Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx) and Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) in Oropharyngeal Cancer Associated with EBV and HPV Coinfection
Abstract
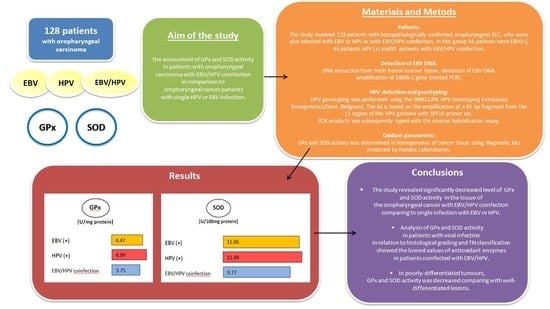
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. DNA Extraction from Fresh Frozen Tumor Tissue
2.3. Detection of EBV DNA
2.4. HPV Detection and Genotyping
2.5. Oxidant Parameters
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zur Hausen, H.; de Villiers, E.-M. Cancer “Causation” by Infections—Individual Contributions and Synergistic Networks. Semin. Oncol. 2014, 41, 860–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Martel, C.; Georges, D.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Clifford, G.M. Global burden of cancer attributable to infections in 2018: A worldwide incidence analysis. Lancet Glob. Heal. 2020, 8, e180–e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plummer, M.; De Martel, C.; Vignat, J.; Ferlay, J.; Bray, F.; Franceschi, S. Global burden of cancers attributable to infections in 2012: A synthetic analysis. Lancet Glob. Heal. 2016, 4, e609–e616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mesri, E.A.; Feitelson, M.A.; Munger, K. Human Viral Oncogenesis: A Cancer Hallmarks Analysis. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trakoli, A. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Volume 99: Some Aromatic Amines, Organic Dyes, and Related Exposures. International Agency for Research on Cancer. Occup. Med. 2012, 62, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Moustafa, A.-E.; Chen, D.; Ghabreau, L.; Akil, N. Association between human papillomavirus and Epstein-Barr virus infections in human oral carcinogenesis. Med. Hypotheses 2009, 73, 184–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makielski, K.R.; Lee, D.; Lorenz, L.D.; Nawandar, D.M.; Chiu, Y.-F.; Kenney, S.C.; Lambert, P.F. Human papillomavirus promotes Epstein-Barr virus maintenance and lytic reactivation in immortalized oral keratinocytes. Virology 2016, 495, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, L.S.; Dawson, C.W. Epstein-Barr virus and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chin. J. Cancer 2014, 33, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, S.-W.; Tsang, C.M.; To, K.-F.; Lo, K.-W. The role of Epstein-Barr virus in epithelial malignancies. J. Pathol. 2014, 235, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hau, P.M.; Lung, H.-L.; Wu, M.; Tsang, C.M.; Wong, K.-L.; Mak, N.K.; Lo, K.-W. Targeting Epstein-Barr Virus in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedham, V.; Divi, R.L.; Starks, V.L.; Verma, M. Multiple Infections and Cancer: Implications in Epidemiology. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 13, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, K.; Hisamatsu, K.; Suzui, N.; Hara, A.; Tomita, H.; Miyazaki, T. A Review of HPV-Related Head and Neck Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kesarwala, A.H.; Krishna, M.C.; Mitchell, J.B. Oxidative stress in oral diseases. Oral Dis. 2015, 22, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guruprasad, Y.; Naik, R.; Pai, A.; Sujatha, D.; Ganapathy, K.; Gurudath, S. Superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase in oral submucous fibrosis, oral leukoplakia, and oral cancer: A comparative study. J. Orofac. Sci. 2012, 4, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargouri, B.; Nasr, R.; Ben Mansour, R.; Lassoued, S.; Mseddi, M.; Attia, H.; Feki, A.E.F.E.; Van Pelt, J. Reactive Oxygen Species Production and Antioxidant Enzyme Expression after Epstein–Barr Virus Lytic Cycle Induction in Raji Cell Line. Boil. Trace Element Res. 2011, 144, 1449–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, H.; Luo, X.; Li, Y.; Bode, A.; Cao, Y. The role of oxidative stress in EBV lytic reactivation, radioresistance and the potential preventive and therapeutic implications. