Simian Foamy Viruses in Central and South America: A New World of Discovery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
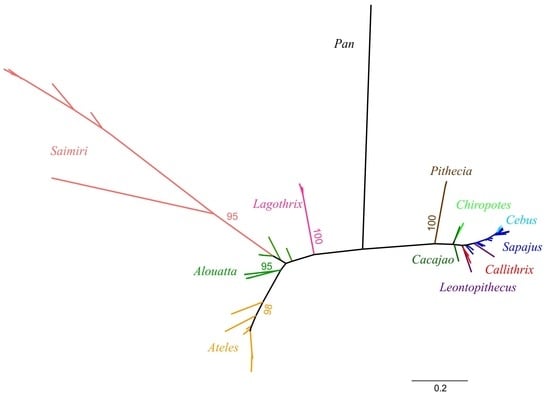
2. Neotropical Primates: Taxonomy and Evolution
3. Diversity and Origin of SFVs in the Americas
4. NP SFV Prevalence and Viral Detection Methodologies
5. NP SFV Epidemiology and Transmission
6. SFV Cross-Species Transmission
7. Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, S.M.; Linial, M.L. Foamy virus infection in primates. J. Med. Primatol. 2006, 35, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooks, J.J.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr.; Chou, S.; Howk, R.; Lewis, M.; Gajdusek, D.C. Isolation of a new simian foamy virus from a spider monkey brain culture. Infect. Immun. 1973, 8, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Estrada, A.; Garber, P.A.; Rylands, A.B.; Roos, C.; Fernandez-Duque, E.; Di Fiore, A.; Nekaris, K.A.; Nijman, V.; Heymann, E.W.; Lambert, J.E.; et al. Impending extinction crisis of the world’s primates: Why primates matter. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1600946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perelman, P.; Johnson, W.E.; Roos, C.; Seuanez, H.N.; Horvath, J.E.; Moreira, M.A.; Kessing, B.; Pontius, J.; Roelke, M.; Rumpler, Y.; et al. A molecular phylogeny of living primates. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, M.; Porter, C.A.; Czelusniak, J.; Page, S.L.; Schneider, H.; Shoshani, J.; Gunnell, G.; Groves, C.P. Toward a phylogenetic classification of Primates based on DNA evidence complemented by fossil evidence. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1998, 9, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandon-Jones, D.; Eudey, A.A.; Geissmann, T.; Groves, C.P.; Melnick, D.J.; Morales, J.C.; Shekelle, M.; Stewart, C.-B. Asian Primate classification. Int. J. Primatol. 2004, 25, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, S.I.; Tejedor, M.F.; Novo, N.M.; Aristide, L. Divergence times and the evolutionary radiation of new world monkeys (platyrrhini, primates): An analysis of fossil and molecular data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberger, A.L. Evolution of feeding niches in New World monkeys. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 1992, 88, 525–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, S.B. The Making of the Fittest: DNA and the Ultimate Forensic Record of Evolution, 1st ed.; W.W. Norton & Co.: New York, NY, USA, 2006; p. 301. [Google Scholar]
- Garber, P.A.; Leigh, S.R. Ontogenetic variation in small-bodied New World primates: Implications for patterns of reproduction and infant care. Folia Primatol. 1997, 68, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, K.R.; Martinez-Mota, R.; Righini, N.; Raguet-Schofield, M.; Corcione, F.P.; Marini, E.; Humphrey, G.; Gogul, G.; Gaffney, J.; Lovelace, E.; et al. Phylogenetic and ecological factors impact the gut microbiota of two Neotropical primate species. Oecologia 2016, 180, 717–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubli, J.P.; Byrne, H.; da Silva, M.N.F.; Silva-Junior, J.; Costa Araujo, R.; Bertuol, F.; Goncalves, J.; de Melo, F.R.; Rylands, A.B.; Mittermeier, R.A.; et al. On a new species of titi monkey (Primates: Plecturocebus Byrne et al., 2016), from Alta Floresta, southern Amazon, Brazil. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 132, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, M.; D’Arc, M.; Delaporte, E. Origin and diversity of human retroviruses. AIDS Rev. 2014, 16, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Katzourakis, A.; Aiewsakun, P.; Jia, H.; Wolfe, N.D.; LeBreton, M.; Yoder, A.D.; Switzer, W.M. Discovery of prosimian and afrotherian foamy viruses and potential cross species transmissions amidst stable and ancient mammalian co-evolution. Retrovirology 2014, 11, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.S.; Bodem, J.; Buseyne, F.; Gessain, A.; Johnson, W.; Kuhn, J.H.; Kuzmak, J.; Lindemann, D.; Linial, M.L.; Lochelt, M.; et al. Spumaretroviruses: Updated taxonomy and nomenclature. Virology 2018, 516, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooks, J.J.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr. The foamy viruses. Bacteriol. Rev. 1975, 39, 169–185. [Google Scholar]
