevalence of anti-hev in Argentina. Ann. Hepatol. 2014, 13, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mirazo, S.; Gardinali, N.R.; Cecilia, D.; Verger, L.; Ottonelli, F.; Ramos, N.; Castro, G.; Pinto, M.A.; Re, V.; Pisano, B.; et al. Serological and virological survey of hepatitis e virus (hev) in animal reservoirs from uruguay reveals elevated prevalences and a very close phylogenetic relationship between swine and human strains. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 213, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nantel-Fortier, N.; Letellier, A.; Lachapelle, V.; Fravalo, P.; L'Homme, Y.; Brassard, J. Detection and phylogenetic analysis of the hepatitis e virus in a Canadian swine production network. Food Environ. Virol. 2016, 8, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Profio, F.; Melegari, I.; Sarchese, V.; Robetto, S.; Marruchella, G.; Bona, M.C.; Orusa, R.; Martella, V.; Marsilio, F.; Di Martino, B. Detection and genetic characterization of hepatitis e virus (hev) genotype 3 subtype c in wild boars in Italy. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 2829–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salines, M.; Andraud, M.; Rose, N. From the epidemiology of hepatitis e virus (hev) within the swine reservoir to public health risk mitigation strategies: A comprehensive review. Vet. Res. 2017, 48, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| ID | # of Samples | Type of Sample | Origin | Production Stage | RT-PCR Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16 | Liver, bile, feces | Slaughterhouse | Finishers | N |
| 2 | 16 | Liver, bile, feces | Slaughterhouse | Finishers | N |
| 3 | 16 | Liver, bile, feces | Slaughterhouse | Finishers | P* |
| 4 | 16 | Liver, bile, feces | Slaughterhouse | Finishers | N |
| G1 | 10 | Feces | Farm | Gestation | P |
| G2 | 10 | Feces | Farm | Gestation | N |
| G3 | 10 | Feces | Farm | Gestation | P |
| D1 | 10 | Feces | Farm | Weaning | P |
| D2 | 10 | Feces | Farm | Weaning | P |
| D3 | 10 | Feces | Farm | Weaning | P |
| E1 | 10 | Feces | Farm | Finishers | N |
| E2 | 10 | Feces | Farm | Finishers | P |
| E12 | 10 | Feces | Farm | Finishers | P |
| M1 | 10 | Feces | Farm | Nursing | N |
| M2 | 10 | Feces | Farm | Nursing | P |
| M3 | 10 | Feces | Farm | Nursing | N |
| R | 10 | Feces | Farm | Breeding | N |
| S | 10 | Feces | Farm | Boars | N |
| H1 | 3 | Liver | Farm | Finishers | P |
| H2 | 4 | Liver | Farm | Finishers | P |
| H3 | 1 | Liver | Farm | Finishers | P |
| B1 | 4 | Bile | Farm | Finishers | P |
| B2 | 4 | Bile | Farm | Finishers | P |
| C1 | 4 | Feces | Farm | Finishers | P |
| C2 | 4 | Feces | Farm | Finishers | N |
| * only 1 bile positive | |||||
| Sequence Identification | Genome | ORF1 | ORF2 | ORF3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Full-Length% (nt) | % (nt) | % (aa) | % (nt) | % (aa) | % (nt) | % (aa) |
| USHM|AF060669.1|g3a|_1998 | 91 | 90 | 97 | 92 | 98 | 98 | 98 |
| JPHM|AB089824.1|g3|_1993 | 91 | 90 | 98 | 92 | 98 | 96 | 98 |
| USHM|JQ679014.1|g3|_2010 | 91 | 90 | 97 | 92 | 98 | 96 | 98 |
| USCD|AY575857.1|g3|_1997 | 91 | 90 | 98 | 92 | 98 | 96 | 98 |
| USMN|JN837481.1|g3|_2008 | 91 | 90 | 97 | 92 | 99 | 97 | 97 |
| JPHM|AB074920.3|g3|_2002 | 91 | 90 | 98 | 92 | 99 | 98 | 98 |
| JPHM|AB074918.2|g3|_2002 | 91 | 90 | 98 | 93 | 99 | 98 | 98 |
| CNCD|KJ507955.1|g3|_2003 | 90 | 90 | 98 | 92 | 98 | 97 | 99 |
| KRCD|FJ426403.1|g3|_2007 | 90 | 90 | 96 | 93 | 97 | 96 | 98 |
| KRCD|FJ426404.1|g3|_2007 | 90 | 89 | 96 | 92 | 98 | 97 | 98 |
| SGHM|KT447526.1|g3|_2010 | 90 | 89 | 97 | 91 | 98 | 96 | 96 |
| USHM|JQ679013.1|g3|_2010 | 90 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 98 | 94 | 97 |
| CHCD|KX981911.1|g3|_2015 | 89 | 89 | 96 | 91 | 98 | 97 | 98 |