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 1722–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kgatle, M.M.; Spearman, C.W.; Kalla, A.A.; Hairwadzi, H.N. DNA Oncogenic Virus-Induced Oxidative Stress, Genomic Damage, and Aberrant Epigenetic Alterations. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 3179421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marullo, R.; Werner, E.; Zhang, H.; Chen, G.Z.; Shin, N.M.; Doetsch, P.W. HPV16 E6 and E7 proteins induce a chronic oxidative stress response via NOX2 that causes genomic instability and increased susceptibility to DNA damage in head and neck cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.M.; Fuentes-Pananá, E.M. Human Viruses and Cancer. Viruses 2014, 6, 4047–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Georgescu, S.R.; Mitran, C.I.; Mitran, M.I.; Caruntu, C.; Sârbu, I.; Matei, C.; Nicolae, I.; Tocut, S.M.; Popa, M.; Tampa, M. New Insights in the Pathogenesis of HPV Infection and the Associated Carcinogenic Processes: The Role of Chronic Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 5315816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sobin, L.H.; Gospodarowicz, M.K.; Wittekind, C. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, 7th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; pp. 22–45. [Google Scholar]
- Cardesa, A.; Gale, N.; Nadal, A.; Zidor, N. Squamous cell carcinoma. In World Health Organization Classifiation of Tumours. Pathology and Genetics of Head and Neck Tumours; Barnes, L., Eveson, J.W., Reichart, P., Sidransky, D., Eds.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2005; pp. 118–121. [Google Scholar]
- Arthur, J.; Boyne, R. Superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase activities in neutrophils from selenium deficient and copper deficient cattle. Life Sci. 1985, 36, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paglia, D.E.; Valentine, W.N. Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1967, 70, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalouli, J.; Jalouli, M.M.; Sapkota, D.; O Ibrahim, S.; Larsson, P.-A.; Sand, L.P. Human papilloma virus, herpes simplex virus and epstein barr virus in oral squamous cell carcinoma from eight different countries. Anticancer. Res. 2012, 32, 571–580. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, R.; Ekshyyan, O.; Moore-Medlin, T.; Rong, X.; Nathan, S.; Gu, X.; Abreo, F.; Rosenthal, E.L.; Shi, M.; Guidry, J.T.; et al. Association between human papilloma virus/Epstein-Barr virus coinfection and oral carcinogenesis. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2014, 44, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidry, J.T.; Scott, R.S. The interaction between human papillomavirus and other viruses. Virus Res. 2017, 231, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drop, B.; Strycharz-Dudziak, M.; Kliszczewska, E.; Polz-Dacewicz, M. Coinfection with Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV), Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) and Polyoma BK Virus (BKPyV) in Laryngeal, Oropharyngeal and Oral Cavity Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strycharz-Dudziak, M.; Kiełczykowska, M.; Drop, B.; Świątek, L.; Kliszczewska, E.; Musik, I.; Polz-Dacewicz, M. Total Antioxidant Status (TAS), Superoxide Dismutase (SOD), and Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx) in Oropharyngeal Cancer Associated with EBV Infection. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5832410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Uehara, T.; Maeda, H.; Hasegawa, M.; Matayoshi, S.; Kiyuna, A.; Agena, S.; Pan, X.; Zhang, C.; Yamashita, Y.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus and Human Papillomavirus Infections and Genotype Distribution in Head and Neck Cancers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzamani, N.; Salehian, P.; Farhadi, M.; Tehran, E.A. Detection of EBV and HPV in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by in situ hybridization. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2006, 81, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laantri, N.; Attaleb, M.; Kandil, M.; Naji, F.; Mouttaki, T.; Dardari, R.; Belghmi, K.; Benchakroun, N.; El Mzibri, M.; Khyatti, M. Human papillomavirus detection in moroccan patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Infect. Agents Cancer 2011, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tung, Y.C.; Lin, K.H.; Chu, P.Y.; Hsu, C.C.; Kuo, W.R. Detection of human papilloma virus and Epstein-Barr virus DNA in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by polymerase chain reaction. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 1999, 15, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Peng, S.-L.; Yang, L.; Chen, X.; Tao, Y.; Cao, Y. Co-infection of Epstein-Barr virus and human papillomavirus in human tumorigenesis. Chin. J. Cancer 2016, 35, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawanishi, S.; Ohnishi, S.; Ma, N.; Hiraku, Y.; Murata, M. Crosstalk between DNA Damage and Inflammation in the Multiple Steps of Carcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.Y.; Mansouri, S.; Frappier, L. Changes in the Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Nuclear Proteome Induced by the EBNA1 Protein of Epstein-Barr Virus Reveal Potential Roles for EBNA1 in Metastasis and Oxidative Stress Responses. J. Virol. 2011, 86, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, V.M.; Filippova, M.; Filippov, V.; Payne, K.J.; Duerksen-Hughes, P. Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E6* Induces Oxidative Stress and DNA Damage. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 6751–6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, L.; Gravitt, P.E.; Song, H.; Maldonado, A.M.; Ozbun, M.A. Nitric oxide induces early viral transcription coincident with increased DNA damage and mutation rates in human papillomavirus-infected cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4878–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choudhari, S.K.; Chaudhary, M.; Gadbail, A.R.; Sharma, A.; Tekade, S. Oxidative and antioxidative mechanisms in oral cancer and precancer: A review. Oral Oncol. 2014, 50, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manasaveena, V.; Akula, K.K.; Sangram, V. A comparative evaluation of enzymatic antioxidant levels in pre and post therapy patients with oral cancer. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, H.; Singh, A.; Pandey, P.; Tewari, M.; Gambhir, I.; Pandey, H. Free radicals hasten head and neck cancer risk: A study of total oxidant, total antioxidant, DNA damage, and histological grade. J. Postgrad. Med. 2016, 62, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-C.; Chang, Y.; Wang, L.H.-C.; Tsai, H.-W.; Huang, W.; Su, I.-J. Pathogenesis of virus-associated human cancers: Epstein–Barr virus and hepatitis B virus as two examples. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2014, 113, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tzellos, S.; Farrell, P.J. Epstein-Barr Virus Sequence Variation—Biology and Disease. Pathogens 2012, 1, 156–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Srivastava, K.C.; Austin, R.D.; Shrivastava, D.; Sethupathy, S.; Rajesh, S. A Case control study to evaluate oxidative stress in plasma samples of oral malignancy. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2012, 3, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Moles, M.; Gutiérrez, J.; Ruiz, I.; A Fernández, J.; Rodriguez, M.; Aneiros, J. Epstein-Barr virus and oral squamous cell carcinoma in patients without HIV infection: Viral detection by polymerase chain reaction. Microbios 1998, 96, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guidry, J.T.; Birdwell, C.E.; Scott, R.S. Epstein-Barr virus in the pathogenesis of oral cancers. Oral Dis. 2017, 24, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| EBV + HPV n = 30 | EBV(+) n = 54 | HPV(+) n = 44 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | N | % | ||
| Sex | female | 3 | 10.0 | 6 | 11.1 | 5 | 11.4 |