- Barahona, H.; Garcia, F.G.; Melendez, L.V.; King, N.W.; Ingalls, J.K. Isolation and characterization of lymphocyte associated foamy virus from a red uakari monkey (Cacajao rubicundus). J. Med. Primatol. 1976, 5, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marczynska, B.; Jones, C.J.; Wolfe, L.G. Syncytium-forming virus of common marmosets (Callithrix jacchus jacchus). Infect. Immun. 1981, 31, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Thumer, L.; Rethwilm, A.; Holmes, E.C.; Bodem, J. The complete nucleotide sequence of a New World simian foamy virus. Virology 2007, 369, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pacheco, B.; Finzi, A.; McGee-Estrada, K.; Sodroski, J. Species-specific inhibition of foamy viruses from South American monkeys by New World Monkey TRIM5{alpha} proteins. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 4095–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncoso, L.L.; Muniz, C.P.; Siqueira, J.D.; Curty, G.; Schrago, C.G.; Augusto, A.; Fedullo, L.; Soares, M.A.; Santos, A.F. Characterization and comparative analysis of a simian foamy virus complete genome isolated from Brazilian capuchin monkeys. Virus Res. 2015, 208, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz, C.P.; Cavalcante, L.T.F.; Dudley, D.M.; Pissinatti, A.; O’Connor, D.H.; Santos, A.F.; Soares, M.A. First complete genome sequence of a simian foamy virus infecting the neotropical primate brachyteles arachnoides. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2018, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniz, C.P.; Troncoso, L.L.; Moreira, M.A.; Soares, E.A.; Pissinatti, A.; Bonvicino, C.R.; Seuanez, H.N.; Sharma, B.; Jia, H.; Shankar, A.; et al. Identification and characterization of highly divergent simian foamy viruses in a wide range of new world primates from Brazil. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniz, C.P.; Jia, H.; Shankar, A.; Troncoso, L.L.; Augusto, A.M.; Farias, E.; Pissinatti, A.; Fedullo, L.P.; Santos, A.F.; Soares, M.A.; et al. An expanded search for simian foamy viruses (SFV) in Brazilian New World primates identifies novel SFV lineages and host age-related infections. Retrovirology 2015, 12, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghersi, B.M.; Jia, H.; Aiewsakun, P.; Katzourakis, A.; Mendoza, P.; Bausch, D.G.; Kasper, M.R.; Montgomery, J.M.; Switzer, W.M. Wide distribution and ancient evolutionary history of simian foamy viruses in New World primates. Retrovirology 2015, 12, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.Z.; Worobey, M. Endogenous viral sequences from the Cape golden mole (Chrysochloris asiatica) reveal the presence of foamy viruses in all major placental mammal clades. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiewsakun, P.; Katzourakis, A. Marine origin of retroviruses in the early Palaeozoic Era. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.Z.; Worobey, M. An endogenous foamy-like viral element in the coelacanth genome. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruboyianes, R.; Worobey, M. Foamy-like endogenous retroviruses are extensive and abundant in teleosts. Virus Evol. 2016, 2, vew032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, G.Z. Extensive retroviral diversity in shark. Retrovirology 2015, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiewsakun, P.; Simmonds, P.; Katzourakis, A. The first co-opted endogenous foamy viruses and the evolutionary history of reptilian foamy viruses. Viruses 2019, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Switzer, W.M.; Salemi, M.; Shanmugam, V.; Gao, F.; Cong, M.E.; Kuiken, C.; Bhullar, V.; Beer, B.E.; Vallet, D.; Gautier-Hion, A.; et al. Ancient co-speciation of simian foamy viruses and primates. Nature 2005, 434, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, A.; Sibley, S.D.; Goldberg, T.L.; Switzer, W.M. Molecular analysis of the complete genome of a simian foamy virus infecting hylobates pileatus (pileated gibbon) reveals ancient co-evolution with lesser apes. Viruses 2019, 11, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Switzer, W.; Shanmugam, J.H.K.V.; Heneine, W. Seroprevalence of human infection with simian foamy virus from new world primates. In Proceedings of the 16th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infection, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–11 February 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mouinga-Ondeme, A.; Betsem, E.; Caron, M.; Makuwa, M.; Salle, B.; Renault, N.; Saib, A.; Telfer, P.; Marx, P.; Gessain, A.; et al. Two distinct variants of simian foamy virus in naturally infected mandrills (Mandrillus sphinx) and cross-species transmission to humans. Retrovirology 2010, 7, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leendertz, S.A.; Junglen, S.; Hedemann, C.; Goffe, A.; Calvignac, S.; Boesch, C.; Leendertz, F.H. High prevalence, coinfection rate, and genetic diversity of retroviruses in wild red colobus monkeys (Piliocolobus badius badius) in Tai National Park, Cote d’Ivoire. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 7427–7436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Worobey, M.; Li, Y.; Keele, B.F.; Bibollet-Ruche, F.; Guo, Y.; Goepfert, P.A.; Santiago, M.L.; Ndjango, J.B.; Neel, C.; et al. Molecular ecology and natural history of simian foamy virus infection in wild-living chimpanzees. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broussard, S.R.; Comuzzie, A.G.; Leighton, K.L.; Leland, M.M.; Whitehead, E.M.; Allan, J.S. Characterization of new simian foamy viruses from African nonhuman primates. Virology 1997, 237, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Wang, H.; Jing, S.; Zeng, W. Simian foamy virus prevalence in Macaca mulatta and zookeepers. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2012, 28, 591–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, S.; Mitchell, J.L.; Sethi, M.; Almond, N.M.; Cutler, K.L.; Rose, N.J. Horizontal acquisition and a broad biodistribution typify simian foamy virus infection in a cohort of Macaca fascicularis. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calattini, S.; Wanert, F.; Thierry, B.; Schmitt, C.; Bassot, S.; Saib, A.; Herrenschmidt, N.; Gessain, A. Modes of transmission and genetic diversity of foamy viruses in a Macaca tonkeana colony. Retrovirology 2006, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewett, E.L.; Black, D.H.; Lerche, N.W.; White, G.; Eberle, R. Simian foamy virus infections in a baboon breeding colony. Virology 2000, 278, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz, C.P.; Zheng, H.; Jia, H.; Cavalcante, L.T.F.; Augusto, A.M.; Fedullo, L.P.; Pissinatti, A.; Soares, M.A.; Switzer, W.M.; Santos, A.F. A non-invasive specimen collection method and a novel simian foamy virus (SFV) DNA quantification assay in New World primates reveal aspects of tissue tropism and improved SFV detection. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenbak, C.R.; Craig, K.L.; Ivanov, S.B.; Wang, X.; Soliven, K.C.; Jackson, D.L.; Gutierrez, G.A.; Engel, G.; Jones-Engel, L.; Linial, M.L. New World simian foamy virus infections in vivo and in vitro. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 982–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliven, K.; Wang, X.; Small, C.T.; Feeroz, M.M.; Lee, E.G.; Craig, K.L.; Hasan, K.; Engel, G.A.; Jones-Engel, L.; Matsen, F.A.; et al. Simian foamy virus infection of rhesus macaques in Bangladesh: Relationship of latent proviruses and transcriptionally active viruses. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 13628–13639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, S.M.; Picker, L.J.; Axthelm, M.K.; Linial, M.L. Expanded tissue targets for foamy virus replication with simian immunodeficiency virus-induced immunosuppression. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcone, V.; Leupold, J.; Clotten, J.; Urbanyi, E.; Herchenroder, O.; Spatz, W.; Volk, B.; Bohm, N.; Toniolo, A.; Neumann-Haefelin, D.; et al. Sites of simian foamy virus persistence in naturally infected African green monkeys: Latent provirus is ubiquitous, whereas viral replication is restricted to the oral mucosa. Virology 1999, 257, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Betts, M.J.; Lei, J.; Wei, G.; Bao, Q.; Kehl, T.; Russell, R.B.; Lochelt, M. Mutagenesis of N-terminal residues of feline foamy virus Gag reveals entirely distinct functions during capsid formation, particle assembly, Gag processing and budding. Retrovirology 2016, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, C.; Couteaudier, M.; Gouzil, J.; Richard, L.; Montange, T.; Betsem, E.; Rua, R.; Tobaly-Tapiero, J.; Lindemann, D.; Njouom, R.; et al. Potent neutralizing antibodies in humans infected with zoonotic simian foamy viruses target conserved epitopes located in the dimorphic domain of the surface envelope protein. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.M.; Picker, L.J.; Axthelm, M.K.; Hudkins, K.; Alpers, C.E.; Linial, M.L. Replication in a superficial epithelial cell niche explains the lack of pathogenicity of primate foamy virus infections. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 5981–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiley Evans, T.; Barry, P.A.; Gilardi, K.V.; Goldstein, T.; Deere, J.D.; Fike, J.; Yee, J.; Ssebide, B.J.; Karmacharya, D.; Cranfield, M.R.; et al. Optimization of a Novel Non-invasive Oral Sampling Technique for Zoonotic Pathogen Surveillance in Nonhuman Primates. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiley Evans, T.; Gilardi, K.V.; Barry, P.A.; Ssebide, B.J.; Kinani, J.F.; Nizeyimana, F.; Noheri, J.B.; Byarugaba, D.K.; Mudakikwa, A.; Cranfield, M.R.; et al. Detection of viruses using discarded plants from wild mountain gorillas and golden monkeys. Am. J. Primatol. 2016, 78, 1222–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schweizer, M.; Schleer, H.; Pietrek, M.; Liegibel, J.; Falcone, V.; Neumann-Haefelin, D. Genetic stability of foamy viruses: Long-term study in an African green monkey population. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 9256–9265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brooks, J.I.; Merks, H.W.; Fournier, J.; Boneva, R.S.; Sandstrom, P.A. Characterization of blood-borne transmission of simian foamy virus. Transfusion 2007, 47, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasse, A.; Calvignac-Spencer, S.; Merkel, K.; Goffe, A.S.; Boesch, C.; Mundry, R.; Leendertz, F.H. Mother-offspring transmission and age-dependent accumulation of simian foamy virus in wild chimpanzees. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 5193–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VandeWoude, S.; Apetrei, C. Going wild: Lessons from naturally occurring T-lymphotropic lentiviruses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 728–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, M.L.; Range, F.; Keele, B.F.; Li, Y.; Bailes, E.; Bibollet-Ruche, F.; Fruteau, C.; Noe, R.; Peeters, M.; Brookfield, J.F.; et al. Simian immunodeficiency virus infection in free-ranging sooty mangabeys (Cercocebus atys atys) from the Tai Forest, Cote d’Ivoire: Implications for the origin of epidemic human immunodeficiency virus type 2. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 12515–12527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Galvin, T.A.; Williams, D.K.; Beren, J.; Bryant, M.A.; Khan, A.S. Influence of naturally occurring simian foamy viruses (SFVs) on SIV disease progression in the rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta) model. Viruses 2013, 5, 1414–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leendertz, F.H.; Zirkel, F.; Couacy-Hymann, E.; Ellerbrok, H.; Morozov, V.A.; Pauli, G.; Hedemann, C.; Formenty, P.; Jensen, S.A.; Boesch, C.; et al. Interspecies transmission of simian foamy virus in a natural predator-prey system. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 7741–7744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betsem, E.; Rua, R.; Tortevoye, P.; Froment, A.; Gessain, A. Frequent and recent human acquisition of simian foamy viruses through apes’ bites in central Africa. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones-Engel, L.; May, C.C.; Engel, G.A.; Steinkraus, K.A.; Schillaci, M.A.; Fuentes, A.; Rompis, A.; Chalise, M.K.; Aggimarangsee, N.; Feeroz, M.M.; et al. Diverse contexts of zoonotic transmission of simian foamy viruses in Asia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1200–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.S. Simian foamy virus infection in humans: Prevalence and management. Exp. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2009, 7, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Switzer, W.M.; Bhullar, V.; Shanmugam, V.; Cong, M.E.; Parekh, B.; Lerche, N.W.; Yee, J.L.; Ely, J.J.; Boneva, R.; Chapman, L.E.; et al. Frequent simian foamy virus infection in persons occupationally exposed to nonhuman primates. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 2780–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Switzer, W.M.H. Foamy virus infection of humans. In Molecular Detection of Human Viral Pathogens; Liu, D., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto-Santini, D.M.; Stenbak, C.R.; Linial, M.L. Foamy virus zoonotic infections. Retrovirology 2017, 14, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, J.I.; Rud, E.W.; Pilon, R.G.; Smith, J.M.; Switzer, W.M.; Sandstrom, P.A. Cross-species retroviral transmission from macaques to human beings. Lancet 2002, 360, 387–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, N.D.; Switzer, W.M.; Carr, J.K.; Bhullar, V.B.; Shanmugam, V.; Tamoufe, U.; Prosser, A.T.; Torimiro, J.N.; Wright, A.; Mpoudi-Ngole, E.; et al. Naturally acquired simian retrovirus infections in central African hunters. Lancet 2004, 363, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calattini, S.; Betsem, E.B.; Froment, A.; Mauclere, P.; Tortevoye, P.; Schmitt, C.; Njouom, R.; Saib, A.; Gessain, A. Simian foamy virus transmission from apes to humans, rural Cameroon. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1314–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Switzer, W.M.; Tang, S.; Ahuka-Mundeke, S.; Shankar, A.; Hanson, D.L.; Zheng, H.; Ayouba, A.; Wolfe, N.D.; LeBreton, M.; Djoko, C.F.; et al. Novel simian foamy virus infections from multiple monkey species in women from the Democratic Republic of Congo. Retrovirology 2012, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouinga-Ondeme, A.; Caron, M.; Nkoghe, D.; Telfer, P.; Marx, P.; Saib, A.; Leroy, E.; Gonzalez, J.P.; Gessain, A.; Kazanji, M. Cross-species transmission of simian foamy virus to humans in rural Gabon, Central Africa. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 1255–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Primate Family | Genus | Common Name | Complete Genome 1 | Partial Genome (LTR/gag and/or pol) 1 | Diagnostic-PCR and/or qPCR and/or WB Serology 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cebidae | Aotus | owl monkey | SFVaaz, SFVatr, SFVani | ||
| Callimico | marmoset | SFVcgo | |||
| Callithrix | marmoset | SFVcja | SFVcge | SFVcau | |
| Cebus | capuchin | SFVcal | SFVcol | ||
| Leontopithecus | tamarin | SFVlro, SFVlcm | SFVlcp | ||
| Mico | marmoset | SFVmhu | |||
| Saguinus | tamarin | SFVsbi, SFVsfu, SFVsmi, SFVsoe | |||
| Saimiri | squirrel monkey | SFVssc | SFVsbo, SFVsus | ||
| Sapajus | capuchin | SFVsxa | SFVsap, SFVsfl, SFVsro | ||
| Atelidae | Alouatta | howler monkey | SFVabe, SFVaca, SFVagu, SFVase | SFVapl | |
| Ateles | spider monkey | SFVaxx | SFVage, SFVahy, SFVach | SFVafu, SFVapn | |
| Brachyteles | wooly spider monkey | SFVbar | |||
| Lagothrix | wooly monkey | SFVlla | |||
| Pitheciidae | Cacajao | uakari | ___ | SFVcca, SFVcme | |
| Callicebus | titi | ___ | ___ | SFVcmo | |
| Pithecia | saki | ___ | SFVppi |
| Study | Methodology | Sites | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hooks, 1975 [2] | Serology | Colony | 61% |
| Marczynska et al., 1981 [18] | Serology | Colony | 54% |
| Muniz et al., 2013 [23] | Diag. PCR 1 | Brazilian zoo and primatology center Wild primates | 23% 29% |
| Ghersi et al., 2015 [25] | Serology and Diag. PCR | Peruvian and US zoos Peruvian rescue center Illegal trade market | 45–47% 19% |
| Muniz et al., 2015 [24] | Serology and Diag. PCR | Brazilian zoo and primatology center | 51% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, A.F.; Cavalcante, L.T.F.; Muniz, C.P.; Switzer, W.M.; Soares, M.A. Simian Foamy Viruses in Central and South America: A New World of Discovery. Viruses 2019, 11, 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100967
Santos AF, Cavalcante LTF, Muniz CP, Switzer WM, Soares MA. Simian Foamy Viruses in Central and South America: A New World of Discovery. Viruses. 2019; 11(10):967. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100967
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, André F., Liliane T. F. Cavalcante, Cláudia P. Muniz, William M. Switzer, and Marcelo A. Soares. 2019. "Simian Foamy Viruses in Central and South America: A New World of Discovery" Viruses 11, no. 10: 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100967
APA StyleSantos, A. F., Cavalcante, L. T. F., Muniz, C. P., Switzer, W. M., & Soares, M. A. (2019). Simian Foamy Viruses in Central and South America: A New World of Discovery. Viruses, 11(10), 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100967