| CNCD|AY115488.1|g3|_2002 | 87 | 86 | 95 | 90 | 98 | 96 | 98 |
| JPHM|AB091394.1|g3|_2002 | 87 | 86 | 97 | 89 | 99 | 97 | 97 |
| JPCD|AB740232.1|g3|_2013 | 87 | 86 | 96 | 89 | 98 | 96 | 98 |
| JPHM|LC131066.1|g3|_2016 | 87 | 86 | 96 | 90 | 99 | 96 | 96 |
| JPHM|AB437317.1|g3|_2003 | 87 | 86 | 97 | 89 | 99 | 97 | 96 |
| JPHM|LC176492.1|g3k|_2015 | 87 | 86 | 96 | 90 | 98 | 96 | 96 |
| JPHM|AB369689.1|g3|_2004 | 87 | 86 | 96 | 90 | 99 | 97 | 97 |
| JPHM|AB291963.1|g3|_2005 | 87 | 86 | 96 | 90 | 98 | 95 | 93 |
| JPJB|AB222184.1|g3|_2004 | 87 | 86 | 96 | 88 | 98 | 96 | 96 |
| JPMN|AB236320.1|g3|_2002 | 87 | 86 | 97 | 89 | 98 | 97 | 97 |
| JPJB|AB222182.1|g3|_2004 | 87 | 86 | 96 | 89 | 98 | 96 | 96 |
| CNCD|KJ507956.1|g3|2003 | 87 | 86 | 97 | 89 | 98 | 96 | 93 |
| JPJB|AB222183.1|g3|_2004 | 87 | 86 | 97 | 89 | 98 | 96 | 93 |
| JPCD|AB073912.1|g3|_2001 | 87 | 86 | 96 | 89 | 98 | 96 | 96 |
| JPJB|AB189070.1|g3|_2004 | 87 | 85 | 96 | 89 | 98 | 96 | 96 |
| JPHM|AB437319.1|g3|2003 | 87 | 91 | 97 | 89 | 99 | 96 | 95 |
| JPHM|AB291960.1|g3|_2006 | 86 | 86 | 97 | 89 | 98 | 96 | 95 |
| JPHM|AB291952.1|g3|_2005 | 86 | 86 | 97 | 88 | 99 | 97 | 96 |
| JPHM|AB369691.1|g3|_2005 | 86 | 86 | 97 | 89 | 99 | 98 | 96 |
| JPHM|AP003430.1|g3|_2001 | 86 | 86 | 96 | 88 | 98 | 97 | 98 |
| JPHM|AB291962.1|g3|_2004 | 86 | 85 | 96 | 89 | 98 | 96 | 97 |
| CHCD|FJ527832.2|g3|2008 | 86 | 86 | 96 | 88 | 98 | 97 | 98 |
| JPND|AB246676.1|g3|_2006 | 86 | 85 | 97 | 89 | 98 | 99 | 93 |
| ALJB|FJ998008.1|g3|_2007 | 85 | 84 | 96 | 87 | 99 | 95 | 94 |
| CHCD|FJ610232.1|G4|_2008 | 78 | 79 | 85 | 81 | 93 | 87 | 85 |
| TWHM|HQ634346.1|G4|_2010 | 78 | 78 | 86 | 81 | 94 | 90 | 88 |
| CHCD|KC692453.1|G4|_2011 | 78 | 78 | 85 | 80 | 94 | 88 | 86 |
| EACM|KJ496143.1|g7|_2013 | 78 | 78 | 87 | 80 | 92 | 87 | 80 |
| CHCD|GU119960.2|G4a|_2009 | 78 | 77 | 85 | 81 | 94 | 89 | 88 |
| JPJB|AB573435.2|G5|_2009 | 78 | 77 | 84 | 80 | 91 | 86 | 80 |
| CDCH|GU206559.1|G4|_2008 | 78 | 79 | 85 | 81 | 92 | 86 | 85 |
| INHM|JF443724.1|G1|_2005 | 77 | 77 | 82 | 80 | 92 | 85 | 82 |
| CHHM|NC_001434.1|G1|_1987 | 77 | 77 | 82 | 80 | 92 | 85 | 82 |
| CHHM|JQ655734.1|G1|_2012 | 77 | 77 | 82 | 79 | 91 | 86 | 82 |
| MXHM|M74506.1|g2|_1992 | 76 | 77 | 81 | 79 | 91 | 85 | 80 |
| JPWB|AB602441.1|g6|_2006 | 76 | NS | 83 | 79 | 91 | 84 | 73 |
| * NS. No similarity found | |||||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sotomayor-González, A.; Trujillo-Ortega, M.E.; Taboada-Ramírez, B.I.; Sandoval-Jaime, C.; Sarmiento-Silva, R.E. Phylogenetic Analysis and Characterization of the Complete Hepatitis E Virus Genome (Zoonotic Genotype 3) in Swine Samples from Mexico. Viruses 2018, 10, 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10080391
Sotomayor-González A, Trujillo-Ortega ME, Taboada-Ramírez BI, Sandoval-Jaime C, Sarmiento-Silva RE. Phylogenetic Analysis and Characterization of the Complete Hepatitis E Virus Genome (Zoonotic Genotype 3) in Swine Samples from Mexico. Viruses. 2018; 10(8):391. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10080391
Chicago/Turabian StyleSotomayor-González, Alicia, María E. Trujillo-Ortega, Blanca I. Taboada-Ramírez, Carlos Sandoval-Jaime, and Rosa E. Sarmiento-Silva. 2018. "Phylogenetic Analysis and Characterization of the Complete Hepatitis E Virus Genome (Zoonotic Genotype 3) in Swine Samples from Mexico" Viruses 10, no. 8: 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10080391
APA StyleSotomayor-González, A., Trujillo-Ortega, M. E., Taboada-Ramírez, B. I., Sandoval-Jaime, C., & Sarmiento-Silva, R. E. (2018). Phylogenetic Analysis and Characterization of the Complete Hepatitis E Virus Genome (Zoonotic Genotype 3) in Swine Samples from Mexico. Viruses, 10(8), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10080391