| male | 27 | 90.0 | 48 | 88.9 | 39 | 88.6 | |
| p | 0.9817 | ||||||
| Age | <50 | 5 | 16.7 | 9 | 16.7 | 7 | 15.9 |
| 50–69 | 18 | 60.0 | 34 | 63.0 | 28 | 63.6 | |
| ≥70 | 7 | 23.3 | 11 | 20.3 | 9 | 20.4 | |
| p | 0.9975 | ||||||
| Place of residence | Urban | 24 | 80.0 | 43 | 79.6 | 34 | 77.3 |
| Rural | 6 | 20.0 | 11 | 20.4 | 10 | 22.7 | |
| p | 0.9469 | ||||||
| Smoking | Yes | 23 | 76.7 | 41 | 75.9 | 33 | 75.0 |
| No | 7 | 23.3 | 13 | 24.1 | 11 | 25.0 | |
| p | 0.9861 | ||||||
| Alcohol abuse | Yes | 27 | 90.0 | 49 | 90.7 | 40 | 90.9 |
| No | 3 | 10.0 | 5 | 9.3 | 4 | 9.1 | |
| p | 0.9906 | ||||||
| Histological grading | G1-G2 | 13 | 43.3 | 23 | 42.6 | 19 | 43.2 |
| G3 | 17 | 56.7 | 31 | 57.4 | 25 | 56.8 | |
| p | 0.9972 | ||||||
| T stage | T1-T2 | 22 | 73.3 | 39 | 72.2 | 32 | 72.7 |
| T3-T4 | 8 | 26.7 | 15 | 27.8 | 12 | 27.3 | |
| p | 0.9939 | ||||||
| N stage | N1-N2 | 23 | 76.7 | 41 | 75.9 | 33 | 75.0 |
| N3-N4 | 7 | 23.3 | 13 | 24.1 | 11 | 25.0 | |
| p | 0.9860 | ||||||
| M | M0 | 30 | 100.0 | 54 | 100.0 | 44 | 100.0 |
| Pearson’s Chi-square test | |||||||
| n | GPx | Kruskal–Wallis Test | ||||||
| M | SD | Min | Max | Me | H | p | ||
| EBV+ | 54 | 4.47 | 2.11 | 2.05 | 9.55 | 4.73 | 8.169148 | 0.0168 * |
| HPV+ | 44 | 4.99 | 1.89 | 2.37 | 9.55 | 4.91 | ||
| EBV+/HPV+ | 30 | 3.75 | 2.09 | 1.22 | 9.55 | 3.32 | ||
| n | SOD | Kruskal–Wallis Test | ||||||
| M | SD | Min | Max | Me | H | p | ||
| EBV+ | 54 | 11.06 | 1.59 | 9.11 | 13.91 | 10.83 | 13.37263 | 0.0012 * |
| HPV+ | 44 | 11.49 | 1.44 | 9.25 | 13.91 | 11.97 | ||
| EBV+/HPV+ | 30 | 9.77 | 2.24 | 5.22 | 12.44 | 9.81 | ||
| EBV + HPV | EBV | HPV | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPx | SOD | GPx | SOD | GPx | SOD | |
| G1-G2 | 5.74 ± 1.50 | 11.88 ± 0.55 | 6.33 ± 1.51 | 12.66 ± 0.57 | 6.58 ± 1.55 | 12.83 ± 0.42 |
| G3 | 2.23 ± 0.76 | 8.15 ± 1.58 | 3.10 ± 1.26 | 9.87 ± 0.90 | 3.77 ± 1.03 | 10.47 ± 1.04 |
| p value | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| T1-T2 | 4.54 ± 1.88 | 10.87 ± 1.35 | 5.34 ± 1.85 | 11.77 ± 1.29 | 5.79 ± 1.58 | 12.19 ± 0.99 |
| T3-T4 | 1.58 ± 0.32 | 6.76 ± 1.09 | 2.22 ± 0.21 | 9.21 ± 0.12 | 2.85 ± 0.31 | 9.62 ± 0.28 |
| p value | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| N1-N2 | 4.43 ± 1.91 | 10.77 ± 1.39 | 5.21 ± 1.90 | 11.65 ± 1.35 | 5.71 ± 1.62 | 12.13 ± 1.05 |
| N3-N4 | 1.52 ± 0.30 | 6.47 ± 0.80 | 2.16 ± 0.12 | 9.17 ± 0.07 | 2.82 ± 0.30 | 9.59 ± 0.27 |
| p value | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Strycharz-Dudziak, M.; Fołtyn, S.; Dworzański, J.; Kiełczykowska, M.; Malm, M.; Drop, B.; Polz-Dacewicz, M. Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx) and Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) in Oropharyngeal Cancer Associated with EBV and HPV Coinfection. Viruses 2020, 12, 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12091008
Strycharz-Dudziak M, Fołtyn S, Dworzański J, Kiełczykowska M, Malm M, Drop B, Polz-Dacewicz M. Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx) and Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) in Oropharyngeal Cancer Associated with EBV and HPV Coinfection. Viruses. 2020; 12(9):1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12091008
Chicago/Turabian StyleStrycharz-Dudziak, Małgorzata, Sylwia Fołtyn, Jakub Dworzański, Małgorzata Kiełczykowska, Maria Malm, Bartłomiej Drop, and Małgorzata Polz-Dacewicz. 2020. "Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx) and Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) in Oropharyngeal Cancer Associated with EBV and HPV Coinfection" Viruses 12, no. 9: 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12091008
APA StyleStrycharz-Dudziak, M., Fołtyn, S., Dworzański, J., Kiełczykowska, M., Malm, M., Drop, B., & Polz-Dacewicz, M. (2020). Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx) and Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) in Oropharyngeal Cancer Associated with EBV and HPV Coinfection. Viruses, 12(9), 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12091008